Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fcs Timeline
Încărcat de
api-322059527Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fcs Timeline
Încărcat de
api-322059527Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Kristyn Koch - FCS 101
May 6, 2013
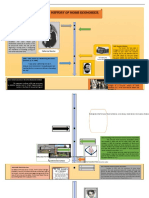
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline Date:
Dame Schools: taught counting, prayers, the Bible, reading and sewing
1635
Schools began to include classes related to domestic concerns Late 1700’s
Catharine Beecher wrote 33 books related to home economics
1827-1874
Catharine Beecher wrote A Treatice on Domestic Economy: first home 1841
economics textbook recognized by a state department of education
Edward Youmans wrote Household Science: the book gave a definition of 1857
household science and was later adapted by home economists
First Morrill Act 1862
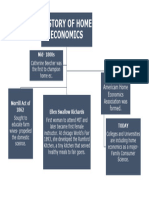
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 1
Domestic Economy Curriculum 1873
MIT grants Ellen Richards BS 1873
Vassar grants a Doctorate
The Chemistry of Cooking &Cleaning 1872
Domestic Science courses 1877
The Great Sanitary Survey 1887
Hatch Act passed: developed the Central Office of the Agricultural
Experimental Stations, of which W. O. Atwater, the father of nutrition, was
the first director
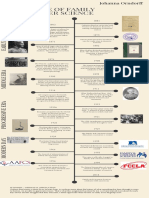
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 2
Lake Placid Conference: eleven attendees adapted the name "home 1887
economics" to this field
The 2nd Morrill Act 1890
Rumford Kitchen 1893
1894 School lunch- women are hired to prepare food for students 1894
Lake Placid Conference 1899
Childcare and Parenting
Education beyond 8th grade 1901
10th Lake Placid Conference: American Home Economics Association
emerged- AHEA chartered on January 1 1909
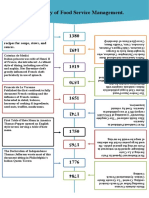
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 3
First Girls Tomato club 1909
Ellen Richards dies 1911
Home demonstration agents 1912
Smith-Lever Act passed: created the Agricultural Extension Services, 1914
including home economics
Commission on vocational education presented report to congress, this
report suggested occupational training in several fields: dietitian, cook,
housemaid, institution manager, and household director
Smith-Hughes Act passed on February 23: established the Federal Board 1917
of Vocational Education, established home economics and provided
financial aid
WWI 1917-1919
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 4
Instruction in schools 1918
Home Economics section added 1920
High school home economics clubs had developed
1925
Childcare recognized
1926
Food Corps hire Home Economist
1931
Accepted expert in nutrition
1941
First Nutrition Congress
1943
Bureau of Human Nutrition & Home Ec.
1960
Integration
Feminists
Specialized programs
Accreditation of undergrad programs 1963
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 5
Capper-Ketcham Act: extended Smith-Lever Act to cover home economics 1927
and agriculture
George-Reed Act: authorized added appropriations for home economics 1929
and agriculture which were to increase annually for five years, made home
economics funding more equitable in comparison with other service areas,
permitted more funding for rural areas than urban areas
George-Ellzey Act: annual appropriations of 3 million dollars to each field 1934
for three year, resulted in increased enrollment in vocational programs
George-Dean Act: authorized appropriations of 4 million dollars to each 1936
field
Committee appointed by AHEA: recommended that home economics 1943
clubs should form a national organization
Future Homemakers of America officially drafted a temporary 1945
constitution on June 11
1946
George-Barden Act: allowed flexible use of funds, the largest share went
to rural areas
Caroline L. Hunt wrote The Life of Ellen H. Richards: biography of the first
1958
president of AHEA, Hunt was a friend of Richards and also was present at
Lake Placid
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 6
National Defense Education Act: resulted in increased understanding of 1958
technical education and its part in a technical society
"New Directions" published 1959
Manpower Development and Training Act: laid the groundwork for 1962
occupational home economics, produced curriculum materials useful for
occupational home economics
Racial tensions
Vocational Education Act of 1963 (Perkins Bill): in society, the household 1963
had become a consumer rather than a producer, resulted in two types of
home economics -- useful employment (consumer) and gainful
