Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Food and Nutrition
Încărcat de
ChauhanDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Food and Nutrition
Încărcat de
ChauhanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Secondary School Certificate
Examination Syllabus
FOOD AND NUTRITION
CLASSES IX-X
(based on National Curriculum 2007)
Published by
Aga Khan University Examination Board
Bungalow # 233 / E.I.Lines,
Daudpota Road, Karachi, Pakistan.
November 2004
Last Revised July 2009
All rights reserved
This syllabus is developed by Aga Khan University Examination Board for distribution
to all its affiliated schools
Secondary School Certificate
Examination Syllabus
FOOD AND NUTRITION
CLASSES IX-X
This subject is examined in the
May Examination session only
S. No. Table of Contents Page No.
Preface 5
1. Aims/Objectives of the National Curriculum (2007) 7
2. Rationale of the AKU-EB Examination Syllabus 7
3. Topics and Student Learning Outcomes of the Examination Syllabus 10
4. Scheme of Assessment 26
5. Teaching-Learning Approaches and Classroom Activities 29
6. Recommended Texts and Reference Materials 30
7. Definition of Cognitive Levels and Command Words 30
Annex: SSC Scheme of Studies 33
For queries and feedback
Address: The Aga Khan University Examination Board
Bungalow No. 233/ E.I.Lines, Daudpota Road, Karachi-Pakistan.
Phone: (92-21) 35224702-10
Fax: (92-21) 35224711
E-mail: examination.board@aku.edu
Website: http://examinationboard.aku.edu
http://learningsupport.akueb.edu.pk
Facebook: www.facebook.com/akueb
Last Revised July 2009 Page 4
PREFACE
In pursuance of National Education Policy (1998-2010), the Curriculum Wing of the
Federal Ministry of Education has begun a process of curriculum reform to improve the quality
of education through curriculum revision and textbook development (Preface, National
Curriculum documents 2000 and 2002).
AKU-EB was founded in August 2003 with the same aim of improving the quality of
education nationwide. As befits an examination board it seeks to reinforce the National
Curriculum revision through the development of appropriate examinations for the Secondary
School Certificate (SSC) and Higher Secondary School Certificate (HSSC) based on the
latest National Curriculum and subject syllabus guidance.
AKU-EB has a mandate by Ordinance CXIV of 2002 to offer such examination services to
English and Urdu medium candidates for SSC and HSSC from private schools anywhere in
Pakistan or abroad, and from government schools with the relevant permissions. It has been
accorded this mandate to introduce a choice of examination and associated educational
approach for schools, thus fulfilling a key objective of the National Curriculum of Pakistan:
“Autonomy will be given to the Examination Boards and Research and Development cells
will be established in each Board to improve the system” (ibid. para. 6.5.3 (ii)).
AKU-EB is committed to creating continuity of educational experience and the best
possible opportunities for its students. In consequence it offered HSSC for the first time in
September, 2007 to coincide with the arrival of its first SSC students in college or higher
secondary school. Needless to say this is not an exclusive offer. Private candidates and
students joining AKU-EB affiliated schools and colleges for HSSC Part 1 are eligible to
register as AKU-EB candidates even though they have not hitherto been associated with
AKU-EB.
This examination syllabus exemplifies AKU-EB’s commitment to national educational
goals.
• It is in large part a reproduction, with some elaboration, of the Class IX and X National
Curriculum of the subject.
• It makes the National Curriculum freely available to the general public.
• The syllabus recommends a range of suitable textbooks already in print for student purchase
and additional texts for the school library.
• It identifies areas where teachers should work together to generate classroom activities and
materials for their students as a step towards the introduction of multiple textbooks,
another of the Ministry of Education’s policy provisions for the improvement of secondary
education (ibid. para. 6.3.4).
Last Revised July 2009 Page 5
This examination syllabus brings together all those cognitive outcomes of the National
Curriculum statement which can be reliably and validly assessed. While the focus is on the
cognitive domain, particular emphasis is given to the application of knowledge and
understanding, a fundamental activity in fostering “attitudes befitting useful and peaceful
citizens and the skills for and commitment to lifelong learning which is the cornerstone of
national economic development” (Preface to National Curriculum documents 2000 and
2002).
To achieve this end AKU-EB has brought together university academics, teacher trainers,
writers of learning materials and above all, experienced teachers, in regular workshops and
subject panel meetings.
AKU-EB provides copies of the examination syllabus to subject teachers in affiliated schools
to help them in planning their teaching. It is the syllabus, not the prescribed text book which
is the basis of AKU-EB examinations. In addition, the AKU-EB examination syllabus can
be used to identify the training needs of subject teachers and to develop learning support
materials for students. Involving classroom teachers in these activities is an important part of
the AKU-EB strategy for improving the quality of learning in schools.
The Curriculum Wing of the Federal Ministry of Education has recently released new
subject specifications and schemes of study to take effect in September, 2008. These
documents are a major step forward towards a standards-related curriculum and have been
welcomed by AKU-EB. Our current SSC syllabuses have been revised to ensure conformity
with the new National Curriculum 2006.
We stand committed to all students entering the SSC course as well as those who have
recently embarked upon the HSSC course in facilitating their learning outcome. Our
examination syllabus document ensures all possible support.
Dr. Thomas Christie
Director,
Aga Khan University Examination Board
July 2009
Last Revised July 2009 Page 6
1. Aims/Objectives of the National Curriculum (2007)1
Aims
The curriculum for Food and Nutrition for grades IX-X aims to help individual
students to:
• Develop knowledge of food and Nutrition with special reference to healthy living
• Develop professional attitude towards meeting food needs of the family
• Build capacity for utilization of available resources to meet human needs
(production, consumption, and services)
• Develop skill in planning, preparing and serving meals.
