Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fluid
Încărcat de
kalaivananmekDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluid
Încărcat de
kalaivananmekDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluid
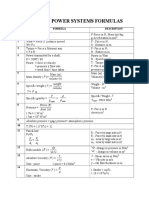
Dynamic Viscosity:
Property of fluid which offers resistance to the movement of one layer of fluid over
another adjacent layer of the fluid. Unit is kgs/m2.
Kinematic Viscosity
Ratio between dynamic viscosity and density of fluid. Unit is m2/s
Newton’s Law of Viscosity states that shear stress is directly proportional to the velocity
gradient.
Surface Tension:
Tensile force acting on the surface of a liquid in contact with a gas or on the surface
between two immiscible liquids such that the contact surface behaves like a membrane.
Unit is N/m.
Rain droplets are formed due to this property.
Capillary Effect:
Phenomenon of rise or fall of a liquid surface in a small tube relative to the adjacent
general level of liquid when the tube is held vertically in the liquid.. If the fluid rises it is
called capillary rise or else it is called capillary depression.
Value depends upon specific weight of the liquid, diameter of the tube and surface
tension of the liquid.
Pressure:
Force acting per unit area of the fluid surface is called pressure..
Pascal’s Law:
Pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
Bernoulli’s Equation:
Assumptions are inviscid , steady, incompressible and irrotational flow. So when
applying to real fluids which are viscous losses have to be taken into consideration.
Pressure Head + Kinetic Head + Datum Head = constant.
Applications are Venturimeter, Orifice meter and Pitot tube.
Archimedes Principle:
Buoyancy
When a body is immersed in a fluid, an upward force is exerted by the fluid on the body.
This upward force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body and is called
the force of buoyancy.
Reynolds Number:
Ratio of Inertia Force to Viscous Force. Less than 2000 means laminar flow. If it is
greater than 4000 that it is turbulent flow.
Steady Flow
Fluid properties do not change with time.
Uniform Flow:
Velocity at any given time does not change with respect to space
Laminar Flow:
Fluid particles move along well defined paths or stream line and all the stream-lines are
straight and parallel.
Turbulent Flow
Moves in a zig-zag flow and eddy formation takes place.
Compressible Flow:
Density of fluid changes from point to point
Rotational Flow
Fluid particles while traveling along stream-lines, also rotate about their own axis.
Continuity Equation
Based on conservation of mass. States that discharge is constant.
Euler Equation:
States that net force acting on the fluid is the sum of gravity force, pressure force,
turbulent force and force due to compressibility. Assumption is that the flow is ideal i.e
the viscosity is zero.
Navier Stokes Equation:
It states that the net force is the sum of gravity force, pressure force, viscous force and
force due to compressibility. Assumption is that the flow is laminar.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Properties and Applications of Ferrous AlloysDocument11 paginiProperties and Applications of Ferrous Alloyskalaivananmek100% (1)
- Microscale Heat Transfer - Fundamentals and Applications PDFDocument516 paginiMicroscale Heat Transfer - Fundamentals and Applications PDFAndréRocha100% (1)
- Human Simulation in PS - ImprovementDocument10 paginiHuman Simulation in PS - ImprovementkalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Savings Charges PDFDocument2 paginiSavings Charges PDFPramod NaikareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rent Receipt Format PDFDocument1 paginăRent Receipt Format PDFkalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molding FormatDocument12 paginiMolding FormatkalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kutzbach CriterianDocument3 paginiKutzbach CriteriankalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument5 paginiStress Strain DiagramkalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych Rome TryDocument3 paginiPsych Rome TrykalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMTD:: AS Heat Transfer Surface AreaDocument2 paginiLMTD:: AS Heat Transfer Surface AreakalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of MachinesDocument6 paginiMechanics of MachineskalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMTD:: AS Heat Transfer Surface AreaDocument2 paginiLMTD:: AS Heat Transfer Surface AreakalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThermalDocument4 paginiThermalkalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive MaterialsDocument3 paginiAutomotive MaterialskalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundry Process:: Casting TermsDocument23 paginiFoundry Process:: Casting TermskalaivananmekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Influence of Lubricant Type in Gear ScuffingDocument10 paginiInfluence of Lubricant Type in Gear ScuffingAnibal RiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spill ManagementDocument33 paginiSpill ManagementRajendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Viscometry - Anton Paar WikiDocument17 paginiBasics of Viscometry - Anton Paar WikiBeshoy RedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products: Standard Test Method ForDocument9 paginiRamsbottom Carbon Residue of Petroleum Products: Standard Test Method ForMuhannad NasifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics - I: DR Muhammad Sajid Assistant Professor Nust, SmmeDocument26 paginiFluid Mechanics - I: DR Muhammad Sajid Assistant Professor Nust, SmmeAsaad WaqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treball de Fi de GrauDocument51 paginiTreball de Fi de GrauSikandar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review of Mathematical ModellingDocument15 paginiA Review of Mathematical ModellingParamita HaldarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yoon 1987Document10 paginiYoon 1987Dersein SaraozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadband Acoustic Silencer With Ventilation Based On Slit-Type Helmholtz ResonatorsDocument6 paginiBroadband Acoustic Silencer With Ventilation Based On Slit-Type Helmholtz Resonators威淳王Încă nu există evaluări
- Brochure GOLU 20160321 enDocument12 paginiBrochure GOLU 20160321 enalaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Introduction To Fluid Mechanics For Chemical EngineersDocument11 pagini1 - Introduction To Fluid Mechanics For Chemical Engineersonikith1751Încă nu există evaluări
- AA200 CH 06 The Conservation Equations CantwellDocument38 paginiAA200 CH 06 The Conservation Equations CantwellbhargavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems FluidmechanicsDocument5 paginiProblems Fluidmechanicsanon_182348362Încă nu există evaluări
- FPS FormulasDocument5 paginiFPS FormulasthamaraikkaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals in Mixing ProcessDocument12 paginiFundamentals in Mixing ProcesssakthivelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spe 211481 MsDocument30 paginiSpe 211481 MsMursal ZeynallıÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantifying Oil - Water Separation Performance in Three-Phase Separators-Part 1 PDFDocument12 paginiQuantifying Oil - Water Separation Performance in Three-Phase Separators-Part 1 PDFRaghulal SethumadhavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid DynamicsDocument70 paginiFluid DynamicsH Aries OñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chocolate Mass Processing Technologies - An Overview PDFDocument16 paginiChocolate Mass Processing Technologies - An Overview PDFKSXÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESSEX Receptacle PropertiesDocument9 paginiESSEX Receptacle PropertiesRomario Kreyder Rojas HuaynalayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Strengthhigh PerformancelightweightconcreteareviewDocument16 paginiHigh Strengthhigh PerformancelightweightconcreteareviewMustafaMahdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VISCOSITYDocument1 paginăVISCOSITYKrishna PATELÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-Thurs-O2 Absorption-ReportDocument25 paginiA-Thurs-O2 Absorption-ReportQuang TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydraulicsDocument234 paginiHydraulicsChristine CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiochemDocument4 paginiBiochem.100% (1)
- 2017 Gear Pump Catalog No Address R0517 WebDocument28 pagini2017 Gear Pump Catalog No Address R0517 WebCARLOS FERNANDO GOMEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seleccion y Diseño GerotorDocument28 paginiSeleccion y Diseño GerotoremersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relief, Bi-Directional CR10-28Document2 paginiRelief, Bi-Directional CR10-28tungÎncă nu există evaluări