Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Electrical Equipment Testing
Încărcat de
kubera uDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Electrical Equipment Testing
Încărcat de
kubera uDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
OBJECTIVES OF INDUSTRIAL TRAINING
The primary objective of Industrial Training is to gain through practical
experience, a sound appreciation and understanding of the theoretical principles learnt
as a postgraduate at the University. Industrial Training is oriented towards developing
the skills, knowledge and attitudes needed to make an effective start as a member of the
engineering profession.
Chapter 1:
ABOUT THE COMPANY
Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited(KPTCL)
1.1. About KPTCL
Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited is a registered company
under the Companies Act, 1956 was incorporated on 28-7-1999 and is a company
wholly owned by the Government of Karnataka with an authorized share capital
of Rs. 1455 crores. KPTCL was formed on 1-8-1999 by carving out the
Transmission and Distribution functions of the erstwhile Karnataka Electricity
Board.
KPTCL is headed by a Chairman and Managing Director at the Corporate office.
He is assisted by four functional Directors. The Board of KPTCL consists of a
maximum of twelve directors.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 1
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited is mainly vested with the
functions of Transmission of power in the entire State of Karnataka and also
Construction of Stations & Transmission Lines and maintenance of
400/220/110/66 KV Sub-Stations. Many new lines and Sub-Stations were added
& existing stations were modified in the Transmission network. It operates under
a license issued by Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission.
KPTCL has 4 No. 400 KV Station, 97 No. of 220 KV Station, 385 No. of 110 KV
Station and 602 No. of 66 KV Station. The Total Transmission Line in CKMs is
34251 as on 31.03.2016.
The various wings of KPTCL is as follows: Corporate Office at Kaveri Bhavan,
Bangalore, Six Transmission zones, each zone is headed by a Chief Engineer.
State Load Despatch Centre SCADA(Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition).
The annual turnover of the Organisation was nearly Rs. 2395.80 crores during the
year 2014-15.
1.1.1. KPTCL Unbundled
Government vide order No. 69 BSR 2001 Bangalore, dated 15/02/2002 has
unbundled KPTCL and formed four distribution companies.
Consequent to this the function of distribution of power has been totally separated
from KPTCL. KPTCL is now vested with the responsibility of transmitting power
all over the State and construction and maintenance of Stations and lines of 66KV
and above.
The four newly formed independent distribution companies, which were
registered on 30/04/2002, are Bangalore Electricity Supply Company, Mangalore
Electricity Supply Company, Hubli Electricity Supply Company and Gulbarga
Electricity Supply Company. They have started functioning w.e.f.. 01/06/2002.
These companies are incharge of distribution of power within their jurisdiction.
The Fifth Distribution Company Chamundeshwari Electricity Supply Corporation
limited is a company incorporated under the company act 1956 and is a successor
entity to Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited (KPTCL) and
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 2
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
MESCOM in respect of Distribution and retail supply of Electric power for five
districts. Its operation started from 01.04.2005 as per the GOK order E.N.08
P.N.R 2005/262.
PCKL was incorporated on 20th August, 2007 under the Companies Act, 1956
and commenced its business operations with effect from 16th October, 2007.
PCKL is responsible for capacity addition and procuring power on behalf of the
ESCOMs from various sources including purchase of power through Energy
Exchange, Banking (SWAP) as well bilateral transactions. PCKL also co-
ordinates with other States and Central Government agencies on power related
issues.
1.1.2. History of KPTCL
The erstwhile Mysore State had the enviable and glorious position of
establishing the first major hydro-electric generating station at Shivasamudram as
earlyas 1902 for commercial operation. The art at that time was still in its infancy,
even in the advanced countries. The longest transmission line, at the highest voltage
in the world, was constructed to meet the power needs of mining operations at Kolar
Gold Fields. The generating capacity of the Shivasamudram Power House gradually
increased to 42 MW in stages. To meet the increasing demand for power, the
Shimsha Generating Station, with an installed capacity of 17.2 MW, was
commissioned in the year 1938.
The power demand was ever on the increase, for industries and rural
electrification, and additions to generating became imperative. The 1st stage of 48
MW and 2nd stage of 72 MW of the Mahatma Gandhi Hydro-Electric Station were
commissioned during 1948 and 1952, respectively. Subsequently, the Bhadra
Project, with an installed capacity of 33.2 MW, and the Thungabhadra Left Bank
Power House, with an installed capacity of 27 MW at Munirabad were
commissioned during 1964 and1965, respectively.
The state of Karnataka, with availability of cheap electric power, and other
infrastructure facilities, was conducive for increased tempo of industrial activity. It
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 3
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
became necessary therefore, to augment power generating capacity by harnessing the
entire potential of the Sharavathi Valley.
The first unit of 89.1 MW was commissioned in 1964 and completed in 1977.
The demand for power saw a phenomenal increase in the mid sixties and onwards
with the setting up of many public sector and private industries in the state. As power
generation in the state was entirely dependent on monsoon and was subject to its
vagaries, the state government set up a coal based power plant at Raichur. The
present installed capacity of the power plant at Raichur is 1260 MW. To augment the
energy resources of the state, the Kalinadi Project with an installed capacity of 810
MW at Nagjhari Power House and 100 MW at Supa Dam Power House, with an
energy potential of 4,112 kWh were set up.
The transmission and distribution system in the state was under the control of
the Government of Karnataka (then Mysore) till the year 1957. In the year
1957,Karnataka Electricity Board (KEB) was formed and the private distribution
companies were amalgamated with Karnataka Electricity Board.
Till the year 1986, KEB was a profit making organization. However, in the
subsequent years, like other State Electricity Boards in the country, KEB also started
incurring losses, mainly due to the increase in agricultural consumption and due to
the implementation of the socio economic policies of the government, the
performance of the power sector was affected.
To improve the performance of the power sector and in tune with the reforms
initiated by Government of India, the Government of Karnataka came out with a
general policy proposing fundamental and radical reforms in the power sector.
Accordingly a bill, namely Karnataka Electricity Reforms Act was passed by the
Karnataka Legislature.
The reform bill has mandated major restructuring of the Karnataka Electricity
Board and its corporatization. As part of corporatization, the Karnataka Electricity
Board ceased to exist and the Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited to
look after transmission and distribution in the state and VVNL (Visweshwaraiah
Vidyut Nigama Limited) to look after the generating stations under the control of
erstwhile Karnataka Electricity Board were constituted from 01.08.99.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 4
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
1.2. Mission Statements
Mission statement of KPTCL:
The mission statement of Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Ltd. is,
To ensure reliable and quality power to customers. It is committed to put in
place the best systems and a robust Network of Transmission.
To be the best transmission utility in the country, the KPTCL pledges to
optimize its human and technical resources for the benefit of all its
customers
The KPTCL is committed to achieving this mission through
Encouraging Best practices in transmission & distribution.
Ensuring high order maintenance of all its technical facilities.
Emphasizing the best standards in customer service.
