Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
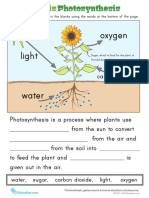
Life Science Lesson Plan-Cells
Încărcat de
api-372385087Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Life Science Lesson Plan-Cells
Încărcat de
api-372385087Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GSE Lesson Planning Template
Grade/ Grade Band: 5th Topic: Classifying Organisms Lesson Timeline:
Brief Lesson Description: STEM Classifying Organisms, cells
Essential Question(s):
How can I use my knowledge of the classification system for living things to model what makes vertebrates and invertebrates?
Why do scientists classify things?
How do scientists group organisms?
How have classification systems changed?
What do scientists do when something doesn’t fit in the classification system?
Narrative / Background Information
Prior Student Knowledge: Students should be able to name a variety of living things and describe a few general characteristics of plants and
animals. Students should also know some basic needs of organisms. If students have no prior knowledge of living things, remediate
characteristics of living things. (See Differentiation). It will also be helpful if students have had some experience with classification. For
example, it will be useful if students can name the kingdoms of life and identify some organisms from each kingdom. However, prior
knowledge of classification is not required for this lesson.
Science & Engineering Practices: Georgia Standard Excellence (GSE): Crosscutting Concepts:
1. Asking Questions (for science) and S5L1. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate 1. Patterns
Defining Science (for engineering) information to group organisms using 2. Cause & Effect: Mechanisms and
2. Developing and Using Models scientific classification procedures. Explanations
3. Planning and Carrying Out a. Develop a model that illustrates 3. Scale, Property, and Quantity
Investigations how animals are sorted into 4. Systems and System Models
4. Analyzing and Interpreting Data groups (vertebrate and 5. Energy & Matter: Flows, Cycles, and
5. Using Mathematics and Computational invertebrate) and how vertebrates Conservations
Thinking are sorted into groups (fish, 6. Structure & Function
6. Constructing Explanations (for science) amphibian, reptile, bird, and 7. Stability & Change
and Designing Solutions (for mammal) using data from
engineering) multiple sources.
7. Engaging in Argument from Evidence b. Develop a model that illustrates
8. Obtaining, Evaluating, and how plants are sorted into groups
Communicating Information (seed producers, non-seed
producers) using data from
multiple sources.
Possible Preconceptions/Misconceptions:
They may think that organisms with similar features are always grouped together; in fact, organisms with similar features may not
be closely related. For example, bats and birds both have wings, but bats are classified as mammals.
Differentiation strategies to meet diverse learner needs:
Students should also know some basic needs of organisms. If students have no prior knowledge of living things, remediate characteristics of
living things. (See Differentiation). It will also be helpful if students have had some experience with classification.
Provide graphic organizers
allowing students to re- watch videos, re-read passages, or re- do activities multiple times.
LESSON PLAN – 5-E Model
Engage:
* The students will decide if organisms on board are plant or Not a plant – will mark with X or check. (Keeley Probe)
* The students will categorize plants and give claim, evidence, and reasoning for how choose categories(allow them to choose the
categories and identify reason categorized).
*The students will present to class.
EXPLORE:
*The students will finish sharing how categorized plants in their groups and claims, evidence, and reasoning for categorizing along with any
examples.
*The students will discuss (whole group) and look at diagram (projector board) at plants with seeds vs. plants without seeds (spores) and
how alike and different.
*The students will view video and do “Test Yourself” activity on Studyjams.com – science- plants – plants with seeds.
The students/teacher will choral read pages 324/325 and observe charts and diagrams in Science text book and discuss organelles of plant
and animal cells and some of functions and likes and differences.
*The students will observe diagram/model of plant cell and animal cell on projector board (whole-group).
*The students will partner read in discoveryeducation.com science tech book and complete formative assessments
EXPLAIN
The students will complete “What Do Cells Do?” activity sheet using text pages 324-328.
*Students will receive and glue cell with organelles model into journal. Observe plant cell model displayed on projector board. Discuss each
organelle’s function (whole group).
*The students will explain what organelle’s do (on sticky note) and put on classroom cell models on wall around the room.
*Students will receive instructions/check list for constructing cell model.
Essential Question: what is the function of a nucleus?
* The students will construct tab foldables for their science journals defining vocabulary for Chapter 8 (Cells) and identifying cell
structure/function.
*Students will identify parts of a cell in an animal cell on the outer part of two-door foldable and compare/contrast the two on a double
bubble map on the inside.
*Studyjams.com - science – plants- plant cells.
