Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Remaining Files For Print
Încărcat de
Anne KathrineTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Remaining Files For Print
Încărcat de
Anne KathrineDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
e. On the circuit of Figure 2, set the Vi =15 V, adjust the value of R2 and fill up the table below.
R2 (ohms) 500 1000 2200 10000
VFL 2.813 2.872 2.944 2.962
VNL − VFL
VR = 16.08% 14.3198% 12.1718% 11.6348%
VNL
What can you say about the output voltage?
The output voltage is now a lot lesser than the Vi. The values are increasing as the
load resistance increases but they still have a poor voltage regulation because all values are
far from the ideal 0% regulation.
Is the regulator maintaining its output voltage?
Yes because the circuit is expected to produce a constant or regulated output voltage.
Which type of series regulator you preferred to use and why?
The group prefers the improved series regulator because its voltage regulation is
smaller and the value is nearly zero, which means that it is more productive than the
simple series regulation.
OBSERVATION:
For the pre-laboratory experiment, the group encountered two types of series regulators.
The first one which is the simple series regulator circuit and the second one which is the
improved series regulator circuit. Referring to the data gathered when the two circuits were
simulated, the improved series regulator circuit comes out as the more efficient one. Even when
the percent regulation is taken, the improved series regulator circuit is still the better one.
For Table 4-1 the input voltages were varied. At 4 volts, the output voltage is 1.667
volts. At 9 volts, the output voltage is 1.958 volts. At 10 volts, the output voltage is 2.048 volts.
At 11 volts, the output voltage is 2.052 volts. At 12 volts, the output voltage is 2.097 volts. At 15
volts, the output voltage is 2.206 volts. At 20 volts, the output voltage is 2.311 volts. Looking at
the results or data gathered, one will notice that as the input voltage in a simple series regulator
increases, the output voltage also increases. Same goes with the current flowing through the
circuit. All parameters mentioned above are directly proportional with each other. For Table-2,
the same thing is done but this time, the resistance is varied and the voltage at full load is taken.
The voltage at full load is then compared to the no load voltage which is 15.23 volts. The group
has noticed that as the load resistance value is increased, the percent voltage regulation decreases
which is a good thing since it gets closer to zero.
For Table 4-1 of the improved series regulator circuit, the same thing is done as the
series regulator voltage where the value of the resistor is varied. From the data gathered, the
group has seen the relationship of the parameters. As the value of the resistor increases, the full
load voltage also increases. This increase in the full load voltage causes the percent regulation to
decrease.
Looking at the two circuits and comparing their results, one can conclude that the
improved series regulator circuit is better than the simple series circuit. The theoretical and
measured data gathered validates the Multisim values where the improved series regulator circuit
is a better option.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Math Pre BoardDocument5 paginiMath Pre BoardAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orange Pi Zero With Expansion Board: Related TechnologiesDocument4 paginiOrange Pi Zero With Expansion Board: Related TechnologiesAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 21 - Introduction To Data Communications and NetworkingDocument3 paginiChapter 21 - Introduction To Data Communications and NetworkingAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Background and Rationale: Global Forum For Health Research) The World Health Organization Defines Social DeterminantsDocument7 paginiBackground and Rationale: Global Forum For Health Research) The World Health Organization Defines Social DeterminantsAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions - Wireless CommunicationDocument3 paginiMultiple Choice Questions - Wireless CommunicationAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layer 7: The Application LayerDocument7 paginiLayer 7: The Application LayerAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Aviation Authority of The Philippines: FOR: Ronald M. SantiagoDocument1 paginăCivil Aviation Authority of The Philippines: FOR: Ronald M. SantiagoAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- D. Procedures and TestingDocument5 paginiD. Procedures and TestingAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trapping Incidents Are LessDocument2 paginiTrapping Incidents Are LessAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake) Alarm System Is ADocument1 paginăEarthquake) Alarm System Is AAnne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
