Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Notes Gender Justice
Încărcat de
Sittie Aina Munder0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
102 vizualizări2 paginiXU Law
Titlu original
notes Gender Justice
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentXU Law
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
102 vizualizări2 paginiNotes Gender Justice
Încărcat de
Sittie Aina MunderXU Law
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Gender justice gender discrimination
undewual or unfair treatment based solely on sex
Basic assumptions
“this is not the war of the sexes” pre colonial period
“this is not anti-male” each brgy had their own leader women and men
“both women and men are victims relationship of men and women was more egalitarian
but women are more disadvantaged owndership of resources was communal and not private
both have a stake in the struggle for gender equality daily sustenance and admin were joint responsibility
women struggles Spanish colonization
chastity belt Women were categorized with children and the imbecile
bride burning Women not cpable of independent and rational thinking
honor killing Two roles – mother and non
Not allowed to study except as nuns or mothers
sex Law gave power to men to become “kings” in their families
referes to the biological charac wc defines humans as Wife and children under the authority of father
either male or female Women could not engage in any economic, political or
cultural activites except with concept of husband
determinants of sex Properties controlled by husband
male, female Unfaithful wife – adultery
vag clit, penis Unfaithful husband – the extra marital affair should be
uterus, testes scandalous
xx, xt
estrogen progesterone, androgen, testosterone American colonization
Women had right to vote
gender Education was opened for all
economic, social and cultural attributes and opportnunies Divorce has two grounds – concubinage and adultery
associated with being male or female in a particular point Revised penal code
and time and the societal structure that supports them
sex gender Japanese period
what makes one male or female = what makes one mascule Comfort women
or feminine
biologically determined = social determined, culturall Republic
defined NCC – legal separation and annulment, rights and
constant across time = changed across time obligations of spouses, property relations
constant across diff societies and cultures = changes across National commission of the role of Filipino women
places and cultures (NCFRW)
biological = socially constructed
born with = not born with 1986- present
declaration of principles and policies
culture etc
set of peoples values, beliefs, behavior, language, and gender and det law
artifacts party list law
distinguishes a group of people from another group of anti sexual harassment law
people anti-rape law
it is transmitted from generation to generation
women in nation building law
anti mail order vride law
culture tells us repatriation law
what we ought to be non discrimination in labor code
what we ought to think
ought to be CEDAW
ought to expect of others Dec 18 1979
Came into force sept 1981
“don’t tell me how to dress, tell them not to rape” 185 countries
gender relations are power relations manifestations of gender bias
gender socialization is shaped by family school religion gender stereotyping
mass media state multiple burden
differential valuation of men and women
marginalization there is a man who is tired of appearing strong when he
subordination feels vulnerable
diminished sense of personhood
violence against women for every women who is tired of acting dumb, there is a
man who is burdened with the constant expectation of
salient features of RA 9262 anti violence against knowing everything
women and their children
march 8 2004 for every women who is tired of being called emotional
GMA female, there is a man who is denied the full right to weep
March 12 2004 and be gentle
March 27 2004
for every women who feels tired down by her children,
II. VAWC as a public crime there is a man who is denied the full pleasure of equal
Physical parenting
Psychological
Sexual gender sensitivity
Economic a perspective
Violence a way of thinking, manner of viewing things
conscious of the gender issue that the other half enjoys
life to the fullest because of gender bias
Victims:
Women and children
Perpetrators
Men, women
Jurisdiction
Any RTC where the crime was committed
9262, prosecution of VAWC acts a public crime or a
protection order
-provides immediate protection to a victim/survivor of
violence
-may be a separate relief of an indicental
brgy: BPO – prohibit respondent from threatening or
committing physical harm
court: TPO, PPO – removal or exclusion of the respondent
from respondent, custody, support, prohibit use of firearm
women vs men
civil case: legal separation art 36
crim case: anti VAWC
application for a protection order
battered women syndrome
an exempting circumstance
no civil/criminal
not a ground to deny custody
other features:
legally mandated paid leave 10 days
prohibition against conciliation/mediation
mandatory obligation of LGU/govt agencies
