Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Genetics 9 10
Încărcat de
Anelya TurgambayevaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Genetics 9 10
Încărcat de
Anelya TurgambayevaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
TOPIC-1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF _________ Types of genes.
GENETICS _________Weaker allele on a gene.
_________ Father and mother
_________ Different alleles for a trait.
Below each of the following words are
choices.
CCiirrccllee tthhee cchhooiicceess tthhaatt aarree eexxaam
mpplleess
ooff eeaacchh ooff tthhoossee w woorrddss.
1. Dominant allele
D e k L N n R S
Key Words
2. Recessive allele
Inheritance
Genetics M n d F G r k P
Gene
Homozygote 3. Homozygous dominant
Heterozygote
Dominant AA Gg KK mm uu Rr TT
Phenotype
Genotype 4. Homozygous recessive
P generation
F Genetation ee Ff HH Oo qq Uu ww
Independent gene
Linked gene 5. Genotypes in which dominant gene
must show
A
A.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS..
AA Dd EE ff Jj RR Ss
Use above key words and fill in the blanks
given below.
_________ Short length of DNA that is
code for traits or protein.
_________The passing on traits from
family to children.
_________ Offspring.
_________ Physical appearance of
organism.
___________is the study of inheritance.
_________ Identical alleles for a trait.
_________ Stronger allele on a gene.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
B
B.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE A) allele B) region
C) locus. D) type
1._ (…)_ The father of genetics is Gregor
Mendel SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
2._ (…)_Each characteristic is inherited
with two alleles. 1. Compare gene and allele?
3. _(…)_ Traits are variations of two
characteristics.
4. _(…)__ AA; represent a homozygous
dominant characterisitics.
5. __(…)_Tall,short,red and white are
phenotypes.
2. Compare linked and independent gene?
C
C.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
1. Different forms of a gene are called
_______________
A) traits B) phenotypes
C) genotypes D) alleles.
2. Which of the followings is the
homozygote recessive gene?
A) Aa B) DD C) Ee D) ee
3. Genes are code for ____________?
A) Traits B) Proteins
C) Enzymes D) All of the above
4. Phenotype of organism is determined
by _____
A) Genotypes B) Environment
C) Desire D) a and b
5. Phenylketonuria is an autosomal
recessive disorder. Using "P" and "p" to
represent the alleles, what is the genotype
of a phenylketonuric person?
A) PP B) Pp
C) pp D) Pp or pp
6. The site on the chromosome occupied
by a gene is called a(n)
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
SOME HUMAN CHARACTERISTICS
1. Shape of Oval dominant, square
face recessive
No cleft dominant, cleft
2. Cleft in chin
recessive
Curly:
3. Hair curl
homozygous,Wavy:
(incomplete
heterozygous, Straight:
dominance)
homozygous
Widow peak dominant,
4. Hairline straight hairline
recessive
5. Eyebrow Broad dominant, slender
size recessive
6. Eyebrow Separated dominant,
shape joined recessive
7. Eyelash Long dominant, short
length recessive
Dimples dominant, no
8. Dimples
dimples recessive
Free lobe dominant,
9. Earlobes
attached recessive
Almond dominant,
10. Eye shape
round recessive
Freckles dominant, no
11. Freckles
freckles recessive
12. Tongue Roller dominant,
rolling nonroller recessive
13. Tongue Inability dominant,
folding ability recessive
14. Finger mid- Hair dominant, no hair
digital hair recessive
Straight thumb
15. Hitch-
dominant, hitch-hiker
hiker's thumb
thumb recessive
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
TOPIC-2. THE LOW OF PROBABLITY 6. The probability of being male in 10th
birth is ____
Key Words 7. The chance of being all girls in 3 births
of a female is ________
Probability
Chance B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
Independent events
Product rule
1. AaBb genes of two traits. What is the
A
A.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS.. chance of formation of a gamete that
contain AB alleles?
A) 1 B) 1/2 C) 1/4 D) 1/8
1. Chance of certain event is calculated in
________________ 2. Aa X Aa
2. Two principles of probability used in In crossing of above generation what is
genetics are: the chance of F1 generation becoming
a.____________________________ same genotype as family?
b. ___________________________ A) 1 B) 1/2 C) 1/4 D) 1/8
3. The sum of all possible products of a 3. Aa X aa
single event is equal to ___ According to above cross, what is the
chance of getting an offspring with the
homozygous recessive phenotype?
A) 0% B) 25% C)50% D)75%
4. The probability that four coins will
come up heads when flipped
simultaneously is _______
4. If we flip a dice probability of coming 5
is _________
A) 1/4 B) 1/2 C) 1/8 D) 1/16
5. A woman has six sons. The chance that
her next child will be a daughter is
A) 1 B) 0 C) 1/2 D) 1/6
5. Bb represents the eye color of a person.
The chance of coming ‚b‛ allele in his
gamete is ________
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
FFU
UNN FFA
ACCTTSS A
ABBO
OUUTT G
GEEN
NEETTIIC
CSS
Nucleotides are the alphabet of DNA.
There are only four "letters" in DNA :
adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and
cytosine (C). They always go by pairs, A
with T, and G with C. Such pairs are
called "base pairs".
Almost every cell in our body contains
a complete copy of our genome. The
exceptions are egg/sperm cells, which
only carry half of our genome, as well as
red blood cells and some white blood
cells, which have no DNA at all
(otherwise blood transfusions would
often cause an immune reaction, like
organ transplants).
If unfolded the DNA in each cell's
nucleus would be 2 metres long. Humans
have an estimated 100 trillion cells. In
other words, if the all the DNA from
every cell in a person's body were
patched up together they would form a
strand of 200 billion kilometres, or more
than 1,000 times the distance between
Earth and the Sun.
D
D.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
1. Explain the rules of independent event
shortly.
2. Two green pea pod were crossed. Find
the probability of being GG, Gg, gg shown
in punnet square?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
TOPIC-3. GAMETE FINDING A) AAbbcc B) aabbcc
C) AaBBcc D) AABBCc
E) none of the above
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE
3. Segregation of alleles occurs
A) during gamete formation.
1. _(…)_Number of gamete types B) at fertilization.
produced for traits depend on number of C) during mitosis.
heterozygous traits. D) during development
2. _(…)_ Only one type of gametes can be
produced from homozygous 2 traits. 4. During meiosis each gametes receive
3. _(…)_ Genetic cross cannot be made only one allele of a gene. This is the ____
without knowing gamete types. A) Independent assortment
4. _(…)_ 4 types of gametes can be B) Dominance rules
produced from AaBB genotype? C) Principle of segregation
5. _(…)_ Modern principle of Genetics D) Transmission of trait
based on Mendel works.
6. _(…)_ According to rule of dominance,
alleles segregate in to gametes C
C.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
independently.
1. How many different kinds of gametes
can be formed from following genotypes?
AaSsEERrTThh:
aaDdGgHHkkNn:
EeBbNnMmKkOo:
PPYyTtRrEeFf:
GgHHKkLlOoYy:
2. Compare independent assortment and
the principle of segregation.
B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
1. How many unique gametes could be
produced through independent 3. What is dominance rule?
assortment by an individual with the
genotype AaBbCcDdEE?
A) 4 B) 8 C) 16 D) 32
2. In a certain plant, the alleles A, B, and 4. Write the types of gametes that are
C are completely dominant to the alleles a, produced from following genotypes at
b, and c. A plant with the genotype end of meiosis?
AABbcc will have the same phenotype as
the plant with the genotype _____. Genotypes Gametes
AaBB: AB, aB
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
AaBb:
AaBBCc:
DdMm:
DdAaBb:
5. Find the genotypes of organisms that
produce gametes given below.
Gametes: Genotype:
A; a
AB; Ab
AB; Ab; aB; ab
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 4: THE RULES OF MENDEL AND A) P generation B) F1 generation.
THEIR APLICATIONS C) F2 generation D) F1 crosses.
2. Which of the following methods was not
Key Terms used by Mendel in his study of the
genetics of the garden pea?
Independent assortment A) Maintenance of true-breeding lines
Principle of dominance B) Cross-pollination
Principle of segregation C) Microscopy
D) Production of hybrid plants
3. Mendel concluded that each pea has
two units for each character, and each
gamete contains one unit. Mendel’s ‚unit‛
is now referred to as a(n)
A) allele. B) gene.
