Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nutrition 6
Încărcat de
Faith Dianasas Requina0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
5 vizualizări2 pagininutrition notes for NLE
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentnutrition notes for NLE
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
5 vizualizări2 paginiNutrition 6
Încărcat de
Faith Dianasas Requinanutrition notes for NLE
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Initially periumbilical pain • Warm sitz baths to ease pain and swelling
• Later localizes to McBurney’s point • Stool softeners, high fiber diet
• Mild fever, elevated WBC count • Avoid straining
• Abdominal rigidity • Surgery: ligation, sclerotherapy or surgical
• Rebound tenderness excision
ANALYSIS TOPICAL MEDICATIONS
• Risk of perforation > peritonitis • Anti-inflammatory: hydrocortisone cream
IMPLEMENTATION • Astringents: witch hazel cream
• Maintain bed rest POSTOPERATIVE
• Keep client NPO if surgery is likely • Watch for rectal bleeding
• Semi-Fowler’s position decreases pain • Good anal hygiene – keep dry
• Monitor for signs of perforation and INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
systemic infection CROHN’S DISEASE
POSTOPERATIVE: (regional enteritis)
• Monitor vital signs • Cramping abdominal pain
• Monitor fluid intake and output • Fever, anorexia, weight loss
• Monitor bowel sounds PATHOLOGY
• Monitor dressing for drainage or signs of • Transmural thickening
infection • Granulomas
DIVERTICULITIS • Usually involves ileum
Diverticula = bulging pouches of mucosa • Rectum often spared
through sorrounding muscle • Affects several bowel segments
Diverticulosis: presence of diverticula COMPLICATIONS
Diverticulitis: inflammation of diverticula • Perianal disease
ASSESSMENT • Fistulas
• Pain in lower left quadrant • Perforation
• May be relieved by bowel movement OUTCOME
• Bowel irregularities • Many patients will have disease
• Rectal bleeding recurrence a few years after surgery
• Mild fever ULCERATIVE COLITIS
• Elevated WBC • Less abdominal pain
• Diagnosis: Barium enema, Sigmoidoscopy, • More bloody diarrhea
colonoscopy PATHOLOGY
IMPLEMENTATION • Mucosal ulceration
• NPO if peritonitis or massive bleeding • Begins at rectum and progresses
• Liquid or soft diet during acute phase • Towards ileocecal junction
• High fiber and bulk-forming diet after pain • Limited to colon (but involve terminal
subsides ileum)
• Stool softeners COMPLICATIONS
• Temporary colostomy necessary: • Increased risk for colon carcinoma
perforation, peritonitis or obstruction OUTCOME
POSTOPERATIVE • Surgery is curative
• Monitor vital signs Note: The cause of Crohn’s disease and
• Monitor fluid intake and output ulcerative colitis are unknown. These
• Watch for bleeding: hemoratic and patients often have additional chronic
hemoglobin inflammations such as sacroiliitis, iritis or
• Watch for signs of infection: pus or foul conjunctivitis.
odor ASSESMENT
HEMORRHOIDS • Abdominal pain and cramping
Varicosities of anal and rectal veins • Malaise, weakness
Predisposing factors: • Anxiety
• Hereditary • Chronic diarrhea with blood, pus or mucus
• Chronic constipation • Fever , elevated WBC count
• Pregnancy • Weight loss
• Liver cirrhosis • Diagnoosis: Baruim enema, endoscopy
ASSESSMENT with biopsy
• Rectal pain and itching ANALYSIS
• Bleeding (bright red blood on stool) • Adequate nutritional intake?
IMPLEMENTATION • Fluid and electrolyte balance?