confidentiality provision
immunity from suit
“for every woman”
for every women who is tired of acting weak when she
knows she is strong
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1 GAD Lecture 2k19 NoPassDocument46 pagini1 GAD Lecture 2k19 NoPassDraven Ignacio100% (1)
- Col Ella 2012Document130 paginiCol Ella 2012Gina Carmen FășieÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 8 Gender and PoliticsDocument19 paginiCH 8 Gender and PoliticsLouise San BuenaventuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Gender and Sexuality As A Social RealityDocument45 paginiLesson 1 Gender and Sexuality As A Social RealityJean Grace GumasingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Gned-10Document44 pagini1 Gned-10rfvpausÎncă nu există evaluări
- FeminismDocument24 paginiFeminismreyeselis0823Încă nu există evaluări
- 09 Chapter 1Document18 pagini09 Chapter 1Avneet GhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mga Isyu at Hamong Pangkasarian - FINALDocument65 paginiMga Isyu at Hamong Pangkasarian - FINALHa Zy AC98% (48)
- Gender and Society NotesDocument4 paginiGender and Society NotesAndriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- m3 Lecture 3 Sociopolitical IssuesDocument20 paginim3 Lecture 3 Sociopolitical Issuesapi-676932201Încă nu există evaluări
- Gender&Seuxality Across TimeDocument23 paginiGender&Seuxality Across Timedarren chenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 3rd QuarterDocument12 paginiGrade 10 3rd Quarterzheafrances8177Încă nu există evaluări
- Patriarchy Article PublishedDocument3 paginiPatriarchy Article PublishedShweta SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feminist Theology NotesDocument10 paginiFeminist Theology NotesTaz KuroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender Discrimination by AltheaDocument3 paginiGender Discrimination by AltheaelyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Feminist Sexual Politics (Hooks)Document5 paginiA Feminist Sexual Politics (Hooks)Đejmi HadrovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patriarchy - V. GeethaDocument57 paginiPatriarchy - V. GeethaGautam Bharti100% (2)
- Women' S Right: Naryastu Pujyante Ramante Tatra Devta Means Where Women AreDocument7 paginiWomen' S Right: Naryastu Pujyante Ramante Tatra Devta Means Where Women AreSHIVANI PANDEYÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Honour and Practical KinshipDocument6 paginiNational Honour and Practical KinshipMaddila SatishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 GenSoc-2Document29 paginiWeek 1 GenSoc-2Vonreev OntoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Lovendino Samantha Nicole A.Document6 paginiInterview Lovendino Samantha Nicole A.Ramirez Mark IreneaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G and S Across Time Group 2Document29 paginiG and S Across Time Group 2ampoloquiozachary4Încă nu există evaluări
- Gender and The Law: Husband"Document2 paginiGender and The Law: Husband"meriiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender Equality in The Workplace: Ronalyn Bergado Lucena-Barawid Attorney III SDO-QuirinoDocument71 paginiGender Equality in The Workplace: Ronalyn Bergado Lucena-Barawid Attorney III SDO-QuirinoAtty RonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document15 paginiChapter 3echo fateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes 4 PDFDocument11 paginiLecture Notes 4 PDFRachelle SalcedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Gender: Session 1Document43 paginiIntroduction To Gender: Session 1Nicholas NkrumahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patriarchy and Everyday Life - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Document23 paginiPatriarchy and Everyday Life - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Ivy ApolinarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- INFO - Honour KillingDocument3 paginiINFO - Honour KillingRachita WaghadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masculinity and Femininity:: Understanding The Role of Culture in Gender ConstructionDocument33 paginiMasculinity and Femininity:: Understanding The Role of Culture in Gender ConstructionJanica Crizel MagdalenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quotations About Sex DifferencesDocument61 paginiQuotations About Sex DifferencesOlivera VukovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 To 4Document8 paginiLesson 1 To 4Alaiza Maas LanonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender Roles in Colonial SocietyDocument2 paginiGender Roles in Colonial SocietyMicah Joy DiominoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - Chapter 1Document27 pagini02 - Chapter 1Vrindha VijayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fa2 - Diomino, Micah Joy - Sec 48Document2 paginiFa2 - Diomino, Micah Joy - Sec 48Micah Joy DiominoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GensocDocument3 paginiGensocf7pxnshq9jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part I. Lesson 2Document22 paginiPart I. Lesson 2Gawa GawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 1 GE11 (Lesson2)Document1 paginăActivity 1 GE11 (Lesson2)Sinco, Ma. VictoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender Sensitivity Orientation in Relation To GADDocument48 paginiGender Sensitivity Orientation in Relation To GADEver Grace T. Castro100% (1)