C) character. D) None of the above
4. Mendel’s crossing of spherical-seeded
pea plants with wrinkled-seeded pea
Independent assortment
plants resulted in progeny that all had
spherical seeds. This indicates that the
wrinkled-seed trait is
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE
A) heterozygous. B) dominant.
C) recessive. D) Both a and b
1. _(…)_ Traits are inherited by genes.
2. _(…)_ Mendel started his experiment 5. A plant with purple flowers is allowed
with crossing individuals bearing to self-pollinate. Generation after
homozygous trait. generation, it produces purple flowers.
3. _(…)_ Mendel’s F2 generation exhibited This is an example of
same phenotype with F1 generation. A) hybridization
4. _(…)_ Mendel used self-fertilization of B) incomplete dominance.
pea plants to prove his hypothesis. C) true-breeding
5. _(…)_ If all F1 individuals are same, D) the law of segregation.
both parental generations are
homozygous. D
DIID
D YYO
OUUK
KNNO
OWW!!
1. Our entire DNA sequence would fill 200
B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
1,000-page New York City telephone
1. If two strains of true-breeding plants directories.
that have different alleles for a certain 2. It would take a person typing 60 words
character are crossed, their progeny are per minute, eight hours a day, around 50
called the ____________ years to type the human genome.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
3. We eat DNA every day.
4. Many things can cause mutations, 3. Demonstrate Mendel studies by
including UV irradiation from the sun, completing following cross.
chemicals like drugs, etc. Male Female
5. If all three billion letters in the human Parental yy x YY
genome were stacked one millimeter Generation
apart, they would reach a height 7,000
times the height of the Empire State Gametes _____ ______
Building.
6. Over 99% of our DNA sequence is the F1 Generation
same as other humans. ________ Genotype ______ Phenotype
7. If the human genome was a book, it
would be equivalent to 800 dictionaries. Male Female
8. Genes make up only 2-3% of the human Parental Yy x Yy
genome. Generation
9. It takes about 8 hours for one of your
cells to completely copy it's DNA Gametes ( ____ ____) X ( _____ _____)
10. It would take 57 years to recite your
ATCGs at a rate of 100 per minute if you
started tomorrow morning. F2 _______ _______ _______ _____
11. You could fit one million threads of Genotypes
DNA across the period at the end of this Gen.
sentence. _______ _______ _______ ______
12. There are three billion (3,000,000,000) Phenotypes
base pairs in the DNA code within each
cell.
13. Humans have approximately 30,000
genes.
C
C.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
1. Why Mendel chose pea plant in his
experiments? Explain the features of pea
plant.
2. What is the difference between self-
fertilization and cross-fertilization?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 5: MONOHYBRIDE CROSS heterozygous offspring. Leave all the
homozygous recessive offspring
unshaded.
N N N n
n N
n N
N n N n
N n
n n
3. In pea plant, tall pea, T, is dominant to
short pea, t. Complete the following
Punnett squares according to the
directions given. Then, fill in the blanks
1. Examine the following Punnett squares
beside each Punnett square with the
and circle those that are correct.
correct numbers.
D d D D
d Dd dd d Dd DD a. One pea plant is Tt and one is tt.
d Dd dd d Dd Dd
A a A a
Expected number of offspring:
A AA aa a Aa aa ____ Tall pea (TT or Tt)
____ Short pea (tt)
a Aa Aa a Aa aa b. Both pea plants are heterozygous for
lenght.
2.In corn plants, normal height, N, is
dominant to short height, n. Complete
these four Punnett squares showing
different crosses.
Expected number of offspring:
Then, shade red all the homozygous ____ Tall pea (TT or Tt)
dominant offspring. Shade green all the ____ Short pea (tt)
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
F1
4. Hornless (H) in cattle is dominant over Gametes:
horned (h). A homozygous hornless bull
is mated with a homozygous horned cow.
What will be the genotype and phenotype
of the first generation? F2
P1
Genotype ratio:
Gametes:
Phenotype ratio:
5. The possible offspring that are
F1 produced at the end of fertilization are
given below. Find the genotypes of
parents. P: Parents F: Offspring
a) P: ____ x ____ b) P:____ x ____
F: AA, 2Aa, aa F: Aa, aa
c) P: ____ x ____ d) P: ____ x ____
5. In tomatoes, red fruit (R) is dominant
over yellow fruit (r). A plant that is
homozygous for red fruit is crossed with a F: AA, Aa F: AA
plant that has yellow fruit. What would
be the genotypes and phenotypes of the
B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
P1 and F1 generations?
P1 1. 50 % AA , 50 % Aa
Which of the following parent’s genotypes
Gametes: would produce the proportions in their
offspring shown above?
A) Aa x aa B) Aa x Aa
F1 C) AA x Aa D) AA x aa
2. When crossing two heterozygote
6. If two of the F1 generation from tomato yellow pea, what is the chance of getting
were mated, what would be the genotypes an offspring with the green pea?
and phenotypes of the F2? A) 0% B) 25%C) 50%D) 75%
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
3. Two brown-eyed adults had two with a homozygous tall plant, what is the
children, one with brown eyes and one probability that the offspring will be
with blue eyes. short?
This shows that for eye color, both parents A) 1/2 B) 1/4C) 0D) 1
were _______________
A) homozygous recessive
B) Heterozygous
C) homozygous dominant
D) dihybrid
4. Assume tall (T) is dominant to dwarf (t).
If a homozygous dominant individual is
crossed with a homozygous dwarf, the
offspring will ______.
A) all be intermediate in height
B) all be tall
C) be 1/2 tall and 1/2 dwarf
D) be 3/4 tall and 1/4 dwarf
E) all be short
5. 25 % AA , 50 % Aa, 25%aa
Which of the following parent’s genotypes
would produce the proportions in their
offspring shown above?
A) Aa x aa B) Aa x Aa
C) Aa x Aaa D) AA x Aa
6. P = purple, pp = white. The offspring of
a cross between two heterozygous purple-
flowering plants
(Pp × Pp) results in
A) all purple-flowered plants.
B) 3 purple-flowered plants and 1 white-
flowered plants.
C) two types of white-flowered plants: PP
and Pp.
D) all white-flowered plants.
E) all pink-flowered plants.
7. In certain plants, tall is dominant to
short. If a heterozygous plant is crossed
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 6: DIHYBRID AND TRYHYBRID
CROSS Gamete types SY Sy
SY
Sy
sY
sy
Yellow, smooth phenotype : _____
Yellow, wrinkled phenotype: ____
Green, smooth phenotype:_______
Green, wrinkled phenotype: _____
B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
1. In pea plant genes, one for purple
A
A.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
flower (P) and one for axial flower (A). If
1. The law of ___________________ pea genotype is PpAa, which of the
states that each allele will be inherited sep following genotypes is possible in a
arately from the others. gamete from this plant?
A) PA B) Pp
2. 9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio is the result we C) PpAa D) P E) aa
would expect to see from a cross between
parents with ___________ 2. A 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio is
genotypes for both traits. characteristic of which of the following?
A) monohybrid cross B) dihybrid cross
3.As you know in pea plants the yellow co C) trihybrid cross D) linked genes
lor (Y) allele is dominant to the green colo
r (y) allele and smooth pea texture (S) is d 3. A trihybrid cross is made between two
ominant to wrinkled (s). yeast, both with genotypes AaBbCc.
Calculate the probabilities of genotype/ph What proportion of the offspring will be
enotypes in the offspring from a cross bet of genotype aabbcc?
ween a SSYy and a SsYy parent. A) 1/64 B) 1/12
C) 1/16 D) 1/32
4. In the cross MMnn x mmNN, what
proportion of the resulting F1 would be
homozygous dominant for both genes?
A) none B) 1/16
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
C) 3/16 D) all 1. In rabbits, gray hair is dominant to
white hair. Also in rabbits, black eyes are
5. If AaBb is crossed with AaBb, what dominant to red eyes. These letters
proportion of the offspring will be dominant represent the genotypes of the rabbits:
for the 'A/a' trait and recessive for the 'B/b'
trait (i.e. A-bb)? GG = gray hair BB = black eyes
A) 9/16 B) 3/16 C) 1/16 D) 0 Gg = gray hair Bb = black eyes
gg = white hair bb = red eyes
6. If a heterozygous tall, heterozygous
round (TtRr) pea is crossed with another 1. What are the phenotypes (descriptions)
heterozygous tall, heterozygous round of rabbits that have the following
(TtRr) pea, the phenotypes of their genotypes?
offspring would be _________.