employment (occupational), no categorical funding was specifically
earmarked for home economics, and 10% of home economic funds must
be used for related occupational programs
Vocational Amendments of 1968: consumer homemaking earmarked for 1968
funds, occupational programs were still block grants, stressed the dual
role of the wage earner and homemaker, name changed to consumer and
homemaking education, 1/3 of funds was set aside for "economically
depressed" areas
Approved Home Economics Related Occupations (HERO) chapters 1971
nationally
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 7
FHA national advisory board and national executive council voted
to included HERO chapters with FHA chapters
Eeleventh Lake Placid Summit Conference: developed a list of issues that 1973
should take top priority in home economics programs
"New Directions II" published: developed a new statement of purpose, 1975
listed five new priorities in home economics
Gear work towards males 1976
Unified statement of purposes, recommendations, and programs for 1976
vocational home economics: developed by home economics division of
American Vocational Association, American Home Economics Association,
and Home Economics Education Association
Vocational Amendments of 1976: provided vocational funding of over $1 1976
to $1.7 billion dollars until 1982, devised categories for funding, required
state administration, developed national priorities for spending of grant
monies, funded vocational education for displaced homemakers,
attempted to remove stereotypes
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 8
First black national president of FHA/HERO 1981
New national FHA/HERO building constructed in Reston, VA 1983
First male national president of FHA/HERO 1986
Project 2000 1989
Rethinking women’s ….conference 1991
Profession changed its name to Family and Consumer Sciences: 100 1993
invited professionals representing 21 related professional organizations
met in Scottsdale, Arizona, in June and voted to change the name
AHEA changed name to American Association of Family and Consumer 1994
Sciences
School-to-Work Opportunities Act passed
Membership declines 1998
Carl Perkins Act of 1998: new funding program passed in October, not all
of the details have been released yet
Celebrations 2008
First Lake Bonneville Summit 2009
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 9
2nd Lake Bonneville Summit at BYUI 2011
Kristyn returns from her mission and interns at a bridal shop to 2015
further her sewing skills while attending school at BYUI
Kristyn opens her own sewing school and quilt shop 2025
Kristyn will revolutionize sewing with her new sewing techniques 2050
and styles
Family & Consumer Sciences Timeline 10
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Uwi Open Campus (St. Augustine) : Name: Hannah JackDocument11 paginiUwi Open Campus (St. Augustine) : Name: Hannah JackHannah DCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aboriginal Condensed TimlineDocument1 paginăAboriginal Condensed TimlineMaryAnne WilhelmÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSS AndersonDocument13 paginiNSS AndersonsatmayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Home Economics LiteracyDocument19 paginiIntroduction To Home Economics LiteracyClarice Gavilan100% (1)
- Meidner (1992) - Rise and Fall of The Swedish ModelDocument13 paginiMeidner (1992) - Rise and Fall of The Swedish ModelmarceloscarvalhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LABOR STANDARDS Master Reviewer With NotesDocument126 paginiLABOR STANDARDS Master Reviewer With Notesethel hyuga100% (1)
- Loughmore Collected Histories Mark 2Document93 paginiLoughmore Collected Histories Mark 2moldbawn100% (2)
- TLE 103 Home Economics - History, Concepts, Principles and PhilosophyDocument17 paginiTLE 103 Home Economics - History, Concepts, Principles and PhilosophyBENEDICT JAMES ARADAÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP V Velasco DigestDocument3 paginiPP V Velasco DigestChrisel Joy Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Home Economics Timeline PDFDocument8 paginiHistory of Home Economics Timeline PDFfaker korea100% (1)
- Home Economics 1Document27 paginiHome Economics 1rushy121Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Home EconomicsDocument2 paginiIntroduction To Home EconomicsNica Garcia80% (5)
