Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bab 8 DLP Ms 149 Betul
Încărcat de
C. EvanTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bab 8 DLP Ms 149 Betul
Încărcat de
C. EvanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 8 Graphs of Functions
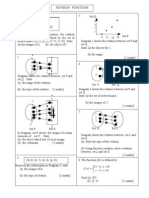
(c) One-to-many relations
Relation where the object in the domain has more than one image.
(i) (ii) Q
P Q
f : addition 6
•2 5
1• •3 4
3• •4 3
5• •5 2
•6 1
O P
1 2 3 4 5
(iii) Ordered pair, R = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)}
(d) Many-to-many relations
Relation where at least one object has more than one image, and more than one object has the
same image.
(i) (ii)
P f : can be Q Q
divided by 8
24 • •4 6
18 • •6 4
16 • •8 2
O P
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
(iii) Ordered pair, S = {(24, 4), (24, 6), (24, 8), (18, 6), (16, 4), (16, 8)}
CHAPTER 8
FLASHBACK
Provide justification based on the observation of the relation A straight line graph is
represented by a graph in the example above. obtained when all ordered
pairs for linear equations
are plotted and connected.
8.1.2 Function representation LEARNING
STANDARD
The diagram below shows the function f that maps x to which is
Identify functions and
represented by f (x) = . provide justifications
Set P Set Q based on function
f representations in the
•1 form of ordered pairs,
9•
•3 tables, graphs and
16 •
•4 equations.
25 •
•5
36 •
•6
Domain Codomain
Set P = {9, 16, 25, 36} is the domain and the element is the object. Set Q = {1, 3, 4, 5, 6} is the
codomain. The elements in set Q that is matched to the object in set P is the image. Set {3, 4, 5, 6}
is the range of the function.
149
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Modular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)De la EverandModular Forms and Special Cycles on Shimura Curves. (AM-161)Încă nu există evaluări
- Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesDe la EverandMultivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- McDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch04Document76 paginiMcDougal Littell - Algebra 1 Ch04gsparksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz #3Document1 paginăQuiz #3Alfred BOzzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionDocument10 pagini2.2 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions: Essential QuestionSaad KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 1 - FunctionDocument3 paginiMODULE 1 - FunctionSiti HajarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AddmathDocument162 paginiAddmathMuhammad Amirul AdlieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.4 Exercises: NumericalnoteDocument3 pagini1.4 Exercises: NumericalnotePaulo Luis SempeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.5 (Lesson 7) CompletedDocument4 pagini4.5 (Lesson 7) Completedj2r72c7dp2Încă nu există evaluări
- TB 2.1 Pgs (47-54)Document8 paginiTB 2.1 Pgs (47-54)Harsh NagoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CALCULUS & ANALYTIAL GEOMETRY Chapter#02Document23 paginiCALCULUS & ANALYTIAL GEOMETRY Chapter#02syeda zainabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus & Analytial Geometry Chapter#02Document23 paginiCalculus & Analytial Geometry Chapter#02syeda zainabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise Set 2.7: Functions and GraphsDocument3 paginiExercise Set 2.7: Functions and Graphsunknown :)Încă nu există evaluări
- FAEN 101: Algebra: Dr. Joseph K. AnsongDocument22 paginiFAEN 101: Algebra: Dr. Joseph K. Ansongnimdie jacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Functions: 1.1 RelationsDocument10 paginiChapter 1: Functions: 1.1 RelationsPuteri HaslindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 180 Notes From Darlene PDFDocument165 paginiMath 180 Notes From Darlene PDFMubasher Sultan MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 RelationsDocument4 pagini1.1 RelationsLim CYÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCR3U Unit 1 Notes - Rational ExpressionsDocument21 paginiMCR3U Unit 1 Notes - Rational ExpressionsHassan SubhieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Tutorial TestsDocument7 pagini2022 Tutorial TestsSakhile GumedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aga A2 0102 ApDocument1 paginăAga A2 0102 Apdeepaksharma1976Încă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 4 in Math in The Modern WorldDocument8 paginiLESSON 4 in Math in The Modern WorldAresta, Novie MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 1 Review Problems 1) - (0.1 To 2)Document3 paginiExam 1 Review Problems 1) - (0.1 To 2)esanture8Încă nu există evaluări
- CombinepdfDocument162 paginiCombinepdfSoby K ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parent Functions and Transformations Essential QuestionDocument8 paginiParent Functions and Transformations Essential QuestionAN NGUYENÎncă nu există evaluări
- CombinepdfDocument32 paginiCombinepdfSoby K ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMIR WALLACE - Coordinate Geo - CirclesDocument1 paginăAMIR WALLACE - Coordinate Geo - CirclesAMIR WALLACEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra 2 Midterm Exam Review - Short Answer 2feb12Document9 paginiAlgebra 2 Midterm Exam Review - Short Answer 2feb12idkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Multivariable Calculus 11th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Multivariable Calculus 11th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFcukmanselu100% (15)
