Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Psychiatry Mnemonics
Încărcat de
Nur Atiqah Mohd AzliTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Psychiatry Mnemonics
Încărcat de
Nur Atiqah Mohd AzliDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
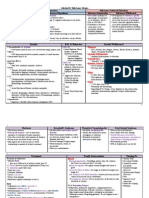
A) Pharmacology
1) Anti-Depressants
a) A/E of Moclobemide = SNATCH
- Sleep Distrubances
- Nausea
- Agitation
- Tyramine ingestion
- Confusion
- HPT due to tyramine ingestion
b) Examples of TCA’s = DICA
- Dotheipin
- Imipramine
- Chlomipramine
- Amitriptyline
c) Side Effect of TCA’s = Anti-HAM
- Anti-Histaminic
- Anti-Adrenergic
- Anti-Muscarinic
d) Examples of SSRI’s = ESFF
- Escritalopram
- Sertraline
- Fluoxetine
- Fluvoxamine
e) Side Effect of SSRI’s = MASH N
- MSK (Rash; Cutaneous Bleeding; Tremor; Sweating)
- Abdominal Symptoms (N&V, Epigastric Pain. diarrhea) (COMMONEST!!!!!)
- Sexual Dysfunction (2ND COMMONEST)
- Hyponatremia
- Neurological (HAID) (3rd COMMONEST)
f) Neurological Side Effect of SSRI’s = HAID
- Headache
- Anxiety + Agitation
- Insomnia
- Discontinuation Symptoms
g) A/E most commonly a/e Fluoxetine = AIR
- Agitation
- Insomnia
- Rash
h) A/E of SNRI’s = HIS ND
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Somnolence
- Nausea
- Dizziness
i) A/E associated with Venlafaxine on top of the Common A/E of SNRI’s = SEA
- Sexual Dysfunction
- Elevation of BP
- Anxiety
j) Discontinuation Symptoms A/w SSRI’s = ABCDEF
- A = Agitation & Anxiety
- B = Balance Problems; Bad Dreams
- C = Concentration Problems
- D = Dizziness; Diarrhea; N&V
- E = Electric Shock-like symptoms
- F = Flu-like symptoms
k) Serotonin Syndrome = SAD MF watching HenTai
3 out of the 10 following
- S = Shivering; Sweating
- A = Ataxia; Agitation
- D = Diarrhea
- M = Myoclonus; Mental State Changes
- F = Fever
- H = Hyper-reflexia
- T = Tremors
2) Mood Stabilizers
a) A/E of Carmabezapine = GAD
- Generalised Erythematous Rash
- Ataxia
- Dizziness, Diplopia, Drowsiness
b) Toxic Features of Carbamazepine = AS
- Agranulocytosis
- Steven-Johnson Syndrome
c) A/E of Sodium Valproate = WATE
- Weight Gain
- Alopecia
- Thrombocytopenia, Tremor
- Epigastric pain
d) Toxic Features of Sodium Valproate = HEP
- Hepatotoxicity
- Encephalopathy
- Pancreatitis
e) Lithium S/E = LITHIUM
- L = Leukocytosis; Loss of Hair
- I = Increased Urination (Blocks ADH receptors >> Diabetes Insipidus)
- T = Tremors (Early = Fine , Late = Gross) ; Tiredness
- H = Hypothyroidism ; Hypokalemia
- I = Increased Thirst
- U = Underactive Memory
- M = Metallic Taste (Dysguesia) ; Mothers (Teratogenicity = Ebstein’s anomaly)
f) Mild toxicity for Lithium >1.5mmol/L = BAT
- B= Blindness
- A = Ataxia
- T = Tinnitus
g) Severe toxicity for Lithium >2.5mmol/L = 3 C’s
- Convulsion
- Circulatory Failure
- Confusion
3) Anti-Psychotics
a) Common A/E of ALL Anti-psychotics = PISA
- P = Prolactin Increase; Prolongation of QT; Pyramidal symptoms extra
- I = Increased Weight
- S = Seizures, Sedation
- A = Anti-cholinergic, Anti-adrenergic
b) AP with the higher risks for Orthostatic Hypotension = CRC
- Chlorpromazine
- Risperidone
- Clozapine
c) CF of Hyperprolactinemia = GLAD
- Gynaecomastia
- Lactation
- Amenorrhea
- Decreased Libido
d) Main differences between NM$, Serotonin $, Anti-cholinergic Toxidrome and
Malignant Hyperthermia = EMBER
- Exposure : Anti-Psychotics ; Serotinergics; Anti-cholinergics; Inhalational
anaesthethics and muscle relaxants
- Muscle : Tensed; Tensed; Normal; Tensed
- Mucosa and Skin : Wet ; Wet; Dry; Wet
- Biochemical CHanges : Leukocytosis & Increased CK; Others normal
- Bowel Sounds : Normal ; Increased; Decreased; Decreased
- Eyes : Normal; Dilated; Dilated; Normal
- Reflexed : Bradykinesia ; Hyper-reflexia; Normal; Hyporeflexia
e) Clinical Features of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) = HEAD Long
- H = Hyperthermia
