Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Coperhensive Stracture 2010
Încărcat de
abraamTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Coperhensive Stracture 2010
Încărcat de
abraamDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1 Comprehensive Exam
TABLE OF CONTENT
BACKGROUND.....................................................................................................................3
I. CURRENT SITUATION..........................................................................................4
CURRENT PERFORMANCE.............................................................................................4
STRATEGIC POSTURE...................................................................................................4
1. Mission.........................................................................................................4
2. Objectives....................................................................................................5
Strategic Audit - ___________
3. Strategies.....................................................................................................6
4. Policies.........................................................................................................9
II. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.................................................................................9
BOARD OF DIRECTORS.................................................................................................9
TOP MANAGEMENT..................................................................................................10
SHAREHOLDERS............................................................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
LEADER SHIP STYLES…………………………………………………………………………….11
III. EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT: OPPORTUNITIES AND THREATS (SWOT).................12
KEY TREND IN THE BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT………………………………………………………….12
SOCIETAL ENVIRONMENT (P.E.S.T FACTORS).................................................................13
1. Political - Legal Factors...............................................................................13
2. Economic Factors.......................................................................................14
3. Socio-cultural Factors................................................................................14
4. Technological Factors.................................................................................14
TASK ENVIRONMENT (INDUSTRY)................................................................................15
Porter’s Approach.......................................................................................................15
1. Threat of New Entrants.............................Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. Rivalry among Existing Firms....................Error! Bookmark not defined.
3. Threat of Substitute Products or Services Error! Bookmark not defined.
4. Bargaining Power of Buyers......................Error! Bookmark not defined.
5. Bargaining Power of Suppliers..................Error! Bookmark not defined.
6. Relative Power of Other Stakeholders......Error! Bookmark not defined.
EXTERNAL FACTOR ANALYSIS SUMMARY EFAS (AS ATTACHED) .................................................17
IV. INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT: STRENGTH AND WEAKNESSES (SWOT)...................19
CORPORATE STRUCTURE............................................................................................19
CORPORATE CULTURE................................................................................................21
CORPORATE RESOURCES............................................................................................21
1. Marketing...................................................................................................21
2. Finance.......................................................................................................22
3. Research and Development.......................................................................26
4. Operations and Logistics............................................................................26
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
2 Comprehensive Exam
5. Human Resources......................................................................................26
6. Information Systems..................................................................................29
INTERNAL FACTOR ANALYSIS SUMMARY IFAS (AS ATTACHED) ...................................................30
V. ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIC FACTORS (SWOT)........................................................32
risk for the multinational company located in egypt…………… ……….32
SITUATION ANALYSIS.................................................................................................32
REVIEW OF MISSION AND OBJECTIVES.........................................................................32
VI. STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVE AND RECOMMENDED STRATEGY...............................33
STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVE............................................................................................36
RECOMMENDED STRATEGY.........................................................................................38
Strategic Audit - ___________
VII. IMPLEMENTATION............................................................................................40
1. MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT.................................................................................40
2. EMPLOYEE EMPOWERMENT....................................................................................40
3. REWARD SYSTEM..................................................................................................40
4. INTEGRATING TRAINING..........................................................................................40
5. PROCESS IMPROVEMENT.........................................................................................40
6. QUALITY AT SOURCE..............................................................................................40
VIII.EVALUATION AND CONTROL................................................................................41
International entry options…………………………..……………………..42
Marketing plan outline…….…………………………………………….…43
conclusion and recommendations……………………………………..…...48
Examples of symptoms and cases in marketing……………………….…..51
.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
3 Comprehensive Exam
Background:
A)Company Profile
Size of business
Large /med/ enterprenuer
Strategic Audit - ___________
Organizational structures:
Simple structure, few people own the business and do every things.
Functional structure, in which there were many functional entities.
Divisional Structure many divisions or SBUs with separate management
Firm Strategic type:
Prospector focus on product innovations and broad products.
Defender focus on improve the efficiency of current products .
Management Philosophy
Short term Vs. Long or Both
Marketing oriented Vs. financial oriented
B)Market
Existing Market Segment (size / growth)
Geographic domain local – international
C) Type of Industry:
Goods, service or integrated solutions
“Consolidated industry”. the industry is dominated by few #
large firms. Monopoly---Oligopoly
“fragmented industry”. dominated by large# firms. —
hypercompetitive
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
4 Comprehensive Exam
A. Current Situation
ㄱ Current Performance
Use the case given information to comment on the firm’s current
performance.
Ex Wal-Mart is the largest retailer, discount store chain, and company in the
U.S. and the world. Its combination of low prices and excellent customer
Strategic Audit - ___________
satisfaction continue to lead the way and insure growth. Rapid growth in
sales and profits. Strong financials, increasing net income, increasing
earning per share, return on assets and return on equity. However, current
liabilities exceed current assets with a less-than one current ratio and
negative working capital. Yet it is still a very healthy position with one only
threat in hand and that is the increasing current liabilities
ㄴ Strategic Posture
1. Mission
ㄱto be stated and comment whether it is generic or limited and is it implied from
performance (this comment can be done later in “Review of Mission and Objectives”
ㄴ Customers – who are the firm’s customers?
ㄷ Product or Service – what are the forms major products or services?
ㄹ Market - geographically where does the firm compete?
ㅁ Technology – is the firm technologically current?
ㅂ Concern for survival, growth and profitability – is the firm committed to
survival and financial soundness?
ㅅ Philosophy - what are the basic beliefs, values, aspirations and ethical
priorities of the firm?
ㅇ Self concept – What is the firm’s distinctive competence or major
competitive advantage?
ㅈ Concern for public image – Is the firm responsive to social, community
and environmental concerns?
ㅊ Concern for employees – Are employees a valuable asset of the firm ?
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
5 Comprehensive Exam
ㄷ Objectives
ㅋ Comment whether it is Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timable
realistic or not
ㅌ Ex Wal-Mart
Strategic Audit - ___________
ㅍ To provide customers with what they want, when they want it, and with value
ㅎ To develop and maintain team spirit with its employees (The associates)
ㄱ To remain the number one retailer, discount chain, and company
ㄴ To pursue growth while maintaining growth in sales and profits; profits will not
be sacrificed for growth
ㄷ To be the very best in our business
ㄹ To expand internationally and be number one
ㅁ To have the store provide the customer with a clean, pleasant and friendly
shopping experience To keep the company leadership allover the world
ㅂ To be truly nationwide retailer operated in all the 50 states.
ㅅ Sales and earnings growth structure over 5 years period as follows:
ㅇ Domestic markets with Wal-Mart stores and supercenters (60%-70%), Sam’s Club
& McLane (10%-15%), and international markets (20%)
ㅈ Introducing no more than10 “small-marts” per year.