Objectives
• To inculcate dear understating of the terminology used in food science
• To give the knowledge to students for the special nutrient needs of people through
the life cycle-expectant and lactating mothers, infancy, preschool, teenagers and
old age
• Understanding the principles of nutrition and ability to use this knowledge in the
feeding of normal and sick persons of all ages
• To describe the essential components of a nutritionally adequate diet
• To be able to plan a variety of nutritionally adequate meals
• To build capacity of the students to plan appropriate meals in accordance with the
body needs and available resources
• Monitor and control the changes occurring in food during preparation and cooking
• To select appropriate equipment and be able to use it in a safe and appropriate
manner
• To create understanding and ability for storage of food
2. Rationale of the AKU-EB Examination Syllabus
2.1 General Rationale
2.1.1 In 2007, the Curriculum Wing of the Federal Ministry of Education (MoE)
issued a revised part-wise Scheme of Studies according to which the total
marks for the SSC examination have been increased from 850 to 1100 from
the year 2008 and onwards. All subjects are to be taught and examined in both
classes IX and X. It is therefore important for teachers, students, parents and
other stakeholders to know:
(a) that the AKU-EB Scheme of Studies for its SSC examination
(Annex A) derives directly from the 2007 Ministry of Education
Scheme of Studies;
(b) which topics will be examined in Class IX and in Class X;
1
Government of Pakistan (2007), National Curriculum; Food and Nutrition Classes IX-X, Islamabad,
Ministry of Education (Curriculum Wing)
Last Revised July 2009 Page 7
(c) at which cognitive level or levels (Knowledge, Understanding,
Application and other higher order skills) the topics and sub-topics will
be taught and examined;
2.1.2 This AKU-EB examination syllabus addresses these concerns. Without such
guidance teachers and students have little option other than following a single
textbook to prepare for an external examination. The result is a culture of rote
memorization as the preferred method of examination preparation. The
pedagogically desirable objectives of the National Curriculum which
encourage “observation, creativity and other higher order thinking [skills]” are
generally ignored. AKU-EB recommends that teachers and students use
multiple teaching-learning resources for achieving the specific objectives of
the National Curriculum reproduced in the AKU-EB examination syllabuses.
2.1.3 The AKU-EB examination syllabuses use a uniform layout for all subjects to
make them easier for teachers to follow. Blank sheets are provided in each
syllabus for writing notes on potential lesson plans. It is expected that this
arrangement will also be found helpful by teachers in developing classroom
assessments as well as by question setters preparing material for the AKU-EB
external examinations. The AKU-EB aims to enhance the quality of education
through improved classroom practices and improved examinations.
2.1.4 The Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) in Section 3 start with command
words such as list, describe, relate, explain, etc. The purpose of the command
words is to direct the attention of teachers and students to specific tasks that
candidates following the AKU-EB examination syllabuses are expected to
undertake in the course of their subject studies. The examination questions
will be framed using the same command words or the connotation of the
command words to elicit evidence of these competencies in candidates’
responses. The definitions of command words used in this syllabus are given
in Section 8. It is hoped that teachers will find these definitions useful in
planning their lessons and classroom assessments.
2.1.5 The AKU-EB has classified SLOs under the three cognitive levels Knowledge
(K), Understanding (U) and Application of knowledge and skills (A) in order
to derive multiple choice questions and constructed response questions on a
rational basis from the subject syllabuses ensuring that the intentions of the
National Curriculum should be met in full. The weighting of marks to the
Multiple Choice and Constructed Response Papers is also derived from the
SLOs, command words and cognitive levels. In effect the SLOs derived from
the National Curriculum determine the structure of the AKU-EB subject
examination set out in Section 4.
2.1.6 Some topics from the National Curriculum have been elaborated and enriched
for better understanding of the subject and/or to better meet the needs of
students in the twenty-first century. These additional topics have been
italicized in Section 3 of this syllabus.
Last Revised July 2009 Page 8
2.2. Specific Rationale of the AKU-EB Food and Nutrition Examination Syllabus
2.2.1 The Curriculum Development team for Food and Nutrition for grades
IX-X was framed involving subject experts and teachers of Food and Nutrition
from colleges all over Pakistan.
Following strategies were adopted in designing/revising the curriculum:
• Need assessment by critically reviewing current curriculum
• Consultative meetings with the working teachers and professors to get
feedback and comments on existing curriculum
• Identification of eminent areas of study
• Identification of standards for communicating the impending areas
• Study of foreign curricula for comparison and guidelines
• Drafting of contents
• Preparation of detailed contents in the light of competencies to be
developed
• Preparation of specific learning outcomes according to the contents
• Preparation of study and evaluation scheme for implementing the
curriculum
2.2.2 The requirement to revise and update Food and Nutrition curriculum is based
on the aspirations of the government and the society envisages vibrant and
responsive curriculum.
The prime focus of this curriculum is based on the broad areas of Food and
Nutrition. This document is based on three broad categories of activities that
connect Food and Nutrition with health and wellbeing of people:
• Knowing how to use knowledge scientifically
• Developing an understanding of home making tasks relating to foods,
based on scientific knowledge
• Utilization of all the resources of modern science to improve the nutrition
of the family
2.2.3 This curriculum will broaden the horizon and vision of the students by
teaching them latest techniques and developing scientific and practical
approach. It will prepare the students for the world of work, as will as for
pursuit of professional and specialized education.
Last Revised July 2009 Page 9
3. Topics and Student Learning Outcomes of the Examination Syllabus
Part I (Class IX)
Cognitive Level2
Topic Student Learning Outcomes
K U A
1. Introduction to the Study of Candidates should be able to:
Food and Nutrition
1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 define food and diet; *
1.1.2 differentiate between food and diet; *
1.1.3 define nutrition; *
1.1.4 differentiate among malnutrition, under nutrition and over-nutrition; *
1.1.5 define a calorie; *
1.1.6 explain the term Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) and state the *
RDA of different food groups (proteins, vitamin A, B1, B2, C and D,
calcium and iron) for children, males, females, pregnant and lactating
mothers;
1.2 Role of Nutrition in Health 1.2.1 define nutrients; *
1.2.2 explain the role of nutrition in *
• physical health;
• mental health;
• preventing diseases;
1.3 Functions of Foods 1.3.1 describe the basic functions of food; *
1.3.2 explain the role of food as a source of energy; *
1.3.3 describe the role of food in tissue building and maintenance; *
1.3.4 discuss the role of food in preventing diseases; *
2
K = Knowledge, U = Understanding, A= Application (for explanation see Section 7: Definition of command words used in Student Learning Outcomes and in Examination
Questions).