- E = Extreme Lead Pipe Muscle Ridgidity ; Elevated CPK
- A = Autonomic Instability ; Alteration in Consciousness
- D = Delirium
- L = Leucocytosis
B) Psychiatric Diseases
1) Mania 3 of for >1 week = DIG FAST
D = Distractibility and easy frustration
I = Irresponsibility and erratic uninhibited behavior
G = Grandiosity
F = Flight of ideas
A = Activity increased with weight loss and increased libido
S = Sleep is decreased
T = Talkativeness
2) Hypomania
3 of for >4 days
Less functional impairment compared to mania
3) MDD. 5 of for 2 weeks = de SAGECAPS
Depressed Mood
Sleep disturbance
Anhedonia
Guilt/worthlessness
Energy loss
Concentration low
Appetite increase or decrease
Psychomotor retard/agitation
Suicidality
4) Pathological grief. 5 of 9 for 6 months
Mainly emptiness and loss
Yearning
Disbelief
Bitterness of loss
Confused of own identity
Sense of numbness
Distrust others
Meaningless life
Difficulty accept
Stunned
5) Persistent complex bereavement disorder
Death
1 of 4 for 12 months
Yearning
Intense sorrow
Thoughts of deceased
Thoughts of circumstances of deceased
Reactive distress
Identity disruption
6) Postpartum depression: mdd + 4 weeks post delivery
Assess suicide risk
Wish to be dead
Feeling of hopelessness
Regret/remorse over attempt
Expectation bout outcome of selfharming
Specific plans
Lethality
Assess current suicidal intent
If wanna suicide, assess
Duration
Method
Preparation
7) Panic attack: PANICS Dude
4 of 13
Palpitation
Abdominal distress
Numbness, nausea
Intense fear of death/going crazy
Choking, chills, chest pain
Sweating, shaking, SOB
Depersonalization/derealization
Ask: how long to resolve, duration of attack
8) GAD - BE SKIM
3 of > 6 months
Blank mood, difficult to concentrate
Easy fatigue
Sleep disturbance
Keyed up/restless
Irritability
Muscle tension
9) Stimulant use disorder
2 of 11 within 12 months
WhaT a Craving FOOL
W = Withdrawal
T = Tolerance
C = Craving despite it being physically dangerous
C = Craving to use it especially in places where substance was obtained or used before
C = Continued use of substance despite knowledge of negative effects
C = Continued use despite social and interpersonal problems
F = Failure to quit substances use
O = Obligations to home, work and school impaired
O = Obtaining, using and recovering from substance effects takes a long time
L = Large amounts or longer periods of substance use (Basically Overdosed)
L = Let go of ROS (Recreational, Occupational or Social activities) due to substance use
10) Stimulant intoxication
Psy sx: irritabilty, anger, elated mood, impaired judgement
Tachycard/bradycard
High/low bp
Perspiration
Confusion, altered gcs
Chest pain
Resp depression
Nausea/v
Seizure
11) Withdrawal:
Fatigue
Unpleasant dream
Insomnia/hypersomnia
Increased appetite
Psy retard/agitation
12) Dementia
- self care
- biological fx
- langugage fx
- behavioural
13) PTSD (trigger, re-experience, dissociation, hyperarousal, avoidance)
- Easy way to remember :Exposure , Reexperience, Avoidance, Hyperarousal
1. Exposure to threatening situation
2. 9 of following intrusion,negative mood, dissociation, avoidance, arousal for >1 month
Intrusion
- recurrent intrusive memory
- re-experience/nightmares
- flashback/dissociative rxn
- intense psychological distress/physio rxn
Negative mood
- inability to experience positive emotions
Dissociative symptoms
- sense of unreal
- dissociative amnesia
Avoidance symptoms
Arousal symptoms
- hypervigilance
- easily startled
14) Schneider’s First Rank Symptoms 1959
PP MDS
1) Perception (Thought Echo, 2nd person and 3rd person auditory hallucinations)
2) Posession (Thought insertion, Thought Withdrawal, Thought Broadcasting)
3) Made (Made Affect; Made Volition; Made Impulse)
4) Delusional Perception
5) Somatic Passivity
15) Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia
AAAAAA
A = Alogia
A = Anhedonia
A = Asocial