Further to the reforms process initiated, based on the Karnataka Electricity
Reforms Act, 1999 the Distribution activity was to be separated from the
Transmission Activity. Accordingly the distribution activity has been separated with
effect from 1st June 2002 and five distribution companies were formed. The four
newly formed independent distribution companies, which were registered on
30.01.2002, are Bangalore Electricity Supply Company (BESCOM), Mangalore
Electricity Supply Company (MESCOM), Hubli Electricity Supply
Company (HESCOM), Gulbarga Electricity Supply Company (GESCOM), and
Chaumundeshwari Electricity Supply Company (CESCOM). These companies are
in charge of distribution of power within their jurisdiction.
Mission Statement of Escoms:
The mission statement of electricity supply companies is
To ensure complete customer satisfaction by providing its customers quality,
reliable power at competitive rates.
ESCOMs are committed to achieve this mission through:
Best practices in the construction and maintenance of its distribution network
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 5
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
High standards in customer service.
Optimum usage of technical and human power.
1.3. Power Sector at a Glance as on 31.10.2016
Installed Capacity:
Table 1.1: Power sector details
KPC Hydro and Thermal 7232.00 MW
CGS(Karnataka Share) 2694.00 MW
NCE,IPPs and Others 7673.32 MW
Total Installed Capacity 17599.3 MW
No. of Consumers 2.22 Crores.
Length of Transmission Lines 43052.792 CKms
No. of Stations 1435
No. of DTCs 6,35,663
HT Lines (Length in CKms) 294652.12
LT Lines (Length in CKms) 522105.60
The Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited (KPTCL) is the
sole electricity transmission and distribution company in state of Karnataka. Its
origin was in Karnataka Electricity Board. This electricity transmission and
distribution entity was corporatized to provide efficient and reliable electric power
supply to the people of Karnataka state.
1.4. Power Sector Reforms in Karnataka
Government Initiatives
The Government of Karnataka initiated the reforms in state by issuing a
policy statement on “Power Sector Reforms and Restructuring”, on 30th January
1997. This policy indicated corporatization of KEB, unbundling of the sector,
promotion of generation through independent power producers (IPPs) and
privatization of distribution. All these issues have been addressed in a more
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 6
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
elaborate manner in the detailed policy statement and the IPP policy framed by
the Government of Karnataka. To provide a statutory frame work, the KER Act
99 came into force from 1st June 1999.
Corporatization of KEB
As a first step in the reform process, the erstwhile KEB was corporatized
to form Karnataka Power Transmission Corporation Limited (KPTCL) and
operationalized w.e.f 01.08.1999 under the Companies Act 1956. KPTCL was
then vested with transmission and distribution functions. Simultaneously, another
entity called Visvesvaraya Vidyut Nigama Limited (VVNL) was also formed to
take care of the generation portion of the erstwhile KEB. (This VVNL is now
merged with KPCL Karnataka Power Corporation Limited).
Formation of Regulatory Commission (KERC)
As per the provisions of the Central Regulatory Commissions Act 98 and
also as per the KER Act 99, the State Government must establish a State
Regulatory Commission with a view to regulate the activities of the sector in the
areas of generation ,transmission , and distribution .
Accordingly the Government of Karnataka established the Karnataka
Electricity Regulatory Commission (KERC), a quasi judicial body and
operationalized it from 15.11 1999. It is a three member commission that looks
into various operational parameters of the power sector utilities, prescribes
standards and enforces them through regulations. KERC is the sole authority for
determining electricity tariff. Without the order of the commission, neither
KPTCL nor ESCOM can alter the electricity tariff to the consumer.The
commission determines the tariff through a transparent process wherein all the
stake holders are involved and sufficient opportunity given to them in public
hearings.
Unbundling-Formation of ESCOMs.
In the second phase of reforms, the KPTCL was unbundled, to separate the
transmission and distribution functions. Four Electricity Supply Companies
(ESCOMs) were formed on regional basis, viz Bengaluru Electricity Supply
Company, (BESCOM),Mangalore Electricity Supply Company (MESCOM),
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 7
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Hubli Electricity Supply Company(HESCOM) and Gulbarga Electricity Supply
Company (GESCOM).
These ESCOMs were registered under the Companies Act 1956 and were
operationalized w.e.f. 01.06.2002. In 2005, the MESCOM was bifurcated to form
one more ESCOM by name Chamundeshwari Electricity Supply Corporation,
(CESC) with Mysore as head quarters. As a result the present scenario in the state
looks like this. Generation function – KPCL, Transmission function – KPTCL
and Distribution function – Five Electricity supply Companies.
1.5. Present scenario in the state:
GENERATION : KPCL
TRANSMISSION : KPTCL
DISTRIBUTION : ESCOMs--BESCOM, HESCOM, GESCOM,
MESCOM, CESCOM.
KPTCL is now vested with responsibility of transmitting power all over the
State and construction and maintenance of Stations and lines of 66kV and above.
KPTCL will transmit power from various power producers to it to the distribution
companies. To enable easier operation of the system, KPTCL has been divided into
six zones, each headed by a Chief Engineer, fifteen circles, each headed by a
Superintending Engineer, fifty-seven divisions, each headed by an Executive
Engineer and over two hundred and seventy sub-divisions, each headed by an
Assistant Executive Engineer.
Following are the six Transmission Zones of KPTCL each headed by a Chief
Engineer.
1. Bangalore Transmission Zone
2. Tumkur Transmission Zone
3. Hassan Transmission Zone
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 8
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
4. Mysore Transmission Zone
5. Bagalkot Transmission Zone
6. Gulbarga Transmission Zone
1.6. Recent Developments
The Electricity Act 2003 does not permit the transmission utility to
involve in electricity trading. (i.e. bulk buying and selling electricity). Therefore
from 10th June 2005, trading activity has been detached from KPTCL and vested
with the respective ESCOMs.
However, for providing guidance to the ESCOMs and coordination purposes, the
State Government has established a State Power Procurement and Coordination
cell(SPPCC).
Government of India initiatives
Formulation of National Electricity Policy and National Electricity Plan.
Formulation of National Tariff Policy (6th January 2006).
Release of 4th Report on Rating of State Power Utilities.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 9
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Chapter 2
ABOUT THE DEPARTMENT
2.1. Relay Testing Circle
Relay Testing circle is the main testing unit of KPTCL is engaged in cognitive
process of testing, re-creation of the best modes of functioning of facilities in KPTCL
premises. Its responsibility includes control over the testing, repair & maintenance
activities of State transmission system utilities under its jurisdiction.
R.T.Circle, coordinates its operations in to ensure effective operation of the
receiving stations and substations entailed to the jurisdictional area and thus ensuring
effective transmission and distribution of energy with minimum outages in congruence to
encourage TL&SS staff to maintain the maintenance standard of KPTCL.
In compliance with the set tasks and accomplishment of the set objectives and
standards of KPTCL and effective utilization of manpower and resources, R.T Circle, has
established for carrying activities of periodical testing, calibration, troubleshooting,
Inspection, witnessing and assisting TL&SS staff during overhauls, breakdowns, repair &
maintenance works.
R.T subdivision Ballari one among the RT circle Mnirabad and is actively engaged
in the activities of Pre-Commissioning and Commissioning of equipment’s in New &
existing substations. There are 13 substations which comes under RTSD Ballari, where if
any fault or problem occurs among them will be solved by RT AEE/AE/mechanics.