Last Revised July 2009 Page 10
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 11
K U A
1.4 Good and Poor Nutrition 1.4.1 identify poor and good nutrition; *
1.4.2 describe the effects of nutrition on growth in children; *
1.4.3 list the effects of nutrition on skin, hair, nails and gums; *
1.4.4 discuss the effects of weight (gain / loss) on children and adults. *
2. Energy and Nutrients Candidates should be able to:
2.1 Nutrients 2.1.1 describe basic nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals *
(calcium and iron), vitamins (A, C and D) and water;
2.1.2 describe the functions of each nutrient; *
2.1.3 identify the food sources of each nutrient; *
2.1.4 discuss the effect of deficiencies of each nutrient; *
2.1.5 describe the sources and functions of dietary fibre; *
2.2 Energy Value of Food 2.2.1 compare energy value of different foods; *
2.2.2 identify proper sources of energy in daily diet; *
2.2.3 describe factors affecting energy requirement of the individuals (growth, *
daily physical activities, pregnancy).
3. Balanced Diet Candidates should be able to:
3.1 Importance of Balanced 3.1.1 define balanced diet; *
Diet 3.1.2 state the importance of balanced diet; *
3.1.3 differentiate between balanced and unbalanced diet; *
3.1.4 describe the different food groups (cereals, fruits and vegetables, milk *
products, meat);
Last Revised July 2009 Page 12
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 13
K U A
3.1.5 explain the requirement of a balanced diet; *
i. at different ages-infancy, pre-school, adolescence, adulthood, old
age;
ii. between genders;
iii. in relation to intensity of daily physical activity;
iv. during pregnancy and lactation;
3.2 Health and Dietary 3.2.1 define health; *
Practices 3.2.2 define dietary practices; *
3.2.3 describe the factors influencing dietary practices; *
3.2.4 discuss the role of unhealthy dietary practices on health; *
3.3 Planning Balanced Diets 3.3.1 discuss the importance of healthy food choices; *
3.3.2 compare and contrast serving size and the concept of portion size; *
3.3.3 identify food groups in food pyramid; *
3.3.4 plan a balanced diet from basic food groups; *
3.4 Food Composition Table 3.4.1 use the food composition table; *
3.4.2 estimate energy, protein content of given foods; *
3.4.3 interpret food tables. *
4. Nutrient Composition Candidates should be able to:
4.1 Nutrient Composition of 4.1.1 describe the nutrient composition of the various foods; (milk, eggs, meat, *
the Various Foods fish, poultry, vegetables and fruits, cereals, pulses and nuts, fats, oils and
sugar);
4.2 Significance of Nutrient 4.2.1 explain the importance of knowing nutrient composition of different *
Composition foods;
4.2.2 identify food items keeping in mind nutrient composition. *
Last Revised July 2009 Page 14
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 15
K U A
5. Preparation and Cooking Candidates should be able to:
5.1 Preparation and Cooking 5.1.1 explain the effects of cooking on colour, texture, palatability and *
Methods digestibility of various foods;
• Milk and milk products
• Eggs
• Meat and meat products
• Vegetable and fruits
• Cereals and starch
5.1.2 describe the appropriate methods of preparing food; *
5.1.3 demonstrate the different cooking methods; *P
5.1.4 describe proper cooking methods for different foods; *
5.1.5 explain cooking methods which minimizes nutrient losses; *
5.1.6 plan, prepare and serve some common dishes from the following; *P
• Milk and milk products (custard, kheer, etc)
• Eggs (omelet, egg sandwiches, egg roll, etc)
• Meat and meat products (biryani, etc)
• Vegetable and fruits (potato and spinach bhujiya, vegetable rice, pea
pulao, etc)
• Cereals and starch (paratha, cutlets, daal, etc)
5.2 Safety in the Kitchen 5.2.1 explain the importance of the safety measures in the kitchen; *
5.2.2 identify potential danger areas in the kitchen; *
5.2.3 practise safety precautions in the kitchen; *P
5.2.4 handle minor accidents in the kitchen. *P
________________________________
*Practical Activity
Last Revised July 2009 Page 16
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 17
Part II (Class X)
Cognitive Level
Topic Student Learning Outcomes
K U A
6. Family and Community Candidates should be able to:
Nutrition
6.1 Nutrition of Vulnerable 6.1.1 define community nutrition; *
Groups in the Community 6.1.2 define vulnerable groups; *
6.1.3 identify nutritional problems of different vulnerable groups; *
6.1.4 explain the dietary needs of the vulnerable groups: *
• pregnant and lactating females
• infants
• preschools
• teenagers / adolescents
• elderly
6.1.5 compare the additional food requirements of pregnant and lactating *
mothers;
6.1.6 compare breast-feeding and bottle-feeding; *
6.1.7 compare the choices between home-made and commercial baby foods; *
6.1.8 compare healthy snacks vs. junk food among teenagers; *
6.1.9 modify family diets to suit the food needs of elderly in the family; *
6.2 Preventing Malnutrition in 6.2.1 list various measures for preventing malnutrition; *
Community 6.2.2 discuss the prevention of nutrition disorders related to food shortage; *
6.2.3 discuss the role of economics in community nutrition; *
6.2.4 discuss awareness through nutrition education; *
6.2.5 explain distribution of food in family and community; *
6.2.6 discuss the importance of avoiding food wastage at family and *
community levels.
Last Revised July 2009 Page 18
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 19
K U A
7. Meal Management Candidates should be able to:
7.1 Principles of Meal 7.1.1 define meal planning; *
7.1.2 state the principles of meal planning; *
7.1.3 explain the importance of meal planning; *
7.2 Menu Planning for 7.2.1 define menu planning; *
Families of Different 7.2.2 describe a useful format for writing a menu; *
Income Levels 7.2.3 plan menu for three different income levels: *P
• low
• middle
• high
7.3 Menu Planning for 7.3.1 plan menus for different stages (pregnancy, infancy, early childhood, *P
Different Stages teenage and elderly);
7.4 Menu Planning for 7.4.1 plan menus for different occasions like eid, birthday and wedding. *P
Different Occasions
8. Table Setting and Meal Candidates should be able to:
Services
8.1 Food Service and Table 8.1.1 describe food service; *
Setting 8.1.2 explain significance of food service; *
describe the different methods of food service formal, buffet, trolley and *
8.1.3
tray;
8.1.4 describe appropriate methods of food services for different occasions; *
8.2 Table Manners and 8.2.1 describe and demonstrate table manners and etiquettes, e.g. washing *P
Etiquettes hands before eating meals, saying prayers while starting meal, using
right hand while eating, use of table napkins.
________________________________
*Practical Activity
Last Revised July 2009 Page 20
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 21
K U A
9. Purchases and Storage of Food Candidates should be able to:
9.1 Purchase of Food 9.1.1 explain the principles of purchase; *
9.1.2 discuss the criteria of purchasing different types of food (fruits, *
vegetables, bread);
9.2 Storage 9.2.1 compare different types of food storage; *
9.2.2 explain why food must be properly stored; *
9.2.3 list correct storage procedures (refrigeration and freezing) for various *
food types.