A) 9 round, tall; 3 round, wrinkled; 3 Ggbb ____________________
short, wrinkled, 1 short, tall ggBB ____________________
B) 9 tall, round: 3 tall, wrinkled: 3 short, ggbb ____________________
round: 1 short, wrinkled GgBb ____________________
C) 8 round tall: 8 short, wrinkled
D) All rounds, tall 2. A male rabbit with the genotype GGBB
E) All wrinkled, short is crossed with a female rabbit with the
genotype ggbb. What would be the
7. Which offspring’s genotype of the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1
following is impossible from parents that generations?
have AaBb X AaBB genotypes?
A) AABB B) AaBB C) aaBb P
D) Aabb E) AaBb Generation
8. Two organisms that have Gametes
AABbCCDdEe x aaBBCcDdEE genotypes
are crossed. What fraction of the offspring F1
will have AaBBCcDdEe genotype? Generation
A) 3/4 B) 1/16
C) 1/8 D) 1/32
9. In a dihybrid cross, AaBb x AaBb, what
fraction of the offspring will be
homozygous for both traits?
A) 1/16 B) 1/8 C) 3/16 D) ¼
C
C.. A
ANNSSWWEER
RT TH
HEE FFO
OLLLLO
OWWIIN
NGG
Q U E S T
QUESTIONSIO N S
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
3. If two F1 generation from above cross Gamete types:
mated
what would be the genotypes and F1
phenotypes of the F2?
F1
Gametes
B b B b
G GB G
g g
TOPIC 7:
F2 GB Gb gB gb A.TEST CROSS
B. INCOMPLATE DOMINANCE AND
GB CODOMINAMCE
__
__
__
How many out of 16 have gray fur and
black eyes? ________
How many out of 16 have gray fur and
red eyes? ________
How many out of 16 have white fur and
black eyes?
________
How many out of 16 have white fur and
red eyes?________
Write ratio of possible phenotypes of Figure: Test cross
offsprings.
A
A.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
3. Cross ddGgMm and DdGgmm
genotypes. 1. What is a genetic cross called between
an individual of unknown genotype and a
P homozygous recessive?
Generation A) a self-cross B) a test cross
C) a dihybrid cross
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
D) an F1 cross
B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
2. Which of the following is a test cross?
A) AABB X AaBb B) AaBB x AaBB
C) AABb x aabb D) AaBb x AaBb 1. Eye color in dragons shows incomplete
dominance. Red eyes (R) is dominant
3. A 1:2:1 phenotypic ratio in the F2 over yellow eyes (r) and heterozygotes
generation of a monohybrid cross is a sign have orange eyes. If a heterozygous male
of _______________________ mates with a heterozygous female:
A) complete dominance.
B) multiple alleles. a. Write out the genotypes for both
C) incomplete dominance. parents.
D) polygenic inheritance.
Male_Rr____ Female__Rr____
4. A zebra has a gene for black hair (B)
and a gene for white hair (W). Both of b. Write out the phenotypes for both
these traits are expressed in the phenotype parents. Male____Orange eye_____
of the zebra by forming black and white Female__ Orange eye ___
stripes. This genetic pattern is an example
of ______________________ c. Write out the alleles that will segregate
A) codominance into the male and female gametes
B) law of probability
C) incomplete dominance
D) law of dominance
5. When snap dragons with red (RR)
flowers are crossed with snap dragons
with white (rr) flowers, the resulting
offspring have pink flowers. This
illustrates the principle of:
A) dominance B) codominance
C) probability D) incomplete
dominance
d. Fill in the Punnett square boxes with
the correct allele combinations
e. List all possible genotypes and describe
Picture: Codominace the corresponding phenotypes.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
GenotypePhenotype 3. In radishes when a plant with red
radishes crossed with white radishes
purple radishes are produced.
a. What would the offspring look like in a
cross between a purple and a white?
f. What is the probability that the b. A red and a white?
offspring will have red eyes? c. A red and a purple?
g. What is the probability that the
offspring will have yellow eyes?
h. What is the probability that the
offspring will have orange eyes?
4. In humans straight hair (ss) and curly
hair (cc) are incomplete dominant traits,
that result in hybrids who have wavy hair
(sc).
a. Cross a curly hair female with a wavy
haired male.
b. What are the chances of having a curly
haired child?
C
C.. A
ANNSSWWEER
RT TH
HEE FFO
OLLLLO
OWWIIN
NGG
Q
QUUEESSTTIIO
ONNSS
1. Why test cross is made?
2. Compare and contrast incomplete
dominance and codominance. Give
example to each of them.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
TOPIC 8: B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
a. MULTIPLE ALLELE
b. EPISTASIS, PLEIOTROPY, 1. Which of the following include effect of
POLYGENIC INHERITANCE more alleles in single locus?
A) Polygenic inheritance
A. TRUE-FALSE B) Epistasis
1. _(…)_ In multiple allele more than two C) Multiple allele
alleles for one characteristics are found in D) Pleiotropy
different locus of DNA.
2. _(…)_ Mendel discovered multiple 2. AABBCC are three genes for skin color
allelic condition. of human. This is an example to ___
3. _(…)_ Four different genes determine A) Polygenic inheritance
the fur color of rabbit. B) Epistasis
4. _(…)_ In epistasis expression of one C) Multiple allele
gene is modified by other gene. D) Pleiotropy
5. _(…)_ ABO Blood groups are example
to polygenic inheritance. 3. Albinism is a genetic illness in which no
6. _(…)_ AB Blood group is an example to pigmentation occurs in skin and hair. This
codominance. in an example of _________
7. _(…)_ In pleiotropy one gene has A) Polygenic inheritance
multiple effect in phenotype of organism. B) Epistasis
C) Multiple allele D) Pleiotropy
4. In mice two genes determine coat color.
Gene C gives color while gene B gives
Black color. Which colors occur if both C
alleles are recessive?
A) Black B) Brown
C) Gray D) White
5. Sickle cell anemia is example to ______
A) Pleiotropy B) Epistasis
C) Multiple allele
D) Polygenic inheritance
6. Effect one gene depend on other gene in
___
A) Pleiotropy B) Epistasis
Epistasis in horse skin color
C) Multiple allele
D) Polygenic inheritance
7. Which of the following matings can
NOT produce a child with blood type O?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
The letters refer to blood types
(phenotypes). A B
A) A x A B) A x B
C) O x AB D) O x O AB
8. If one parent is blood type AB and the 3. Compare multiple allele and polygenic
other is type O, what fraction of their inheritance. Write their similarity and
offspring will be blood type A? difference.
A) 1/4 B) ½
C) 3/4 D) All of the above
9. 3. A woman with type O blood is 4. If a dark intermediate man and a dark
expecting a child. intermediate woman get married what is
Her husband is type A. Both the woman's the probability of their progeny being
father and her husband's father had type B born with light intermediate skin color.
blood. What is the probability that the (AaBbcc, AabbCc,aaBbCc)?
child will have type O blood?
A) 100% B) 75%
C) 50% D) 25%
C
C.. A
ANNSSWWEER
RT TH
HEE FFO
OLLLLO
OWWIIN
NGG 5. What is the probability of a child
Q U E S T
QUESTIONSIO N S having type O blood if one of its parents is
heterozygous for A blood and the other is
heterozygous for B?
1. Fill the following table about ABO
blood group system.
Blood Genotype Phenot
group ype
Homo- Hetero-
zygus zygous 6. Cross the following genotypes.
A a) RR x rr R: Rh (+) gene
B
AB r: Rh (-) gene
O
b) Rr x Rr
e) AB RR x 00 rr
2. Draw the pattern of transfusion
between blood groups with arrows as
shown below.
O f) A0 RR x B0 rr
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
B
BLLO
OOOD
D TTYYP
PEESS threat. Specialised white blood cells will
make antibodies designed to kill Rh-
The two main ways to classify blood positive blood cells.
groups are the ABO system and the Rh If the woman later conceives another
system. Together, they comprise the eight Rh-positive baby, her immune system will
main blood groups. Other blood group flood the fetus with antibodies. These
systems exist and, to date, researchers antibodies then destroy the baby’s red
have identified around 300 minor factors. blood cells. If left untreated, this can result
in severe anaemia or even death.