ㅊ Delivering huge sales and earnings increase
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
6 Comprehensive Exam
2. Strategies
A)Corporate Directional strategies:
Strategic Audit - ___________
1- Growth Strategy
internally through expanding of operations both globally and domestically or it can
grow
externally through mergers, acquisitions and strategic alliance.
vertical growth through vertical integration with some of its distributors outside and
suppliers
Horizontal growth expanding COMPANY X's products in range
expanding in other geographical locations
and/or increasing the range of products in the same location
2- Stability strategy: if the company is operating in reasonably stable environment,
stability strategy will be very appropriate for successful operation) /Profit
3- Retrenchment strategy: when the company is in a weak competitive position, some
or all of its products results in a poor performance, sales are down and profits are
becoming losses. Therefore using retrenchment strategy to eliminate the weakness that
are dragging the company down)
Strategy excell sheet at the main folder
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
7 Comprehensive Exam
B)Porter's Generic Strategies: (Business strategy)
Type of Ways to achieve the strategy Benefits Possible problems
strategies
Cost - Globalization Relocating to low- The ability to: -Vulnerability to even
Leadership cost parts of the world -Out perform rivals lower cost operators
Strategic Audit - ___________
Size and economies of scale -make barriers to -Possible price wars
-Modification/simplification of entry -The difficulty of
designs -Resist the five forces sustaining it in the long
-Greater labour effectiveness term
-Greater operating effectiveness
-Strategic alliances
-New source of supply
Focus Concentration upon on or a small -A more detailed -Limited opportunities
number of a strong and specialist understanding of for sector growth
reputation particular segments -The possibility of
-The creation of outgrowing the market
barriers to entry -The decline of the
-A reputation for sector
specialization -A reputation for
-The ability to specialization which
concentrate efforts ultimately inhibits
growth and
development into other
sectors
Differentiation -The creation of strong brand -A distancing from -The difficulties of
identities others in the market sustaining the bases for
-The consistent pursuit of pursuit -The creation of a differentiation
of those factors which customers major competitive -Possibly higher costs
perceive to be important advantage -The difficulty of
-High performance in one or -Flexibility achieving true and
more of a spectrum of activities meaningful
differentiation
Cost Leadership
Being the low-cost competitor in an industry while maintaining satisfactory profit
margins
Sources of Cost Reduction
Product Design------------------------
Government Subsidies---------------
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
8 Comprehensive Exam
Efficient Labor --------- ---------------
New Delivery Methods--------------
Production Innovations--------------
Obtain inexpensive raw materials
Create efficient operations----------
Control overhead costs--------------
Avoid marginal customers---------
2-Differentiation Competitive Advantage
Advantage achieved when a firm provides something that is unique and valuable to
buyers beyond simply offering a lower price
Strategic Audit - ___________
Common Differential Advantages
Brand names------------
Strong dealer network
Product reliability------
Image---------------------
Service-------------------
Niche Competitive Advantage
Advantage achieved when a firm target and effectively serve a small segment of the
market
Used by small companies with limited resources
used in a limited geographic market
focused on a specific product line
Ex Wal-Mart
1. International growth strategy
2. Concentric diversification strategy—focus growth on core
competencies horizontal growth for Wal-Mart to the extent that new
product mixes are being offered in new store formats, it could be
concentric diversification
3. International acquisitions and new ventures
4. new store openings, expansion to more states, upgrading and
remodeling existing stores, and opening new distribution centers.
5. Developing new retail formats/concepts1-stop shopping offering
everyday low price
6. Encourage community relations and social programs on both local and
national level.
7. Putting emphasis on human resources management
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
9 Comprehensive Exam
3. Policies
ㅋ State whether the firm has clear and written policies and fitting to its
mission and objectives. Company polices: regulation, limitation,
boundaries
ㅌ Ex Wal-Mart
ㅍ To sell products that are environmentally friendly (green marketing policy)
ㅎ Satisfaction Guaranteed refund and exchange policy
Strategic Audit - ___________
ㄱ To provide quality, value, selection and low price
ㄴ “The Wal-Mart Way”
ㄷ HRM policies that Wal-Mart employed that tied employees to corporate culture
ㄹ “The good life at a great price. Guaranteed.”
ㅁ Leveraging technology awareness and usage
ㅂ Stressing high standard of honesty, morality, and business ethics
ㅅ Dress code policy
ㅇ Customer handling policy
ㅈ Associates/management communication policiesFriendly working environment
ㅊ Customer satisfaction is the ultimate goal.
ㅋ HRM policies that employed that tied employees to corporate culture.
ㅌ Full training and follow up programs for employees and executives.
ㅍ Creativity is the company driving force
ㅎ Friendly working environment
B. Corporate Governance
ㄹ Board of Directors
ㄱ Who are they, are they internal or external, do they own
shares, do they have different voting rights and for how long
they are serving on the board?
ㄴ Do they contribute knowledge, skills and connections to the
firm? And if the firm has international operations do they
have international experience?
ㄷ What is there level of involvement in strategic management?
(refer to board continuum
Ex
the number of directors.
main names mentioned in the case:
…………., Chairman.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
10 Comprehensive Exam
…………., President.
One-insider member members, ……………….
ㅁ Top Management
ㄹ Who are the top managers and what are their
characteristics in terms of knowledge, skills, background and
style? do they have international experience?
Ex
As outlined in the case, company has been appointed Mr. ……. as CEO from within the
Strategic Audit - ___________
company or outside
He is Very experienced in the industry – long history.
Responsible for the current situation to on improvements; he was the driving engine
and the reason of having the creativity atmosphere in the company
Mr. ……. (Style = Active participation).
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
11 Comprehensive Exam
Leadership Styles
Strategic Audit - ___________
1. Laissez-faire shows low concern for both people and task. Turn most
decisions over the work group and show less interest in the work
process or its results.
2. Directive or Autocratic, High concern for task and low concern for
people. Make most of the decisions, gives directions and expect his
orders to be followed.
3. Supportive leader shows high concern for people and low concern
for tasks. Warm in interpersonal relationships, avoid conflict, and
seek harmony in decision-making.
4. Participative or democratic, shows high concern for both people and
task. Share decisions with the work group, encourage participation
and support the work efforts of others.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
12 Comprehensive Exam
C. External Environment: Opportunities and Threats (SWOT)
External environmental factors include a very wide range of variables under
the main categories of societal and task environment also key trends in the
Strategic Audit - ___________
business environment as
ㅂ key trends in the business environment
Globalization Free trade agreements via regional associations
like European Union, NAFTA, and ASEAN, allow common
standards and enable global competition; privatization,
Internet, and transportation improvements allow companies
to compete globally.etc.
.
Disintermediation Intermediaries, such as insurance brokers,
travel agents, and retailers, are being strongly affected by IT
developmentse.g. direct banking and insurance, airline call
centres, e-commerce and the rise of .com firms
Dematerializationtion Knowledge is increasingly more
important than materials in the value of what we produce and
consume - e.g. the capital value of Microsoft is less than 5% of
its share value An increasing proportion of the value of a
product is in the service rather than the physical object
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
13 Comprehensive Exam
ㅅ Societal Environment (P.E.S.T Factors)
1. Political - Legal Factors
Strategic Audit - ___________
EgyptPolitical changes
Capitalism
Private ownership
Private and business sector
Open markets
Severe competition
High quality
High customer & market focus
limited price control
Punishment & reward systems
Moderate to high income
Digital technology/ Western
1. Tax and customs Laws: the modified tax law in Egypt (as the group is an Egyptian Group) will be
reflected on the net income of the company and accordingly on its overall results.
2. Political situation and Terrorist attacks: the political situation and terrorist attacks in Egypt and
allover the world and the image linked to the Arab community and its projection on doing business
with such community.