A = Affective flattening
A = Avolition
A = Attention noob
16) 5 Component of High Expressed Emotion (EE)
ECHO
Excessive Warmth (Treat like useless)
Excessive Positive Remarks (Pampered Baby)
Critism (Treat like useless)
Hostility (Treat like useless)
Over-involvement (Can go both ways)
17) Features of “True Hallucinations”
SONIC
S = Sensory Organ
O = Objective Space
N = No Stimulus
I = Independent of Control
I = Insight
C = Clear & Conscious
18) Aetiology of Delirium
I WATCH DEATH
Infection
Withdrawal (Alcohol; Barbiturates; Hypnotics)
Acute Metabollic (Acidosis ; Alkalosis ; Electrolyte Imbalance; Hepatic Failure; Renal
Failure)
Trauma (Closed Head Injury; Heatstroke; Post-Op; Severe Burns)
CNS Pathology (Abscess; Hemorrhage; Stroke; Tumours; Seizures; Vasculitis)
Hypoxia (@; CNS Pathology; Hypotension; Lung or Heart Failure)
Deficiences (Vitamin B12 deficiency; Niacin Deficiency; Thiamin deficiency; Folate
deficiency)
Endocrinopathies (Hyperparathyroidism; Hypercalcemia; Hyper/Hypocortisolism;
Hyper/Hypoglycemia)
Acute Vascular (HPT Encephalopathy; Arryhtmia; Stroke; Dehydration)
Toxins or Drugs (Ilicit Drugs; Pesticides; Solvents; Medications & Chemo)
Heavy Metals (Lead; Magnanese; Mercury)
19) Clinical Features of Delirium Tremens (DT)
DT'S A HELL
Delirium = which is worse at night
Delusions = Commonly Grandiosity
Tremors
Seizures of Withdrawal ("Rum Fits") = Occurs within 12-48 hours after withdrawal
Autonomic Instability (Common Manifestations are Fever; Tachycardia; HPT; Profuse
Sweating)
Hallucinations (Commonly Tactile or Visual)
ESR Raised
Leucocytosis
LFT Impaired
20) Types of Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders according to DSM-5
ASSOC2IATE
A = Alcohol - Related Disorders
S = Sedative-, Hypnotic-, or Anxiolytic- Related Disorders
S = Stimulant-Related Disorders
O = Opioid- Related Disorder
C = Caffeine-Related Disorder
C = Cannabis-Related Disorder
I = Inhalant-Related Disorders
A = Hallucinogen-Related Disorders (Because A written with bad-handwriting looks like a
“H”)
T = Tobacco-Related Disorders
E = Etc. (Other, Unspecified , Non-substance related disorders)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Psychiatry Note BookDocument37 paginiPsychiatry Note BookMustafa Kamal BangashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric Case History NotesDocument8 paginiPsychiatric Case History NotesTysle100% (1)
- 10 Cognitive DisordersDocument16 pagini10 Cognitive DisordersFarrah MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROS For Psych ChecklistDocument7 paginiROS For Psych ChecklistPAschoolstuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Treatments in PsychiatryDocument56 paginiBiological Treatments in PsychiatryNurul AfzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry NIMHANS Evaluation ProformaDocument11 paginiChild and Adolescent Psychiatry NIMHANS Evaluation Proformasharmamahika89100% (1)
- Psychiatry Rating ScalesDocument4 paginiPsychiatry Rating ScalesFerry GhifariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 7 Psychiatric AssessmentDocument54 paginiSession 7 Psychiatric AssessmentPetroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDDocument85 paginiAssessment and Evaluation: 2008 Edition Rhoda K Hahn, MD Lawrence J. Albers, MDAlbghdadi CristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric Clinical SkillsDocument376 paginiPsychiatric Clinical SkillsSamuel Agunbiade100% (5)
- Study Notes PsychiatryDocument50 paginiStudy Notes PsychiatryMedShare90% (10)
- Common Psychiatric TermsDocument6 paginiCommon Psychiatric TermsKatrina Heart Rauto AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychiatryDocument52 paginiPsychiatryEma100% (13)
- The Neuropsychiatric Mental Status ExaminationDe la EverandThe Neuropsychiatric Mental Status ExaminationÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSM-IV Criteria MnemonicsDocument4 paginiDSM-IV Criteria Mnemonicsleonyap100% (1)