The ABO group
Out of 100 donors . . . . .
The four different blood groups in the
ABO system are A, B, AB and O. A 84 donors are RH+ 16 donors are RH-
person’s blood group is determined by a
38 are O+ 7 are O-
pair of genes, one each inherited from
their mother and father. Each blood group 34 are A+ 6 are A-
is identified by its own set of molecules 9 are B+ 2 are B-
(called antigens), which are located on the 3 are AB+ 1 is AB-
surface of red blood cells. When a person
needs a blood transfusion, it is important
that the donated blood matches their
particular blood group.
The Rh factor
A person’s blood type used to be
called their ‘Rhesus type’ but now we
simply say ‘Rh type’. Our Rh type is
determined by a pair of genes, one
inherited from each parent. Blood is either
Rh-positive or Rh-negative, depending on
whether or not certain molecules are
present.
A person who is Rh-negative will
experience a severe immune system
reaction if Rh-positive blood gets into
their bloodstream. This can happen
during pregnancy if an Rh-negative
woman carries an Rh-positive baby. If
blood cells from the baby travel across the
placenta, the woman’s immune system
will regard the Rh-positive cells as a
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 9: CHROMOSOME THEORY 4. A linkage map ______________
A) can show actual loci of genes.
A. TRUE-FALSE B) requires preparation of karyotypes.
1. _(…)_ Sutton proposed that genes are C) is a genetic map based on
located on chromosomes. recombination frequencies.
2. _(…)_ Passing of genes from one D) reflects the frequency of crossing over
generation to next on same chromosome is between X and Y sex chromosomes.
called linkage.
3. _(…)_ Number of genes smaller than 5. When does crossing over occur, during
the chromosome in same organism. ___?
4. _(…)_ In linked genes recombination A) meiosis B) mitosis
occur by crossing over. C) Asexual reproduction
5. _(…)_ The more distant genes on a D) Development
chromosome the more possible to separate
by crossing over. 6. The frequency of crossing over between
6. _(…)_ Distance between genes of same any two linked genes is
chromosome can be measured exactly. A) determined by their relative
dominance.
B. MULTIPLE CHOICES B) higher if they are recessive.
C) proportional to the distance between
1. Four genes (A, B, C, and D) are on the them.
same chromosome. The recombination D) difficult to predict.
frequencies are as follows: A-B: 19%; B-C:
14%; A-C: 5%; B-D: 2%; A-D: 21%; C-D: C
C-- SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
16%. Based on this information, which
sequence of genes is correct? 1. What is gene chromosome theory?
A) ABCD B) ABDC
C) ACBD D) ACDB
2. New combinations of linked genes are
due to __________
A) crossing over.
B) environmental changes such as 2. Why the rule of independent
temperature extremes. assortment is not always correct for genes
C) independent assortment. on the same chromosome?
D) nondisjunction. 3. In a particular species of mammal, black
hair (B) is dominant to green hair (b), and
3. If two genes are linked _____. red eyes (R) are dominant to white eyes
A) they are on different chromosomes (r). When a BbRr individual is mated with
B) they assort independently a bbrr individual, the observed
C) they code for the same protein distribution of offspring was as follows:
D) they are on the same chromosome black-red 1,060; black-white 187; green-
red 170; green-white 1,082. Based on these
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
data, what is the recombination
frequency?
2. Five genes are on the same
chromosome. Recombination frequencies
are as follows; A-B: 14%, A-E: 20%, A-D:
11%, A-C: 5%, B-E: 6%, D-E: 9%
According to this information find gene
sequence of this chromosome.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
4. The chromosomes that carry the genes
Topic 10: SEX DETERMINATION that have a role in sex determination are
called ________
_____________________________
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE
5. In every cell of all organisms, the
1. _(…)_ Phenotypic sex determination chromosomes (not including the sex
include environmental factors. chromosomes) carrying genes for the
2._ (…)_ If new hatchling of sea worm formation of somatic traits are called
attach to mother’s body it becomes female. ________________________.
3. _(…)_ If larvae of honey bee nourished
with sufficient food it develop in to queen. 6. Sex chromosomes are found in either
4. _(…)_ XX or XY chromosomes are sex homologous _____, or non-homologous
chromosomes or gonosomes in human. ______ condition.
5. _(…)_ ZZ chromosome give female
characteristic to some birds.
6. _(…)_ In some social insect diploid (2n) 33.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
organisms are male while haploids (n) are
male. 1. Which of the following factor is not
phenotypic in sex determination?
A) Temperature C) Nutrition
B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS B) XX chromosome D) Attaching to
mother
1. In some ______________ male and 2. Which of the following is a mechanism
females have similar genotypes but of genotypic sex determination in
stimuli from environmental sources drosophlia?
initiate development toward one sex or A) ZZ-ZW C) XX-XY
the other. B) XX-XO D) Diploid- Haploid
2. Phenotypic ______________ is also 3. Which of the following is a mechanism
observed in some plants. If the bulb of genotypic sex determination in birds?
shapes roots of Arisaema japonica are big A) ZZ-ZW C) XX-XY
(because of extra reserves), that plant B) XX-XO D) Diploid- Haploid
forms only __________ flowers. If surplus
nutrients are in small amounts, the plant 4. Which of the following is a mechanism
forms only _________ flowers. of genotypic sex determination in
grasshopper?
3. Genotypic sex determination is A) ZZ-ZW C) XX-XY
controlled by the ______________ of the B) XX-XO D) Diploid- Haploid
organism.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
5. Which of the following factors in the substances necessary to sustain life,
vertebrate animals determine secondary including enzymes, vitamins, minerals,
characteristics? and water
A) Reproductive hormones secreted by 5. Honey bees have 6 legs, 2 compound
sex organs eyes made up of thousands of tiny lenses
B) Environmental factors (one on each side of the head), 3 simple
C) Nerve impulses produced by brain. eyes on the top of the head, 2 pairs of
D) They develop spontaneously wings, a nectar pouch, and a stomach.
6. Honey bees have 170 odorant receptors,
PPHHEENNOOTTYYP
PIIC
C SSEEX
X compared with only 62 in fruit flies and 79
in mosquitoes.
D
DEETTEER
RMMIIN
NA ATTIIO
ONN IIN
NHHO ONNEEYY B
BEEEE
7. The honey bee's wings stroke incredibly
fast, about 200 beats per second, thus
making their famous, distinctive buzz. A
honey bee can fly for up to six miles, and
as fast as 15 miles per hour.
8. The average worker bee produces about
1/12th teaspoon of honey in her lifetime.
9. A hive of bees will fly 90,000 miles, the
The term queen bee is typically used to
equivalent of three orbits around the earth
refer to an adult, mated female that lives
to collect 1 kg of honey.
in a honey beecolony or hive; she is
10. A colony of bees consists of 20,000-
usually the mother of most, if not all, the
60,000 honeybees and one queen. Worker
bees in the hive. The queens are developed
honey bees are female, live for about 6
from larvae selected by worker bees and
weeks and do all the work.
specially fed in order to become sexually
mature. There is normally only one adult,
mated queen in a hive.
(www.wikipedia.org)
Amazing Facts about honey bee!
1.The honey bee has been around for
millions of years.
2. Honey bees are environmentally
friendly and are vital as pollinators.
3. It is the only insect that produces food
eaten by man.
4.Honey is the only food that includes all
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
2. _(…)_ Nucleotides are named according
44.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R to their nitrogenous base, like Adenine
nucleotide.
1. Explain how phenotypic or genotypic 3. _(…)_ In DNA number Adenine joins
sex determination related with with Cytosine and Guanine joins with
complexity? Tymine.
4. _(…)_ Two chain of DNA is connected
with Hydrogen bonds.
5. _(…)_ DNA replicate itself by
conservative replication.
2. Why do human sex chromosomes 6. _(…)_ Replication and duplication are
represented with double X letters in synonyms which refers copy ability of
female and XY letters in males? DNA.
7. _(…)_ RNA has deoxyribose sugar
which differ from DNA.
3. Which parent (male and female) 8. _(…)_ tRNA is transport amino acids
determines the sex of child? Why? from cytopladsm to ribosome.
B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
4. Write chromosome numbers of the
following organisms.