- Bachelor With Honours Algebra - I (DC-1.2) SEM-I (7847)Document5 paginiBachelor With Honours Algebra - I (DC-1.2) SEM-I (7847)Sachin KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Multivariable Calculus 11th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiFull Download Multivariable Calculus 11th Edition Larson Solutions Manualkarey273121100% (27)
- 1.4 Notes - Even and Odd FunctionsDocument2 pagini1.4 Notes - Even and Odd FunctionsJohn MixerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-Functions QuadraticEquations QuadraticFunctions 2003-2009Document5 pagini01-Functions QuadraticEquations QuadraticFunctions 2003-2009Samion AwaldinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CombinepdfDocument52 paginiCombinepdfSoby K ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- r1. FunctionDocument2 paginir1. FunctionTan Chai AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signature Printed NameDocument16 paginiSignature Printed NameMojgan tabatabaeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precalculus 10th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiPrecalculus 10th Edition Larson Solutions Manuallawerslowbackplpy100% (20)
- Dwnload Full Precalculus 10th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Precalculus 10th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFrepourmyositic.79lc88% (8)
- Forms of Linear FunctionsDocument12 paginiForms of Linear FunctionsGiovani JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23 Transformations III: 1) The Coordinates of The Image (3, 1)Document10 pagini23 Transformations III: 1) The Coordinates of The Image (3, 1)GOH CHUN JIE SKTMÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Sample Paper 2015 16Document6 paginiCBSE Class 12 Maths Sample Paper 2015 16lakshy02910Încă nu există evaluări
- Page 459Document1 paginăPage 459HaythemÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH30-1 Unit 2 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsDocument40 paginiMATH30-1 Unit 2 - Lecture Notes: Homework Listing Textbook Sections Question Numbers WorksheetsBecca BobsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elliptic Curves: C H A P T E R 5Document26 paginiElliptic Curves: C H A P T E R 5Omaar Mustaine RattleheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alg2 Ch2 Review 2Document10 paginiAlg2 Ch2 Review 2f4kzd8cdwvÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAC 1105 - Worksheet #3 (Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2Document4 paginiMAC 1105 - Worksheet #3 (Sections 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2Marco P. CórdovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Mathematical ConceptsDocument568 paginiAdvanced Mathematical ConceptsSi Mi83% (6)
- 4.1+4.2 Practice ADocument2 pagini4.1+4.2 Practice Ahyperxfc7Încă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Test - Grade 10 - 230926 - 214512Document5 paginiMonthly Test - Grade 10 - 230926 - 214512Almas HushamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra For College Students 8Th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual PDFDocument8 paginiAlgebra For College Students 8Th Edition Blitzer Solutions Manual PDFkathy.gallardo572Încă nu există evaluări
- Graph Quadratic Functions in Vertex or Intercept Form: For Your NotebookDocument7 paginiGraph Quadratic Functions in Vertex or Intercept Form: For Your Notebook미나Încă nu există evaluări
- Bskytree: Scalable Skyline Computation Using A Balanced Pivot SelectionDocument12 paginiBskytree: Scalable Skyline Computation Using A Balanced Pivot SelectionNeti SuherawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selected ResponceDocument3 paginiSelected Responceapi-458193889Încă nu există evaluări
- Addmaths Kacang Form 4 Chapter 1: Functions: Notes & Past SPM QuestionsDocument17 paginiAddmaths Kacang Form 4 Chapter 1: Functions: Notes & Past SPM QuestionssanjeniÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 4 in Math in The Modern WorldDocument8 paginiLESSON 4 in Math in The Modern WorldLeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument2 paginiAssignmentVishwansh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Precalculus With Limits 4th Edition Larson Solutions ManualDocument20 paginiFull Download Precalculus With Limits 4th Edition Larson Solutions Manualhesseesarahjeanne100% (32)
- Dwnload Full Precalculus With Limits 4th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Precalculus With Limits 4th Edition Larson Solutions Manual PDFkyackvicary.n62kje100% (10)
- Questions Based On SPM Format: X G X HDocument3 paginiQuestions Based On SPM Format: X G X HAtiqah Abd RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebraic Geometry in Coding Theory and CryptographyDe la EverandAlgebraic Geometry in Coding Theory and CryptographyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFDocument1 paginăExtra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 217Document65 pagini217C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParablesDocument118 paginiParablesC. Evan67% (3)
