Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Acid Base Solutions Student Directions
Încărcat de
loly62006Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Acid Base Solutions Student Directions
Încărcat de
loly62006Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Student directions Acid Base Solutions: Concentration and Strength
http://phet.colorado.edu
Learning goals: Students will be able to
a) Generate or interpret molecular representations (words and/or pictures) for acid or base solutions
b) Provide or use representations of the relative amounts of particles in acid or base solutions to
estimate strength and/or concentration
c) Use common tools (pH meter, conductivity, pH paper) of acid or base solutions to estimate
strength and/or concentration
Prelab:
1. Water molecules are not shown. Each beaker contains the same volume of solution;
Key: = HA (unreacted acid) = A- = H+ (or H3O+)
Beaker A Beaker B Beaker C Beaker D
0.1 M HCl
1a.Which might be the label on Beaker C?
A. 0.01 M HC2H3O2 B. 0.1 M HC2H3O2 C. 0.3 M HC2H3O2 D. 0.01 M HCl E. 0.3 M HCl
1b. Which beaker would have the lowest pH? A B C D
1c. Explain your reasoning: for both questions
2. You have two beakers. One beaker contains 100 mL of NaOH (a strong base);
the other contains 100 mL of aqueous Na3PO4 (a weak base). You test the pH of
each solution. Which of the following statements is true?
a. The Na3PO4 has a higher pH because it has more sodium ions than NaOH.
b. It is possible for the solutions in each beaker to have the same pH. 100 mL 100 mL
c. If the pH of the NaOH solution is 12.00, the pH of the Na3PO4 solution has NaOH (aq) Na 3PO4(aq)
to be greater than 12.00.
d. If the pH of the NaOH solution is 12.00, the pH of the Na3PO4 solution has to be less than 12.00.
Explain your reasoning.
Lab: Visualizing acid strength, concentration, and pH
A. Explore the simulation with your group and discuss these questions. Use the molecular view, pH,
conductivity, and bar graphs.
1. For an acid, what happens to the molecule when it is in a water solution?
2. What is different about what happens to a weak acid molecule and what happens to a strong acid
molecule?
3. How do the representations of a weak acid reaction differ from a strong one?
4. If you increase the concentration of an acid, what changes in both types of acids?
3/10/2018 Loeblein Some materials adapted from an activity by Lancaster /Langdon
Student directions Acid Base Solutions: Concentration and Strength
http://phet.colorado.edu
B. These images (molecular view of solution/graph/pH/conductivity) depict a strong acid solution:
KEY:
unreacted acid Water molecules are not shown in molecular views
a. How does the Key change for a weak acid?
b. How would the images change for a weak acid solution of the same concentration? Draw the
images as well as describing them in words.
c. Draw the images for a weak acid and a strong acid solution of the greater concentration? Make
any notes that might help you remember.
d. Write the chemical reactions for a weak acid and a strong acid.
e. Is there one type of representation that might be the best one for you to remember information
about weak and strong acids? Make any notes that might help you remember how to
compare/contrast the two types.
C. Repeat parts A and B for base solutions.
D. If your lab partner explains to you that concentration and strength effect acid base solution
representations the same way, are they right? Make notes of ideas that support the statement and
those that contradict.