1. Triple nucleotide units on m RNA is
Queen: ___ Soldier: ___ called ________
Worker:___ Male: ___ 2. DNA copy itself in the rule of
________________________
Topic 11: MOLECULAR BASIS OF 3.First strand of DNA
INHERITANCE is__________________to the second
strand.
4. Synthesis of mRNA from DNA is called
Key Words ____________________
5.Production of polypeptide according to
Nucleotide Replication mRNA code is called
Transcription Translation ___________________
Codon Anticodon 6. Represor proteins
mRNA tRNA are coded by
Operon Promoter __________________
Operator _______
7. The site of DNA in
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE which RNA
polymerase binds
1. _(…)_ DNA is the blueprint of for transcription is
organism. called_____________
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
____. 4. 15. In mRNA the "start" sequence is
8. The part of DNA that controls _____________________________
expression of structural genes is called A) UAA B)UAG C)UGA D)AUG
_________________
5. In a process called _____________, the
initial tRNA is ejected from the ribosome.
A) elongation B) translocation
C) initiation D) transcription
6. The process of _______________ cuts
introns from the primary transcript and
the final "processed" mRNA is produced.
A) RNA cleaving B) RNA translocation
C) RNA elongation D) RNA splicing
7. The direct result of transcription is:
____________________________
A) a duplicate DNA molecule
B) Nrna C) a protein D) mRNA
8. Which one of the following is not
associated with transcription?
A) tRNA B) mRNA
C) RNA polymerase D) DNA
33.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
9. In an analysis of the nucleotide
composition of DNA, which of the
1. The order in which nucleotides are following is true?
moved along the ribosomes binding sites A) A = C B) A = G and C = T
is C) A + C = G + T D) T + A = G + C
A) APE B) PEA
C) EPA D) EAP 10. A repressor protein binds with
A) messenger RNA B) the operator
2. In eukaryotes, there are __________ C) the regulator D) a product
codons that specify amino acids.
A) 21 B) 24 C) 61 D) 64 E) 60 11. In a DNA there are 24000 nucleotides.
If number of Adenines are 4500, find the
3. In eukaryotes, the "start" codon also number of cytosine nucleotides?
specifies the amino acid, A) 6500 B) 7000
A) phenylalanine B) valine C) 7500 D) 8000
C) aspartate D) methionine
E) methionine 12. The lactose operon includes
A) an operator
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
B) three structural genes that
manufacture lactose-metabolizing
enzymes
C) a promoter
D) an operator, three structural genes
that manufacture lactose- 2. What is central dogma?
metabolizing enzymes, and a
promoter
Answer questions 13–17 in reference to
the five items of gene regulation listed
below.
a. operon b. operator 3. Compare regulation of transcription in
c. promoter d. lactose lac operon and Trp operon? What are their
e. regulator gene differences?
13. This item contains regulator,
promoter, and operator regions.
14. A repressor protein can shut down
transcription by binding to this item.
4. What is mRNA processing? Why it is
15. This item codes for the production of necessary?
the repressor.
16. When the repressor is inactivated,
RNA polymerase can bind to this item
and allow transcription to occur.
17. The molecule that can activate the
operon is represented by this item.
Answers: 13.___ 14.___ 15. ___
16. ___ 17. ___
44.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
1. What are differences between DNA and
RNA?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
LLA
ACC ((LLA
ACCTTO
OSSEE)) O
OPPEER
ROON
N
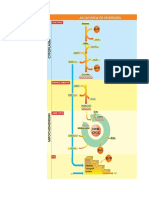
Operon is a part of DNA that
control production of a protein. It is made
of regulatory gene, promoter, operator
and genes for transcription.
Lactose operon is a type of operon
that is found in bacillus bacteria.
Production of enzymes for lactose sugar
is managed by this operon.
If lactose is absent repressor protein
remains active and binds to operator since
lac operon is switched off.
If lactose is present it binds to
repressor protein and makes it inactive. So
repressor cannot bind to operator and Lac
operon is switched on. It start to produce
necessary enzymes to break down lactose
sugar.
Figure: Lac operon switched off
Figure: Lac operon switched on.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 12: CHANGES IN GENETIC very important in formation of new
MATERIAL genetic variations.
4. If the chromosome number is some
multiple of n it is called _____________.
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE 5. A cross between a tetraploid plant and a
diploid hybrid individual of the same
1. _(…)_ Genetic material of eukaryotic species gives a ___________ plant.
cell is highly protected with proteins and 6. If one chromosome is missing in a
nuclear membrane. diploid individual (2n-1) it is called
2. _(…)_ Change in the whole genetic _______________________.
material is called macromutation or 7. _______________ occur in the structure
chromosomal mutation. of DNA during replication, formed
3. _(…)_ In inversion a non homologous abnormal genes.
chromosomes swap pieces. 8. Mutation causing factor is called
4. _(…)_ All mutations are harmful. ____________________.
5. _(…)_ In euploidy chromosome number
multiples or turn in to haploid condition.
6. _(…)_ In triploidy chromosome number 33.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
becomes 3n+1.
7. _(…)_ Male honey bee is a monoploid
(n) organism. 1. Which of the following mutation is not
8. _(…)_ Colchisin is a chemical that a structural change?
prevent crossing over during meiosis. A) Deletion B) Inversion
C) Translocation D) Transduction
Answer questions 2–6 in reference to the
five items of mutation listed below.
A. Translocation B. Inversion
C. Deletion D. Dublication
Picture: Polydactyly (extra digits) is a
E. Polyploid
type of mutation
2. Removal a piece of chromosome
B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
3. Two non-homologous chromosome
swap pieces 4. Repeating a piece of
1. Change in the genetic material is chromosome
called______________.
2. In ____________ one segment of 5. Multiple of usual chromosome number.
chromosome comes two times.
3. ____________ is types of change in the 6. A segment flips 1800 and reattach
structure of chromosome in which it is
2. ___ 3. ___ 4.___ 5.___ 6.___
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
7. All of the following chromosomal 14. Which of the following mutations
mutation except; cause to lose of genes from Karyotype?
A) Diploidy B) Trisomy A) Polyploidy B) Deletion
C) Nucleotide reduction C) Inversion D) Dublication
D) Deletion
8. Which of the following is a form of D
D.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
aneuploidy?
A) Diploidy B) Turner syndrome 1. What are mutagens?
C) Point mutation D) Deletion
9. Abnormal change in nucleotide level of
chromosome is called _____ 2. What is the difference between
A) Diploidy B) Turner syndrome Chromosomal and Point mutations?
C) Monosomy D) Point mutation
10. Which of the following is a visible
effect of mutation? 3. Which type of change in the structure of
A) Change in DNA code chromosomes are harmful and which are
B) Change in protein structure beneficial?
C) Change in phenotype
D) Change in genes
11. Which of the following illnesses 4. Why polyploidy can be a beneficial
caused by mutation? mutation? Explain it?
I. Cancer II. AIDS
III. Sickle cell anemia
IV. Down syndrome
V. Pneumonia 4. Compare euploidy and aneuploidy?
A) I-II-III B) II-III-V Write their difference?
C) I-IV-V D) I-II-IV
12. Polyploidy especially can be seen in SSM
MOOK
KIIN
NGGCCA
AUUSSEESS G
GEEN
NEE::
_________________ M
MUUT
TAAT
TIIO
ON N
A) Plant B) Human
C) Animal D) Bacteria Recent studies have uncovered yet
13. Which of the following most another negative effect of smoking – the
threatening mutagens of people in this genetic mutation of DNA. A recent
century? Canadian study has demonstrated that
A) Chemicals B) Cigarette smoking causes DNA mutations within
C) Light D) Acids sperm cells, implementing that children of
male smokers may inherit permanent and
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
negative changes to their DNA before
they are even born.
Two comprehensive studies
conducted in the United States and the
United Kingdom have further revealed
that a single lung tumor is likely to
contain tens of thousands of genetic
mutations, and that additionally fifteen
cigarettes will cause a single genetic
mutation. If you’re wondering whether
genetic mutation is really a big deal, let
me assure you, it is. When cells are caused
injury because of the body’s condition,
which may include being exposed to the
sun’s harmful UV rays or smoke
inhalation, the cell becomes a genetic
‚error‛ and begins to multiply in an out-
of-control fashion. This mutated cell
literally becomes cancerous, and as it
continues to multiply, it will either form a
malignant or benign tumor.