10. Food Preservation Candidates should be able to:
10.1 Food Preservation 10.1.1 define preservation; *
10.1.2 discuss the importance of food preservation; *
10.1.3 explain the principles of preserving food; *
10.1.4 compare different methods of preservation; *
• heating–canning, bottling
• removal of moisture–drying
• reduction in temperature–freezing
• chemical preservation–sugar, salt, vinegar
• pasteurization;
10.2 Food Spoilage 10.2.1 define spoilage; *
10.2.2 describe the mode of action of different spoiling agents (bacteria, fungi, *
action of enzyme);
10.2.3 explain different methods of controlling food spoilage at home *
(refrigeration, kitchen hygiene, waste disposal);
Last Revised July 2009 Page 22
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 23
K U A
10.3 Food Additives 10.3.1 define additives; *
10.3.2 list the food additives; *
10.3.3 discuss the role of additives in food preservation; *
10.3.4 explain the role of food additives in relation to health hazards. *
Last Revised July 2009 Page 24
NOTES
Last Revised July 2009 Page 25
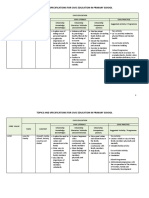
4. Scheme of Assessment
Class IX
Table 1: Number of Student Learning Outcomes by Cognitive Level
Topic No. of SLOs
Topics Total
No. Sub-topics K U A
1. Introduction to the study of Food and
4 6 10 0 16
Nutrition
2. Energy and Nutrients 2 2 6 0 8
3. Balanced Diet 4 5 9 2 16
4. Nutrient Composition 2 1 2 - 3
5. Preparation and Cooking 2 1 5 4 10
Total 14 15 32 4 53
Percentage 28 60 12 100
Table 2: Allocation of Marks for the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs),
Constructed Response Questions (CRQs) and
Extended Response Questions (ERQs)
Marks
No. of
Topic Multiple Constructed Extended
Topics Sub- Total
No. Choice Response Response
topics
Questions Questions Questions
1. Introduction to the
study of Food and 4 8 6 6 20
Nutrition
2. Energy and Nutrients 2
10 12 6 28
3. Balanced Diet 4
4. Nutrient Composition 2 4 6 0 10
5. Preparation and
2 3 4 0 7
Cooking
Total 25 28 12 65
Practical 10
Total 75
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 26
Table 3: Paper Specifications
Topic Total
Topics Marks Distribution
No. Marks
MCQs 8 @ 1 Mark
Introduction to the study of Food and CRQs 2 @ 3 Marks
1. 20
Nutrition *ERQ 1 @ 6 Marks
Choose any ONE from TWO
MCQs 10 @ 1 Mark
2. Energy and Nutrients
CRQs 4 @ 3 Marks each
28
ERQ 1 @ 6 Marks
3. Balanced Diet
Choose any ONE from TWO
MCQs 4 @ 1 Mark
4. Nutrient Composition 10
CRQs 2 @ 3 Marks
MCQs 3 @ 1 Mark
5. Preparation and Cooking 7
CRQ 1 @ 4 Marks
Total MCQs CRQs ERQs
65
25 28 12
Practical 10
Total 75
* Extended response questions (ERQs) will require answers in more descriptive form.
The answers will be in a paragraph rather than a word or a single sentence.
Class X
Table 4: Number of Student Learning Outcomes by Cognitive Level
Topic No. of SLOs
Topics Total
No. Sub-topics K U A
6. Family and Community Nutrition 2 4 11 0 15
7. Meal Management 4 3 2 3 8
8. Table Setting and Meal Services 2 0 4 1 5
9. Purchases and Storage of Food 2 1 4 0 5
10. Food Preservation 3 4 7 0 11
Total 13 12 28 4 44
Percentage 27 64 9 100
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 27
Table 5: Allocation of Marks for the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs),
Constructed Response Questions (CRQs) and
Extended Response Questions (ERQs)
Marks
No. of Multiple Constructed Extended
Topic
Topics Sub- Choice Response Response Total
No.
topics Questions Questions Questions
Family and
6. 2
Community Nutrition 11 10 6 27
7. Meal Management 4
Table Setting and Meal
8. 2 4 6 0 10
Services
Purchases and Storage
9. 2 4 8 0 12
of Food
10. Food Preservation 3 6 4 6 16
Total 25 28 12 65
Practical 10
Total 75
Table 6: Paper Specifications
Topic Total
Topics Marks Distribution
No. Marks
MCQs 11 @ 1 Mark
6. Family and Community Nutrition CRQs 2 @ 5 Marks each
27
*ERQ 1 @ 6 Marks
7. Meal Management Choose any ONE from TWO
MCQs 4 @ 1 Mark
8. Table Setting and Meal Services 10
CRQs 2 @ 3 Marks
MCQs 4 @ 1 Mark
9. Purchases and Storage of Food 12
CRQs 2 @ 4 Marks each
MCQs 6 @ 1 Mark
CRQ 1 @ 4 Marks
10. Food Preservation 16
ERQ 1 @ 6 Marks
Choose any ONE from TWO
Total MCQs CRQs ERQs
65
25 28 12
Practical 10
Total 75
* Extended response questions (ERQs) will require answers in more descriptive
form. The answers will be in a paragraph rather than a word or a single
sentence.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 28
4.1 Tables 1 and 4 summarize the number and nature of SLOs in each topic in
classes IX and X. This will serve as a guide in the construction of the
examination paper. It also indicates that more emphasis has been given to
Understanding (60% and 64%), Application and higher order skills (12 and 9%)
to discourage rote memorization. Tables 1 and 4 however do not translate directly
into marks.
4.2 There will be two examinations, one at the end of Class IX and one at the end of
Class X.
4.3 In each class, the theory paper will be in two parts: paper I and paper II. Both papers
will be of duration of 3 hours.
4.4 Paper I theory will consist of 25 compulsory, multiple choice items. These questions
will involve four response options.
4.5 Paper II theory will carry 40 marks and consist of a number of compulsory, structured
questions and a number of extended response questions. Each extended response
question will be presented in an either/or form.
4.6 Practical examination will be conducted separate from the theory paper. It will be
based on the practical activities indicated in the syllabus.