- Labor Review 2020-21 (2nd Sem) Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. Sscr-Col Bar Questions On Employer-Employee Relationship and Jurisdiction Q1Document3 paginiLabor Review 2020-21 (2nd Sem) Atty. Paciano F. Fallar Jr. Sscr-Col Bar Questions On Employer-Employee Relationship and Jurisdiction Q1RVirayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doctrines Applied in Medical Malpractice CasesDocument20 paginiDoctrines Applied in Medical Malpractice CasesMJ CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timeline of Family and Consumer SciencesDocument5 paginiTimeline of Family and Consumer SciencesAiren UnabiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fcs Timeline 1Document4 paginiFcs Timeline 1api-534370181Încă nu există evaluări
- Time Line Home EconomicsDocument8 paginiTime Line Home Economicsfaker koreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Home Economics: Mid-1800sDocument1 paginăHistory of Home Economics: Mid-1800skeithdagumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historia BeliceDocument28 paginiHistoria BeliceCyber TeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fcs 101 - Timeline FcsDocument2 paginiFcs 101 - Timeline Fcsapi-544252233Încă nu există evaluări
- College Elem12Document31 paginiCollege Elem12St. Veronica Learning CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- He ReviewerDocument8 paginiHe ReviewerAndrea Franchezka MasagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- M1 - L1 - Intro To World and Phil AgricultureDocument7 paginiM1 - L1 - Intro To World and Phil AgricultureHerman Inac ColonganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tleic104 Week2Document20 paginiTleic104 Week2Wawa KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edu201 History of EducationDocument7 paginiEdu201 History of Educationapi-393467982Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of Home EconomicsDocument5 paginiEvolution of Home EconomicsAlthea Grace AbalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 EconomicsDocument5 paginiChapter 1 Economicsjordan cedeñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home-Economics G1Document41 paginiHome-Economics G1Campos , Carena JayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 Items Multiple Choice: Topic: Introduction To Home Economics MembersDocument4 pagini20 Items Multiple Choice: Topic: Introduction To Home Economics MembersStephanie Catcho100% (1)
- Home Economics: A History: Young Ladies at Home" This Books Helped Young Girls and Women OnDocument6 paginiHome Economics: A History: Young Ladies at Home" This Books Helped Young Girls and Women OnCharlynjoy Abañas100% (2)
- HISTORY OF EXTE-WPS OfficeDocument5 paginiHISTORY OF EXTE-WPS OfficeShainabe RivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Economics G1Document42 paginiHome Economics G1CARENA JAY CAMPOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Class Notes: Modern HistoryDocument25 paginiDaily Class Notes: Modern HistoryShubham SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of ExtensionDocument2 paginiHistory of ExtensionAdrian Paga100% (1)
- AH8-HC6 Lecture Chapter 04Document33 paginiAH8-HC6 Lecture Chapter 04thomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alberni Indian Residential SchoolDocument3 paginiAlberni Indian Residential SchoolSidney Brett GrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of HEDocument15 paginiHistory of HEAnielof TandogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Economics - A History - SutoriDocument26 paginiHome Economics - A History - SutoriLhon Drake Marco ReguyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Home EconomicsDocument3 paginiHistory of Home EconomicsGABAS, MARIAN A.Încă nu există evaluări
- Cantong, Heralyn - TimelineDocument4 paginiCantong, Heralyn - TimelineMikee Betinol DomalaonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFF Intro To Agriculture Coursepack 1Document72 paginiAFF Intro To Agriculture Coursepack 1jennita garciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lord William BentinckDocument16 paginiLord William BentinckIshan LakhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Early Moves Toward Formal OrganizationDocument4 paginiEarly Moves Toward Formal OrganizationRhriszelle Jean BendolÎncă nu există evaluări
- TimelineDocument5 paginiTimelineapi-527201993Încă nu există evaluări
- Text Book of DomestDocument236 paginiText Book of DomestBianca PradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShortfinquiryprojectDocument8 paginiShortfinquiryprojectapi-283951467Încă nu există evaluări
- Kelompok 2 - MAKE LIFE EASIERDocument7 paginiKelompok 2 - MAKE LIFE EASIERRATIH FITRIYA NINGRUMÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Agri ExtDocument29 paginiHistory of Agri ExtocampokurtlouieÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Home Economics EducationDocument3 paginiHistory of Home Economics Educationinayahjunaid89Încă nu există evaluări