Vision:
The vision of the R.T circle is to maintain high standards in electrical power
system testing through its technical competence and espousing accredited standards. With
a relentless pursuit of safety compliance, economical operation and a perpetual focus on
training and education in a quest to educate the masses to adopt the best practices of
operations in order to achieve the best Quality and Un interrupted supply to our
consumers.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 10
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Mission:
R.T circle aids substations, transmission lines and Distribution networks to
maintain high dexterity in power transmission, distribution by rendering qualitative
functioning of all protective equipment’s and devices in substations.
As mentioned earlier, testing of electrical equipments will be done so during
internship period we have come across the testing of CT(current transformer), Breaker
timing test, OC and SC test on transformer, insulator dielectric strength test and these
tests are explained below in detail.
Values:
Safety, quality, system reliability and adaptation of ethical practices in operations
of protection systems are basic foundations of the R.T Division Ballari..
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 11
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
2.2. Organization Chart of RT Division Ballari
Fig.2.1: Organization Chart of RTD
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 12
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Chapter 3
TESTING OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
Electrical safety testing is essential to ensure safe operating standards for any
product that uses electricity. Various governments and agencies have developed stringent
requirements for electrical products that are sold world-wide. In most markets it is
mandatory for a product to conform to safety standards promulgated by safety and
standard agencies and To conform to such standards, the product must pass safety tests
such as the high voltage test (also called as Dielectric voltage-withstand test or high
potential test), Insulation Resistance Test, Ground (Earth) Bond & Ground Continuity
Test & Leakage Current Test (also called as Line Leakage Test, Earth Leakage Current
Test, Enclosure Leakage Current Test or Patient Leakage Current Test). These tests are
described in IEC 60335, IEC 61010 and many other national and international standards.
During internship period the some of the electrical equipment test were conducted
and they are explained below,
3.1. CURRENT TRANSFORMER TESTING
A current transformer (CT) is a transformer that is used to produce an alternating
current (AC) in its secondary which is proportional to the AC current in its primary.
Current transformers, together with voltage transformers (VTs) or potential transformers
(PTs), which are designed for measurement, are known as instrument transformers.
When a current is too high to measure directly or the voltage of the circuit is too
high, a current transformer can be used to provide an isolated lower current in its
secondary which is proportional to the current in the primary circuit. The induced
secondary current is then suitable for measuring instruments or processing in electronic
equipment.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 13
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Objective:
To confirm the physical condition and electrical characteristics of current transformer
installed in the installation. Ensure the CT is connected to system properly in all respect
(primary and secondary).
CT Rating:
5P20/0.2 class, 600/1-1-1A
The above 5P20 refers to even though there is increase in rated current upto 20
times the percentage error will be only 5%. And 0.2 class means CT with a burden rating
of B-0.2 can tolerate an impedance of up to 0.2 Ω on the secondary circuit before its
accuracy falls outside of its specification
CT Used For Testing:
Fig.3.1: current transformer
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 14
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Test includes,
Megger test(insulation resistance test)
Ratio test
Polarity test
MEGGER TEST:
This test is conducted by using hand driven motor megger tool where it generates
1000v dc, the insulation resistance is measured w.r.t primary, secondary and ground.This
is done to know whether the resistance of the winding is capable of carrying the rated
current and also which do not degrades, the test results are shown below,
Table 3.1: CT Megger test results
PRI-GRD 2000 Ω
PRI-SEC CORE1 10000 Ω
CORE2 10000 Ω
CORE3 10000 Ω
SEC-GND CORE 2000 Ω
1
CORE 2000 Ω
2
CORE 2000 Ω
3
BETWEEN CORES 5000 Ω
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 15
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
RATIO TEST:
This test is to ensure the turn’s ratio of CT at all taps. The primary current of minimum of
25% rated primary current to be injected on primary side of CT with secondaries
shorted and the secondary current can be measured and recorded for all cores.
Limits: The obtained turn’s ratio should match with rated nameplate ratio.
This test is done by connecting booster transformer with the rating of 200A,
usually test will be done at 10% & 25% of the rated current and this test is the most
important test where in the test results are above 5% error then this test will fails so the
test results are must carefully taken in order to avoid error in measurement and results are
tabulated below,
Table 3.2: CT Ratio test result
PRI CURRENT IN SEC CURRENT
CURRENT EXPECTED
APPLIED CORE1 CORE2 CORE3 AS PER
RATIO
10% i,e 60A 0.098 0.1 0.098 0.10
25% i,e 150A 0.245 0.24 0.245 0.25
POLARITY TEST:
Polarity test is to confirm the polarity marking on the CT primary and secondary
and verify it is matching with drawing. More ever it is giving an idea, how to connect the
secondaries to make the protection (like directional, differential) and metering function
properly.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 16
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
This test is done by connecting galvanometer as shown in the fig,
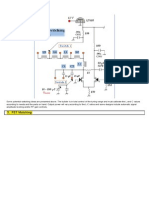
Fig.3.2: Polarity check connection diagram
This test gives the polarity of the CT to which side it has to connect in the line.
Conclusion of the Test:
The above tests are performed to ensure proper working of current transformer, if
the CT is fails in ratio test then it should not be used for further application and it has to
be replaced. So ratio test is very important in this case and it has to be carried out
carefully.
The polarity test should be as per the markings otherwise, it would cause different
problems which causes failure of its operation.
3.2. OC AND SC TEST ON TRANSFORMER
It is possible to predict the performance of a transformer at various loadings by
knowing all the equivalent circuit parameters. These circuit parameters are supplied in
terms Open Circuit (OC) and Short Circuit (SC) test data of a transformer. Without
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 17
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
actually loading the transformer, these two assessed tests give the test results which are
used to determine the equivalent circuit parameters.
By these parameters, we can easily predetermine the efficiency and regulation of
the transformer at any power factor condition as well as at any load condition. This
method of finding the parameters of a transformer is called as an indirect loading method.
This article enumerates how to perform these tests, how determine the equivalent
parameters from test data and significance HV or LV side in which the calculation to be
performed.
• These tests are usually performed to know the core losses and copper losses
• Core losses are constant and copper losses are variable
• But here this test is done to check whether the alignment of OLTC has done
successfully after the maintainance work has been done by the concerned contractors.
Rating of the Transformer:
100MVA 220/110kv BHEL make with OLTC
This test results are tabulated below,
Table 3.3: OC Test results
Tap no. Primary applied vtg in volts Seccondary measured vtg in v
RY YB BR ry yb br
1 425 423 425 204.2 203 204
2 206.6 205.4 206.7
3 209 207.8 209.3
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 18
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
4 211 210.5 211.7
5 426 424 427 212.2 212 212.5
6 216.7 215.7 216.9
7 219.7 218.5 220
8 222.8 221.3 222.7
9 225.2 223.7 225.3
10 425 423 426 227.9 226.5 228.1
11 231.1 229.7 231.1
12 234.1 232.5 234.3
13 237.4 235.9 237.3
14 240.6 239.1 240.9
15 426 423 426 244.2 242.8 244.4
16 247.7 246.3 247.7
17 425 422 425 251.2 249.5 250.9
Usually the tap number 5 gives the exact transform of voltage as per ratio, the
designers had designed like that we have 17 taps in the transformer and the voltages are
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 19
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
shown in above table we can see at tap number 5 the voltage transform is nearly close to
ratio.