*Give students cell project rubric and assignment description.
*”I will Survive” (alien video on youtube)
*Explain to students that unicellular organisms must have all it needs to survive in the ONE CELL.
Tier 2:
The students will fill out partially labeled foldables for their science journals defining vocabulary for Chapter 8 (Cells) and identifying cell
structure/function.
*Students will identify parts of a cell in an animal cell on the outer part of two-door foldable and compare/contrast the two on a double
bubble map on the inside.
Extension Activities (may do’s):
• Sheppard Software – cell games
• Brainpop – Science – Cellular Life and Genetics – cells
• Blendspace – KB5 Cells
ELABORATE:
**Professor Greg Ford and Charis coming to look at cells under microscope with students.
EQ: What does an plant cell look like and what are its parts?
*The students will look at different cells including that of a plant and animal and protest.
*The students will describe what they saw and if/what different (cell wall/cell membrane)
*The students will identify and use different parts of a microscope and realize specimen that cannot be seen with naked eye can be seen
with microscope.
EVALUATE:
*The students will create a model of a plant cell and present to class, explaining the functions of the main organelles and how a plant cell is
different from an animal cell.
*This will be assessed with a rubric for a grade.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Unit Plan Cells and Micro k5 CellDocument7 paginiUnit Plan Cells and Micro k5 Cellapi-371640211Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Unit PlanDocument15 paginiScience 10 Unit Planapi-537568147Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Parts FoldablesDocument3 paginiCell Parts Foldablesapi-270241956Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Theory and Cell Function (7th Grade)Document13 paginiCell Theory and Cell Function (7th Grade)Kerwin SoriaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Lesson 2Document8 paginiCells Lesson 2api-372328325Încă nu există evaluări
- Edtpa Lesson Plan - Callie AdamsDocument5 paginiEdtpa Lesson Plan - Callie Adamsapi-375768165Încă nu există evaluări
- Ecosystem Unit PlanDocument10 paginiEcosystem Unit Planapi-535715280Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Cells-1Document3 paginiLesson Plan Cells-1api-371640211Încă nu există evaluări
- S1l1-Animals-Lesson 2Document4 paginiS1l1-Animals-Lesson 2api-371196243100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Energy Transformation 1 1Document4 paginiLesson Plan - Energy Transformation 1 1api-313793053Încă nu există evaluări
- LP Week Two 5th Science Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument5 paginiLP Week Two 5th Science Physical and Chemical Changesapi-311117657Încă nu există evaluări
- Fifth Grade s5l2 Traits Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiFifth Grade s5l2 Traits Lesson PlanJordan100% (1)
- Evolution Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiEvolution Lesson Planapi-252795781Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Plan Dna 2Document7 paginiUnit Plan Dna 2api-513750879Încă nu există evaluări
- Dyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry PaperworkDocument7 paginiDyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry Paperworkapi-250608665Încă nu există evaluări
- 5e Lesson PlanDocument6 pagini5e Lesson Planapi-299537438Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology 20 Ecological Organization Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiBiology 20 Ecological Organization Lesson PlanSean MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhotosynthesisDocument5 paginiPhotosynthesisapi-285970439Încă nu există evaluări
- Kahoot Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiKahoot Lesson Planapi-361085000Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiLesson Planapi-272708709100% (1)
- Science Lesson Plan: REFERENCES (Exclude Class Text Include Page Numbers)Document4 paginiScience Lesson Plan: REFERENCES (Exclude Class Text Include Page Numbers)Darren AtwarooÎncă nu există evaluări
- About Heredity and Genetics Pacing and PlanningDocument6 paginiAbout Heredity and Genetics Pacing and Planningmohammed hassainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5th Grade Cells Lesson PlanDocument5 pagini5th Grade Cells Lesson Planapi-255511422Încă nu există evaluări
- Maddie Koontz Educ 424A Dr. Mckenzie Unit Plan: 1St Grade 2/11/2016Document9 paginiMaddie Koontz Educ 424A Dr. Mckenzie Unit Plan: 1St Grade 2/11/2016api-309172857Încă nu există evaluări
- Mixtures and Solutions Lesson Plan AssignmentDocument14 paginiMixtures and Solutions Lesson Plan AssignmentDonn NiñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ubd Lesson Plan OutlineDocument3 paginiUbd Lesson Plan Outlineapi-355847135Încă nu există evaluări
- Active Passive Transport Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiActive Passive Transport Lesson Planapi-238148465100% (1)
- Lesson Plans For Utm - Microteaching Cells - 5th GradeDocument12 paginiLesson Plans For Utm - Microteaching Cells - 5th Gradeapi-385809004Încă nu există evaluări