3. Egypt new Governmental regulation: favor any new business as indicated from the statistics.
Demographic Facts
Population 75,396,909
Population Growth 1.75% P.a.
GDP / Capita $1,426
Literacy Rate 57.7%
Population Distribution 60% <age 25
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
14 Comprehensive Exam
2. Economic Factors
Strategic Audit - ___________
1- Exchange rate: exchange rate is stable and as expected to last for the coming two years ;
considered as a very good chance to boost its sales level locally as well as export.
2- Availability and price of Labor the labor in Egypt are available and with low cost.
3- Economic growth: slow overall economic growth worldwide and especially in Egypt
4- Free trade agreements: The availability of free trade agreements. Open egyption market
5- Lack of Governmental Price Fixation: incourages many businesses
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
15 Comprehensive Exam
Real GDP US$ 85.98bn
Real GDP Growth 6.8%
Inflation 4.2%
Foreign Currency Reserves US$ 28.6bn
FDI US$ 10.5bn
Strategic Audit - ___________
3. Socio-cultural Factors ( Need upate)
the majority of Egyptians come from poor backgrounds and evidently cannot afford to buy more than
one product so they usually purchase one product that can be used for multiple purpose , introduction
of supermarkets and hypermarkets catering to the middle class changing Egyptians consumer
behavior. This will serve as a further contribution to potential future growth of household care
.products
4. Technological Factors
Internet Subscribers 449.056
Fixed Line Subscribers 11.216.751
Mobile Subscribers 32.176.930
Fixed Line Penetration 15.1%
Mobile Penetration 42.9%
ㅇ Task Environment (Industry)
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
16 Comprehensive Exam
Is represented in the forces drive industry competition and
whether they are the same globally or vary from country to
another.
Porter’s Approach
Potential
Potential
Entrants
Entrants
Relative power of Threat of New
Unions, Governments Entrance
Other
Strategic Audit - ___________
Other Industry
Shareholders Industry Buyers
Shareholders Competitors Buyers
Competitors
Rivalry among
Rivalry among
Suppliers Existing firms Bargaining power
Suppliers Existing firms
of Buyers
Bargaining power
of Suppliers Substitutes
Substitutes
Threat of substitute
product or service
1. Rivalry among existingfirms Criteria
Number of firms, few equally balanced giants
Industry growth rate
Very high or fixed storage cost
Commoditization, low differentiation
Capacity, intermittent overcapacity
Diversity of rivalry
High strategic/corporate stakes
High exit barriers
2. The bargaining power of buyers Criteria, how strong?
A single or very few buyers purchase a high proportion of total sale
Product volume purchased
Products are standard or undifferentiated
Low switching costs
Buyer is in low profit business = sensitive to cost
Real threat of backward integration from buyer
Industry product not important for buyer quality
The buyer has full information on product
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
17 Comprehensive Exam
3. The bargaining power of suppliers Criteria, how strong?
Dominated by few companies, more concentrated than the target industry
The target industry is NOT important to the supplier
Supplier product is unique, or high switching cost
Supplier product is critical for the business of the target
Substitutes are not easily available
Real threat of forward integration from supplier
4. Threat of new entrants – barriers to entry Criteria how high?
powerful economies of scale
Strategic Audit - ___________
Strong customer loyalty by product differentiation
Large capital investment requirements
Switching cost for new products are high
Lack of access to distribution channels
Structural cost disadvantage
Government policy
5. Substitutes:
Relative perceived value tending to improve
Where the threat is to another industry's cash cow
6. Relative Power of Other Stakeholders :
Relative power of Unions, Governments
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
18 Comprehensive Exam
External Factor Analysis Summary EFAS (Threats)
External Factors Comments
Potential Threats
Emergence of substitutes products Due to the global expansion
Government regulations May interfere in company’s policies
Strategic Audit - ___________
Increases in domestic competition? Will increase the companies growth
and reduce risk
Increases in foreign competition?
Like sport field
Change in consumer taste?
Will reduce risk and increases profit
Fall in barriers to entry?
Rise in new or substitute products?
Increase in industry rivalry?
New forms of industry competition?
Potential for takeover?
Existence for corporate raiders?
Increase in regional competition?
Changes in demographic factors?
Changes in economic factors?
Downturn in economy?
Rising labor costs?
Slower market growth?
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
19 Comprehensive Exam
External Factor Analysis Summary EFAS (opportunities)
External Factors Comments
Potential opportunities
Expand core business(es)?
Due to the global expansion
Exploit new market segments?
Strategic Audit - ___________
Will increase the companies growth and reduce risk
Widen new market segments?
Extend cost or differentiation advantage?
Diversify into new growth businesses?
Like sport field
Expand into foreign markets?
Will reduce risk and increases profit
Apply R&D skills in new areas?
Enter new related businesses?
Vertically integrate forward?
Vertically integrate backward?
Enlarge corporate portfolio?
Overcome barriers to entry?
Reduce rivalry among competitors?
Make profitable new acquisitions?
Apply brand name capital in new areas?
Seek fast market growth?
Exchange Rate New Tax Law
Availability and price of Labor
Economic Growth
Free trade agreements
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
20 Comprehensive Exam
D. Internal Environment: Strength and Weaknesses (SWOT)
ㅈ Corporate Structure
ㅊ Mechanistic vs. Organic, Centralized vs. Decentralized
Mechanistic structure( rigid) ,more specialization, formalization, centralization
structure can be applied in the Finance, store, and administrative departments
Strategic Audit - ___________
Organic structure(loose),more creative, less specialization, unformalization,
decentralization structure applied in the Marketing, Public Relations, corporate
communication.
ㅋ COMPANY X Structure
The organization's strategy to grow and go more international must be reflected on the
organization structure to achieve the required result.
Simple structure
Owner-manager makes decisions., Little specialization of tasks.Few rules, little
formalization
Advantages: Provides high flexibility
Rapid product introduction
Few coordination problems
Functional structure,
The company being lead by team of managers who have functional specializations
Advantages
• Centralized control of operations
• Promotes in-depth functional expertise
• Enhances operating efficiency where tasks are routine
Disadvantages
• Functional coordination problems
• Inter-functional rivalry
• Overspecialization and narrow viewpoints
• Hinders development of cross-functional experience
• Slower to respond in turbulent environments
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
21 Comprehensive Exam
Divisional structure:
It occurs especially when the organization is managing diverse product line or when the
organization is expanding to cover wider geographical areas
Advantages:
Decentralized decision making
Each business is organized around products
Puts profit/loss accountability on manager
Facilitates rapid response to environmental changes
Allows efficient management of a large number of units
Disadvantages
Strategic Audit - ___________
May lead to costly duplication of functions
Inter-divisional rivalry
Corporate managers may lose in-depth understanding
Matrix Structure
The matrix structure (some times called the matrix organization) it combines the
functional and divisional structure
Functional & product form are combined simultaneously at the same level.
Employee have 2 superior, functional superior & horizontal product manager
When to use ?