- The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in PsychiatryDe la EverandThe Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in PsychiatryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Psychiatry NotesDocument123 paginiPsychiatry NotesKyoheirwe vanessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry MnemonicsDocument4 paginiPsychiatry MnemonicsHiruni Tharuka100% (2)
- Practical Notebook Adult PsychiatryDocument121 paginiPractical Notebook Adult PsychiatryCarly DyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Mental IllnessDocument6 paginiSummary of Mental IllnessNelsie Duhilag100% (2)
- K P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionDocument36 paginiK P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionArama CristiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (PSYCH) 2.01 The Psychiatric History - Dr. SundiangDocument5 pagini(PSYCH) 2.01 The Psychiatric History - Dr. SundiangKeifer Turtle100% (2)
- A) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsDocument10 paginiA) A/E of Moclobemide SNATCH: A) Pharmacology 1) Anti-DepressantsNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantsDocument9 paginiPsychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantssumithjalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych Exam ReviewDocument18 paginiPsych Exam Reviewdanny_ng08Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry CasesDocument65 paginiPsychiatry CasesakeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychiatryDocument95 paginiPsychiatryJarwoto RoestanajieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case History, MSE and Rating Scales - in Psychological AssessmentDocument29 paginiCase History, MSE and Rating Scales - in Psychological Assessmentsu84Încă nu există evaluări
- Syndrome in PsychiatryDocument12 paginiSyndrome in Psychiatryrahul KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Skull, Meninges and BloodDocument23 paginiAnatomy of The Skull, Meninges and BloodNur Atiqah Mohd Azli100% (1)
- Notes On Psychiatry: TypesDocument17 paginiNotes On Psychiatry: TypesMAY100% (1)
- Antipsychotics HandoutDocument25 paginiAntipsychotics HandoutTeddy Kurniady ThaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPG Management of Osteoarthritis (Second Edition)Document66 paginiCPG Management of Osteoarthritis (Second Edition)Nur Atiqah Mohd Azli100% (1)
- The Child Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric PracticeDe la EverandThe Child Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric PracticeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Psych Ch. 5 NotesDocument7 paginiPsych Ch. 5 NotesHaylle ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geriatric Giants - DR SeymourDocument108 paginiGeriatric Giants - DR SeymourSharon Mallia100% (1)
- Emergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4Document21 paginiEmergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4CetVital100% (1)
- The Relationship Between Percieved Parenting Style and Self-Esteem of Grade 11 Students in Maryhill CollegeDocument51 paginiThe Relationship Between Percieved Parenting Style and Self-Esteem of Grade 11 Students in Maryhill CollegeAereane Keith RubialesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric History GuideDocument8 paginiPsychiatric History GuideBobet ReñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glossary of Psychiatric TermsDocument42 paginiGlossary of Psychiatric TermsÏtz ShãrîÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntipsychoticsDocument22 paginiAntipsychoticsvinodksahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych - OsceDocument6 paginiPsych - OsceRuchira SeneviratneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry History Taking and Physical ExaminationDocument16 paginiPsychiatry History Taking and Physical ExaminationEma100% (17)