If smoking just fifteen cigarettes has
the potential to mutate your genes and
give you cancer, every pack of cigarettes
you buy could put you on your deathbed.
For example, smoking just one pack of
cigarettes per week will leave you with
forty-eight gene mutations at the end of
the year, one of which could be life-
threateningly cancerous.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 13: HUMAN KARYOTYPE AND 5.Distribution of traits among members of
PEDIGREE a family is shown in a diagram called
______________.
T
TRRU
UEE-- FFA
ALLSSEE
C
C.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
1. _(…)_ Human has 23 pairs of body Answer questions 1–5 in reference to the
chromosome and 2 sex chromosome. five items of pedigree listed below.
2. _(…)_ Human karyotype refers
alignment of chromosomes according to A. E group chromosomes.
certain system. B. C group chromosomes.
3. _(…)_ In karyotyping C group have 7 C. Idiogram
similar chromosomes. D. Dark bands on chromosomes.
4. _(…)_ A pedigree is a table, chart or E. Pedigree
diagram that shows the ancestral history
of an individual. 1. Family tree
5._ (…)_ In pedigree shaded circles 2. A diagram of human karyotype.
indicate carrier males of certain traits. 3. Chromosome from 6 to 12.
6. _(…)_ Pedigrees are either autosomal or 4. Chromosomes from 16 to 18
gonosomal. 5. Exons
1. ___ 2.___ 3.___ 4.___ 5.___
6. Chromosomes are numbered from 1 to
22 according to their ____
B. FILL IN THE BLANKS A) Size B) Proteins
C) Centromeres D) Genes
1. Females have _____ pairs of body
chromosome and ____ sex chromosomes. 7. Pedigree is prepared according to
2. According to naming system __________
chromosomes are divided into ___ groups A) Autosomes B) Gonosomes
these are _________________ based on C) Both autosomes or gonosomes
their size and the position of their D) Neither of them
centromeres.
3. A pedigree is used to determine Refer to the pedigree chart in Figure 13.1
whether an individual is heterozygous or for a family, some of whose members
_____________ for a certain trait. exhibit the trait for wooly hair.
4. The sex cells are both the same in
females; ______ but different in males;
____
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
2. Albinism is carried with a recessive
allele. In the following pedigree a normal
male married with albino female. Find the
genotype of I1, II2 , III2
14. What is the genotype of individual B-
5?
A) WW only B) Ww only
C) ww only D) WW or ww
3. Today, with the help of new techniques,
some of the nucleotide sequence of human
15. What is the genotype of individual D-
chromosomes has been defined. What is
3?
the benefit of this development to
A) WW only B) Ww only
humanity?
C) ww only D) WW or ww
D
DIID
D YYO
OUUK
KNNO
OWW!! B
BAAR
RRRB
BOOD
DYY
D
D.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
1. In the following pedigree fill in the
blanks and circle the following items.
A. Normal marriage
B. Father mother and kids.
C. Normal Nephew A Barr body (named after
discoverer Murray Barr) is the inactive X
chromosome in a female somatic cell. The
Lyon hypothesis states that in cells with
multiple X chromosomes, all but one are
inactivated during mammalian
embryogenesis. This happens early in
embryonic development at random in
mammals except in marsupials and in
some extra-embryonic tissues of some
placental mammals, in which the father's
X chromosome is always deactivated.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
The main reason why one of the X
chromosomes goes inactive is very
simple..... gene overdose!!!! another
words, if both X's which contain pretty
identical regions for the most part since
they are usually pertaining to
developmental proteins and shaping of
the brain and what not, if both were
turned on, cells were be toxified so to
speak with all the proteins created by
these two very similar chromosomes.
How cell understood this problem and
inactivated second X chromosome?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 14: SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE 6. A carrier mother get married with a
IN HUMAN hemophilic father. Write possible
genotype and phenotypes of gametes and
their offspring in figure below.
TRUE- FALSE (XH:Normal gene, Xh: Hemophilia gene)
1. _(…)_ Daltonism is an X linked disease.
2. _(…)_ Males can be carrier of
hemophilia
3. _(…)_ Human body unable to control
bleeding in hemophilia.
4. _(…)_Attached finger or toes is an X
linked disease.
5. _(…)_ Colorblindness and hemophilia
especially seen in intermarried families. C
C.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
6. _(…)_ Scaled skin and hair in the ear are
Y linked traits. 1. In an X-linked, or sex-linked trait, it is
the contribution of _____ that determines
whether a son will display the trait.
B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS A) the mother B) the father
C) the paternal grandmother
D) the paternal grandfather
1. A colorblind individual can not
distinguish between _______ and 2. A colorblind woman and a man with
___________ normal vision have a son. What is the
2. Colorblindness can occur in females probability that the son is colorblind?
only if the colorblindness gene is A) 100 percent B) 75 percent
________________ C) 50 percent D) 25 percent
3. If mother have hemophilia all her
________ will born with hemophilia. 3. Red-green color blindness is a sex-
4. Complete colorblindness is carried with linked recessive trait in humans. Two
____________ chromosomes. people with normal color vision have a
5. In humans, sex linked inheritance is color-blind son. What are the genotypes of
based on _______ and _______ the parents?
chromosomes. A) XcXc and XcY B) XcXc and XCY
C) XCXC and XcY D) XCXc and XCY
4. If a daughter expresses an X-linked
recessive gene, she inherited the trait from
A) her mother B) her father
C) both parents D) neither parent
5. Red-green colorblindness is an X-linked
recessive trait in humans. What is the
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
probability that a colorblind woman and a b. What is the probability of parents 1 and
man with normal vision will have a 2 having a hemophiliac child?
colorblind daughter?
A) 0 percent B) 75 percent
C) 50 percent D) 25 percent
D
D.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
1. Colorblindness is carried with a
recessive allele on X chromosome. In the
following pedigree a colorblind male
married with normal female. Find the
genotype of individual II-2, III-3, IV-5
4. What is the probability that a male will
(XrY: Colorblind male), (XRXr: Carrier
inherit an X-linked recessive allele from
female)
his father?
Answer: _________
5. A woman is a carrier for red-green
colorblindness, a sex-linked trait. Her
husband is colorblind. What are the
chances that their newborn daughter will
be red-green color-blind?
Answer: ____
2. A Hemophilia carrier woman marries a
man that has normal genetic structure.
What is the probability of Hemophilia
children in their offspring?
3. a. Females who have more than four
sons, with nonexhibiting hemophilia, are
likely to have the genotype NN. If she has
had four or fewer sons her genotype is
less certain. In such cases her genotype is
labelled N. LABEL THE REST OF THE
FEMALES AS EITHER N? OR NN.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
HUMAN GENETIC DISEASES A) Meta female B) Turner syndrome
Topic 15: NONDISJUNCTION C) Down syndrome D) Meta male
A 5. Which of the following is type of
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE
autosomal nondisjunction?
A) Meta female B) Turner syndrome
1._(…)_ Making genetic experiment with C) Down syndrome D) Meta male
human is illegal in laws.
2. _(…)_ Today diagnosis and treatment of 6. _____s are tall and fertile, but mentally
genetic diseases are easier. subnormal, antisocial.
3. _(…)_ Probablity of being genetic ill in A) Meta female B) Turner syndrome
boy and girl equal. C) Down syndrome D) Meta male
4. _(…)_ Mongolism is a type
nondisjunction.
5. _(…)_ In Turner female one X B
B.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
chromosome is more than usual.
6. _(…)_ Down syndrome can be seen in 1. Research on humans is based on
both female and males. _____________,
7. _(…)_ Nondisjunction occur during twins, ______________, population
meiosis. methods and ___________________.
8. _(…)_ Metamales are infertile.
2. Gene disorders are inherited by
________________ dominant or autosomal
C ___________ inheritance, or
C.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS
______________ linked inheritance.
1. Which one of the following is the only
known viable human Monosomy? 3. ________________; having more
A) XYY B) XO chromosomes than normal.
C) YO D) XY
4. _________________ is characterized by
2. In ______ there is an extra Y varying degrees of mental retardation;
chromosome. short in height, round full face enlarged
A) Down syndrome B) Turner syndrome and creased tongue, and noticeable eye
C) Kleinfelter syndrome D) Meta male folds.