• Scarce resources
• Ideas need to be cross fertilized across projects
• External environment is very complex and changeable
Network structure
• many activities are outsource
• series of independent firms or business units that are linked together by
computers in an IS
• Used when the environment is unstable
Advantages:
• Rapid response time
• Firm’s emphasize their own core competencies
• Very flexible
• Reduces capital intensity
ㅌ Corporate Culture
ㅍ Are shared beliefs, expectations and values well defined? And do the
firm has diversity of cultures?How the corporate culture perceive quality
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
22 Comprehensive Exam
and adaptability to change in conditions. It is the collection of beliefs, expectations
and values learned, shared by a corporation's members, and transferred from one generation of
employees to another. It might be changing or elaborating but hardly completely fades away. It gives
the corporation its identity
Ex
Commitment to quality, Recognize individual achievements
Concern for customer satisfaction
Focus on growth
Emphasis on efficiency and performance
Concern for innovation
Focus on capable, innovative, well-trained, and enthusiastic people
Strategic Audit - ___________
Gaining customer respect
Employees should share in XXXX success
Pleasant work environment
Satisfaction and sense of accomplishment from work
ㅎ Corporate Resources
1. Marketing
What are their objectives is the clearly stated, consistent with
mission, objectives, strategies, and policies with external and
internal environment? Are marketing managers using accepted
techniques? And does marketing provide competitive advantage?
Market Share & Marketing strategy :
Push marketing strategy The producer promotes the product to wholesalers,the wholesalers prom ote it to
retailers, and the retailers promote it to consumers
“pull” marketing strategy A strategy that requires high spending on advertising and consumer promotion to build
up consumer demand for a product.
Strengths
Quality brand identity Brand names. strong Brand image/
names in retail merchandising combining quality products
with low prices(+)
Highly diversified products (+)
Good relationships with major multinational corporations (+)
Respond quickly to changes in consumer market (+)
Tracked consumer buying preferences (+)Large-scale add
campaigns,
Customer satisfaction and building long-term relationships
with them Stresses that the customer matters, Customer
focus is an asset
CRM to strengthen its position
Segmenting their customers
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
23 Comprehensive Exam
positioning strategy depends on putting the firm on top of
industry focusing on the general large market segment of
customers,Positioned as Ex “national discount department
store chain” and worked hard to achieve that.
sponsoring popular social causes like the “Buy American”
program, “Environmentally sound products “(this follows
current U.S. societal trends)
keeping the balance between image, quality and low pricing
emphasizes quality in strategy in terms of merchandise, stores
layout and customer orientation.
Distribution strategies that stress the short distance to
distribution centers and hence enhance availability.
Strategic Audit - ___________
International expansion and growth a strong competitive
advantageLarge-scale ad campaigns
Weaknesses
The lack in new creative ideas.
The lack of cooperation between the department
2. Finance
Liquidity Ratios:
A company's liquidity is a measure of its ability to meet short-term obligations. An asset
is deemed liquid if it can be readily converted into cash. Liquid assets are current assets
such as cash, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and so on. Two commonly
used liquidity ratios are current ratio and quick ratio.
1. Current ratio. The current ratio measures the extent to which the claims of short-
term creditors are covered by assets that can be quickly converted into cash.
Most companies should have a ratio of at least 1, because failure to meet these
commitments can lead to bankruptcy. The ratio is defined as follows:
Current Assets
Current Ratio =
Current Liabilities
2. Quick ratio. The quick ratio measures a company's ability to pay off the claims of
short-term creditors without relying on the sale of its inventories. This is a
valuable measure since in practice the sale of inventories is often difficult. It is
defined as follows:
Current Assets - Inventory
Quick Ratio =
Current Liabilities
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
24 Comprehensive Exam
Profitability Ratios:
Profit ratios measure the efficiency with which the company uses its resources. The
more efficient the company, the greater is its profitability. It is useful to compare a
company's profitability against that of its major competitors in its industry.
1. Gross profit margin. The gross profit margin simply gives the percentage of sales
available to cover general and administrative expenses and other operating
costs. It is defined as follows:
Sales Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold
Gross Profit Margin =
Sales Revenue
Strategic Audit - ___________
2. Net profit margin. Net profit margin is the percentage of profit earned on sales.
This ratio is important because businesses need to make a profit to survive in the
long run. It is defined as follows:
Net Income
Net Profit Margin =
Sales Revenue
Return on total assets. This ratio measures the profit earned on the employment of
assets. It is defined as follows: Net income is the profit after preferred dividends (those
set by contract) have been paid. Total assets include both current and non current assets
Net Income Available to Common Stockholders
Return on Total Assets =
Total Assets
3. Return on stockholders' equity. This ratio measures the percentage of profit
earned on common stockholders' investment in the company. In theory, a company
attempting to maximize the wealth of it stockholders should be trying to maximize this ratio. It is
defined as follows:
Net Income Available to Common Stockholders
Return on Stockholders' Equity =
Stockholders' Equity
Activity Ratios:
Activity ratios indicate how effectively a company is managing its assets. Inventory
turnover and days sales outstanding (DSO) are particularly useful:
1. Inventory turnover. This measures the number of times inventory is turned over.
It is useful in determining whether a firm is carrying excess stock in inventory. It
is defined as follows: Cost of goods sold is a better measure of turnover than
sales, since it is the cost of the inventory items. Inventory is taken at the balance
sheet date
Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
25 Comprehensive Exam
Inventory
2. Days sales outstanding (DSO), or average collection period. This ratio is the
average time a company has to wait to receive its cash after making a sale. It
measures how effective the company's credit, billing, and collection procedures
are. It is defined as follows: Accounts receivable is divided by average daily sales. The use
of 360 is standard number of days for most financial analysis.
Accounts Receivable
DSO =
Total Sales/360
Strategic Audit - ___________
Leverage ratio:
A company is said to be highly leveraged if it uses more debt than equity, including
stock and retained earnings.
capital structure is The balance between debt and equity However, debt can be risky to
the firm because if enough profit is not made to cover the interest and principal
payments, bankruptcy can occur.
1. Debt-to-assets ratio. The debt-to-asset ratio is the most direct measure of the
extent to which borrowed funds have been used to finance a company's
investments. It is defined as follows: Total debt is the sum of a company's
current liabilities and its long-term debt, and total assets are the sum of fixed
assets and current assets
Total Debt
Debt-to-Assets Ratio =
Total Assets
2. Debt-to-equity ratio. The debt-to-equity ratio indicates the balance between
debt and equity in a company's capital structure. This is perhaps the most widely
used measure of a company's leverage. It is defined as follows:
Total Debt
Debt-to-Equity Ratio =
Total Equity
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
26 Comprehensive Exam
3. Times-covered ratio. The times-covered ratio measures the extent to which a
company's gross profit covers its annual interest payments. If the times-covered
ratio declines to less than 1, then the company is unable to meet its interest
costs and is technically insolvent. The ratio is defined as follows:
Profit Before Interest and Tax
Times-Covered Ratio =
Total Interest Charges
Shareholders-Return ratios:
Shareholder-return ratios measure the return earned by shareholders from holding
Strategic Audit - ___________
stock in the company.
1. Price-earnings ratio. The price-earnings ratio measures the amount investors are
willing to pay per dollar of profit. It is defined as follows:
Market Price per Share
Price-Earnings Ratio =
Earnings per Share
2. Market to book value. Another useful ratio is market to book value. This
measures a company's expected future growth prospects. It is defined as
follows:
Market Price per Share
Market to Book Value =
Earnings per Share
3. Dividend yield. The dividend yield measures the return to shareholders received
in the form of dividends. It is defined as follows:
Dividend per Share
Dividend Yield =
Market Price per Share
Cash Flow.
