Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Exp 4
Încărcat de
Elisbeth MurugasTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Exp 4
Încărcat de
Elisbeth MurugasDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EXPERIMENT 4
SINGLE SIDE-BAND MODULATION AND DEMODULATION
1.0 OBJECTIVES
1.1 Demonstrates double and single-sideband suppressed carrier modulation in the
time domain and frequency domain.
1.2 Demonstrate how double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation is produced
using a balance modulator.
1.3 Demonstrate how single-sideband suppressed carrier modulation is produced
using a balance modulator and filter.
1.4 Demonstrate how balance modulator is used as SSB demodulator
1.5 Demonstrate a SSB modulator and demodulator circuit.
2.0 MATERIALS
1.0 Electronic Workbench : MultiSim 8.0
3.0 PROCEDURES
Part 1: Balance-Bridge Modulator
1. Open circuit Figure 1 in the EKT 231_2010 folder. This figure will demonstrate a
double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC) modulation in the time domain and
the frequency domain. Bring down the oscilloscope enlargement and make sure
the following setting are selected:
Oscilloscope: Time base (scale =20us/Div, Xpos = 0,Y/T)
Channel A (scale =500mV/Div, Ypos = 0, DC
Trigger (Pos edge, Level =0, Auto)
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 1
2. Run the simulation to one full screen display and then pause the simulation. Plot
the curve in the space provided.
What is the signal plot on the oscilloscope screen?
Answer: ___________________________________________________
3. Bring down the spectrum analyzer enlargement.
Spectrum Analyzer setting: Centre: 200 kHz
Span: 100 kHz
Amplitude: Lin, range 0.05 V/Div
Resolution: 1 kHz
Run the simulation until the resolution frequency match.
Plot the spectral in the space provided.
What is the signal plot on the Spectrum Analyzer screen?
Answer: ___________________________________________________
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 2
4. Measure the upper side frequency (fusf) and the lower side frequency (f lsf) and the
voltage amplitude of each spectral line and determine the bandwidth of the
DSBSC signal from the frequency spectral plot. Record the all answers on the
spectral plot.
How did the bandwidth of the DSBSC signal compare to the modulating
frequency (fm)?
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
5. Change the frequency on the modulating signal sine wave to 10 kHz. Plot the
curve and spectral (spectrum analyzer) plot in the space provided.
What the difference between this curve plot and the plot of DSBSC in step 2?
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
Time domain
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 3
Frequency domain (Spectral plot)
6. Measure the upper side frequency (fusf) and the lower side frequency (flsf) and the
voltage amplitude of each spectral line and determine the bandwidth of the
DSBSC signal from the frequency spectral plot. Record the all answers on the
spectral plot.
How did this frequency spectrum for double sideband curve plot with 30 kHz
modulating frequency in step 5? Did the bandwidth change? Explain.
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 4
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
Part 2: Single-Sideband Modulator
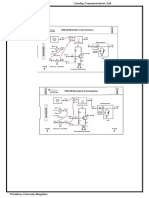
1. Open circuit 2. This circuit shows a single-sideband modulator and the balance
modulator will produce double-sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC) modulation.
The filter, tuned to the upper sideband, will pass the upper sideband and reject the
lower sideband, producing single sideband suppressed carrier (SSBSC)
modulation.
2. This circuit will demonstrate how a single-sideband suppressed carrier signal is
generated. Bring down the oscilloscope enlargement and make sure the following
settings are selected:
Oscilloscope: Time base (scale =20us/Div, Xpos = 0,Y/T)
Channel A (scale =500mV/Div, Ypos = -2.0, DC
Channel B (scale =100mV/Div, Ypos = .0, DC
Trigger (Pos edge, Level =0, Auto)
3. Run the simulation. The display shows the SSBSC filter output (blue) and
DSBSC (red) produce by the balanced bridge modulator in the time domain.
What the difference between SSBSC and DSBSC curve plot?
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 5
4. Bring down the spectrum analyzer enlargement.
Spectrum Analyzer setting: Centre: 200 kHz
Span: 100 kHz
Amplitude: Lin, range 0.02 V/Div
Resolution: 1 kHz
Run the simulation until the resolution frequency match.
Plot the spectral in the space provided. Measure the frequency and the voltage
amplitude of the spectral line and records all the answers on the spectral plot.
Part 3: SSB Modulator – Demodulator
1. Open circuit 3. This circuit will demonstrate how the information in a SSB signal
is recovered. The balance modulator and the filter in the SSB modulator section
will generate a SSB signal modulated with a 30 kHz sine wave. The balance
modulator (product detector) in the SSB demodulator section will recover the
information in the SSB signal. Sine wave generator V 2 in the SSB demodulator
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 6
section will reinsert the carrier at terminal C 1 and C2 of the balance modulator.