- Writtenreportsgenderissues 2Document12 paginiWrittenreportsgenderissues 2Mark Jayson JuevesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Psychology of HomosexualityDocument6 paginiThe Psychology of HomosexualityVane KodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture+1+Sex Gender and Sexuality MergedDocument53 paginiLecture+1+Sex Gender and Sexuality MergedHesed PeñeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: "To Call Woman The Weaker Sex Is A Libel It Is Man S Injustice ToDocument27 paginiChapter-1: "To Call Woman The Weaker Sex Is A Libel It Is Man S Injustice ToJayaraman AdvocateÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFLM-1 Chapter 5Document17 paginiCFLM-1 Chapter 5Rico T. MusongÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Photo CC By-Sa: by Unknown Author Is Licensed UnderDocument52 paginiThis Photo CC By-Sa: by Unknown Author Is Licensed UnderDrRohit GondwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding PatriarchyDocument4 paginiUnderstanding PatriarchyKiezin TengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gensoc ReviewerDocument5 paginiGensoc ReviewerSarah Amie Kaye De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monday Night Articles For Tuesday Discussion - Gender Roles-3Document9 paginiMonday Night Articles For Tuesday Discussion - Gender Roles-3mkorlbeastÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mantsios - Class in AmericaDocument13 paginiMantsios - Class in AmericaDavid HolzmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naryastu Pujyante Ramante Tatra Devta Means Where Women AreDocument7 paginiNaryastu Pujyante Ramante Tatra Devta Means Where Women AreSHIVANI PANDEYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender, Sexuality and MediaDocument33 paginiGender, Sexuality and MediaGustavo Fernandez DalenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.4. Grade 10 - 11 Term 1 - 3 Closing The Gap FinalDocument17 pagini1.4. Grade 10 - 11 Term 1 - 3 Closing The Gap Finaldenise19950406Încă nu există evaluări
- Male Sexual Jealousy: Martin Daly and Margo WilsonDocument17 paginiMale Sexual Jealousy: Martin Daly and Margo WilsonIoni SerbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender and SexualityDocument22 paginiGender and SexualityRaphael DeluteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gensoc: Lecture / First SemesterDocument1 paginăGensoc: Lecture / First SemesterAlenna BenitezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Construction of SexualityDocument6 paginiSocial Construction of Sexualityapi-340926637Încă nu există evaluări
- Gender and SocietyDocument31 paginiGender and SocietyMica EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEE12 (Gendersexualityreviewr)Document6 paginiGEE12 (Gendersexualityreviewr)Bench FuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- REVIEWER SSP (Midterm)Document7 paginiREVIEWER SSP (Midterm)cynthia karylle natividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- SURVIVORS AND THRIVERS: MALE HOMOSEXUAL LIVES IN POSTWAR AUSTRALIADe la EverandSURVIVORS AND THRIVERS: MALE HOMOSEXUAL LIVES IN POSTWAR AUSTRALIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salmon and Black Creative BrochureDocument2 paginiSalmon and Black Creative BrochureSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print 2Document4 paginiPrint 2Sittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class ScheduleDocument1 paginăClass ScheduleSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOLE Department Order 149 Series 2016 and 149-A Series 2017Document3 paginiDOLE Department Order 149 Series 2016 and 149-A Series 2017Sittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omaira Nasra Munder 11-Fr Mayer BibliographyDocument1 paginăOmaira Nasra Munder 11-Fr Mayer BibliographySittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1. Definition of Health Care SystemDocument12 pagini2.1. Definition of Health Care SystemSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- State Salary Compensations/Benefits Job RequirementsDocument1 paginăState Salary Compensations/Benefits Job RequirementsSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethics, Privacy, and SecurityDocument10 paginiEthics, Privacy, and SecuritySittie Aina Munder100% (1)
- Introducing The Issues: Zambas, Cardona, Feliciano, Dagcuta, ManabilangDocument43 paginiIntroducing The Issues: Zambas, Cardona, Feliciano, Dagcuta, ManabilangSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 15Document11 paginiLesson 15Sittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-NSTP-1 Module Prelim To MidtermDocument44 paginiG-NSTP-1 Module Prelim To MidtermSittie Aina Munder67% (3)
- Biorisk 1Document49 paginiBiorisk 1Sittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 8 HisDocument14 paginiLesson 8 HisSittie Aina Munder100% (1)
- Lesson 7 HisDocument16 paginiLesson 7 HisSittie Aina Munder100% (1)