3/10/2018 Loeblein Some materials adapted from an activity by Lancaster /Langdon
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dreams in Islam - The Window To The Heart! by Shaikh. Imran Nazar HoseinDocument105 paginiDreams in Islam - The Window To The Heart! by Shaikh. Imran Nazar Hoseinm.suh100% (10)
- Alkene Reaction GuideDocument41 paginiAlkene Reaction GuideAbhishek Isaac MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Dnastructurereplicationworksheet PDFDocument2 pagini1 Dnastructurereplicationworksheet PDFloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 6 Colligative PropertiesDocument7 paginiWorksheet 6 Colligative Propertiesani illuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab1 TeodoroDocument8 paginiLab1 TeodoroJherby Teodoro100% (1)
- Carboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesDocument45 paginiCarboxylic Acid and Its Derivatives NotesAtirahSakinahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2 Practical - Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument7 paginiWeek 2 Practical - Chemistry of CarbohydratesPranabes Bhattacharyya100% (1)
- Acid Base Concepts (Quiz With Answers)Document12 paginiAcid Base Concepts (Quiz With Answers)heylinssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 31: Reviewer For 2 DepexDocument27 paginiChem 31: Reviewer For 2 DepexAlma PabilaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEORGE BERNARD SHAW On Islam PDFDocument18 paginiGEORGE BERNARD SHAW On Islam PDFIslamicfaith Introspection84% (19)
- Experiment 3 Acid and Base TitrationDocument17 paginiExperiment 3 Acid and Base TitrationRadhwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide For Hifz Ul QuranDocument28 paginiGuide For Hifz Ul Quranloly6200650% (2)
- FFA and Acid Value in OilDocument6 paginiFFA and Acid Value in Oilleah100% (1)
- Chem 31.1 Experiment 1 Lab ReportDocument5 paginiChem 31.1 Experiment 1 Lab ReportMara Krista CooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redefining StutteringDocument649 paginiRedefining StutteringcabanosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM 1412. Chapter 17. Acid-Base Equilibria - Homework - Ky PDFDocument20 paginiCHEM 1412. Chapter 17. Acid-Base Equilibria - Homework - Ky PDFDi Vlad PeÑa PrietoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Document18 paginiTest3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Anas SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizDocument8 paginiAP Chem CH 15 Practice QuizHussain MerchantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Database 2Document2.539 paginiDatabase 2Shreyas07100% (2)
- Acid - Base - Solutions - Remote - LessonDocument5 paginiAcid - Base - Solutions - Remote - LessonAndrew FoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molarity and Molality ANSWERSDocument3 paginiMolarity and Molality ANSWERSNarayanRajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water & PHDocument42 paginiWater & PHBea SamonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- HtwoO and BufferDocument7 paginiHtwoO and BufferManila MedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titration of Amino AcidsDocument21 paginiTitration of Amino AcidsCeleste Schepers0% (1)
- Water and PHDocument17 paginiWater and PHLea TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Document10 paginiSources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Narges Malik100% (1)
- Exercise 9 (Acyl Compounds Soaps and Detergents)Document6 paginiExercise 9 (Acyl Compounds Soaps and Detergents)Johan Tadlas0% (1)
- Experiment 8 31.1Document28 paginiExperiment 8 31.1Jessa Libo-onÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buffers Notes1Document3 paginiBuffers Notes1Lara MonevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument2 paginiCarbohydrate ChemistryLakshmi VenkataramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buffers Booklet - CalbiochemDocument37 paginiBuffers Booklet - CalbiochemAMPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note - Acid and BaseDocument3 paginiNote - Acid and BaseAnwar FadilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precipitation TitrationDocument3 paginiPrecipitation TitrationBanana SenpaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 paginiCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water?Document20 paginiWater?Lei Yamin ChitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Acetanilide SynthesisDocument4 paginiReport Acetanilide SynthesisCamilo Andres Carvajal PinillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0Document44 paginiChapter 2 Lecture Notes - 0KirilKocevskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Rehydration SaltsDocument3 paginiOral Rehydration SaltsKadek Adit WiryadanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocument34 paginiColligative Properties of Solutionstatskopling100% (1)