Cash flow is important for what it tells us about a company's financing needs. A strong
positive cash flow enables a company to fund future investments without having to
borrow money from bankers or investors. This is desirable because the company avoids
the need to pay out interest or dividends.
A weak or negative cash flow means that a company has to turn to external sources to
fund future investments. Generally,
companies in strong-growth industries often find themselves in a poor cash flow
position (because their investment needs are substantial),
whereas successful companies based in mature industries generally find themselves in a
strong cash flow position.
Cash flow is calculated by adding back its depreciation provision to profits after interest,
taxes, and dividend payments.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
27 Comprehensive Exam
1. If this figure is insufficient to cover proposed new-investment expenditures, the
company has little choice but to borrow funds to make up the shortfall or to curtail
investments.
2. If this figure exceeds proposed new investments, the company can use the excess
to build up its liquidity (that is, through investments in financial assets)
Profitability trend:
Trends reflect the development of the same financial figures from year to your and it
indicates a quite high improvement in the company results
Strategic Audit - ___________
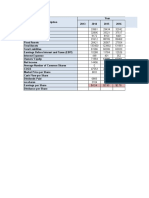
Revenues improvement from 247m in year 2002 to 380m in year 2004
Net income improvement from 74,9 m in year 2002 to 126.2 million in year 2004
All the above ratios are indicating improvement in the company results with time.
In general the indicators of the organization's financial position show a very strong
financial position when detailed study can be conducted it can be added to the
company's basic strengths.
3. Research and Development
Strengths
Continuously looking for new products and services. (+)
Actively implementing the largest technologies to offer innovative services. (+)
An innovator in the industry. (+)
There is a research of competitors and their strategies in order to learn from their mistakes.
There is a research to keep close check on demographics of their consumers.
XXX industry is perceived as offering limited choice of service providers and having a regulator that is
not responsive or transparent. (-)
4. Operations and Logistics
Strengths
up-to-date computer system for everyday operations and inventory control.
Optimized use of distribution channels and proximity of outlets to distribution centers save cost and
guarantee efficient logistical support to operations.
Strategically located distribution centers
Policy to deal only with top officials of producers to ensure price and quality.
Optimize transportation schedules
Track inventory deployment
Track product availability
Develop and maintain delivery service policy
Plan, transport, and deliver product
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
28 Comprehensive Exam
5. Human Resources
Strengths
Corporate policy dedicated to improving employee involvement and expertise.
Special leadership management style
Seminars and training programs to ensure quality in employee performance
Special awards for employee performance lead to a high degree of employees’
involvement in company affairs and management. Employees participate in
decision-making.
Stress on communication among employees.
Employees are hired locally and are provided with training programs.
There seems to be a promotion from within.
maintained a stable growth of the number of employees.
Strategic Audit - ___________
Employees encouraged to ask management questions and offer suggestions.
Weaknesses
May create an atmosphere where employees think they have all the answers or
can do anything they desire.
24-hour stores; threats to unions
1. Human Resource Objectives
The human resource objective reflects the intention of the senior management (strategy) with a
balance to the related topics such as HR functions, society, governing rules, etc.
1. Organizational objectives:
ensure that the organization always has people with the right abilities available to do the right work to
achieve the required organization effectiveness and objectives
2. Functional Objectives:
maintain the department’s contribution at a level appropriate to the org. needs
3. Societal Objective :
respond ethically and socially to the challenges of the environment while minimizing the negative impact
of such demands on the organizations
4. Personal objectives:
assist retain and motivate the employees for achieving their personal goals and guide them to better
achievement
2- Human Resource Strategy:
The human resource Strategy addresses
recruit a low skill, low paid, high turnover employees or
recruit a high skill, high paid, low turnover employees.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
29 Comprehensive Exam
The organization policy to go international must be a highly paid high skill, low turn over employees to
improve creativity of the employees and the turnover must be kept at its minimum levels .
3-Human ResourcePrograms
- Preparation and selection: Review of the employees' job description, job specification and
job performance standard to match the change of the organization.
- Succession Planning: the preparation of the company succession plan will enable the
organization to stand any future challenges.
Strategic Audit - ___________
- Career Path and development: the preparation of the career path for the employees will
help the stability and minimize the turnover of the employees.
- Recruitment: designing a good recruitment process (Selection, interviews) with a high level of
orientation to ensure the compatibility of the new recruited employees with the existing culture to
achieve organizational objectives.
- Training and development: on-the- job” training, Off-the-Job training and Provide career
planning assistance for employees.
- Incentive system will ensure the motivation of the employees to better performance (linking
incentive to production)
4-Human Resource Policies
Compensation Policies and protection:
- What employees get in exchange for their contribution to the organization”, maintain, retain
productive workforce, achieve the org. objectives
Testing:
- Will ensure the qualification of the candidates and their fit in the organization culture.
- Managing workforce diversity
- international operations means dealing with more diversity in home and abroad
National origin, culture, religions, ages, values, skills, educational level, gender, workforce
demographics, cultural and attitudinal diversity
(e.g societal attitude to the work of women create family programs, parental leave, flexible
working hours)
if the organization is going internationally Training programs related to diversity:
o Cultural diversity sensitivity training
o Communication across cultures
o Gender issues training
Enhance employee participation:
- in implementing strategy, all employees from different organizational levels must make a meaningful
contribution in decision-making .this will increase employee's involvement and enhance their working life
balance.
Enhance employee organizational commitment:
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
30 Comprehensive Exam
- by increasing job involvement, which results in lower levels of absenteeism and turnover .
Implementing employee recognition programs:
- starting with personal attention and ending with appreciation for a job well done.
Develop effective staffing plans
- supporting the organizational strategies by allowing to fill job openings proactively (in terms of
number and the quality of the workforce for the short and long term) VIP in case of international
operations.( if the company is multinational)
-
5-Human Resource challenge
- International challenge:
- finding executives and staff with the adequate level of international experience
Strategic Audit - ___________
- Technological challenge:
- assess how jobs and jobs skills are affected by technology that might cause more worker alienation ,
- Organizational challenges:
- (unions, information systems, organizational culture
- {adjust objectives to match the culture and managing conflicts)
6. Information Systems
Information technology is the combination of the hardware, software, networks and data base
supporting the utilization of the informatio and making communication easy, immediate, and
inexpensive The increasing use of IT means that individuals and teams working in different
departments, different floors, different locations, or even different country can easily
communicate together for the best of the organization .
Strengths
very sophisticated information system in inventory control
Computer links between stores and general offices ensure accurate and timely
communication.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
31 Comprehensive Exam
Internal Factor Analysis Summary IFAS (strengths)
Internal Factorss Comments
Potential internal strengths
Strategic Audit - ___________
Many product lines?
Due to the global expansion
Broad market coverage? Will increase the companies growth and
reduce risk
Manufacturing competence?
Good marketing skills?
Good materials management systems?
Like sport field
R&D skills and leadership?
Will reduce risk and increases profit
Information system competencies
Human resource competencies?
Brand name reputation?
Portfolio management skills?
Cost of differentiation advantage?