3. In ____ syndrome the affected people
are female but undeveloped genitals and
sterile.
A) Down syndrome B) Turner syndrome
C) Kleinfelter syndrome D) Meta male 5. Fill in the blanks in the following figure.
4. In _____ syndrome there is an extra X
chromosome.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
D. SHORT ANSWER
1. What is the meaning of Non-
disjunction?
2. What are the symptoms of kleinfelter
syndrome?
3. Compare a mongoloid male and meta
male?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
Topic 16: AUTOSOMAL GENETIC A) albinism B) hemophilia
DISEASES IN HUMANS C) progeria
D) Huntington’s disease
A
A.. T
TRRU
UEE--FFA
ALLSSEE Match the following disorder with their
cause.
3. ___ __Down syndrome
1. _(…)_ If genetic disease caused by 4. _____hemophilia
autosomal recessive genes, an individual 5. _____ Turner syndrome
must be homozygous recessive in order to 6 ____Albinism
be affected. 7. ____Huntington’s disease
2. _(…)_ Today most genetic disease can 8. _____ colorblindness
be cured.
3. _(…)_ PKU sufferers lack enzyme A. autosomal recessive inheritance
carboxylase which convert phenylalanine B. nondisjunction of the twenty-first
to tyrosine. chromosomal pair
4. _(…)_ Albinism is an autosomal C. X-linked recessive inheritance
recessive disorder. D. nondisjunction of the sex
5. _(…)_ Albino person lack melanin chromosomes
pigment in hair. E. Autosomal dominant inheritance
6. _(…)_ In cyctic fibrosis sufferer must eat
low carbohydrate diet. 9. Four of the five answers listed below
7. _(…)_ In sickle cell anemia, abnormal are caused by recessive genes. Select the
erythrocyte block tiny blood vessels. exception.
8. _(…)_ In Tay-Sachs disease lipids A) Huntington disorder
accumulate in the brain and nervous B) hemophilia
system began to breakdown. C) colorblindness
D) phenylketonuria
B
B.. M
MUULLT
TIIPPLLEE C
CHHO
OIIC
CEESS 10. Which of the following disease occurs
either from environmental factors or
1. Albinos have a genotype of (aa), while inheritance.
all other members of a population are A) Huntington disorder
either (Aa) or (AA). The offspring of a B)phenylketonuria
cross between a heterozygous male and an C)Deafness
albino female would be: D) hemophilia
A) 100% albino B) 100% normal
C) 50% normal; 50% albino
D) 25% normal; 75% albino
2. Which of the following is more common
in males?
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
6. Hypertension, cancer, diabetes, harelip,
11. Abnormal mucus secretion in cleft palate are example to ___________
respiratory tract is seen in _____ diseases.
A)phenylketonuria
B) Cystic fibrosis 7. ______________ is an autosomal
C) colorblindness dominant connective tissue disorder
D) hemophilia characterized by unusually long limbs.
12. In which disease glutamic acid replace 8. ____________ is having many finger or
with valine in the structure of toes.
hemoglobin?
A) phenylketonuria
B) Cyctic fibrosis D
D.. SSH
HOOR
RTTA
ANNSSW
WEER
R
C) Sickle cell anemia
D) Color blindness
1. What is the reason of phenylketonuria?
C
C.. FFIILLLL IIN
NTTH
HEE B
BLLA
ANNK
KSS
1. Without melanin an individual appears
completely____________, with
extremely________ skin, _______hair and 2. Why hair loss is seen in male more than
pink eyes. female?
2. A Person who is ____________ with
cystic fibrosis lacks a functional form of a
transmembrane protein that is a CI ion
channel.
3. What are the symptoms of Marfan
syndrome?
3. In sickle cell anemia the abnormal
hemoglobin called S differs from normal
hemoglobin, called ________________.
4. The gene responsible for red and green
vision is located on the ____ 4. What is amnio-synthesis? Explain it
____________________. shortly?
5. In Tay-Sachs disease sufferer unable to
synthesize an ________ that prevents lipid
building up in __________.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
CLASS 9,10 BIOLOGY
FFEETTA
ALL A
ALLC
COOH
HOOLL SSYYN
NDDR
ROOM
MEE
SYMPTOMS
Fetal alcohol syndrome is growth, mental,
and physical problems that may occur
in a baby when a mother drinks alcohol
during pregnancy.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Using or abusing alcohol during
pregnancy can cause the same risks as
using alcohol in general. However, it
poses extra risks to the unborn baby.
When a pregnant woman drinks
alcohol, it easily passes across the A baby with fetal alcohol syndrome may
placenta to the fetus. Because of this, have the following symptoms:
drinking alcohol can harm the baby's Poor growth while the baby is in
development. the womb and after birth
A pregnant woman who drinks any Decreased muscle tone and poor
amount of alcohol is at risk for having a coordination
child with fetal alcohol syndrome. No Delayed development and
"safe" level of alcohol use during problems in three or more major areas:
pregnancy has been established. Larger thinking, speech, movement, or social
amounts of alcohol appear to increase skills
the problems. Binge drinking is more Heart defects such as ventricular
harmful than drinking small amounts septal defect (VSD) or atrial septal
of alcohol. defect (ASD)
Timing of alcohol use during pregnancy is Problems with the face, including:
also important. Alcohol use appears to o Narrow, small eyes
be the most harmful during the first 3 o Small head
months of pregnancy; however, o Small upper jaw
drinking alcohol any time during o Smooth groove in upper lip
pregnancy can be harmful. o Smooth and thin upper lip
TREATMENT
Women who are pregnant or who are
trying to get pregnant should avoid
drinking any amount of alcohol. Pregnant
women with alcoholism should join an
alcohol abuse rehabilitation program and
be checked closely by a health care
provider throughout pregnancy.
Date: ____/_____________/ 2013 Signature: _____________________
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1 ST Periodical Exam 9Document3 pagini1 ST Periodical Exam 9Lordy Joy Geralde CalimpusanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCI8 - Q4 - M3 - Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument18 paginiSCI8 - Q4 - M3 - Mendelian Patterns of Inheritanceapple chanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialDocument9 paginiWeek 3 DNA - The Genetic MaterialCarl Brian L. MonteverdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Practice Problems - Simple Worksheet Name - Class PeriodDocument5 paginiGenetics Practice Problems - Simple Worksheet Name - Class PeriodGar FieldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contextualized Learners ModuleDocument23 paginiContextualized Learners ModuleSou MeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesDocument5 paginiDemonstration Lesson Plan in Genetics 8 Grade: I. ObjectivesCherry MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester Two Examination Genetics Revision (PW 1 and Ext)Document16 paginiSemester Two Examination Genetics Revision (PW 1 and Ext)bk3pgxrthpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2 Complete DominanceDocument4 pagini3.2 Complete DominanceLorelyn VillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 03 Henry PriceDocument2 paginiAssignment 03 Henry PriceHenry PriceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 1 Vocabulary Literay - Student GuideDocument6 paginiActivity 1 Vocabulary Literay - Student Guideapi-233187566Încă nu există evaluări
- Science8 - q4 - CLAS3 - GENETICS - Its - Meaning - and - Principles - v6 - Carissa CalalinDocument13 paginiScience8 - q4 - CLAS3 - GENETICS - Its - Meaning - and - Principles - v6 - Carissa CalalinkennethÎncă nu există evaluări
- ActivityDocument4 paginiActivityDen Angelica DungoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCI19 Q1 M3 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument46 paginiSCI19 Q1 M3 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceJp DiolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 4 Science 8 MENDELIAN GENETICS WORKSHEETSDocument5 paginiQuarter 4 Science 8 MENDELIAN GENETICS WORKSHEETSccam88743Încă nu există evaluări
- Science G9 Q1 W3 M1 PDFDocument21 paginiScience G9 Q1 W3 M1 PDFRandolf CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3. LAS 3. Sci 9Document7 paginiWeek 3. LAS 3. Sci 9Rogin CarvajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment-1 Genetics 341Document4 paginiAssignment-1 Genetics 341damionsimmons10Încă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 14.1 Human Chromosomes: For Questions 1-7, Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Line at The LeftDocument5 paginiWorksheet 14.1 Human Chromosomes: For Questions 1-7, Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The Line at The LeftElizabeth MurtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Study Guide Answer Key 6Document4 paginiChapter 5 Study Guide Answer Key 6Siok Hon HawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics WorksheetsDocument3 paginiGenetics WorksheetsJohn ferdinand TamayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science - G9 - Week 3 (Lessons 7-10)Document44 paginiScience - G9 - Week 3 (Lessons 7-10)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz On Mendelian GeneticsDocument2 paginiQuiz On Mendelian GeneticsslytheraineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 3Document16 paginiScience 8 - Q4 - Week 3AlfielAquino100% (1)