- Titration Solutions PDFDocument3 paginiTitration Solutions PDFBirmej NatapgasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochem Act 1Document31 paginiBiochem Act 1Irene Orzame - VizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry of Carbohydrate PCDocument154 paginiChemistry of Carbohydrate PCAnonymous OrZVTxS2ANÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSES - BIOCHEM - Cellular Metabolism - Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport ChainDocument4 paginiTRANSES - BIOCHEM - Cellular Metabolism - Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport ChainPia LouiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH CalculationsDocument4 paginiPH CalculationsVanandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumDocument55 paginiChapter 4 - Ionic EquilibriumNabilah SyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 paginiUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Organic ChemistryDocument44 paginiPresentation On Organic ChemistryKofi Frimpong-MansonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 365 Midterm #1 NotesDocument14 paginiChem 365 Midterm #1 NotessheilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.0 Ionic EquilibriaDocument124 pagini7.0 Ionic EquilibriaTasya KassimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: Ionic EquilibriaDocument33 paginiSummary: Ionic Equilibriawewwchemistry100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocument58 paginiCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carboxylic Acids and NitrilesDocument35 paginiCarboxylic Acids and Nitrileslorrainebarandon100% (1)
- CH 01 Edited PDFDocument10 paginiCH 01 Edited PDFabbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution of Non-ElectrolytesDocument133 paginiSolution of Non-Electrolytesneha_dand1591Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Complete Acid Base NotesDocument45 pagini1 - Complete Acid Base NotesJohn JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Browning Reactions in Foods: Food TechnologyDocument53 paginiBrowning Reactions in Foods: Food Technologykasun HerathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standardization of Naoh 1Document3 paginiStandardization of Naoh 1api-309208977Încă nu există evaluări
- Factor Affecting SolubilityDocument3 paginiFactor Affecting SolubilityLouie Jay BallenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagini1 HydrocarbonsJuan Miguel Sebasian OrilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReactionDocument54 paginiReactionAhmed ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 40.1 LabDocument21 paginiChem 40.1 LabEve YapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate QuizDocument5 paginiCarbohydrate QuizJoshua Bailey100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsDocument9 paginiOrganic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsAnthony KwofieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryDocument16 paginiBiomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryIshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 8A Formal ReportDocument4 paginiExperiment 8A Formal ReportEj RempilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sn1 and Sn2 Reactions Write UpDocument6 paginiSn1 and Sn2 Reactions Write UpLevy Medina TrayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkyl HalidesDocument54 paginiAlkyl HalidesChandrapal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB 82pHandpOHofstrongacidandbase 61edf8eca0b257.61edf8edc066f0.51892966Document6 paginiTB 82pHandpOHofstrongacidandbase 61edf8eca0b257.61edf8edc066f0.51892966任思诗Încă nu există evaluări
- Slo Review Standard 5 7Document3 paginiSlo Review Standard 5 7api-305204604Încă nu există evaluări
- 4.5 Exercise 1 Aldehydes and KetonesDocument1 pagină4.5 Exercise 1 Aldehydes and Ketonesloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Milimetri I CentimetriHelDocument1 paginăMilimetri I CentimetriHelloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Silver Mirror Experiment ProcedureDocument1 paginăSilver Mirror Experiment Procedureloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- The States of MatterDocument42 paginiThe States of Matterloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- The Childrens BequestDocument177 paginiThe Childrens Bequestloly62006100% (2)
- The States of Matter PDFDocument42 paginiThe States of Matter PDFloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Silver Mirror Experiment ProcedureDocument1 paginăSilver Mirror Experiment Procedureloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8R - Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds Practice Problems PDFDocument7 paginiUnit 8R - Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds Practice Problems PDFFirdausia Rahma PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
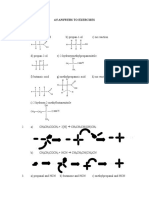