New-venture management expertise?
Appropriate management style?
Appropriate organizational structure?
Appropriate control systems?
Good financial management?
Ability to manage strategic change?
Well-developed corporate strategy?
Quality Products
Horizontal Integration
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
32 Comprehensive Exam
Research and Development
Cost awareness
Internal Factor Analysis Summary IFAS (weaknesses)
Internal Factorss Comments
Strategic Audit - ___________
Potential internal weaknesses
Obsolete, narrow product lines?
Due to the global expansion
Rising manufacturing costs? Will increase the companies growth and
reduce risk
Decline in R&D innovations?
Poor marketing skills?
Poor materials management systems?
Like sport field
Loss of customer good will?
Will reduce risk and increases profit
Inadequate information systems?
Inadequate human resources?
Loss of brand name capital?
Growth without direction?
Bad portfolio management?
Loss of corporate direction?
Infighting among divisions?
Loss of corporate control?
Inappropriate organizational structure and
control systems?
High conflict and politics?
Poor financial management?
Cultural differences
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
33 Comprehensive Exam
Experienced Management
Company Structure
Sales and marketing capabilities
E. Analysis of Strategic Factors (SWOT)
ㄱ Situation Analysis
Strategic Audit - ___________
Risk for the multinational company located in Egypt
Political Risk
the country has just experiencing a new era of the president’s election the change it self is new to the
country and affecting allot the whole business environment in Egypt.
Currency Risk
where the Egyptian pound is almost Pigged to the Dollar (although we have a free exchange rate) any
change of the exchange rate among the main currencies will effect the international sales, as the
European Union have been facing difficulties in exporting since the large appreciation of the EURO with
respect to all other hard currencies and it is taking a serious measures to depreciate the EURO to regain
its exporting advantage
Sales Risk
The companies in other countries have a high potential to sell more than an organization operates from
its headquarter in Egypt in more than a foreign country. It is driving its substantial sales and profit from
many international sources
Operational Risk
- where the new emerging markets such as Qatar, United Arab of Emirates are offering extremely
competitive packages to the Egyptian Market and that would put a high burden on the Egyptian
industry to match.
ㄱ Review of Mission and Objectives
***the organization objectives extracted from the case describes and quantifies the
organization operating objectives in the following fields
1- Cost reduction; highlighting the cost awareness of the organization with good
improvement in figures.
2- Innovation; as one of the competitive advantage in the pharmaceutical business.
3- Co-operation; as an objective to increase enthusiasm between different parts of
the organization
****the operating objectives of the company
1- Profitability
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
34 Comprehensive Exam
2- Efficiency
3- Growth
4- Shareholder wealth
5- Reputation
6- Contributions to the employees
7- Market leadership
8- Technological leadership
9- Survival (avoiding bankruptcy)
F. Strategic Alternative and Recommended Strategy
Use TWOS Matrix and /or the SPACE Matrix to draw the strategic alternatives
Strategic Audit - ___________
TWOS Internal Factors
Strengths Weaknesses
Strong Growth International Market Adaptation
Experianced Top Management Liquidity
Employee Relations Financial position
Financial position Global Position
Internatioal Oriantaion Manufacturing Facilities
Need to adapt to local needs in
Strong Market Position/ Image – Brand
international markets
Experienced top management and Weak Liquidity ratios and increased
employees' relations liabilities
A strong, respected and trusted brand
Distribution Channels
name
Vertical integrations
Corporate Culture
Distribution
External Factors
Opportunities
High Entry barrier ,
High Entry Barriers
New Markets
Diversificdation of
product line Using the strengths of its financial position Focus on training and qualified sessions
Decreased and international orientation to take the for overcoming the different in cultures
competition opportunity of economic development and trainning for the sales staff or
Good use of and diversify its products lines hiring new professional sales team
Technology
Expansion in
international markets
Low Competition
Economic
Development
Threats
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
35 Comprehensive Exam
Government
Regulations
Competition Reduce the production costs to eliminate Working on decreasing the effects of
Seasonal sales the effects of the government fixations the market/ threats and minimizing the
keeping the same quality standards to weakness of the firm while working on
New Products
keep the same image of the company eliminate them
Advances
Increased Specialty of
rivals
Strategic Audit - ___________
A- Porter's Generic Strategies:
Type of strategies Ways to achieve the strategy Benefits Possible problems
Cost Leadership: Being Size and economies of scale The ability to: Vulnerability to even
the low-cost competitor Globalization outperform lower cost operators
in an industry while Relocating to low-cost parts of the world rivals Possible price wars
maintaining satisfactory Modification/simplification of designs erect The difficulty of
profit margins. Greater labour effectiveness barriers to sustaining it in the long
Greater operating effectiveness entry term
Strategic alliances resist the
New source of supply five forces
Government Subsidies-------
New Delivery Methods------
Production Innovations------
Obtain inexpensive raw materials
Create efficient operations--
Control overhead costs------
Avoid marginal customers-
Focus(Niche): Concentration upon on or a small A more detailed Limited opportunities for sector
Advantage achieved number of a strong and specialist understanding of growth
when a firm target and reputation particular segments The possibility of outgrowing
effectively serve a small Used by small companies with limited The creation of the market
segment of the market resources barriers to entry The decline of the sector
used in a limited geographic market A reputation for A reputation for specialization
focused on a specific product line specialization which ultimately inhibits
The ability to growth and development into
concentrate efforts other sectors
Differentiation: The creation of strong brand identities A distancing from The difficulties of sustaining the
Advantage achieved and Image others in the market bases for differentiation
when a firm provides The creation of a Possibly higher costs
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
36 Comprehensive Exam
something that is The consistent pursuit of pursuit of major competitive The difficulty of achieving true
unique and valuable to those factors which customers perceive advantage and meaningful differentiation
buyers beyond simply to be important Flexibility
offering a lower price High performance in one or more of a
spectrum of activities
Strong dealer network
Product reliability and Servic
SPACE
Internal Strategic Position
Strategic Audit - ___________
Financial Strength (FS)
Return on investment,Leverage,Liquidity,Working capital,Cash flow
External Strategic Position
Environmental Stability (ES)
Technological changes Rate of inflation Demand variability
Price range of competing products Barriers to entry
Competitive pressure Price elasticity of demand Ease of exit from market
Risk involved in business
Internal Strategic Position
Competitive Advantage CA
Market share Product quality Product life cycle Customer loyalty
Competition’s capacity utilization Technological know-how
Control over suppliers & distributors
External Strategic Position
Industry Strength (IS)
Growth potential Profit potential Financial stability
Technological know-how Resource utilization Ease of market entry
Productivity, capacity utilization
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
37 Comprehensive Exam
Products
Ansoff'
Markets
Existing Modified New
Existing Sell more of our Modify our current Design new
existing products to products and sell products that will
our existing types more of them to appeal to our
of customers. our existing existing customers.
(Market customers. (Product (New product
penetration) modification) development)
Modified Enter and sell our Offer and sell Design new
Strategic Audit - ___________
products in other modified products products for
geographical areas. to new geographical prospects in new
(Geographical markets. geographic areas.
expansion)
New Sell our existing Offer and sell Design new
products to new modified products products to sell to
types of customers. to new types of new types of
(Segment invasion) customers. customers.