- GMT 409 Psychiatry Student Guide BookDocument43 paginiGMT 409 Psychiatry Student Guide BookAhmad Syahmi YZ100% (1)
- Walmart's Performance Management Practices Training-Performance-ManagementDocument3 paginiWalmart's Performance Management Practices Training-Performance-Managementminhaz50% (2)
- Aa - LMR Georgette - Final VersionDocument47 paginiAa - LMR Georgette - Final Versionpickles.squad11Încă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of Thought & Speech (Psychopathology)Document21 paginiDisorders of Thought & Speech (Psychopathology)Upasana Baruah100% (2)
- Psychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workDe la EverandPsychiatry Practice Boosters 2016: Insights from research to enhance your clinical workÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Methods in Psychiatry 2nd EditionDocument92 paginiClinical Methods in Psychiatry 2nd Editionprachirb100% (1)
- DR - Usama.mahmoud Psychiatry - Notes MSDocument64 paginiDR - Usama.mahmoud Psychiatry - Notes MSMariam A. KarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychiatryDocument92 paginiPsychiatrykimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry Osce PackDocument4 paginiPsychiatry Osce PackzipppppppÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Status ExamDocument2 paginiMental Status ExamNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Status ExamDocument2 paginiMental Status ExamNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mood Disorders: Depressive Disorders: Bipolar DisordersDocument4 paginiMood Disorders: Depressive Disorders: Bipolar DisordersWen Jie LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric Case Clerking for Medical StudentsDe la EverandPsychiatric Case Clerking for Medical StudentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric Disorder.Document127 paginiPsychiatric Disorder.Minlik-alew DejenieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usmle Pharmacology Quiz Multiple ChoiceDocument42 paginiUsmle Pharmacology Quiz Multiple ChoiceSamer Khodor83% (6)
- Notes PsychiatryDocument36 paginiNotes Psychiatryvinodksahu0% (1)
- Normal Lab ValuesDocument5 paginiNormal Lab ValuesNadiya Elfira BilqisÎncă nu există evaluări
- UW Notes - 13 - PsychiatryDocument21 paginiUW Notes - 13 - PsychiatryDor BenayounÎncă nu există evaluări
- WJ - I Insights Discovery An Introduction Journal v1 2010 Spreads (Not For Printing) PDFDocument30 paginiWJ - I Insights Discovery An Introduction Journal v1 2010 Spreads (Not For Printing) PDFAna Todorova100% (1)
- Nutrition QuestionnaireDocument4 paginiNutrition QuestionnaireNitya Krishna100% (1)
- Bone Tumours - I & Ii - 2015Document113 paginiBone Tumours - I & Ii - 2015Nur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership in OrganizationsDocument20 paginiLeadership in Organizationscol_gopikrishna100% (1)
- Pharmacology (Psychosis and Mania)Document53 paginiPharmacology (Psychosis and Mania)lavanyakakarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Seeking BehaviorDocument5 paginiHealth Seeking BehaviorDr Nihar Ranjan Ray100% (2)
- Serotonin SyndromeDocument19 paginiSerotonin SyndromeNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument44 paginiPsychiatric Nursing ReviewramemgarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vascular DementiaDocument5 paginiVascular DementiaAna Ramos LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terms in The Field of PsychiatryDocument18 paginiTerms in The Field of PsychiatryOchie YecyecanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry Case Clearking Updated Feb April 2018Document12 paginiPsychiatry Case Clearking Updated Feb April 2018nurulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clerking TemplateDocument4 paginiClerking TemplateNur Atiqah Mohd Azli100% (1)