- Alphabet SoupchartkeyDocument6 paginiAlphabet SoupchartkeyLOGAN TITUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Scientific American Nutrition For A Changing World Preliminary Edition 1st Edition Pope Test BankDocument36 paginiFull Download Scientific American Nutrition For A Changing World Preliminary Edition 1st Edition Pope Test Bankherbielago366uk100% (27)
- Commissions - Modern HistoryWMDocument5 paginiCommissions - Modern HistoryWMhappyhappie307Încă nu există evaluări
- The Educational Act 1948Document4 paginiThe Educational Act 1948N SalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timeline PaperDocument6 paginiTimeline Paperapi-550363606Încă nu există evaluări
- CHN 2Document3 paginiCHN 2Cassey AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teaching and Education in The TransvaalDocument20 paginiTeaching and Education in The TransvaalBraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- International and Philippines Community and Public Health HistoryDocument55 paginiInternational and Philippines Community and Public Health HistoryRoseJarenMaeAbragan100% (1)
- 18Document13 pagini18gheljoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Education TimelineDocument3 paginiHistory of Education Timelineapi-438904199100% (1)
- Pasteurised MilkDocument40 paginiPasteurised MilkRobin TobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Food RevolutionDocument9 paginiEffects of Food RevolutionAllan CuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- He 201Document3 paginiHe 201Tae IgitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nineteenth Century and The Regime of 1876Document1 paginăThe Nineteenth Century and The Regime of 1876JonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rawanaboutaha Unit3 GenocideDocument10 paginiRawanaboutaha Unit3 GenocideyourmomsdadsfriendÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Calendar: in Collaboration WithDocument13 pagini2019 Calendar: in Collaboration Withapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Initial Support Through Guides To Speech and ActionDocument18 paginiInitial Support Through Guides To Speech and Actionapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Sewing Driver's License:: Children-To-Sew-2977517Document3 paginiSewing Driver's License:: Children-To-Sew-2977517api-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Project Based LearningDocument20 paginiProject Based Learningapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Programa de Actividad Fisica SKIPing - GoodwayBTJ PDFDocument6 paginiPrograma de Actividad Fisica SKIPing - GoodwayBTJ PDFJhonnyNogueraÎncă nu există evaluări
- All They Do Is PlayDocument4 paginiAll They Do Is Playapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- FCS 405 FCS Teaching Methods FinalDocument22 paginiFCS 405 FCS Teaching Methods Finalapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- The Economics of BelongingDocument26 paginiThe Economics of Belongingapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Fcs 160 Home and Family Management Winter 16 SyllabusDocument10 paginiFcs 160 Home and Family Management Winter 16 Syllabusapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- A Pre-Assessment 1Document2 paginiA Pre-Assessment 1api-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Pets Gathering TimeDocument2 paginiPets Gathering Timeapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- BYU-Idaho Preschool Lesson Plan: PETS (Dogs and Cats)Document1 paginăBYU-Idaho Preschool Lesson Plan: PETS (Dogs and Cats)api-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Work Ethic PresentationDocument15 paginiWork Ethic Presentationapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Work Ethic - Research PaperDocument10 paginiWork Ethic - Research Paperapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Like Unto LeavenDocument1 paginăLike Unto Leavenapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat of AdversityDocument2 paginiHeat of Adversityapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- 2017 Idaho Event Contest Info and Rubrics 2Document39 pagini2017 Idaho Event Contest Info and Rubrics 2api-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Career Exploration and Self Assessment Summary Page InstructionsDocument4 paginiCareer Exploration and Self Assessment Summary Page Instructionsapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Fccla Chapter Achievment ChecklistDocument1 paginăFccla Chapter Achievment Checklistapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Stock