4.7 All constructed response questions will be in a booklet which will also serve as an
answer script.
4.8 Practical exams to assess performance skills will carry 10 marks in class IX
and 10 marks in class X.
4.9 The practicals identified by a “P” should be carried out through out the academic
year. It is essential for each school to equip its laboratories with ingredients,
instruments, apparatus, utensils etc. according to the requirements of the practicals.
Each school will be responsible to make sure that each student is provided the
opportunity to do the practicals.
5. Teaching-Learning Approaches and Classroom Activities
• The teaching learning approaches should be student cantered. Teachers should
enter into partnership with the students in the whole learning process, Each child’s
sell image as a learner should be well protected, especially when classroom
discussions beings the socio-cultural values of the home and the community into
high relief.
• Learning should be activity based wherever possible. Some SLOs explicitly
require that students bring their own experience and informal researches to the
classroom, which they can share with others.
• Rote learning of the concepts and principles of Home Economics should not be
encouraged. Teachers should try to develop questions requiring comprehension
and higher order skills like application.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 29
• The content has been elaborated in terms of specific learning objectives that will
help to broaden student’s conceptual understating and learning of life skills
directly relevant to meeting the challenges of 21st century. In particular, care has
been taken to recognize the modern life.
• Finally, SLOs encourage both teachers and students to concentrate on
understanding and application rather then recall and role learning. The sequence
of the topics has been developed to facilitate a deeper and more coherent
understanding.
6. Recommended Texts and Reference Materials
1. Tull, Anita (1997). Food and Nutrition. Karachi: Oxford University Press.
2. Prof. Matina Zia (2006), Food Nutrition and Diet Basic Concepts. Lahore:
Caravan Book House.
3. Mir. Zahida Yaqoob (1995-96). Food and Nutrition. Lahore: Salman
Publishers.
Recommended Websites:
www.kidshealth.org
www.nih.gov
www.eatright.org
www.annecollins.com
7. Definition of Cognitive Levels and Command Words
7.1 Definition of Cognitive Levels
Knowledge
This requires knowing and remembering facts and figures, vocabulary and contexts,
and the ability to recall key ideas, concepts, trends, sequences, categories, etc. It can
be taught and evaluated through questions based on: who, when, where, what, list,
define, describe, identify, label, tabulate, quote, name, state, etc.
Understanding
This requires understanding information, grasping meaning, interpreting facts,
comparing, contrasting, grouping, inferring causes/reasons, seeing patterns,
organizing parts, making links, summarizing, solving, identifying motives, finding
evidence, etc. It can be taught and evaluated through questions based on: why, how,
show, demonstrate, paraphrase, interpret, summarize, explain, prove, identify the
main idea/theme, predict, compare, differentiate, discuss, chart the course/direction,
report, solve, etc.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 30
Application
This requires using information or concepts in new situations, solving problems,
organizing information and ideas, using old ideas to create new ones, generalizing
from given facts, analyzing relationships, relating knowledge from several areas,
drawing conclusions, evaluating worth, etc. It can be taught and evaluated through
questions based on: differentiate, analyze, show relationship, propose an alternative,
prioritize, give reasons for, categorize, illustrate, corroborate, compare and contrast,
create, design, formulate, integrate, rearrange, reconstruct/recreate, reorganize, predict
consequences etc.
7.2 Definition of Command Words
Knowledge
Define: Only a formal statement or equivalent paraphrase is required.
No examples need to be given.
Identify: Recognize with specific examples.
List: Requires a number of points, generally each of one word, with
no elaboration. Where a given number of points is specified,
this should not be exceeded.
Recall: To bring back to mind and write down, as it is given in the text
that you have already memorized.
State: A concise answer with little or no supporting argument, e.g. a
numerical answer that can be obtained “by inspection”.
Understanding
Compare: To list the main characteristics of two entities clearly
identifying similarities or differences.
Demonstrate/ To show how a thing is related to another, usually it is
reference to theory but sometimes it is by physical
manipulation or experiment.
Describe: To state in words (using diagrams where appropriate) the
main points of the topic. It is often used with reference either
to particular phenomena or to particular experiments. In the
former instance, the term usually implies that the answer
should include reference to (visual) observations associated
with the phenomena.
Differentiate: To identify those characteristics which always or sometimes
differentiate two categories.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 31
Discuss: To give a critical account of the points involved in the topic.
Explain: To reason or use some reference to theory, depending on the
context.
Use To employ a tool or skill or method in order to achieve a
result.
Modify To make changes in something in order to improve it or make
it less extreme to bring it to the required criteria.
Estimate To calculate or form an opinion by using available
information.
Application
Differentiate To identify those characteristics which always or sometimes
differentiate two categories.
Interpret Clarify both the explicit meaning and the implications of
given information.
Prepare: A practical activity in which choice of equipment, order of
procedure and accuracy of measurement will all play a part.
Plan To design a series of actions to achieve required results.
Handle To be able to deal successfully with a given situation.
Practise To exercise the given instructions or rules in real situations.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 32
Annex
3
SSC Scheme of Studies
AKU-EB as a national board offers SSC and HSSC qualifications for both English and Urdu
medium schools. The revised SSC Scheme of Studies issued by the Curriculum Wing was
implemented from September 2007. Accordingly, each SSC subject will be taught across
both the classes IX and X. The Science and Humanities group subjects are offered at SSC
level. The marks allocated to subjects in the revised National Scheme of Studies of
September 2007 have been followed.
SSC I and II (Class IX and X) subjects on offer for examination
SSC Part-I (Class IX) Science Group
Marks
Subjects Medium
Theory Practical Total
English Compulsory-I 75 - 75 English
Urdu Compulsory-I OR Urdu
Urdu Aasan a OR 75 - 75 Urdu
History and Geography of Pakistan-I b English
Islamiyat-I OR Ethics-I c *30 - *30 English / Urdu
Pakistan Studies-I *45 - *45 English / Urdu
Mathematics-I 75 - 75 English / Urdu
Physics-I 65 10 75 English / Urdu
Chemistry-I 65 10 75 English / Urdu
Biology-I OR English / Urdu
65 10 75
Computer Science-I English
Total: *495 30 *525
SSC Part-II (Class X) Science Group
Marks
Subjects Medium
Theory Practical Total
English Compulsory-II 75 - 75 English
Urdu Compulsory-II OR Urdu
Sindhi a OR 75 - 75 Sindhi
History and Geography of Pakistan-IIb English
Islamiyat-II OR Ethics-II c *45 - *45 English / Urdu
Pakistan Studies-II *30 - *30 English / Urdu
Mathematics-II 75 - 75 English / Urdu
Physics-II 65 10 75 English / Urdu
Chemistry-II 65 10 75 English / Urdu
Biology-II OR English / Urdu
65 10 75
Computer Science-II English
Total: *495 30 *525
a. Candidates from the province of Sindh may appear in “Urdu Aasan” in SSC Part I and in “Sindhi” in Part II
examination.
b. Foreign students may opt HISTORY and GEOGRAPHY OF PAKISTAN in lieu of Urdu Compulsory, subject to
the Board’s approval.
c. For non-Muslim candidates only.