Table 3.4: SC Test results
Tap Pri applied vtg HV current in A LV current in A
no.
RY YB BR IR IY IB ir iy ib
17 425 423 425 5.6 5.5 5.6 9.9 9.8 9.9
16 5.5 5.4 5.5 9.8 9.7 9.8
15 5.4 5.3 5.4 9.8 9.7 9.8
14 5.2 5.2 5.2 9.7 9.6 9.7
13 5.1 5.1 5.1 9.6 9.5 9.6
12 5 5 5 9.5 9.5 9.6
11 4.9 4.9 4.9 9.5 9.4 9.5
10 4.8 4.8 4.8 9.4 9.3 9.4
9 4.7 4.7 4.7 9.4 9.3 9.4
8 4.6 4.6 4.6 9.3 9.2 9.3
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 20
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
7 4.4 4.4 4.4 9.2 9.1 9.2
6 4.3 4.3 4.3 9.1 9 9.1
5 425 423 425 4.3 4.3 4.3 9 8.9 9
4 4.2 4.2 4.2 8.9 8.8 8.9
3 4.1 4.1 4.1 8.8 8.8 8.8
2 3.9 3.9 3.9 8.7 8.7 8.7
1 3.8 3.8 3.8 8.7 8.6 8.6
In this test the secondary short circuited by TPST swith and measures the primary
and secondary current by applying 425v. The results shows that the primary currents are
less where secondary currents are almost double because the primary is the HV side and
voltage is high and secondary is LV side and voltage is 50% of primary. Again at tap
number 5 the currents at secondary is 2 times greater than the primary current.
After the results are tabulated RT AE has concluded that the transformer is
working properly as per the ratio and informed substation incharge to charge the
transformer.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 21
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
3.3. SF6 Circuit Breaker:
A Circuit Breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to
protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by over current or overload.
Circuit Breaker is classified depending upon the medium used for quenching the
arc.
1. Air blast circuit breaker.
2. Vacuum circuit breaker.
3. Oil circuit breaker.
4. SF6 circuit breaker.
3.3.1. Construction of SF6 Circuit Breaker:
Fig 3.3: Typical SF6 circuit breaker
Fig. above shows the parts of a typical SF6 circuit breaker. It consists of fixed
and moving contacts enclosed in a chamber (called arc interruption chamber) containing
SF6 gas. This chamber is connected to SF6 gas reservoir. When the contacts of breaker
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 22
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
are opened, the valve mechanism permits a high pressure SF6 gas from the reservoir to
flow towards the arc interruption chamber. The fixed contact is a hollow cylindrical
current carrying contact fitted with an arc horn. The moving contact is also a hollow
cylinder with rectangular holes in the sides to permit the SF6 gas to let out through these
holes after flowing along and across the arc.
3.3.2. Working of SF6 Circuit Breaker:
In the closed position of the breaker, the contacts remain surrounded by SF6 gas
at a pressure of about 2·8 kg/cm2. When the breaker operates, the moving contact is
pulled apart and an arc is struck between the contacts. The movement of the moving
contact is synchronised with the opening of a valve which permits SF6 gas at 14 kg/cm2
pressure from the reservoir to the arc interruption chamber. The high pressure flow of
SF6 rapidly absorbs the free electrons in the arc path to form immobile negative ions
which are ineffective as charge carriers. The result is that the medium between the
contacts quickly builds up high dielectric strength and causes the extinction of the arc.
3.3.3. Flashover of SF6 Circuit Breaker:
SF6 circuit breaker consist of two parts, viz,
1. Moving contact
2. Fixed contact.
During normal operation of the power system, both the contacts are closed so that
there is normal flow of current.
And whenever the fault occurs, moving contact gets separated from fixed contact
so as to interrupt the circuit and healthy part of the power system is isolated from the
faulty part. But in the case which we were involved in the sub-station is there was mis-
alignment of the fixed contact and the moving contact as shown below.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 23
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Fig 3.4: Contacts alignment under normal condition and flashover condition
So due to this mis-alignment between the contacts there was arc struck between
these contacts and heat was produced.
Due to this heat produced, the SF6 gas got expanded and one phase limb of the
CB got exploded.
Fig 3.5: Exploded parts of SF6 circuit breaker
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 24
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Remedy:
The faulty or affected limb was replaced and pre-commissioning test carried out.
3.3.4. Pre- Commissioning Test:
1. Megger Test
2. Breaker Timing Test
MEGGER TEST:
The insulation resistance (IR) test (also commonly known as a Megger) is a spot
insulation test which uses an applied DC voltage (typically either 250Vdc, 500Vdc or
1,000Vdc for low voltage equipment <600V and 2,500Vdc and 5,000Vdc for high
voltage equipment) to measure insulation resistance in either kΩ, MΩ or GΩ.
BREAKER TIMING TEST:
• It is the pre commissioning test of the circuit breaker.
• This test is conducted to measure operation times of all types of HV and EHV
breakers under charged switch yard condition.
This test is conducted in three different modes:
Mode1- Close
Mode 2- Trip
Mode 3- Auto recloses (N/A)
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 25
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Fig 3.6: SCOT MXP kit used for breaker timing test
Features of Scot Mxp Kit:
Inbuilt clock to tag date and time of test to the readings.
4 line 20 character back-lit LCD display for menu and results.
Inbuilt memory to hold results of last fifty tests.
Easy to use menu driven user interface for operation.
Inbuilt printer for printing results.
Specification:
Channels: Maximum eight in PIR mode
Control of breaker :Through 300V / 30A SSRs to Trip and Close the
connected circuit breaker
Output :4 line 20 character backlit LCD,RS 232 C port for downloading data
to PC
Printer: Inbuilt, thermal printer
Paper: Thermal, 55 mm wide roll
Test Leads: Set of 15m, wear resistant Test Cables
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 26
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Power: 230V AC ± 15%, 50Hz ± 10%, 25 VA
Dimensions: 430 x 345 x 160 mm
Weight: 6 kg, instrument
TEST RESULTS:
Table 3.5: CB test results
Phase Mode1(Closing Time) ms Mode2(Trip Time) ms
R –Limb 0.22 0.32
Y – Limb 0.22 0.32
B – Limb 0.23 0.33
3.4. TAN DELTA TEST ON INSULATOR:
This test is conducted on cable, winding, current transformer, potential transformer,
transformer bushing.
A pure insulator when is connected across line and earth, it behaves as a capacitor. In
an ideal insulator, as the insulating material which acts as dielectric too, is 100 % pure,
the electric current passing through the insulator, only have capacitive component. There
is no resistive component of the current, flowing from line to earth through insulator as in
ideal insulating material, there is zero percent impurity.
In practice, the insulator cannot be made 100% pure. Also due to the ageing of
insulator the impurities like dirt and moisture enter into it. These impurities provide the
conductive path to the current. Consequently, leakage electric current flowing from line
earth through insulator has also resistive component.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 27
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
For good insulator the resistive component of leakage current is quite low. The
healthiness of an electrical insulator can be determined by ratio of resistive component to
capacitive component.