(Diversification)
+
6 FS
+
5
+ Aggressive
Conservative 4
+
3 Intensive
Intensive + Integration
Concentric Diversification
2 Diversification
+
1
Defensive
CA IS
- - - - - - - + + + + + +
6 5 4 3 2 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6
-
2
Competitive
Retrenchement -
Concentric Diversification Intensive
3 Integration
-
4
- ES
5
-
6
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
38 Comprehensive Exam
ㄱ Strategic Alternative
ㄱ Consider stability, growth and retrenchment as corporate strategies
ㄱ Consider cost leadership and differentiation as business strategies
ㄱ Consider any important functional strategic alternative that might need to be
reinforced as alternative strategy
The company's internal and external environmental scanning reflects its strengths over
its weaknesses and its opportunities over its threats.IF The organization has a very
strong market position with a high market share and strong and improving financial
position it could adopt growth strategy and vise verca
Strategic Audit - ___________
A. Strategic Direction Alternatives
1. Maintain Current Strategy (Horizontal Growth)
Pro: Create a larger market share. Target states and countries currently not serviced.
Also, add new Business in new areas
Con: Requires more debt load.
2. Growth Through Concentric Diversification
Purchase other targeted parks and add Disney distinctive touch.
Pro: Already have excellent experience in large-scale, firm’s operations. Does not
react heavily to business cycles.
Con: Expensive. Not clear if firm’s can financially acquire new parks.
3. No Growth
Maintain current operations.
Pro: Not expensive. Revenues continue to increase. Keep an eye on other
competitors.
Con: Not expanding to markets that are easily accessible. Possibly let market share
be absorbed by other competitors.
B. By using porter’s generic competitive strategies model
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
39 Comprehensive Exam
Lower cost strategy, which is the ability of a company or business unit to design,
produce, and market a comparable product more efficiently than its competitors.
Pros: Will increase market share on the short run
Cons: Requires strong financials
Differentiation Strategy, which is the ability to provide unique and superior value to
the buyer in terms of product quality, special features, or after sale service.
Pros: Will increase market share on the long run
Cons: Rivals are already adopting a differentiation strategy on a product and a market
segment levels.
Strategic Audit - ___________
;
Industry Generic Strategies
Force Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus
Ability to cut price
Customer loyalty can Focusing develops core
Entry in retaliation
discourage potential competencies that can act as an
Barriers deters potential
entrants. entry barrier.
entrants.
Large buyers have less
Ability to offer Large buyers have less power to
Buyer power to negotiate
lower price to negotiate because of few
Power because of few close
powerful buyers. alternatives.
alternatives.
Suppliers have power because of
Better insulated Better able to pass on low volumes, but a
Supplier
from powerful supplier price increases to differentiation-focused firm is
Power
suppliers. customers. better able to pass on supplier
price increases.
Customer's become
Can use low price Specialized products & core
Threat of attached to differentiating
to defend against competency protect against
Substitutes attributes, reducing threat
substitutes. substitutes.
of substitutes.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
40 Comprehensive Exam
Rivals cannot meet
Better able to Brand loyalty to keep
Rivalry differentiation-focused customer
compete on price. customers from rivals.
needs.
ㅅ Recommended Strategy
Explain what are the most feasible alternative strategies available to the firm
and what are the pros and cons of each?
Strategic Audit - ___________
1-Market-leader strategies
1- EXPANDING THE TOTAL MARKET
a-New Users
market-penetration strategy,
new market- segment strategy-
geographical -expansion strategy
b-New Uses
discovering and promoting new uses for the product.
c-More Usage
convince people to use more products per use occasion.
2-Market-challenger strategies
CHOOSING A SPECIFIC ATTACK STRATEGY
Price discount:
Lower price goods
Prestige goods
Product proliferation
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
41 Comprehensive Exam
Product innovation
Improved services:
Distribution innovation
Manufacturing-cost reduction
Intensive advertising promotion
3-Market-follower strategies
present similar offers to buyers by copying the leader.
Strategic Audit - ___________
Imitator: The imitator copies some things from the leader
Adapter: The adapter takes the leader’s products and adapts
4-Market-nicher strategies
The Nichers have three tasks to achieves high margin,not like mass- high volume .:
creating niches,
expanding niches,
protecting niches.
G. Implementation
Management commitment
Employee empowerment
Reward System
Integrating training
Process improvement
Quality at source
The implementation process has already been started by Top management ,as follow.
•Provide financials to implement the recommended strategies as outlined above.
•Board members with more global business experience should be recruited with an eye
on the future and market potential in local and international markets.
Develop more programs that invest in employees’ capability to handle international
operations and increased competition locally and internationally.
•Develop more customer-retail relationship programs
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
42 Comprehensive Exam
•Create new job rotational programs locally and internationally within for more
exposure of employees and creativity.
•A TQM department should be structured to ensure quality and customer service
leadership. As mentioned before the company has implemented several
principles of total quality management philosophy, such as:
1. Management commitment: creating committed management to the process of
continuous improvement, a dedication to empowering people to change, and to
periodically raise the goals for improvement. Adoption and communication of
TQM: using tools like mission statement and slogans.
2. Employee empowerment: giving workers the responsibility for improvements
and the authority to make changes to accomplish them.
3. Reward System: is the missing link that motivates managers and employees to
Strategic Audit - ___________
"walk the talk" and use TQM to the fullest and it's divided into two groups,
monetary and non-monetary rewards.
4. Integrating training: includes different aspects of TQM elements, team skills and
problem-solving techniques.
5. Process improvement: process of reducing waste and cycle times in all areas
through cross-departmental process analysis.
6. Quality at source: the philosophy of making each worker responsible for the
quality of his/her work
H. Evaluation and Control
is a leader in the industry for ,,,,,,,,. All they have to do is continue with
periodic management evaluations and rely on their distinctive competences of
customer service and achieve better utilization of the company current & fixed
assets.
I. Attachments
ㄱ SFAS
ㄴ International entry options
ㄷ marketing plan outline
ㄹ 4PS
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
43 Comprehensive Exam
Strategic Audit - ___________
International entry options:
-Exporting and importing
-Licensing Arrangement: An agreement in which the licensing firm
grants right to another firm in another country or market to produce
and/or sell the original company’s products.
-Franchising: franchiser grant rights to another company to open a
retail using the name.
-Joint Venture: Cooperative business activity formed of two or more
separate organization to form a new independent business entity and
allocates ownership and liabilities.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
44 Comprehensive Exam
-Acquisition: Purchasing another company already operating in the
market or in the area.
-Mutual Service Consortia: Partnership of similar companies in
similar industry who pool their resources to gain a benefit that is too
expensive for each of them separately
-Value Chain Partnership: A strong and close alliance in which a
company forms a long term arrangement with a key supplier or a
distributor for mutual advantage.