Bring down the oscilloscope enlargement and make sure the following settings are
selected:
Oscilloscope: Time base (scale =20us/Div, Xpos = 0,Y/T)
Channel A (scale =2V/Div, Ypos = -2.0, DC
Channel B (scale =2mV/Div, Ypos = .0, DC
Trigger (Pos edge, Level =0, Auto)
2. Run the simulation. You have displayed the SSB demodulator output (blue) and
the information signal input to the SSB modulator (red) in the time domain. Draw
the curve plot in the space provided.
3. Measure the time period for one cycle of the SSB demodulator output (blue) and
SSB modulator sine wave input (red) and record your answers on the curve plots.
What causing the small ripple on the SSB demodulator output (blue)?
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 7
Explain why the carrier must be reinserted in the SSB demodulator?
Answer:
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
4.0 CONCLUSION
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
EKT 231/LAB 4/ver2.0 2011 8
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ask ExperimentDocument11 paginiAsk Experimentdjun033Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 10Document11 paginiLab 10aznia shireenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4A Jun 2018 Introduction of Oscilloscope and Signal GeneratorDocument10 paginiLab 4A Jun 2018 Introduction of Oscilloscope and Signal GeneratorAugustine JR RobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplitude Modulation With No Carrier: ObjectivesDocument27 paginiAmplitude Modulation With No Carrier: ObjectivesRainier RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout 6Document5 paginiHandout 6Barkat Ali KhosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study DSB-SC Demodulation Using Product DetectionDocument4 paginiStudy DSB-SC Demodulation Using Product DetectionTA TiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Escom Electronica AnalogicaDocument9 paginiEscom Electronica AnalogicaEduardo Zamarron MuñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Nuclear ElectronicsDocument6 paginiIntroduction to Nuclear ElectronicsSaRaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplitude & Frequency Modulation Lab ExperimentsDocument35 paginiAmplitude & Frequency Modulation Lab ExperimentsSharmila KrishnaswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT NO. 10. Double Sideband AnalysisDocument12 paginiEXPERIMENT NO. 10. Double Sideband Analysisez shintaishiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAD Lab NUSTDocument6 paginiCAD Lab NUSTHassnain ArshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 4 - Mixer IF Filter and Envelope Detector of AM ReceiverDocument8 paginiExperiment 4 - Mixer IF Filter and Envelope Detector of AM ReceiverJaphetRayModestoCanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE3086F Prelab2 SimulinkDocument4 paginiEEE3086F Prelab2 SimulinkCarlos ZeballosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Ended 14Document5 paginiOpen Ended 14saadshahab080Încă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By:: Muhammad Maab Nawaz FA21-EEE-021Document7 paginiSubmitted By:: Muhammad Maab Nawaz FA21-EEE-021M4MAAB GAMINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- BlakeDocument29 paginiBlakeJERUEL100% (1)
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedDocument11 paginiDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedShabir AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cadence VCODocument59 paginiCadence VCOVăn Công100% (3)
- Passive LPF frequency response analysisDocument7 paginiPassive LPF frequency response analysisNauman AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No - 14Document8 paginiExperiment No - 14Konem SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuuperhetDocument5 paginiSuuperhetnahj.fernandez69Încă nu există evaluări
- 9018-50207 (1)55Document11 pagini9018-50207 (1)55arness22Încă nu există evaluări
- Course: Electronic Circuit Devices Lab No: 06 Title: Frequency Response of Single Stage Common Emitter Amplifier CID: - DateDocument4 paginiCourse: Electronic Circuit Devices Lab No: 06 Title: Frequency Response of Single Stage Common Emitter Amplifier CID: - DateAamir ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabDocument15 paginiLaboratory Manual: Analogue and Digital Communication LabZain HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4k x 2k and 4k x 4k CCD ManualDocument21 pagini4k x 2k and 4k x 4k CCD ManualagudpagudpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 4Document4 paginiExperiment 4Aayan ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 555 Timer Astable OscillatorDocument3 paginiThe 555 Timer Astable Oscillatorregata4Încă nu există evaluări
- Analog Communications Lab: Department:EceDocument62 paginiAnalog Communications Lab: Department:EceSurya Abhi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Op Exp5Document9 paginiOp Exp5Steve Aaron BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator DesignDocument24 paginiRC Phase Shift Oscillator DesignFreddie MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- RIZAL TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY COMMON-SOURCE AMPLIFIER EXPERIMENTDocument4 paginiRIZAL TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY COMMON-SOURCE AMPLIFIER EXPERIMENTSteve Aaron BernardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE133 - Lab 2 Using Oscillators To Generate FM SignalsDocument6 paginiEE133 - Lab 2 Using Oscillators To Generate FM Signalsapi-3725139Încă nu există evaluări