For good insulator this ratio would be quite low. This ratio is commonly known as
tanδ or tan delta.
Method of Tan Delta Test:
The equipment to be tested is first isolated from the system. A very low frequency
test voltage is applied across the equipment whose insulation to be tested. First the
normal voltage is applied. If the value of tan delta appears good enough, the applied
voltage is raised to 1.5 to 2 times of normal voltage, of the equipment. The tan delta
controller unit takes measurement of tan delta values.
There are two ways to predict the condition of an insulation system during tan
delta or dissipation factor test. First, one is, comparing the results of previous tests to
determine, the deterioration of the condition of insulation due ageing effect. The second
one is, determining the condition of insulation from the value of tanδ, directly. No
requirement of comparing previous results of tan delta test.
Test Result:
Table 3.6: Tan delta test results
KV mA C Tan Delta
2.06 0.155 238.5 0.1%
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 28
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
3.5. Commissioning Test of Relay
Installation of protection relays at site creates a number of possibilities for errors
in the implementation of the scheme to occur. Even if the scheme has been thoroughly
tested in the factory, wiring to the CTs and PTs on site may be incorrectly carried out, or
the CTs/PTs may have been incorrectly installed.
The impact of such errors may range from simply being a nuisance (tripping
occurs repeatedly on energization, requiring investigation to locate and correct the errors)
through to failure to trip under fault conditions, leading to major equipment damage,
disruption to supplies and potential hazards to personnel.
The strategies available to remove these risks are many, but all involve some kind
of testing at site. Commissioning tests at site are therefore invariably performed before
protection equipment is set to work. The aims of commissioning tests are:
1. To ensure that the equipment has not been damaged during transit or installation
2. To ensure that the installation work has been carried out correctly
3. To prove the correct functioning of the protection scheme as a whole
The tests carried out will normally vary according to the protection scheme
involved, the relay technology used, and the policy of the client. In many cases, the tests
actually conducted are determined at the time of commissioning by mutual agreement
between the client’s representative and the commissioning team.
The following tests are invariably carried out, since the protection scheme will not
function correctly if faults exist.
Wiring diagram check, using circuit diagrams showing all the reference numbers
of the interconnecting wiring
General inspection of the equipment, checking all connections, wires on relays
terminals, labels on terminal boards, etc.
Insulation resistance measurement of all circuits
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 29
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Perform relay self-test procedure and external communications checks on
digital/numerical relays
Test main current transformers
o Polarity check
o Magnetization Curve
Test main voltage transformers
o Polarity check
o Ratio check
Check that protection relay alarm/trip settings have been entered correctly
Tripping and alarm circuit checks to prove correct functioning
In addition, the following checks may be carried out, depending on the factors noted
above (not covered in this technical article):
Secondary injection test on each relay to prove operation at one or more setting
values
Primary injection tests on each relay to prove stability for external faults and to
determine the effective current setting for internal faults (essential for some types
of electromechanical relays)
Testing of protection scheme logic
Protection relay setting checks (alarm and trip settings):
At some point during commissioning, the alarm and trip settings of the relay
elements involved will require to be entered and/or checked. Where the complete scheme
is engineered and supplied by a single contractor, the settings may already have been
entered prior to dispatch from the factory, and hence this need not be repeated.
The method of entering settings varies according to the relay technology used. For
electromechanical and static relays, manual entry of the settings for each relay element is
required. This method can also be used for digital/numerical relays.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 30
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
However, the amount of data to be entered is much greater, and therefore it is usual to use
appropriate software, normally supplied by the manufacturer, for this purpose. The
software also makes the essential task of making a record of the data entered much easier.
3.5.1. Relay Testing Kit(Electromechanical )
NMC (Neutronics Manufacturing Company) make Relay testing Kit in one unit,
is suitable to test different types of Relays like over current, over voltage, under voltage,
earth fault etc. The Test Kit will be in one unit. Meters, Terminals, Indicators, Regulator
Knob, Timer Display etc. will be fitted on the horizontal panel of the cabinet which can
be approached by opening the top hinged lid. An input chord of 2 meters length
with 3 pin plug will be provided. Loading transformer, Measuring CT& protection circuit
will also be housed within the same unit.
Fig 3.7: Relay Test Kit
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 31
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Technical features:
Input : 230volts, single phase, 50Hz,AC.
Output : Current Output available one at a time
Current Range : 0-1, 2, 5, 10, 20A at 5V, 0-50, 100, 200A at 50V
Fig 3.8: Relay used for testing
2.5.2. Relay Test Procedure:
Connect the kit to the Relay under test
Select the current range to be varied
Set the Time Setting Multiplier(TSM)
Increase the current above pickup valve
Record the trip time which id displayed on kit display
Compare with TSM
If the relay is said to be okay, the recorded time and the TSM must be same. If
any difference between these two then the relay need to be replaced.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 32
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
3.6. Numerical Relay Testing:
Electromechanical relays are electrically operated switches used to isolate
circuits or batteries, detect faults on transmission and distribution lines, and control a
high powered circuit using a low power signal, Due to the advantages of Numerical
relays over Electromechanical relays these relays are replaced by Numerical relays.
Numerical relays was invented in the early 1980s by Edmond O. Schweitzer. SEL,
ARENA, and ABB Group’s are the early forerunners in this area. In the mid-1990s
numerical relays had nearly replaced the solid state and electromechanical relays.
Advantages of Numerical relays are:
Programmability.
Computing function.
Small Size.
The characteristic of digital component do not drift with temperature, ageing,
or supply voltage.
Recorded data will not be corrupted.
2.6.1. Numerical Relay:
Numerical relays are programmable relays. The characteristic and behaviour of
the relay are can be programmed. First generation numerical relays were mainly
designed to meet the static relay protection characteristic, whereas modern
numeric protection devices are capable of providing complete protection with
added functions like control and monitoring. Numerical protection devices offer
several advantages in terms of protection, reliability, and fault detection.
Typically, they use a specialized Digital signal processor (DSP) as the
computational hardware, together with the associated software tools.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 33
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Numerical relays are built with integrated functions like protection, control,
monitoring and measuring are available today in numeric power system protection
devices. Also, the communication capability of these devices facilitates remote
control, monitoring and data transfer.
2.6.2. Operation of Numerical Relay:
Fig 3.9: Operation Diagram
The operation of numerical relay is shown in the above diagram. A current signal
from CT is converted into proportional voltage signal using I to V converter. The
AC voltage proportional to load current is converted into DC using precision
rectifier and is given to multiplexer which accepts more than one input and gives
one output.
Output of Multiplexer is fed to analog to digital converter (ADC) to obtain signal
in digital form. Microprocessor then sends a signal ADC for start of conversion
(SOC), examines whether the conversion is completed and on receipt of end of
conversion (EOC) from ADC, receives the data in digital form. The
microprocessor then compares the data with pick-up value. If the input is greater
than pick-up value the microprocessor send a trip signal to circuit breaker of the
desired circuit.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 34
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Fig 3.10: Connection diagram for Relay testing
The figure above shows the connection diagram for the relay testing.It consist of
omricon test kit, laptop, relay under test connections are done as shown above and proper
grounding is ensured.