- 4.5 Answers To ExercisesDocument4 pagini4.5 Answers To Exercisesloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Acid CU GenChem2 ActivityDocument4 paginiAcid CU GenChem2 Activityloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 LODocument2 paginiChapter 16 LOloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Building Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class XDocument13 paginiBuilding Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class Xloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- The Childrens BequestDocument177 paginiThe Childrens Bequestloly62006100% (2)
- Fatih MostDocument1 paginăFatih Mostloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Clear Skin Cuisines Acne Recipe CookbookDocument151 paginiClear Skin Cuisines Acne Recipe Cookbookloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- N-Butane: C H CH CH CH CHDocument2 paginiN-Butane: C H CH CH CH CHloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Fatih MostDocument1 paginăFatih Mostloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Abeceda: Aa BB CC Č Č Ć Ć DDDocument4 paginiAbeceda: Aa BB CC Č Č Ć Ć DDloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Apch11 EstersDocument2 paginiApch11 Estersloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 DDocument1 pagină3 Dloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Dan HellmanDocument12 paginiDan Hellmanloly62006Încă nu există evaluări
- Surah AlQadr MiracleDreamTafseer KhanDocument20 paginiSurah AlQadr MiracleDreamTafseer Khanspeed2kxÎncă nu există evaluări
- IUPAC HandoutDocument9 paginiIUPAC HandoutjanellamaikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nauka o Ishrani Stanovnistva-SkriptaDocument53 paginiNauka o Ishrani Stanovnistva-SkriptanerminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Kimia DasarDocument5 paginiTugas Kimia DasarOfficial ProtectionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oecd Guidelines For The Testing of ChemicalsDocument6 paginiOecd Guidelines For The Testing of ChemicalsNikita La CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulfuric Acid CorrosionDocument4 paginiSulfuric Acid CorrosionDucVikingÎncă nu există evaluări
- + ( ) ( ) Handerson Hasselbalch EquationDocument2 pagini+ ( ) ( ) Handerson Hasselbalch Equation123123Încă nu există evaluări
- 16 Acids and BasesDocument4 pagini16 Acids and BaseskapanakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titration Complex Systems Acid BaseDocument11 paginiTitration Complex Systems Acid BaseGeorge AggelisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument3 paginiAcids, Bases and SaltsCavene ScottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Aqueous Titrations by Gunja ChtaurvediDocument10 paginiNon Aqueous Titrations by Gunja ChtaurvediGunja Chaturvedi88% (8)
- Unit Test 2 (Acids Bases and Salts)Document3 paginiUnit Test 2 (Acids Bases and Salts)Bhatt AcademyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH Lab 3Document8 paginiCH Lab 3Mohammad Fahim NurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buffers Michaels CalculationDocument5 paginiBuffers Michaels CalculationHassan Haider100% (1)
- Definitions - Topic 8 Acids Bases and Salts - CAIE Chemistry IGCSE PDFDocument2 paginiDefinitions - Topic 8 Acids Bases and Salts - CAIE Chemistry IGCSE PDFAtif BakhshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evans Pka Table PDFDocument2 paginiEvans Pka Table PDFSarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit V PH, Buffers and Isotonic SolutionDocument14 paginiUnit V PH, Buffers and Isotonic SolutionDevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buffer Solution and TITraTION-1Document59 paginiBuffer Solution and TITraTION-1Febi AndrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul 4 Stoi, Bab 4Document11 paginiModul 4 Stoi, Bab 4Agus Ari BowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 SolutionDocument84 paginiChapter 2 Solutionhulk alanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Chemistry Lectures by Rey CapangpanganDocument8 paginiAnalytical Chemistry Lectures by Rey CapangpanganDrakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disociacion de Acidos PoliproticosDocument4 paginiDisociacion de Acidos PoliproticosRonald DelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 102 AbrevsDocument7 pagini102 AbrevsHandugan Quinlog NoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap ChemDocument2 paginiAp ChemEthan NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria: Reading AssignmentsDocument5 paginiAcid-Base Equilibria and Solubility Equilibria: Reading AssignmentsSteven Skinno MunachongaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument22 paginiClass 10 Acids Bases and Salts NotesShreyash VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acids and AlkalisDocument26 paginiAcids and AlkalisYui Hong Ng0% (1)
- Amines and AmidesDocument24 paginiAmines and AmidesAzura Aziz100% (1)
- Acidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidDocument5 paginiAcidic Reactions of Ethanoic AcidKevin DevastianÎncă nu există evaluări