Poultry Lab SheetDocument2 paginiStock Poultry Lab Sheetapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Foods Final Project GuideDocument3 paginiFoods Final Project Guideapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Faith To Flip An EggDocument2 paginiFaith To Flip An Eggapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Dispersions Lab SheetDocument1 paginăDispersions Lab Sheetapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Project Poster FormatDocument1 paginăFinal Project Poster Formatapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Meal Plan FashionDocument4 paginiMeal Plan Fashionapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Exam-ReviewDocument1 paginăMidterm Exam-Reviewapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Meringue Cookies: (Sweet) : IngredientsDocument7 paginiMeringue Cookies: (Sweet) : Ingredientsapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Cheese and Butter LabDocument3 paginiCheese and Butter Labapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Fashion Invite Edited-1Document1 paginăFashion Invite Edited-1api-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Research - Final Draft KalDocument13 paginiResearch - Final Draft Kalapi-322059527Încă nu există evaluări
- Project On "Associate Recruitment Test Paper Revision": Rahulji SinghDocument94 paginiProject On "Associate Recruitment Test Paper Revision": Rahulji SinghDeepak SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samson VS, NLRCDocument11 paginiSamson VS, NLRCJammy Kate100% (1)
- AP The Conundrum Case StudyDocument8 paginiAP The Conundrum Case StudyRupal RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- U.S. Air Force Swot AnalysisDocument9 paginiU.S. Air Force Swot Analysisjigsaw74Încă nu există evaluări
- Ogl 321 Module 6 PaperDocument6 paginiOgl 321 Module 6 Paperapi-399897689Încă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of Kaizen 1Document12 paginiBenefits of Kaizen 1Harry SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Non Resident Indians: Account Opening FormDocument16 paginiFor Non Resident Indians: Account Opening Formshalabh2381Încă nu există evaluări
- Perquisite Results - Attachment ADocument1 paginăPerquisite Results - Attachment AWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Presentation Accident Prevention - PrelimDocument24 paginiSafety Presentation Accident Prevention - PrelimKim Gerald TejadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FTO-PLA-001-5 - WHS Management Plan 2019Document51 paginiFTO-PLA-001-5 - WHS Management Plan 2019Yexiong YIALENGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exit ManagementDocument58 paginiExit ManagementDdevil KinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership Styles and Theories 05-06-19 2020HDocument46 paginiLeadership Styles and Theories 05-06-19 2020HPrince Dkalm PolishedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Collateral ReadingDocument60 paginiReport Collateral ReadingmansiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEC Past Paper 1Document16 paginiBEC Past Paper 1kukushkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Changing Landscape of WorkDocument8 paginiChanging Landscape of WorkA K Azad SumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illinois NurseDocument13 paginiIllinois NurseMimi Lizada BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Background Verification Form - Lodha GroupDocument4 paginiRevised Background Verification Form - Lodha GroupAmrit TejaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-VII: Internal Mobility 1. Promotion: A) Concept B) Objectives C) ImportanceDocument12 paginiUNIT-VII: Internal Mobility 1. Promotion: A) Concept B) Objectives C) ImportanceRahul BarnwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Morning Calm Korea Weekly - June 13, 2008Document30 paginiThe Morning Calm Korea Weekly - June 13, 2008Morning Calm Weekly NewspaperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recritment and Selection ProjectDocument65 paginiRecritment and Selection ProjectGarima SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Human Resource Management: by Anshu Tandon Asst. Prof. NIMT, LucknowDocument45 paginiPresentation On Human Resource Management: by Anshu Tandon Asst. Prof. NIMT, LucknowHealth and Wellness CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bradley ReportDocument3 paginiBradley ReportThe London Free Press100% (1)
- Test Paper 8Document4 paginiTest Paper 8BotezIeftinÎncă nu există evaluări
- FWP Reporting FormDocument6 paginiFWP Reporting FormCfc-sfc Naic ChapterÎncă nu există evaluări