2.6.3. Omicron Relay Test Kit:
Fig 3.11: Omricon relay test kit
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 35
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
The CMC 256plus is the first choice for applications requiring very high
accuracy. This unit is not only an excellent test set for protection devices of all kinds but
also a universal calibrator.
Its high precision allows the calibration of a wide range of measuring devices,
including: energy meters, measuring transducers, power quality measurement devices and
phasor measurement units (PMU).
Its unique accuracy and flexibility make the CMC 256plus ideal for protection
and measurement equipment manufacturers for research and development, production
and type testing.
Features of Omricon kit:
Built in Timer.
Auxiliary DC supply.
Set of voltage outputs.
Two sets of current outputs.
Omricon kit is connected to laptop by using a special 24pin cable. Relay
input/output (RIO) file of the relay under test is selected to configure the settings for the
test.
Once setting is done the test kit will develop the required voltages and currents
which are needed for the testing.
These outputs are given as relay inputs as trip signal, once the relay is tripped then
test kit will calculate the trip timings and other required data and display it in the result
dialog box in the laptop.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 36
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Chapter 4
4.1. Problems Observed:
During our internship period we have visited many sub stations to encounter the
errors or problems in the substation and few important issues are explained below.
Failure of SF6 circuit breaker in 110Kv substation Toranagallu.
Due to aging and heavy operations of the circuit breaker there is a jamming in
contacts of the R-phase limb during breaker opening time. We have inspected for the
fault and suggested for the replacement of the breaker and after replacement megger, and
breaker timing test are done and verified the results with the standards.
Fault in energy meter recording in 110/11 kV Substation Tekkalakote.
Due to interchange in the phase sequence of Y & B energy meter showing the
faulty measurements. We examined by using the online test kit and concluded that the
phase sequence is interchanged by observing the phasor diagram and reversed the
connections to the energy meter and verified the result.
Fault during spring charging of the circuit breaker and CT replacement in
110/11 kV substation P.D. Halli.
Due to manufacture problem there was a problem near the CT terminal which
leads to the crack and burnt of the CT so after inspection of the CT suggested for the
replacement.
Also there was a problem in spring charging mechanism of the circuit breaker.
We inspected the motor and find it was healthy. After inspecting the gear mechanism it is
found that some of the teeth of the gear box are broken and suggested for either
replacement or repair.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 37
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Fault in the Battery Charger in 110/11 Kv substation sridhargadda.
Due to fault in the battery charger DC supply for the protection system is supplied
only when supply mains is ON, after inspection it is found that the diodes used for the
conversion of AC to DC are failed and suggested for replacement.
After replacement also float current is below the specified value so inspected for
any failure in the cell of a battery array, it is found that three cells of the battery array are
faulty and suggested for replacement but for emergency use we bypassed the faulty cells
and restored the required current.
4.2. Trivector Meter
What is a Trivector Meter? Where is it Used?
The Trivector meter is a measuring instrument which measures the kW, kVAr, the
kVA of a power line. These instruments can measure both power as well as energy.
Trivector meters are normally used in substations and to measure the power flowing
through the feeders. They are used for billing power drawn by industrial customers. The
Trivector enables the simultaneous measurement of different electrical parameters which
enables accurate assessment of the power consumed.
Trivector is called so as it measures three vectors representing the active, reactive
and apparent power of a line. Trivector meters come in two quadrant and four quadrant
models. The four quadrant model can measure both the incoming (import) and the
outgoing power (export) while the two quandrant trivector meter can measure either
imported or exported power.
In earlier days, the electromechanical trivector meters were used. Today, though,
almost all Trivector meters are of the static type. Modern Trivector meters can measure
many parameters apart from the active, reactive and apparent power.
The below figure shows the L&T ETV meter and connection diagram. While
doing connections if any one phase is reversed then meter will not record the reversed
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 38
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
phase current i,e energy recording for the phase reversal will be zero so it is noted that
care has to be taken while making connections to terminal boards and to energy meter.
Fig 4.1: ETV meter
Fig 4.2: ETV connction diagram
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 39
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Chapter 5
Reflection Notes (Specific Outcome)
The non-technical benefits due to this internship are immense, to list a few:
Here we could get the practical knowledge about the theory subjects learnt in
power system operation and control, substation automation, digital protection
involved in the system.
We learnt the method of procedure performed during permissions
1. Problem assessment
2. Inspection performed by officers
3. Documentation of same
4. The approval process
5. The purchase of equipment.
6. The equipment’s insulation.
7. Testing and deployment
Hence the tasks performed by any probationary offices were learnt during the process.
5.1. Some of the expected advantages to be gained by a postgraduate
following a program of Industrial Training are:
Systematic introduction to the ways of industry and developing talent and
attitudes, so that he / she can enjoy fully, a career in engineering while
recognizing his / her responsibilities as a professional engineer of the future.
Understanding real life situations in industrial organizations and their related
environment and accelerating the learning process of how his / her knowledge
could be used in a realistic way.
Understanding that the problems encountered in the industry & gaining
experience to select the optimal solution from the many alternatives available.
Learning accepted safety practices in the industry.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 40
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
5.2. Overall Experience at Relay Testing Division (RTD)
I began my internship at Relay Testing Subdivision Ballari. The subdivision is in
the line of study and testing of electrical equipments. It is having qualified engineers,
technicians and various other supporting staff or employees who have put in number of
year of services in the specified field.
It was one of my best experience for carrying out my internship in relay testing
subdivision. We were about 2 students in my orientation group Since it would be an
industrial internship, so I decided to talk to Executive Engineer regarding permission for
internship. They agreed for an internship of 16 weeks. I started my internship from
August 2016 to November 2016.
In the organization I was assigned to gain familiarity with the electrical
equipments used in the substation and there testing and methods of troubleshooting and
match my academic knowledge with the experience of working in a professional
environment along with the learning of different functions of the organization undertakes
through its departments.
The main focus of my internship was to know the procedure of testing and
troubleshooting the electrical equipments used in substation. The report consists of a brief
introduction of the organization and its functions .It also includes my personal learning
what I learnt over there and how was my experience in Relay testing subdivision writing
this report.
My experience at Relay testing subdivision for a period of 16 weeks was
overwhelming. It was important to be able to talk to many different types of people of the
organization. The importance of leadership ability is the most significant thing that I
learned from this experience. The most important thing I have experienced during this
period is public facing.
The internship program was a good platform to learn things such as: Teamwork,
Communication with higher authorities, maintaining records etc and also I learned the
importance of Maintaining time, appearance, leadership qualities.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 41
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
5.2.1. Technical Outcomes:
First of all we learned how to observe single line diagram and layout diagram.
We have studied the manner in which equipments are arranged in the substation.
As we are in relay testing subdivision we are fortunate to observe testing of
various equipments such as:
Current Transformer.
Potential Transformer.
Circuit Breaker.
Relays.
Transformer etc.
We learnt about how to maintain records after testing such as:
Date and Details of substation.
Voltages, Currents and other parameters for further validation.
We learned to operate various kits which are used for testing of equipments such
as:
Circuit Breaker Timer Kit.