- Inheritance ProblemsDocument10 paginiInheritance ProblemsRalph Rezin MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 paginiAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- Genetic Test Review SPDocument6 paginiGenetic Test Review SPapi-316619857Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 - Q1 - Mod3 - Non Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance - VerFinalDocument32 paginiScience 9 - Q1 - Mod3 - Non Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance - VerFinalRica Mae A. AmpilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8''may31 FinalDocument83 paginiScience 8''may31 FinalPrincess Ronquillo - DuqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument20 paginiSCIENCE-8 - Q4-Week 3 Mendelian Geneticsjomarie estibal100% (1)
- Mendel Webquest SHORT KEYDocument3 paginiMendel Webquest SHORT KEYJacob Hunre100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Biology-GeneticsDocument5 paginiLesson Plan in Biology-GeneticsCaryl Pabas75% (4)
- Biology M14 Genetics - The Study of Inherited TraitsDocument33 paginiBiology M14 Genetics - The Study of Inherited TraitsDiana Dealino-SabandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 8: Learning Activity SheetDocument19 paginiScience 8: Learning Activity SheetVan Amiel CovitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genbio2 ModuleDocument47 paginiGenbio2 ModuleAlbert Rosete100% (1)
- Grade 9 Module 3Document20 paginiGrade 9 Module 3Paul AniceteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Q1 Mod3 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument32 paginiScience 9 Q1 Mod3 Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceSkyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10A - Bio - All - Worksheets - Quizzes 4Document49 pagini10A - Bio - All - Worksheets - Quizzes 4Farzad FarhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Melc 3 HeredityDocument37 paginiMelc 3 HeredityJENNIFER DAVIDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Quarter 1 Module 8-SEX-RELATED-TRAITSDocument22 pagini8 Quarter 1 Module 8-SEX-RELATED-TRAITSMah Jane Divina50% (4)
- Biology WDocument31 paginiBiology WAbdulrahman BrghlehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Document34 paginiBiology Module 14. Genetics - The Study of Inherited Traits2Kameshvra92% (12)
- Module 2Document28 paginiModule 2Mark Dantes SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ds85 - Genetics Vocabulary PracticeDocument4 paginids85 - Genetics Vocabulary Practiceapi-110789702Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Basics WorksheetDocument2 paginiGenetics Basics WorksheetEsther CAVERO CLEMENTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- G9 Science Worktext - Attachment For Week 4-5 PRINTEDDocument5 paginiG9 Science Worktext - Attachment For Week 4-5 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm - 2nd - Sem - Biology OnlineDocument3 paginiMidterm - 2nd - Sem - Biology OnlineMa.Janice GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cot 1 - LessonDocument38 paginiCot 1 - LessonEden Rey ParoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO2 - Preliminary ExamDocument2 paginiBIO2 - Preliminary ExamOliver VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Honors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Document4 paginiHonors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Irene AntiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1 Sci9 Mod7Document18 paginiQ1 Sci9 Mod7Regine Rafer EscalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1-Human TraitsDocument5 paginiExperiment 1-Human TraitsNUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aligned Assignment To ObjectiveDocument3 paginiAligned Assignment To ObjectiveJayson_HÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 10 Test PaperDocument3 pagini9 10 Test PaperNaj AzisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)Document9 paginiActivity 1.9 (One For Each Teacher)phathutshedzomudzanani24Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Practice ProblemsDocument4 paginiGenetic Practice Problemsfaezeh zare karizakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution LabDocument8 paginiEvolution LabAnnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZoologyDocument136 paginiZoologyAnelya Turgambayeva100% (3)
- BotanyDocument102 paginiBotanyAnelya Turgambayeva100% (1)
- Human BiologyDocument216 paginiHuman BiologyAnelya Turgambayeva100% (1)
- CytologyDocument223 paginiCytologyAnelya Turgambayeva71% (7)
- Ecology PDFDocument112 paginiEcology PDFAnelya TurgambayevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOLOGY+Specification+NUFYP+2017+v1 0+fDocument12 paginiBIOLOGY+Specification+NUFYP+2017+v1 0+fAnelya TurgambayevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cytology PicturesDocument10 paginiCytology PicturesAnelya TurgambayevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY+Specification+NUFYP+2017+v1 0+fDocument12 paginiCHEMISTRY+Specification+NUFYP+2017+v1 0+fAnelya TurgambayevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBS BreedingDocument24 paginiRBS Breedingbogs8065100% (5)
- Curriculum Pacing Guide For Grade 8 in Science IIDocument28 paginiCurriculum Pacing Guide For Grade 8 in Science IIDon King EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 5 - Principles of InheritanceDocument11 paginiChap 5 - Principles of Inheritanceshreyavjha2020Încă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument429 paginiPDFOki NurpatriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Genetics and Genomics - 2022 - FinalDocument357 paginiMedical Genetics and Genomics - 2022 - FinalCsaba SzalaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 - Heredity & EvolutionDocument18 pagini04 - Heredity & EvolutionSamveg ClassesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polygenic InheritanceDocument2 paginiPolygenic InheritanceAppuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1M5Document29 paginiQ1M5Jesus GombaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modifications To Mendel's Classic Ratios: General Biology II Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDocument22 paginiModifications To Mendel's Classic Ratios: General Biology II Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDyames TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Plant Tissue CultureDocument40 paginiIn Plant Tissue CultureKiran KurhadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extending Mendelian Genetics For Two or More GenesDocument27 paginiExtending Mendelian Genetics For Two or More GenesGerald GuevarraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8Biology-Feb 22Document3 pagini8Biology-Feb 22APRIL DATAHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyd, R., & Silk, J. B. (2008) - How Humans Evolved. Chapter 2. Genetics. (24 - 52) .Document29 paginiBoyd, R., & Silk, J. B. (2008) - How Humans Evolved. Chapter 2. Genetics. (24 - 52) .Paz Victoria Suarez PradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 15 HomeworkDocument5 paginiCH 15 HomeworkChristineSkorupaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 2018Document36 paginiChapter 11 2018Gissele AbolucionÎncă nu există evaluări
- K Kundan: What Is Biology?Document52 paginiK Kundan: What Is Biology?Abhishek ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 10: ProcedureDocument4 paginiExercise 10: ProcedureManoj RacerÎncă nu există evaluări
- GPB-101-Fundamentals of Genetics & CytogeneticsDocument162 paginiGPB-101-Fundamentals of Genetics & CytogeneticsKING ArthurÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLMD4A ScienceG9Document37 paginiCLMD4A ScienceG9Christine Marquez Ramos100% (2)
- Grade 9 DLL Part 2 (1st Quarter)Document25 paginiGrade 9 DLL Part 2 (1st Quarter)leiziah xyrille maturan100% (3)
- Hsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024Document4 paginiHsslive Xii Zoology Vijayabheri 2024ajithaprabhath123Încă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Class1 - Grp.1 - Day 5 (Mendelian Genetics)Document4 paginiDLP - Class1 - Grp.1 - Day 5 (Mendelian Genetics)Valdeleon Taguiam CatherineÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Mendel To Epigenetics, History of Genetics 1Document1 paginăFrom Mendel To Epigenetics, History of Genetics 1Arra ArispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ImmunohematologyDocument58 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To ImmunohematologyBROOK100% (1)
- Cmap 9Document7 paginiCmap 9Emmanuel John PonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer - Key.let Review ExaminationDocument10 paginiAnswer - Key.let Review ExaminationSean Joshuane OlacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 12 BiologyDocument6 paginiGrade 12 BiologyabhijitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Problems.Document18 paginiGenetics Problems.Prof.P.T.Rajasekharan NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03a L3 Bio Genetics ActivitiesDocument6 pagini03a L3 Bio Genetics ActivitiesPamela CambiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Els Q2 ExamDocument13 paginiEls Q2 ExamRuby UriarteÎncă nu există evaluări