* The above will be implemented in
SSC Part I 2013 Examinations and onwards
SSC Part II 2014 Examinations and onwards
3
Government of Pakistan September 2007. Scheme of Studies for SSC and HSSC (Classes IX-XII). Islamabad: Ministry of Education,
Curriculum Wing.
Latest Revision June 2012 Page 33
SSC Part-I (Class IX) Humanities Group
Subjects Marks Medium
English Compulsory-I 75 English
Urdu Compulsory-I OR Urdu
Urdu Aasan a OR 75 Urdu
History and Geography of Pakistan-I b English
Islamiyat-I OR Ethics-I c *30 English / Urdu
Pakistan Studies-I *45 English / Urdu
General Mathematics-I 75 English / Urdu
Any three of the following Elective Subjects 225
1. **Geography-I (75 each) English / Urdu
2. General Science-I English / Urdu
3. Computer Science-I (65+10 practical) English
4. Economics-I English / Urdu
5. Civics-I English / Urdu
6. **History of Pakistan-I English / Urdu
7. **Elements of Home Economics-I English / Urdu
8. **Food and Nutrition-I (65+10 practical) English / Urdu
9. **Art & Model Drawing-I English
10. **Business Studies-I English
11. **Environmental Studies-I English
Total: *525
SSC Part-II (Class X) Humanities Group
Subjects Marks Medium
English Compulsory-II 75 English
Urdu Compulsory-II OR 75 Urdu
Sindhi a Sindhi
History and Geography of Pakistan-II b OR English
Islamiyat-II OR Ethics-II c *45 English / Urdu
Pakistan Studies-II *30 English / Urdu
General Mathematics-II 75 English / Urdu
Any three of the following Elective Subjects 225
1. **Geography-II (75 each) English / Urdu
2. General Science-II English / Urdu
3. Computer Science-II (65+10 practical) English
4. Economics-II English / Urdu
5. Civics-II English / Urdu
6. **History of Pakistan-II English / Urdu
7. **Elements of Home Economics-II English / Urdu
8. **Food and Nutrition-II (65+10 practical) English / Urdu
9. **Art & Model Drawing-II English
10. **Business Studies-II English
11. **Environmental Studies-II English
Total: *525
SSC Part-I and Part-II (Class IX-X) (Additional Subjects)
SSC Part I SSC Part II Marks Medium
d d English
1. **Literature in English-I 1. **Literature in English-II
d
2. **Commercial Geography-I 2. **Commercial Geography-II d 75 each English
3. **Additional Mathematics-I d 3. **Additional Mathematics-II d English
a. Candidates from the province of Sindh may appear in “Urdu Aasan” in SSC Part I and in “Sindhi” in Part II
examination.
b. Foreign students may opt HISTORY and GEOGRAPHY OF PAKISTAN in lieu of Urdu Compulsory, subject to
the Board’s approval.
c. For non-Muslim candidates only. d. Subject will be offered as Additional Subject.
* The above will be implemented in
SSC Part I 2013 Examinations and onwards SSC Part II 2014 Examinations and onwards
**These subjects are offered ONLY in the May examination.
Last Revised July 2009 Page 34
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ch. 3 PHN Nutritional Epidemiology - SlidesDocument24 paginiCh. 3 PHN Nutritional Epidemiology - Slideswelcome martinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition CourseDocument63 paginiNutrition Coursechiranjiv_sandhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- BY: Muhammad Waseem Akhtar Department of Physical Education & Sports Sciences GC University Lahore 03224426152Document17 paginiBY: Muhammad Waseem Akhtar Department of Physical Education & Sports Sciences GC University Lahore 03224426152Za Ki100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiLesson Planapi-284676533100% (1)
- Food, Nutrition and Health SBA # 2 (2020-2022)Document4 paginiFood, Nutrition and Health SBA # 2 (2020-2022)Marvin Bloomfield100% (1)
- Nutritional EpidemiologyDocument3 paginiNutritional Epidemiologylample100% (1)
- Steekell in Class Lesson 1 6 Basic NutrientsDocument6 paginiSteekell in Class Lesson 1 6 Basic Nutrientsapi-315740379100% (1)
- Lesson 5 FOOD PREPARATION TECHNIQUESDocument5 paginiLesson 5 FOOD PREPARATION TECHNIQUESJaylyne Faith Ballog100% (1)
- Grade 6 Kitchen Utensils ProjectDocument4 paginiGrade 6 Kitchen Utensils Projectmtv chelsie100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 1 - TechnologyDocument5 paginiLesson Plan 1 - Technologyapi-316109069100% (1)
- NutritionDocument5 paginiNutritionzarahcarilloabu100% (1)
- Nutrition EpidemiologyDocument15 paginiNutrition EpidemiologyLokesh RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Makes Nutrition Education Programs EffectiveDocument11 paginiWhat Makes Nutrition Education Programs EffectiveMeeta BhalotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dry Method of Cooking WorksheetDocument5 paginiDry Method of Cooking WorksheetGinalie Lorenzo100% (1)
- Year 9 Hpe Nutrition BookletDocument17 paginiYear 9 Hpe Nutrition Bookletapi-314155244100% (1)
- 11 Cooking MethodsDocument8 pagini11 Cooking MethodsIsmaelita CampoamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A RecipeDocument5 paginiWhat Is A RecipeCei mendoza100% (1)
- Food and Nutrition Class 1 Worksheet 0 2022 13 08 115815Document7 paginiFood and Nutrition Class 1 Worksheet 0 2022 13 08 115815Susmita SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepare Stocks, Sauces and SoupsDocument32 paginiPrepare Stocks, Sauces and SoupsJANUS JARIOLNEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional EpidemiologyDocument1 paginăNutritional EpidemiologyEasha Jamil AbbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Lesson PlanDocument13 paginiNutrition Lesson Planjohnson3110100% (2)
- Public Nutrition & Health NCERTDocument15 paginiPublic Nutrition & Health NCERTNidhi SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition QuizDocument32 paginiNutrition QuizAwit100% (1)
- Kitchen Safety Rules and Equipment for StudentsDocument7 paginiKitchen Safety Rules and Equipment for StudentsJustin Rae PunzalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety ActivityDocument3 paginiSafety Activityapi-233143004Încă nu există evaluări
- 1332 Kitchen Tools and Utensils GuideDocument12 pagini1332 Kitchen Tools and Utensils Guideapi-253329505100% (1)
- Multimix PrincipleDocument3 paginiMultimix PrincipleKiand Albert 9CÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRADE-10-COOKERY-SIM3 EditedDocument13 paginiGRADE-10-COOKERY-SIM3 EditedGrechie CortelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity On Recipe ReadingDocument6 paginiActivity On Recipe ReadingRheen ClarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Preparation, Preservation and StorageDocument22 paginiFood Preparation, Preservation and StorageMs.Prachi ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- BAKINGDocument221 paginiBAKINGAiko BacdayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 LAS Cookery Q3 Week 2Document17 paginiGrade 10 LAS Cookery Q3 Week 2Alejandro Timbad Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Diet and Therapy: Micronutrients: MINERALSDocument7 paginiDiet and Therapy: Micronutrients: MINERALSCHINGCHONG SLAYERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title: The Benefits of Running: Weight ControlDocument2 paginiTitle: The Benefits of Running: Weight ControlchinjeanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTIVITY COMPLETION REPORt On Nutrition Month 2023Document12 paginiACTIVITY COMPLETION REPORt On Nutrition Month 2023Aphro DiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techniques To Prevent Food SpoilageDocument30 paginiTechniques To Prevent Food SpoilageCourtney GrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ligaya National High School Technology and Livelihood Education Cookery 8 Module 1: Kitchen Tools and Their UsesDocument54 paginiLigaya National High School Technology and Livelihood Education Cookery 8 Module 1: Kitchen Tools and Their UsesDonna Marie Arcangel100% (1)