IMPLEMENTATION
• Watch for dehydration
• Monitor stool frequency and consistency
• Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit
• Watch for signs of gastrointestinal
obstruction
• Provide psychological support and
counseling
DIET:
• Acute phase: bowel rest > NPO > low-
residue diet
• Low-fat diet for steatorrhea
• Avoid milk (lactose deficiency of chronic
diarrhea)
MEDICATIONS:
• Sulfasalazine, Steroids, Analgesics
SURGERY
• Indicated it perforation, obstruction or
cancer develops
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTON
MECHANICAL OBSTRUCTION:
• Due to adhesions, tumors, vovulus
(twisting)
• Increased bowel sounds
PARALYTIC ILEUS:
• Due to toxins, infections or postoperative
• Absent bowel sounds
ASSESMENT
• Nausea
• Colicky pain
• Constipation
• Vomiting (fecal vomiting in severe lower
bowel obstruction)
• Diagnosis: abdominal film: intestinal gas,
endoscopy
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wash 4Document6 paginiWash 4Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Document1 paginăInventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wash 4Document6 paginiWash 4Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument8 paginiHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Document1 paginăInventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 paginiHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wash 2Document6 paginiWash 2Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wash 4Document6 paginiWash 4Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wash 3Document6 paginiWash 3Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 paginiHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terms: InfectionDocument7 paginiTerms: InfectionFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Document1 paginăInventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wash 1Document6 paginiWash 1Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and Handwashing: InfectionDocument7 paginiHand Hygiene and Handwashing: InfectionFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument8 paginiHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument8 paginiHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMIapril 2021Document2 paginiBMIapril 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document1 pagină1Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
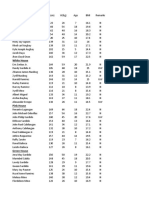
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index (Bmi) : Name H (CM) W (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (Bmi) : Name H (CM) W (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventorymeds 2021Document1 paginăInventorymeds 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Document1 paginăInventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicines 2021Document1 paginăMedicines 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMIapril 2021Document2 paginiBMIapril 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Document1 paginăInventory of Medicines: July 9, 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMIapril 2021Document2 paginiBMIapril 2021Faith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseDocument2 paginiBody Mass Index (BMI) : Name HT (CM) WT (KG) Age BMI Remarks Orange HouseFaith Dianasas RequinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- ImdrfDocument30 paginiImdrfborrellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Placenta PreviaDocument9 paginiJurnal Placenta Previasheva25Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Topic: Nursing Records and Reports Subject: Nursing Managemnt Date of Submission: 27Document21 paginiAssignment Topic: Nursing Records and Reports Subject: Nursing Managemnt Date of Submission: 27Priyanjali Saini100% (3)
- Teen DepressionDocument8 paginiTeen Depressionsirthana697547Încă nu există evaluări
- Revision OssiculoplastyDocument14 paginiRevision Ossiculoplastyapi-19500641Încă nu există evaluări
- History Taking PDFDocument1 paginăHistory Taking PDFSanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Exposure ChecklistDocument1 paginăHospital Exposure Checklistapi-3739910Încă nu există evaluări
- 4.05 Virtual Blood Typing / Transfusion Lab Simulation LabDocument3 pagini4.05 Virtual Blood Typing / Transfusion Lab Simulation LabMichael TownsendÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA, OA, Gout: A Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis and GoutDocument51 paginiRA, OA, Gout: A Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis and GoutКеиÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemorrhoids - Causes, Treatments, and PreventionDocument5 paginiHemorrhoids - Causes, Treatments, and PreventionSAIFUL ISLAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Grouping by MechanismDocument11 paginiAntibiotic Grouping by MechanismalterÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Immunotherapy?Document19 paginiWhat Is Immunotherapy?Najia ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shock Management, by Ayman RawehDocument15 paginiShock Management, by Ayman RawehaymxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sympathetic OphthalmiaDocument4 paginiSympathetic Ophthalmiatiara_kusumaningtyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traditional Filipino healing practices and beliefsDocument70 paginiTraditional Filipino healing practices and beliefsJennifer BolongÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBI Medical PolicyDocument80 paginiSBI Medical PolicyRajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume-New GradDocument1 paginăResume-New Gradapi-269394926Încă nu există evaluări
- Menieres DiseaseDocument43 paginiMenieres DiseaseChlodette Eizl M. Laurente100% (4)
- Satelec Tip Book 2011Document9 paginiSatelec Tip Book 2011akash_81087Încă nu există evaluări
- Kheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Document5 paginiKheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Anonymous wnCXWd3Încă nu există evaluări
- Sanford Resume 3 21 18Document2 paginiSanford Resume 3 21 18api-329968843Încă nu există evaluări
- Tamsulosin Hydro ChlorideDocument2 paginiTamsulosin Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (3)
- Diagnosis and Examination in OrthopaedicsDocument34 paginiDiagnosis and Examination in OrthopaedicsinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Triage: Code Tags and Triage TerminologyDocument5 paginiMedical Triage: Code Tags and Triage TerminologyAnna Mae SuminguitÎncă nu există evaluări
- JciDocument5 paginiJcialfredsamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDocument2 paginiNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFNoel Cabamongan88% (8)
- Customer Satisfaction - Literature Review - FinalDocument28 paginiCustomer Satisfaction - Literature Review - FinalSaumya SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DreamsDocument52 paginiDreamsNill SalunkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graded Exercise Testing (GXT) NewDocument8 paginiGraded Exercise Testing (GXT) Newf3rd110Încă nu există evaluări