- Inquiry Lesson Cell Theory Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic and Cellular OrganellesDocument4 paginiInquiry Lesson Cell Theory Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic and Cellular Organellesapi-263275919Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan GR 11 BioDocument8 paginiLesson Plan GR 11 Bioapi-278566859Încă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Respiration LessonDocument3 paginiCellular Respiration Lessonapi-263259815100% (1)
- DP 2 Biology Theme UnitDocument3 paginiDP 2 Biology Theme Unitapi-246544437Încă nu există evaluări
- Chap TestDocument114 paginiChap TestLori Napolitano0% (1)
- Enzymes Lesson Plan TemplateDocument5 paginiEnzymes Lesson Plan Templateapi-529884372Încă nu există evaluări
- DP Biology - Speciation Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiDP Biology - Speciation Lesson Planapi-257190713100% (1)
- 2nd Edtpa Lesson PlanDocument6 pagini2nd Edtpa Lesson Planapi-269802069Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan ReproductionDocument11 paginiLesson Plan Reproductionmiss int0% (1)
- Unit Plan Science Unit Plan 5thDocument14 paginiUnit Plan Science Unit Plan 5thapi-371640211100% (2)
- Ict Miscroscope Lesson ThreeDocument2 paginiIct Miscroscope Lesson Threeapi-280941862100% (1)
- DLP FungiDocument6 paginiDLP FungiVia German BorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ubd Unit PlanDocument8 paginiUbd Unit Planapi-335115362100% (1)
- Pond WaterDocument4 paginiPond Waterapi-264011999Încă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction Unit Plan NewDocument9 paginiReproduction Unit Plan Newapi-315460032Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFDocument24 paginiAP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFJayCesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ds72-Review Summative Mitosis AssessmentDocument4 paginiDs72-Review Summative Mitosis Assessmentapi-110789702Încă nu există evaluări
- Transport in PlantsDocument11 paginiTransport in Plantszafarsulehri100% (3)
- MypplanneradaptationandevolutionDocument5 paginiMypplanneradaptationandevolutionapi-282478282Încă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument1 paginăPhotosynthesis WorksheetSadia Irfan100% (4)
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 4 2012Document47 paginiYearly Plan Biology Form 4 2012Hazimah YusofÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan VIII CellDocument2 paginiLesson Plan VIII CellShital KotkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Lesson For ElDocument3 paginiScience Lesson For Elapi-279742832Încă nu există evaluări
- 3-1 Cell Cycle ActivityDocument3 pagini3-1 Cell Cycle Activityanon_374314835Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Micro Teaching EtemsDocument3 paginiLesson Plan Micro Teaching EtemsEl YusoufiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ms Cell Theory TestDocument6 paginiMs Cell Theory Testapi-375761980Încă nu există evaluări
- Ds47-Cell Types Organelles Summative AssessmentDocument6 paginiDs47-Cell Types Organelles Summative Assessmentapi-110789702100% (1)
- Energy Flow-Lesson 4 Days 1 and 2Document29 paginiEnergy Flow-Lesson 4 Days 1 and 2jamieprudhomme77% (13)
- Myp Unit 2 Plan BiologyDocument7 paginiMyp Unit 2 Plan BiologyBUSE EROĞLU0% (1)
- Flower Dissection Lesson Plan-Science-4th-WeeblyDocument8 paginiFlower Dissection Lesson Plan-Science-4th-Weeblyapi-302127338Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12De la EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Reflection - Integration Earth Science UnitDocument1 paginăUnit Reflection - Integration Earth Science Unitapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Changes To Surface ReflectionDocument1 paginăChanges To Surface Reflectionapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Exemplary Teacher Observation Reflection Form Used by Endorsement CandidatesDocument1 paginăExemplary Teacher Observation Reflection Form Used by Endorsement Candidatesapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Deposition Lesson ReflectionDocument1 paginăDeposition Lesson Reflectionapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Stem Lesson Plan - Beach ErosionDocument4 paginiStem Lesson Plan - Beach Erosionapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- K5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Weathering and Erosion Kelly BarrereDocument3 paginiK5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Weathering and Erosion Kelly Barrereapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Plate Boundaries and EffectsDocument3 paginiPlate Boundaries and Effectsapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Static Electricity ReflectionDocument1 paginăStatic Electricity Reflectionapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Reflection - Differentiation Physical Science UnitDocument1 paginăUnit Reflection - Differentiation Physical Science Unitapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Changes To Earths SurfaceDocument3 paginiChanges To Earths Surfaceapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- States of