- Legaspi Street, Tanjay City, Negros Oriental: Grade Level Xi Maribel G. Glodove Student TeacherDocument14 paginiLegaspi Street, Tanjay City, Negros Oriental: Grade Level Xi Maribel G. Glodove Student TeacherMaribel B GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Nutritional EpidemiologyDocument9 paginiIntroduction to Nutritional EpidemiologyM IKHSAN AMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meat MarinadesDocument45 paginiMeat MarinadesYana Dela CuestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FBS Las W3Document6 paginiFBS Las W3Herman Glen Marc SegoviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eating Habits Questionnaire Coach Version PDFDocument8 paginiEating Habits Questionnaire Coach Version PDFNoemiKissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Month QuizDocument127 paginiNutrition Month QuizFil Libres Ilagan0% (1)
- CSEC Food and Nutrition June 2006 P2Document5 paginiCSEC Food and Nutrition June 2006 P2rampee charlesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Proper For Week 1 - ELEC3Document2 paginiLesson Proper For Week 1 - ELEC3Jaypee Sembillo100% (1)
- Lesson Tools and UtensilsDocument29 paginiLesson Tools and UtensilsPrincess Joy MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Food PreservationDocument42 paginiMethods of Food PreservationSimone Jean MarieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Portfolio - Year 8 Food Technology Term 1Document9 paginiDesign Portfolio - Year 8 Food Technology Term 1api-486808651Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3Document1 paginăActivity 3Sheina Villaroza100% (1)
- Raising AgentsDocument8 paginiRaising AgentsDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Measuring Ingredients AccuratelyDocument48 paginiMeasuring Ingredients AccuratelyLyndie Lim100% (1)
- Week 3-2 SoupsDocument57 paginiWeek 3-2 SoupsKim CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food PreservationDocument16 paginiFood Preservationdayallen100% (5)
- Learning Module: Technology and Livelihood Education 9Document11 paginiLearning Module: Technology and Livelihood Education 9Kc Villavicencio100% (1)
- Baking Quality of Wheat FlourDocument77 paginiBaking Quality of Wheat FlourLe Ha Hoang YenÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 1 TleDocument19 paginiLESSON 1 TleEbiz MarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL - April 24-28, 2023Document10 paginiDLL - April 24-28, 2023Elma Manguiat HonradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSSC G PhysicsDocument78 paginiHSSC G Physicshasnain ghazalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pakistan Studies: Secondary School Certificate Examination SyllabusDocument53 paginiPakistan Studies: Secondary School Certificate Examination SyllabusKhadija KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATLAB DSP Programs: Raja Rajasakeran Venkat Peddigari Pete BernardinDocument11 paginiMATLAB DSP Programs: Raja Rajasakeran Venkat Peddigari Pete Bernardinprajoth_07Încă nu există evaluări
- Wordpress AssignmentDocument3 paginiWordpress AssignmentChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Xi:Chapter 01 Measurements Punjab Text Book Board LahoreDocument42 paginiPhysics Xi:Chapter 01 Measurements Punjab Text Book Board LahoreChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC Presentation 1Document32 paginiPLC Presentation 1ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stephan Hawking BooksDocument1 paginăStephan Hawking BooksChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of HEC Journals (Social Science)Document18 paginiList of HEC Journals (Social Science)chinidonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear System AnalysisDocument73 paginiLinear System Analysissahar100% (1)
- Linear System AnalysisDocument73 paginiLinear System Analysissahar100% (1)
- RFC 2026 - The Internet Standards Process - Revision 3Document37 paginiRFC 2026 - The Internet Standards Process - Revision 3ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qatar JobsDocument1 paginăQatar JobsChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatima Jinnah Women University The Mall Rawalpindi: Pre-Qualification NoticeDocument2 paginiFatima Jinnah Women University The Mall Rawalpindi: Pre-Qualification NoticeChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPSC Computer MCQDocument66 paginiPPSC Computer MCQChauhan67% (24)
- Qatar JobsDocument1 paginăQatar JobsChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qatar JobsDocument1 paginăQatar JobsChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISSB TestDocument1 paginăISSB TestChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-Level Computing - AQA - Pr... Books For An Open World1Document144 paginiA-Level Computing - AQA - Pr... Books For An Open World1ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TL-WN727N V4 User Guide 1910010945Document46 paginiTL-WN727N V4 User Guide 1910010945ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle20111112 DLDocument80 paginiOracle20111112 DLJor SungÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDDBDocument6 paginiPDDBChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSBWHS401 - Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative RequirementsDocument11 paginiBSBWHS401 - Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative RequirementsPattaniya KosayothinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM104-FNCP ColladoDocument3 paginiNCM104-FNCP ColladoProplays ytÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care Plan Handbook TemplateDocument34 paginiCare Plan Handbook TemplateBreanna Hopkins100% (1)
- MGMT 2 Week 15Document3 paginiMGMT 2 Week 15DarkxeiDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirsch SprungDocument4 paginiHirsch SprungRy AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Neurocognitive DisorderDocument4 paginiA Neurocognitive Disordersitty upamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepal Development Update Post Pandemic Nepal Charting A Resilient Recovery and Future Growth Directions PDFDocument62 paginiNepal Development Update Post Pandemic Nepal Charting A Resilient Recovery and Future Growth Directions PDFSanjeev PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prescription: Sudha Assistant Professor Gnit College of Pharmacy Greater NoidaDocument28 paginiPrescription: Sudha Assistant Professor Gnit College of Pharmacy Greater NoidaNilanjan MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- LRT (Light Rapid Transit) Pulo Gadung Accident Report 1. Description 1.1 Chronology of AccidentDocument4 paginiLRT (Light Rapid Transit) Pulo Gadung Accident Report 1. Description 1.1 Chronology of AccidentYogi GuntaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionDocument10 paginiMindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy For DepressionCMValmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specifications For Civic Education in Primary School PDFDocument44 paginiSpecifications For Civic Education in Primary School PDFNordiana Abd RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Mental Status Exam GuideDocument17 paginiHistory and Mental Status Exam Guideyeney armenterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- K-37 Septic Tank Treatment SDSDocument7 paginiK-37 Septic Tank Treatment SDSRicardo AlvaradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Talk On ContraceptionDocument32 paginiHealth Talk On Contraceptionvaishali TMU studentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physio Assess Form Oct 2022Document5 paginiPhysio Assess Form Oct 2022RishaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Click To Download June2020 Edition PDFDocument30 paginiClick To Download June2020 Edition PDFJomon JohnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balantidium ColiDocument7 paginiBalantidium ColiOmar GhoneimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bryana Russell Cover LetterDocument1 paginăBryana Russell Cover Letterapi-303090959Încă nu există evaluări
- Progestin Only ContraceptionDocument4 paginiProgestin Only ContraceptionTareq SawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CureDocument338 paginiCureThiago Cavalli Azambuja100% (1)
- Personal Development: Understanding Yourself and Building RelationshipsDocument6 paginiPersonal Development: Understanding Yourself and Building RelationshipsYelhsa Ramos100% (2)
- ARIMIDEX Patient Education Brochure - No Cropmarks - v2Document4 paginiARIMIDEX Patient Education Brochure - No Cropmarks - v2maryannemacaraigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Betty Neuman's Contributions to Nursing TheoryDocument2 paginiBetty Neuman's Contributions to Nursing TheoryBrecelle DelvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support AsystoleDocument14 paginiAdvanced Cardiac Life Support AsystoleKar TwentyfiveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lupus and Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument4 paginiLupus and Pregnancy ComplicationsDivika ShilvanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- REPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Document126 paginiREPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Yogacharya Dr Ananda Balayogi BhavananiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TFNVirginia HendersonDocument13 paginiTFNVirginia HendersonJheslyn BalagulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gun Control PowerpointDocument11 paginiGun Control Powerpointapi-319208107Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Malaria Microscopy - Part 1 Learner's Guide, 2nd Edition, WHO, 2010Document87 paginiBasic Malaria Microscopy - Part 1 Learner's Guide, 2nd Edition, WHO, 2010Joey MarcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual On Minimum Standards of Care in Addiction Treatment CentresDocument61 paginiManual On Minimum Standards of Care in Addiction Treatment CentresGlobal Law FirmÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Summary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesDe la EverandSummary: Atomic Habits by James Clear: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad OnesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1632)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (327)
- The One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsDe la EverandThe One Thing: The Surprisingly Simple Truth Behind Extraordinary ResultsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (708)
- Can't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsDe la EverandCan't Hurt Me by David Goggins - Book Summary: Master Your Mind and Defy the OddsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (382)
- Summary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessDe la EverandSummary of The Anxious Generation by Jonathan Haidt: How the Great Rewiring of Childhood Is Causing an Epidemic of Mental IllnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodDe la EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- The Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessDe la EverandThe Compound Effect by Darren Hardy - Book Summary: Jumpstart Your Income, Your Life, Your SuccessEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (456)
- Summary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosDe la EverandSummary of 12 Rules for Life: An Antidote to ChaosEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (294)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyDe la EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- Make It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningDe la EverandMake It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (55)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellDe la EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryDe la EverandHow To Win Friends and Influence People by Dale Carnegie - Book SummaryEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (555)
- Metabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeDe la EverandMetabolism Revolution: Lose 14 Pounds in 14 Days and Keep It Off for LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomDe la EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingDe la EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (59)
- The War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesDe la EverandThe War of Art by Steven Pressfield - Book Summary: Break Through The Blocks And Win Your Inner Creative BattlesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (273)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleDe la EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Essentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessDe la EverandEssentialism by Greg McKeown - Book Summary: The Disciplined Pursuit of LessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (187)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsDe la EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (49)
- Summary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsDe la EverandSummary of The Galveston Diet by Mary Claire Haver MD: The Doctor-Developed, Patient-Proven Plan to Burn Fat and Tame Your Hormonal SymptomsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthDe la EverandThe Fast800 Diet: Discover the Ideal Fasting Formula to Shed Pounds, Fight Disease, and Boost Your Overall HealthEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (37)
- Happy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainDe la EverandHappy Gut: The Cleansing Program to Help You Lose Weight, Gain Energy, and Eliminate PainEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (6)
- Summary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietDe la EverandSummary of Mary Claire Haver's The Galveston DietEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Eat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouDe la EverandEat to Lose, Eat to Win: Your Grab-n-Go Action Plan for a Slimmer, Healthier YouÎncă nu există evaluări