- Legres NEws ReportDocument3 paginiLegres NEws ReportSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Study Law and Take Law Exams in A NutshellDocument15 paginiHow To Study Law and Take Law Exams in A NutshellJill Bacani100% (3)
- Who Attends OYW PDFDocument1 paginăWho Attends OYW PDFSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biosafety and BiosecurityDocument98 paginiBiosafety and BiosecuritySittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH IHL Case StudyDocument4 paginiPH IHL Case StudySittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
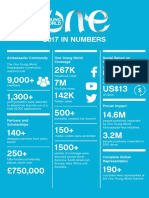
- OYW in NumbersDocument1 paginăOYW in NumbersSittie Aina MunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacant CollegeDocument89 paginiVacant CollegeAviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intersectionality, Explained - Meet Kimberlé Crenshaw, Who Coined The Term - VoxDocument8 paginiIntersectionality, Explained - Meet Kimberlé Crenshaw, Who Coined The Term - VoxRenata Andrade100% (1)
- Equal Play Equal Pay Moral Grounds For Equal Pay in Football PDFDocument22 paginiEqual Play Equal Pay Moral Grounds For Equal Pay in Football PDFMalcolmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ain - T I A Feminist African American Men Speak Out On Fatherhood, Friendship, Forgiveness, and Freedom PDFDocument288 paginiAin - T I A Feminist African American Men Speak Out On Fatherhood, Friendship, Forgiveness, and Freedom PDFValeria LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Ethics - EssaysDocument11 paginiBusiness Ethics - EssaysKemal RovčaninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bisexual Drag Queen ExtravaganzaDocument11 paginiBisexual Drag Queen ExtravaganzaDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reconsidering The Work of Claire JohnstonDocument30 paginiReconsidering The Work of Claire JohnstonMariela CantúÎncă nu există evaluări
- New SAT 4 Practice Tests: Ivy GlobalDocument24 paginiNew SAT 4 Practice Tests: Ivy GlobalSmart Learn for MBA & PhDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women and Children's WelfareDocument16 paginiWomen and Children's WelfareOppo A830% (1)
- ELC 411 - Language and GenderDocument12 paginiELC 411 - Language and GenderIan Paul Hurboda DaugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexism in Professional SportsDocument9 paginiSexism in Professional SportsWaqas AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speak Topnotch 2 Section 2Document8 paginiSpeak Topnotch 2 Section 2TânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sex Education and SexismDocument2 paginiSex Education and SexismManuel CedeñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SK Murnen and R Seabrook - Feminist Perspectives On Body Image and Physical AppearanceDocument8 paginiSK Murnen and R Seabrook - Feminist Perspectives On Body Image and Physical AppearanceLorena AnderaosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criticism - Lord of The Flies - Roy - Boys Club - No Girls AllowedDocument2 paginiCriticism - Lord of The Flies - Roy - Boys Club - No Girls AllowedShirshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- استراليا فيتزجيرالدDocument14 paginiاستراليا فيتزجيرالدAlaa RashedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrative Circular NO. 82-2006, September 19, 2006Document3 paginiAdministrative Circular NO. 82-2006, September 19, 2006JemaicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VictimologyDocument19 paginiVictimologyRuruni Kenchin Batusai100% (1)
- Persuasive EssayDocument4 paginiPersuasive Essayapi-338650494100% (7)
- Paragraph On Gender Discrimination, Load SheddingDocument3 paginiParagraph On Gender Discrimination, Load SheddingAtique Bin Zohur Boby100% (1)
- Role of Women in Development SectorDocument9 paginiRole of Women in Development SectorAnshul VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- When Rights Are Wronged: Gender-Based Violence & Human Rights in AfricaDocument26 paginiWhen Rights Are Wronged: Gender-Based Violence & Human Rights in AfricaStephannie EstherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade Appeal Psu KinsellaDocument3 paginiGrade Appeal Psu Kinsellamary engÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender Studies CompleteDocument87 paginiGender Studies CompleteAmmar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Gender, Politeness and Stereotypes PDFDocument40 pagini8 - Gender, Politeness and Stereotypes PDFNurul Iman100% (1)
- Chapter II.-wps Office - 1Document22 paginiChapter II.-wps Office - 1Kimberlyn Getalla100% (1)
- How To Stop Violence in SchoolsDocument35 paginiHow To Stop Violence in SchoolsKarelia Larenas RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examination of Anime Content and Associations Between Anime Consumption, Genre Preferences, and Ambivalent SexismDocument20 paginiExamination of Anime Content and Associations Between Anime Consumption, Genre Preferences, and Ambivalent SexismBEATRICE PILAR LUISA CUIZONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brgy. VAW Desk Handbook - Guide PDFDocument117 paginiBrgy. VAW Desk Handbook - Guide PDFArnoldAlarcon100% (2)