- Introduction To Cranial NervesDocument14 paginiIntroduction To Cranial NervesNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contents in The Breast MilkDocument2 paginiContents in The Breast MilkNur Atiqah Mohd AzliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAS 104-Human Relations and Group DynamicsDocument46 paginiCAS 104-Human Relations and Group DynamicsERVY BALLERASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Confilct Management Chapter5Document31 paginiConfilct Management Chapter5botchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom Behavior Management PlanDocument4 paginiClassroom Behavior Management Planapi-664023439Încă nu există evaluări
- Italy vs. Norway - FinalDocument12 paginiItaly vs. Norway - FinalLucija MajstrovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTET - & - STETs - Child - Development Himanshi SinghDocument618 paginiCTET - & - STETs - Child - Development Himanshi SinghRavindraSamriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rrl-PsychDocument5 paginiRrl-PsychMavis VermillionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peace Theme 6Document30 paginiPeace Theme 6Rx ChauÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Unit-1Document18 paginiOB Unit-1cat lostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harmony Task RubricDocument1 paginăHarmony Task Rubricapi-299946609100% (1)
- Implementing Project-Based Learning Challenges and SolutionsDocument4 paginiImplementing Project-Based Learning Challenges and SolutionsConsultor Académico BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotional EquanimityDocument22 paginiEmotional EquanimityRoxy Shira AdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rbi ResourcesDocument3 paginiRbi Resourceskarthikkalla01Încă nu există evaluări
- Running Head: DRIVING MISS DAISY 1Document11 paginiRunning Head: DRIVING MISS DAISY 1api-216578352Încă nu există evaluări
- Orthographic Coding in Illiterates and Literates: Jon Andoni Duñabeitia, Karla Orihuela, and Manuel CarreirasDocument7 paginiOrthographic Coding in Illiterates and Literates: Jon Andoni Duñabeitia, Karla Orihuela, and Manuel CarreirasprasanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eaclipt Cpe 2019Document9 paginiEaclipt Cpe 2019inas zahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perceiving Emotions Is About Being Aware of and Sensitive To Others' Emotions. in Other Words, It'sDocument9 paginiPerceiving Emotions Is About Being Aware of and Sensitive To Others' Emotions. in Other Words, It'srasha mostafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management, Leadership, Supervision and AdministrationDocument5 paginiManagement, Leadership, Supervision and AdministrationWasim Rajput Rana100% (3)
- Trauma For Parent Groups 10 - 10 - 19Document44 paginiTrauma For Parent Groups 10 - 10 - 19Htet HtinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Team by Delicia Ann SDocument3 paginiMental Health Team by Delicia Ann SDelicia SohtunÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerdevDocument9 paginiPerdevDryxlyn Myrns OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aristotles 7 Elements of Good StorytellingDocument2 paginiAristotles 7 Elements of Good StorytellingNick100% (1)
- Mental Health in Tamil CinemaDocument6 paginiMental Health in Tamil CinemaNandha KishoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- PART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesDocument11 paginiPART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesLoLiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing The Material SelfDocument20 paginiManaging The Material SelfShamel OrdillanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psy 1303 - Psychological Report Assessment DetailsDocument1 paginăPsy 1303 - Psychological Report Assessment DetailsMorish Roi YacasÎncă nu există evaluări