- MW & Oc LabDocument71 paginiMW & Oc Labssm52Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 Oscope Proc SPR 2011 PDFDocument3 pagini10 Oscope Proc SPR 2011 PDFShamoon WahedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS Lab 7 17102022 051437pmDocument6 paginiCS Lab 7 17102022 051437pmYOUMNA MALLICKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment Number ThreeDocument10 paginiExperiment Number ThreeGallardo, Jeny Babe M.Încă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Experiment 4 Frequency ResponseDocument10 paginiLaboratory Experiment 4 Frequency ResponseFrodolfre Reginald LazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oscilloscope and Function Generator GuideDocument14 paginiOscilloscope and Function Generator GuideAyuguÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12th Electronics Most Likely Questions SetDocument19 pagini12th Electronics Most Likely Questions SetomdombareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 - AC MeasurementDocument7 paginiExperiment 1 - AC MeasurementmixchescakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC CoupledDocument3 paginiRC CoupledRavi TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- T 7.2.1.1 Multiplicación de FrecuenciaDocument40 paginiT 7.2.1.1 Multiplicación de FrecuenciaBlademir Parra GayosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecad Lab ManualDocument83 paginiEcad Lab ManualJacklyn Untalan100% (1)
- Oscilloscope Experiment FundamentalsDocument5 paginiOscilloscope Experiment FundamentalsMuhammad ZikryÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE3TR4 - Lab - 2 2019Document3 paginiEE3TR4 - Lab - 2 2019RezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Exercises 3aDocument9 paginiLaboratory Exercises 3aIan VillarojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE370 Lab Experiment 04Document4 paginiEE370 Lab Experiment 04Gellie Anne MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSB Generation: Lab Report # 5Document11 paginiSSB Generation: Lab Report # 5zahraaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocument6 pagini1.amplitude Modulation and DemodulationKondapalli Abdul Lathief0% (1)
- Experiment No. 1Document5 paginiExperiment No. 1Rainier RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Communication Lab Manual 1.1.13Document72 paginiAdvance Communication Lab Manual 1.1.13rockettekcor50% (2)
- BJT Frequency Response - Module 3Document4 paginiBJT Frequency Response - Module 3JaphetRayModestoCanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 5 - Inverter CharacteristicsDocument7 paginiExperiment 5 - Inverter CharacteristicsGowtham SpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 - Function Generator and Oscilloscope - Revised22Oct2010Document9 paginiLab 2 - Function Generator and Oscilloscope - Revised22Oct2010QuynhNhu TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- CA Lab Manual ScopeDocument10 paginiCA Lab Manual Scopea2367916100% (1)
- Be Lab ManualDocument96 paginiBe Lab ManualBhargav garlapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Lab ManualDocument43 paginiDC Lab ManualSowmya KharviÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.0 Rancangan KewanganDocument4 pagini7.0 Rancangan KewanganElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Sem 4 2019Document54 paginiCourse Outline Sem 4 2019Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jadual Cadangan Sangkutan IndustriDocument1 paginăJadual Cadangan Sangkutan IndustriElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Measurement: Work Study TIME STUDY (Direct Time Study & Activity Sampling) Job Design Principles of Motion StudyDocument53 paginiWork Measurement: Work Study TIME STUDY (Direct Time Study & Activity Sampling) Job Design Principles of Motion StudyElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Exp 1Document20 paginiLab Report Exp 1Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT1Document3 paginiEXPERIMENT1Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taksanomi Pembelajaran PDFDocument6 paginiTaksanomi Pembelajaran PDFElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Exp 1Document20 paginiLab Report Exp 1Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document54 paginiChapter 2Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Number Systems & Codes: Digital Electronics & Systems (Beku1413) CHAPT.02Document19 paginiChapter 2: Number Systems & Codes: Digital Electronics & Systems (Beku1413) CHAPT.02Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infrared LEDDocument1 paginăInfrared LEDElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrintDocument1 paginăPrintElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bengkel 2 Teknologi Elektronik Function Generator PM Schedule For Year 2018Document1 paginăBengkel 2 Teknologi Elektronik Function Generator PM Schedule For Year 2018Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rancangan Pengajaran KV Unit Teknologi Elektronik: Semester 1 DVM/ 2016Document20 paginiRancangan Pengajaran KV Unit Teknologi Elektronik: Semester 1 DVM/ 2016Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- WDN Lab3 Results Ws11 210515Document6 paginiWDN Lab3 Results Ws11 210515Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imogen SlidesCarnivalDocument29 paginiImogen SlidesCarnivalZarith Emily Burgoa AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communications - NotesDocument26 paginiData Communications - NotesNarasimha Murthy YayavaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation 10Document1 paginăPresentation 10Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Img 