Tan Delta Test Kit.
Omricon Numerical Relay Test Kit.
NMC Make Electro Mechanical Relay Test Kit.
Megger.
We also observed Trouble Shooting of some of the equipments.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 42
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
5.2.2. Non-Technical Outcomes:
Time Management:
Time management is very important aspect in our subdivision because delay may
cause complete failure in the equipment, huge amount of revenue loss due to shutdown of
equipments, also sometimes causes risk to human life. working here gave us an
opportunity to learn efficient time management and resource management. Time
Management plays a very important role not only in organizations but also in our
personal lives.
Communication Skills:
Communications skills play a major role in communicating your ideas and
thoughts, also key factor for success. Working with RTSD has provided a fabulous
opportunity to discuss with various levels of engineers, technicians, and employes and to
share our ideas and suggestions. Hence the communication skill helps in putting your
idea modeled in different perspective.
Personality Development:
Every individual comes with a unique set of strengths and weakness, but working
in RTSD gave us an opportunity to overcome my weakness with proper suggestions from
higher authorities. Also observed lot of things about our appearance from the authorities
during field work, meetings, and office hours.
Written Skills:
Many employers consider written skills to be one of the most important job skills,
working in RTSD gave us a platform in learning and exhibiting our written skills.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 43
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
Some of the benefits due to this internship:
Here we could get the practical knowledge about the theory subjects learned in
the previous classes.
Recognizing that financial and economic limitations play a more important role in
all engineering activities.
Understanding the formal and informal relationships in an industrial organization
so as to promote favorable human relations and teamwork.
Appreciating that engineering is an expanding field and that learning has no
limitations.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 44
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
CONCLUSION
Overall training was very helpful in gaining technical knowledge as well as the
professional ethics followed in industries. Training was highly beneficial for
understanding the various operational aspects of substations and RT division. The
training involved thorough learning, understanding and application of various technical
aspects in real time. Training gave exposure to practical application of theoretical aspects
in real time.
I believe this training would help me in building a good platform for my career.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 45
Study and Testing of Electrical Equipment
REFERENCES
1. www.kptcl.in
2. www.Elecrical4u.com
3. www.electricalstudy.com
4. Testing and commissioning of Electrical Equipments by Ramesh
L.Chakrasali Electrical Dept SDMCET Dharwad.
M.Tech (EPS) EEE Dept. SDMCET Dharwad. Page 46
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- KPTCL Ppt's (Sahana)Document13 paginiKPTCL Ppt's (Sahana)sreekanthm00001Încă nu există evaluări
- KPTCL Sunil 0593Document91 paginiKPTCL Sunil 0593Parveen Ks25% (4)
- Internship REPORTDocument30 paginiInternship REPORTVipin KshirasagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BESCOM Proj - ReportDocument76 paginiBESCOM Proj - Reportbaba amte100% (1)
- KPTCL's Role in Karnataka's Power TransmissionDocument74 paginiKPTCL's Role in Karnataka's Power TransmissionKashyapboss Hr0% (2)
- Internship Final ReportDocument46 paginiInternship Final ReportSiddesh Sanju100% (2)
- Karnataka Power Corporation Limited ProfileDocument66 paginiKarnataka Power Corporation Limited Profileravikumar198775% (8)
- Study KPTCL's 220/66/11kV NRS SubstationDocument45 paginiStudy KPTCL's 220/66/11kV NRS SubstationSiddesh Sanju100% (4)
- HESCOM Report 3Document27 paginiHESCOM Report 3Nikita GajabarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration of Distribution Generation: AssignmentsDocument6 paginiIntegration of Distribution Generation: AssignmentsnfjnzjkngjsrÎncă nu există evaluări
- KPTCL Pratap DTDocument34 paginiKPTCL Pratap DTGlyjojosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- AICTE Energy Conservation ReportDocument24 paginiAICTE Energy Conservation ReportLaxmi sirke Laxmi sirkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Based Transformer Fault Monitoring SystemDocument5 paginiGSM Based Transformer Fault Monitoring SystemEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Srs Report NewDocument69 paginiSrs Report NewPreethi SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- InternshipDocument52 paginiInternshipAishwarya AishuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship Report (KAVIKA)Document28 paginiInternship Report (KAVIKA)arnav sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BESCOMDocument3 paginiBESCOMsunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Report On SubstationDocument13 paginiTraining Report On SubstationAbhishek Dave100% (2)
- HESCOM Report 1Document39 paginiHESCOM Report 1Nikita Gajabar0% (1)
- WBSEDCLDocument39 paginiWBSEDCLSanjiv Shome100% (2)
- Nithya KPCL Internship ReportDocument69 paginiNithya KPCL Internship ReportNithya RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 220 KV Gss Sanganer ReportDocument55 pagini220 KV Gss Sanganer ReportSonu Lovesforu64% (11)
- Final Presentation 1Document42 paginiFinal Presentation 1Yashas Yashu100% (2)
- KPTCL ProjectDocument38 paginiKPTCL ProjectSalman Khan50% (2)
- Solar Power Plant Internship Report at HIEEDocument20 paginiSolar Power Plant Internship Report at HIEEBhargavÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPPCL 33/11KV Substation GuideDocument35 paginiUPPCL 33/11KV Substation Guidefitzlko100% (1)
- Summer Training Report: Badarpur Thermal Power Station (A Unit of NTPC)Document72 paginiSummer Training Report: Badarpur Thermal Power Station (A Unit of NTPC)mansi_angel100% (1)
- IDG - Important QuestionsDocument2 paginiIDG - Important QuestionsMahesh MÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPPTCL 220KV Substation ReportDocument9 paginiUPPTCL 220KV Substation ReportAakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFDocument10 paginiPSA-2 15EE71 Question Bank PDFsagar R Rao0% (1)
- Internship ReportDocument6 paginiInternship ReportEngr Syed Numan ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kavika Company ProfileDocument14 paginiKavika Company ProfileSujata Narasaiah100% (1)
- Solar Guidelines - TelganaDocument31 paginiSolar Guidelines - Telganavineets058Încă nu există evaluări
- SRLDC IntroductionDocument9 paginiSRLDC Introductions_jmi2345Încă nu există evaluări
- Report On Industrial Visit To Punnapra SubstationDocument73 paginiReport On Industrial Visit To Punnapra SubstationAravind N100% (3)
- Varahi ReportDocument5 paginiVarahi ReportbesttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visvesvaraya Technological University ADocument28 paginiVisvesvaraya Technological University AHira ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRS Peenya Substation ReportDocument65 paginiSRS Peenya Substation ReportYashaswiniAnantharaju Achiever86% (7)
- PHASE 1 Agri Job Opportunities 3KC19CV021Document10 paginiPHASE 1 Agri Job Opportunities 3KC19CV02119CV021 SUHAIB.TAUQEER100% (1)
- A Project Report On Scada System: Submitted By:-Sanskar Sagar Electrical 2017/130Document27 paginiA Project Report On Scada System: Submitted By:-Sanskar Sagar Electrical 2017/130Sharma Saab100% (1)
- BHEL Haridwar Summer TrainingDocument38 paginiBHEL Haridwar Summer TrainingAyush SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Dr. S.N. Singh - Technology For Generation, Transmission and Distribution PDFDocument32 pagini3 - Dr. S.N. Singh - Technology For Generation, Transmission and Distribution PDFGanta Venkata RajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 400kv Nelamangana SubstationDocument4 pagini400kv Nelamangana Substationtanwar_anuj199067% (3)