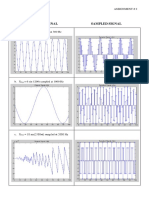
- Original Signal Sampled Signal: Anne Kathrine A. Chong Assignment # 2 Bs Ece - 4Document1 paginăOriginal Signal Sampled Signal: Anne Kathrine A. Chong Assignment # 2 Bs Ece - 4Anne KathrineÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Davis A. Acclimating Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei, To Inland, Low-Salinity WatersDocument8 paginiDavis A. Acclimating Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei, To Inland, Low-Salinity WatersAngeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTRLX Automation BrochureDocument60 paginiCTRLX Automation BrochureNinja do SofáÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5Document20 paginiLecture 5Paylaşım KanalıÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 Uco 578Document20 pagini19 Uco 578roshan jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMiT Products Solutions 2022 1 En-SmallDocument60 paginiAMiT Products Solutions 2022 1 En-SmallMikhailÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Scanjet N9120 (Service Manual) PDFDocument394 paginiHP Scanjet N9120 (Service Manual) PDFcamilohto80% (5)
- KSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsDocument22 paginiKSP Solutibilty Practice ProblemsRohan BhatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tecsun Pl310et PDFDocument30 paginiTecsun Pl310et PDFAxel BodemannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacity Analysis of Kashmir Highway IslamabadDocument71 paginiCapacity Analysis of Kashmir Highway Islamabadm saadullah khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE-23113-SP-902-R01-00 Asset SpecificationDocument14 paginiCE-23113-SP-902-R01-00 Asset SpecificationСветлана ФайберÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bamboo People - An Interdisciplinary Unit For High SchoolDocument6 paginiBamboo People - An Interdisciplinary Unit For High SchoolChipo Jean MarundaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Supply Chain Management in Hospitality IndustryDocument39 paginiModule 1 Supply Chain Management in Hospitality IndustryHazelyn BiagÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Trends in Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDocument11 paginiWorld Trends in Municipal Solid Waste ManagementNeima EndrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skirmishes Graham Harman PDFDocument383 paginiSkirmishes Graham Harman PDFparaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slup 230Document24 paginiSlup 230Jelena TodorovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pascal Die Casting Machine SystemDocument20 paginiPascal Die Casting Machine Systemenascimento32Încă nu există evaluări
- Surge Protection Devices CatalogueDocument134 paginiSurge Protection Devices CatalogueNguyen Doan QuyetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions of Inverse Geodetic Problem in Navigational Applications PDFDocument5 paginiSolutions of Inverse Geodetic Problem in Navigational Applications PDFLacci123Încă nu există evaluări
- ISO-50001-JK-WhiteDocument24 paginiISO-50001-JK-WhiteAgustinusDwiSusantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DTS 600 GDO Installation ManualDocument12 paginiDTS 600 GDO Installation Manualpiesang007Încă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Casting - Pump Station ADocument13 paginiConcrete Casting - Pump Station ABright MuzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tekla SoakwayDocument2 paginiTekla SoakwayBalaji Naik100% (1)
- Typical Cable Laying Details For Direct Buried, Low Tension CablesDocument9 paginiTypical Cable Laying Details For Direct Buried, Low Tension CableslataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natal Chart Report PDFDocument17 paginiNatal Chart Report PDFAnastasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Most Dangerous City - Mainstreet/Postmedia PollDocument35 paginiMost Dangerous City - Mainstreet/Postmedia PollTessa VanderhartÎncă nu există evaluări
- MidsemDocument6 paginiMidsemAravind SomasundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powering Laser Diode SystemsDocument134 paginiPowering Laser Diode SystemsNick100% (1)
- Antenna Systems - Standard Format For Digitized Antenna PatternsDocument32 paginiAntenna Systems - Standard Format For Digitized Antenna PatternsyokomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in PE&H 1st Quarter 18-19Document7 paginiReviewer in PE&H 1st Quarter 18-19rhex minasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practicewith Argument Athletesas ActivistsDocument30 paginiPracticewith Argument Athletesas ActivistsRob BrantÎncă nu există evaluări