20170312 0001Document1 paginăImg 20170312 0001Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PM For OsciloscopeDocument2 paginiPM For OsciloscopeElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muka Amali k1Document1 paginăMuka Amali k1Elisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre Employment ChecklistDocument1 paginăPre Employment ChecklistElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- mvsubtitles.com.txtDocument1 paginămvsubtitles.com.txtElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 25 Waysfor TWT2Document18 pagini25 Waysfor TWT2Avijit SenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proteus Guidline Logic CircuitDocument16 paginiProteus Guidline Logic CircuitElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ja ChimoDocument28 paginiJa ChimotwinkletwinkleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Perfect Multi-Purpose Umbrella: Introducing "UmbrelifeDocument24 paginiThe Perfect Multi-Purpose Umbrella: Introducing "UmbrelifeElisbeth MurugasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imogen SlidesCarnivalDocument29 paginiImogen SlidesCarnivalZarith Emily Burgoa AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEM 650 Week 1 Quality BasicsDocument18 paginiMEM 650 Week 1 Quality BasicsmmadhulitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pic Soft ModemDocument1 paginăPic Soft ModemRicardo Silva CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AM Modulator Efficiency and Modulation Index QuestionsDocument5 paginiAM Modulator Efficiency and Modulation Index QuestionsAkashdeep BhattacharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CommunicationDocument76 paginiCommunicationconnor walshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 28 MHZ Channel BandwidthDocument6 pagini28 MHZ Channel BandwidthEze Alexander IkÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBUT Question Analog CommunicationDocument4 paginiWBUT Question Analog CommunicationSoumyadeep GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- SATELLITI Radio AmatorialiDocument1 paginăSATELLITI Radio AmatorialiAndrea Il MiodoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Phase Shift KeyingDocument2 paginiDifferential Phase Shift KeyingamulyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEET2465 Lecture 6Document64 paginiEEET2465 Lecture 6ben1151986Încă nu există evaluări
- WINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500822 Reference Material I 10-01-2023 Module 3 - Bandwidth and Power Efficient AM SystemsDocument13 paginiWINSEM2022-23 BECE304L TH VL2022230500822 Reference Material I 10-01-2023 Module 3 - Bandwidth and Power Efficient AM SystemsYaganti pavan saiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC CA Curs 03 Digital Transmission ASK FSK PSKDocument54 paginiRC CA Curs 03 Digital Transmission ASK FSK PSKRed FoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Communication Question BankDocument8 paginiPrinciples of Communication Question BankShaniya FathimuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital modulation techniques for communication systemsDocument12 paginiDigital modulation techniques for communication systemsAngelinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numericals On AMDocument2 paginiNumericals On AMV Sree Suswara SuswaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog TransmissionDocument57 paginiAnalog TransmissionMohamedNofalÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM cell configuration parameters extracted from XML fileDocument407 paginiGSM cell configuration parameters extracted from XML filenoName314Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Modulation Course NotesDocument11 paginiDigital Modulation Course NotesCHIM ZOE CANDAWAN CATALANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itm University Gwalior, (M.P) : Q 1. Define PSK?Document3 paginiItm University Gwalior, (M.P) : Q 1. Define PSK?S M Nafiul HossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5. Analog TransmissionDocument24 paginiChapter 5. Analog Transmissionnoril NitunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modulation and Demodulation TechniquesDocument16 paginiModulation and Demodulation TechniquesAli ShamkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3g E N H ZDocument97 pagini3g E N H Zmoj900Încă nu există evaluări
- PSK Generation and DetectionDocument1 paginăPSK Generation and DetectionChetan Naik JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plist Wo Shu Tangerang Tgl.26.07.2023Document3 paginiPlist Wo Shu Tangerang Tgl.26.07.2023Fita LokaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document14 paginiChapter 5PATRICIA ANNE ELEDAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double Sideband Full CarrierDocument20 paginiDouble Sideband Full CarrierIzzat Rodzman0% (2)
- M-PSK Modulation and DemodulationDocument50 paginiM-PSK Modulation and DemodulationFirmansyah KobongsatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bis 101Document11 paginiBis 101Sally MallatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Call Fail CauseDocument17 paginiCall Fail CauseIindwiayu MardianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog & Digital ModulationDocument11 paginiAnalog & Digital Modulationsowmya_iway_5946012Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch4 Amplitude ModulationDocument55 paginiCh4 Amplitude ModulationsrijanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upgrade Huawei E303 FirmDocument6 paginiUpgrade Huawei E303 Firmdurmotz50% (2)