- Training Final ReportDocument45 paginiTraining Final ReportRK K100% (1)
- Internship ReportDocument62 paginiInternship ReportNITHIN R PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome: Australia's Solar CitiesDocument3 paginiWelcome: Australia's Solar CitiesLF23802Ps7854]m)59322m)758)Încă nu există evaluări
- Kishenpur Grid Station CompleteDocument39 paginiKishenpur Grid Station CompletepunitkapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV Report NewDocument83 paginiIV Report Newsruthy100% (2)
- Integration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsDe la EverandIntegration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- KPTCL Design of Ehv Transmission LineDocument48 paginiKPTCL Design of Ehv Transmission LineCharan Raj100% (1)
- HR Project BESCOM Proj Report PDFDocument75 paginiHR Project BESCOM Proj Report PDFthanushreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR Project BESCOM Proj ReportDocument75 paginiHR Project BESCOM Proj ReportPravin SanapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mission and Vission of CompaniesDocument4 paginiMission and Vission of CompaniesAshu YashuÎncă nu există evaluări
- KPTCL Final Report NewdocxDocument75 paginiKPTCL Final Report Newdocxmd shoebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerala State Electricity Board - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 paginiKerala State Electricity Board - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMohamed Anwar K100% (1)
- Vocational Training: Distribution & Maintance of SubstationDocument49 paginiVocational Training: Distribution & Maintance of SubstationPrince Mishra100% (1)
- Industry ProfileDocument15 paginiIndustry ProfileUma DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF FileDocument57 paginiPDF Filepunith hiregoudarÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPTCLDocument3 paginiOPTCLAbinash SarangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Executive Summary: Industry ProfileDocument53 paginiExecutive Summary: Industry ProfileBhumi JaanviÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Year Academics: Criterion 8Document12 paginiFirst Year Academics: Criterion 8kubera u100% (2)
- BEE Question Bank PDFDocument2 paginiBEE Question Bank PDFkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Year Academics: Criterion 8Document12 paginiFirst Year Academics: Criterion 8kubera u100% (2)
- PSOC Module 1Document36 paginiPSOC Module 1kubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCADA in Bottle Filling PlantDocument15 paginiSCADA in Bottle Filling Plantkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSOC Module 1Document36 paginiPSOC Module 1kubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- State EstimationDocument13 paginiState Estimationkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimal SVC Placement for Voltage Improvement and Loss ReductionDocument10 paginiOptimal SVC Placement for Voltage Improvement and Loss Reductionkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kubi Synopsis FinDocument5 paginiKubi Synopsis Finkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCSC ModifiedDocument63 paginiTCSC Modifiedkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enhance Power Transfer Using TCSCDocument20 paginiEnhance Power Transfer Using TCSCkubera uÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Zeeman EffectDocument20 paginiThe Zeeman Effectkrishna mohan mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TW - Datasheet Piercing RPGDocument2 paginiTW - Datasheet Piercing RPGarthur9mozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMDS0511 Lightning Protection SystemDocument70 paginiFMDS0511 Lightning Protection SystemMohamed Rafi MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Equilibrium of Beams Lab ReportDocument14 paginiStatic Equilibrium of Beams Lab Reportperis annÎncă nu există evaluări
- How much torque can a cone clutch transmit with specific parametersDocument4 paginiHow much torque can a cone clutch transmit with specific parametersMat ComiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 FME TransactionsDocument9 pagini2018 FME TransactionsEduardo Leal SalgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE TestDocument8 paginiCE TestBrooke ClineÎncă nu există evaluări
- suggestedDemosToCorrespondingPhysicsTextbooks PDFDocument292 paginisuggestedDemosToCorrespondingPhysicsTextbooks PDFWilliam SaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Electric Circuits EeDocument16 paginiDe Electric Circuits EeLilet P. DalisayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winding Failures of Electrical Motors: Winding Shorted Turn-To-Turn Winding With Shorted CoilDocument4 paginiWinding Failures of Electrical Motors: Winding Shorted Turn-To-Turn Winding With Shorted CoilalexmontellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sizing A MV Generator Circuit Breake1Document25 paginiSizing A MV Generator Circuit Breake1Afifah Zuhroh0% (1)
- Calibration ManualDocument21 paginiCalibration Manualjosealvaro073391Încă nu există evaluări
- Construction of DC GeneratorDocument58 paginiConstruction of DC GeneratorRajeev ValunjkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Class Section Code-Subject Name of The FacultyDocument2 paginiDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Class Section Code-Subject Name of The Facultyv srinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miniaturization of A Microstrip Antenna Using A Compact and Thin Magneto-Dielectric SubstrateDocument3 paginiMiniaturization of A Microstrip Antenna Using A Compact and Thin Magneto-Dielectric SubstrateaparnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pcc-Ee 303Document2 paginiPcc-Ee 303Amlan SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Vibration Training For Engro EnergyDocument70 paginiBasic Vibration Training For Engro EnergyHesham IbrahemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force Due To Magnetic Field and Sources ofDocument29 paginiForce Due To Magnetic Field and Sources ofChriSaberÎncă nu există evaluări
- METHOD FOR GROUNDING RESISTANCE TESTDocument8 paginiMETHOD FOR GROUNDING RESISTANCE TESTHân TiênÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 TOP AUTOMATIC CONTROL SYSTEMS Questions and Answers PDF AUTOMATIC CONTROL SYSTEMS QuestionsDocument15 pagini100 TOP AUTOMATIC CONTROL SYSTEMS Questions and Answers PDF AUTOMATIC CONTROL SYSTEMS QuestionsEr PavankumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Startup Guide TPM Tpma 004 110 Siemens Simodrive en PDFDocument12 paginiStartup Guide TPM Tpma 004 110 Siemens Simodrive en PDFtmsxptoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dispersion Analysis in Broadband Helix TWTDocument2 paginiDispersion Analysis in Broadband Helix TWTRaktim GuhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravitation Important Numerical Questions (Solved) Class 11 PhysicsDocument11 paginiGravitation Important Numerical Questions (Solved) Class 11 PhysicsStudy ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics - Alternative FET Matching MethodsDocument4 paginiElectronics - Alternative FET Matching MethodsRadu TaşcăÎncă nu există evaluări
- UniGear Technical Guide: Single Busbar System OverviewDocument159 paginiUniGear Technical Guide: Single Busbar System OverviewwakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance Protection RelayDocument20 paginiDistance Protection Relayerkamlakar2234100% (9)
- Brushless Doubly-Fed Induction Machines ForDocument10 paginiBrushless Doubly-Fed Induction Machines Forاحمد صالحÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Power Line Carrier CommunicationDocument22 paginiOn Power Line Carrier CommunicationAshish Jain100% (2)
- OriginalDocument2 paginiOriginalAbdul KarimÎncă nu există evaluări