Matter Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiStates of Matter Lesson Planapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- K5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Deposition Kelly BarrereDocument3 paginiK5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Deposition Kelly Barrereapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- States of Matter ReflectionDocument1 paginăStates of Matter Reflectionapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Student Assessment DataDocument1 paginăStudent Assessment Dataapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Reflective SummaryDocument1 paginăLesson Reflective Summaryapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- K5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiK5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Planapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Chemical Changes PT 2Document3 paginiPhysical Chemical Changes PT 2api-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- K5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Physical and Chemical Changes Kelly BarrereDocument3 paginiK5 Science Endorsement GPS Lesson Plan: Physical and Chemical Changes Kelly Barrereapi-372385087Încă nu există evaluări
- Sabir K Maitheen Curriculam Vitae Kotteparambil House Instrumentation Engineer Thrickalathoor P.O, Muvattupuzha Ernakulam District, Kerala, India - 683541Document3 paginiSabir K Maitheen Curriculam Vitae Kotteparambil House Instrumentation Engineer Thrickalathoor P.O, Muvattupuzha Ernakulam District, Kerala, India - 683541Thusith WijayawardenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UoM Directory 2020 - 0Document61 paginiUoM Directory 2020 - 0Damith CostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anil LaulDocument18 paginiAnil LaulSmriti SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milat Profile - Final VersionDocument24 paginiMilat Profile - Final VersionE BÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROFIBUS DP Diagnostics MonitoringDocument8 paginiPROFIBUS DP Diagnostics MonitoringJulio Mercado WagnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0 Matlab Simulink ModelDocument6 pagini0 Matlab Simulink Modelpreety rajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument12 paginiClass 12 Physics Investigatory Projectdjjeena619Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Turbine and Associated EquipmentDocument47 paginiHydraulic Turbine and Associated Equipmentpavankumar0010% (1)
- Res 6Document81 paginiRes 6Amith BhatkalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Errata Aci 318-08aDocument3 paginiErrata Aci 318-08agodfreye1Încă nu există evaluări
- JISDocument9 paginiJISpalm hillsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of COTTER JOINT Using Autodesk Inventor 2013 and ANSYS WorkbenchDocument22 paginiDesign and Analysis of COTTER JOINT Using Autodesk Inventor 2013 and ANSYS WorkbenchamuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adoption IEC 60146 1 3Document7 paginiAdoption IEC 60146 1 3dfcghvbhjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discharge of Conditions - P - 2016 - 00474 Drawing - Drainage - Long SectionsDocument2 paginiDischarge of Conditions - P - 2016 - 00474 Drawing - Drainage - Long SectionsRyeanKRumanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Techtextil 2011 Press Release 1Document4 paginiTechtextil 2011 Press Release 1Héctor LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NnewmarkDocument14 paginiNnewmarkJosé ChávezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flyer-CJX & CZX Interposing Relay SetDocument1 paginăFlyer-CJX & CZX Interposing Relay SetsavvymovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Labs: (EE-455) Electrical Power System ProtectionDocument4 paginiPre-Labs: (EE-455) Electrical Power System ProtectionJurair SaqibÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPI Verification Guide PDFDocument3 paginiSPI Verification Guide PDFImtiyaz Pasha Shaik100% (1)
- Sohail CV PDFDocument3 paginiSohail CV PDFSohail LarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- VHDL TutorialDocument68 paginiVHDL TutorialPedro Pablo Parra AlbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R961006855 EHTG-Flyer USD WebDocument2 paginiR961006855 EHTG-Flyer USD Webmarc271986Încă nu există evaluări
- Contoh CV IowDocument6 paginiContoh CV IowMohd AzwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bottom Plate ReplacementDocument1 paginăBottom Plate ReplacementYo Wee LiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Culvert ThicknessDocument23 paginiCulvert ThicknessNilaAbubakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhule 22km Structure Proposal - R1Document15 paginiDhule 22km Structure Proposal - R1Ganesh ChakoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agile E0 Key With AnswersDocument13 paginiAgile E0 Key With AnswersAbraham MorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing Cycle FLOWCHARTDocument2 paginiTesting Cycle FLOWCHARTPhani Raj ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection & Test Plan TemplateDocument11 paginiInspection & Test Plan Templatefanghao5345Încă nu există evaluări