- Extra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFDocument1 paginăExtra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Classes 2019 - Batch 1Document1 paginăExtra Classes 2019 - Batch 1C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFDocument1 paginăExtra Classes 2019 - Batch 1 PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anylysis of SPM BK Questions Section A For The Book of ActsDocument22 paginiAnylysis of SPM BK Questions Section A For The Book of ActsC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solving Simultaneous Eqns L7Document2 paginiSolving Simultaneous Eqns L7C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Leave Application ExampleDocument1 paginăOn Leave Application ExampleC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden CurriculumDocument1 paginăHidden CurriculumC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz For Habit 5Document1 paginăQuiz For Habit 5C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Calendar 2018 PDFDocument12 paginiSchool Calendar 2018 PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easter QuizDocument2 paginiEaster QuizC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LPKPM SPM 2013 Bible Knowl PDFDocument5 paginiLPKPM SPM 2013 Bible Knowl PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Calendar 2018 PDFDocument12 paginiSchool Calendar 2018 PDFC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2Document63 paginiLatihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2cgazmi87% (23)
- Maths Answer Times 2008Document3 paginiMaths Answer Times 2008C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Leave Application ExampleDocument1 paginăOn Leave Application ExampleC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weekend Away by Alpha Programme Under Christian Fellowship ClubDocument1 paginăWeekend Away by Alpha Programme Under Christian Fellowship ClubC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotations of ShapesDocument4 paginiRotations of ShapesThanusha DhanarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution of Triangle 1Document7 paginiSolution of Triangle 1Iman ZaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Act 11 & 12Document1 paginăAct 11 & 12C. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2Document63 paginiLatihan Math Th6-Upsr Kertas 2cgazmi87% (23)
- Solving Simultanoeus Linear EquationDocument2 paginiSolving Simultanoeus Linear EquationC. EvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Part ListDocument6 paginiElectrical Part ListdachajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automine For Trucks Brochure EnglishDocument4 paginiAutomine For Trucks Brochure EnglishJH Miguel AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No: 3: Aim: Objective: Theory:-Inverted IndexDocument2 paginiAssignment No: 3: Aim: Objective: Theory:-Inverted IndexPratik BÎncă nu există evaluări
- JCMONDocument5 paginiJCMONDevender5194Încă nu există evaluări
- Synopsys Tutorial v11 PDFDocument64 paginiSynopsys Tutorial v11 PDFJinu M GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Sourcing OptionsDocument25 paginiGlobal Sourcing OptionsKazi ZamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iq Bot v6.0 en PDFDocument146 paginiIq Bot v6.0 en PDFfjgutierrezpaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 SC 2240Document6 pagini2 SC 2240silvertronicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 35 MG2 and 38DLP Series Gage Upgrade Using GageviewDocument3 pagini35 MG2 and 38DLP Series Gage Upgrade Using GageviewBoulHich BoulHichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bibliometrix PresentationDocument41 paginiBibliometrix Presentationdaksh gupta100% (1)
- Kanban Excercise-1Document2 paginiKanban Excercise-1Viraj vjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Briefly Explain Compiler Construction ToolsDocument1 paginăBriefly Explain Compiler Construction ToolsAbhishek RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automated Billing SystemDocument24 paginiAutomated Billing SystemjamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reliability CalculationsDocument35 paginiReliability CalculationsEkoFujisyahMaulwantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel Number FormatDocument18 paginiExcel Number Formatshaktibansal198920Încă nu există evaluări
- 3rd GradingDocument3 pagini3rd GradingWinnie Mae Santiago EstampadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airpods Pro QSGDocument2 paginiAirpods Pro QSGAndrés M. Argüelles LandínezÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutocadDocument17 paginiAutocadRaju Kumar GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prosafe Rs Maintenance Training: Course #9001Document2 paginiProsafe Rs Maintenance Training: Course #9001daviqueirozdemedeirosÎncă nu există evaluări
- S6206 Thales Point MachineDocument32 paginiS6206 Thales Point Machineمعتز يحيى100% (2)
- Project On A Population CalculatorDocument42 paginiProject On A Population CalculatorNnamdi ChimaobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7701821350PL AvayaDocument830 pagini7701821350PL AvayaVincent NormanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Users Guide To Taking A Nutanix Certification ExamDocument12 paginiUsers Guide To Taking A Nutanix Certification ExamAdi YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- PowerMill Robot - PostProcessorsDocument28 paginiPowerMill Robot - PostProcessorselmacuarro5100% (1)
- Superhero Abc 2 PDFDocument10 paginiSuperhero Abc 2 PDFuthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual For Miller and Freunds P PDFDocument4 paginiSolution Manual For Miller and Freunds P PDFKuttyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 13-Design of An Intelligent Combat Robot For War FieldDocument7 paginiPaper 13-Design of An Intelligent Combat Robot For War FieldDhruv DalwadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SET 7 Soal Latihan MTCREDocument3 paginiSET 7 Soal Latihan MTCREErik Martin S., S.Kom. SMKS YADIKA 11 Jatirangga100% (1)
- De Thi Thu Vao THPT 2022 - Online 03.4.2022Document5 paginiDe Thi Thu Vao THPT 2022 - Online 03.4.2022mai.nguyen.thi.phuongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP 300 410 Enarsi Networktut May 2020Document65 paginiCCNP 300 410 Enarsi Networktut May 2020Pak ChannÎncă nu există evaluări