Strategic Audit - ___________
Marketing plan outline
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
45 Comprehensive Exam
Business Mission
Statement
Objectives
Situation or
SWOT Analysis
Strategic Audit - ___________
Marketing
Strategy
Target Market
Strategy
Marketing
Product MixDistributionn
n
Promotion Price
Implementation
Evaluation
Control
ㅁ 4PS
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
46 Comprehensive Exam
4Ps
Product and Pricing The The
Service Policies Promotional Distribution
Strategies and Plan Plan
Strategies
A- Promotion:
Advertising Sales Public Sales Force Direct
Promotion Relations Marketing
Print and Contests, Press kits Sales Catalogs
Strategic Audit - ___________
broadcast games, sweep presentations
ads
Packaging- Stakes, lotteries Speeches Sales Mailings
outer meetings
Packaging Premiums and Seminars Incentive Telemarketing
inserts gifts programs
Motion Sampling Annual Samples Electronic
pictures reports shopping
Brochures Fairs and trade Charitable Fairs and TV shopping
and shows donations trade shows
booklets
Posters and Exhibits Sponsorships Fax mail
leaflets
Directories Demonstrations Publications E-mail
Reprints of Coupons Community Voice
ads relations
Billboards Rebates Lobbying
Display Low-interest Identity
signs financing media
Point-of- Entertainment Company
purchase magazine
Displays Trade-in- Events
allowances
Audio- Continuity
visual programs
material
Symbols Tie-ins
and logos
Videotapes
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
47 Comprehensive Exam
B- Product & Service Strategy:
1. How do people become aware of their need for your products or service?
2. How do consumers find your offering?
3. How do consumers make their final selections?
4. How do consumers order and purchase your product or service?
5. How is your product or service delivered?
6. What happens when your product or service is delivered?
7. How is your product installed?
8. How is your product or service paid for?
9. How is your product stored?
10. How is your product moved around?
Strategic Audit - ___________
11. What is the customer really using your product for?
12. What do customers need help with when they use your product?
13. What about returns or exchanges?
14. How is your product repaired or serviced?
15. What happens when your product is disposed of or no longer used?
C- Distribution & Place:
Channel Decisions:
• Channels Coverage
• Assortments
• Locations
• Inventory
• Transport
Channel design decisions:
• Push strategy
• Pull strategy
Establish Objectives and Constraints
Identify Major Channel Alternatives
o Types of Intermediaries
o Number of Intermediaries
• Exclusive distribution
• Exclusive dealing
• Selective distribution
• Intensive distribution
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
48 Comprehensive Exam
D-Pricing Strategies
Pricing is one of the most important elements of the marketing mix, as it is the only mix, which generates
a turnover for the organisation. The remaining 3p’s are the variable cost for the organisation.
It costs to produce and design a product, it costs to distribute a product and costs to promote it. Price
must support these elements of the mix. Pricing is difficult and must reflect supply and demand
relationship. Pricing a product too high or too low could mean a loss of sales for the organisation.
Pricing should take into account the following factors:
1. Fixed and variable costs.
Strategic Audit - ___________
2. Competition
3. Company objectives
4. Proposed positioning strategies.
5. Target group and willingness to pay.
Pricing Strategies
An organisation can adopt a number of pricing strategies. The pricing strategies are
based much on what objectives the company has set itself to achieve.
ㄱ Penetration pricing: Where the organisation sets a low price to increase sales and
market share.
ㄴ Skimming pricing: The organisation sets an initial high price and then slowly lowers
the price to make the product available to a wider market. The objective is to skim
profits of the market layer by layer.
ㄷ Competition pricing: Setting a price in comparison with competitors.
ㄹ Product Line Pricing: Pricing different products within the same product range at
different price points. An example would be a video manufacturer offering different
video recorders with different features at different prices. The greater the features
and the benefit obtained the greater the consumer will pay. This form of price
discrimination assists the company in maximising turnover and profits.
ㅁ Bundle Pricing: The organisation bundles a group of products at a reduced price.
ㅂ Psychological pricing: The seller here will consider the psychology of price and the
positioning of price within the market place. The seller will therefore charge 99p
instead £1 or $199 instead of $200
ㅅ Premium pricing: The price set is high to reflect the exclusiveness of the product.
An example of products using this strategy would be Harrods, first class airline
services, porsche etc.
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
49 Comprehensive Exam
ㅇ Optional pricing: The organisation sells optional extras along with the product to
maximise its turnover. This strategy is used commonly within the car industry.
Strategic Audit - ___________
1. Conclusion & Recommendations
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
50 Comprehensive Exam
Problem solution Strategy
1. Current distributors – expensive or unreliable
Availability of quality distributors –
Gain Control
2. limited Firm competes in industry expected to grow
Over --
markedly Forward Integration Strategies
Distributors or
3. Firm has both capital & HR to manage new business of
Retailers
distribution
4. Current distributors have high profit margins
Strategic Audit - ___________
5. Current suppliers – expensive or unreliable
6. # of suppliers is small;
Ownership or
7. # competitors is large
Control Firm’s Backward Integration
8. High growth in industry sector
suppliers Strategies
9. Firm has both capital & HR to manage new business
10. Stable prices are important
11. Current suppliers have high profit margins
12. Gain monopolistic characteristics w/o federal government
challenge
Ownership or
13. Competes in growing industry
Control Firm’s Horizontal Integration
14. Increased economies of scale – major competitive
competitors Strategies
advantages
15. Faltering due to lack of managerial expertise or need for
particular resource
Increased
Market Share :
16. Current markets not saturated Present
17. Usage rate of present customers can be increased products/
significantly services
Market Penetration Strategies
18. Shares of competitors declining; industry sales increasing Present
19. Increased economies of scale provide major competitive markets
advantage Greater
marketing
efforts
20. New channels of distribution – reliable, inexpensive, good New Markets
quality Present
21. Firm is successful at what it does products/servi Market Development
22. Untapped/unsaturated markets ces to new Strategies
23. Excess production capacity geographic
Basic industry rapidly becoming global areas
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
51 Comprehensive Exam
Increased
Sales
24. Products in maturity stage of life cycle Improving
25. Industry characterized by rapid technological development present
26. Competitors offer better-quality products @ comparable products/servi Product Development
prices ces Strategies
27. Compete in high-growth industry Developing
Strong R&D capabilities new
products/servi
ces
28. Compete in no/slow growth industry
Addition
New & related products increases sales of current products Concentric Diversification
New & related
Strategic Audit - ___________
29. New & related products offered at competitive prices Strategies
products/servi
30. Current products—decline stage of product life cycle
ces
31. Strong management team
Addition
32. Declining annual sales & profits
New &
Capital & managerial ability to compete in new industry Conglomerate Diversification
unrelated
33. Financial synergy between acquired and acquiring firms Strategies
products/servi
34. Current markets for present products - saturated
ces
35. Adding new products/services would significantly increase
Addition New
revenues
& unrelated
36. Highly competitive and/or no-growth industry; low margins Horizontal Diversification
products/servi
& returns Strategies
ces for current
37. Current distribution channels can be used
customers
38. New products have counter cyclical sales patterns
39. Failed to meet objectives & goals consistency; has distinctive
Regrouping
competencies
Cost & asset
40. Firm is one of weaker competitors Inefficiency, low
reduction to
profitability, poor employee morale, pressure for Retrenchment Strategies
reverse
stockholders
declining sales
41. Strategic managers have failed
& profit
42. Rapid growth in size; major internal reorganization necessary
43. Retrenchment failed to attain improvements
44. Division needs more resources than are available Selling a
45. Division responsible for firm’s overall poor performance division or part
Divestiture Strategies
46. Division is a mis-fit with organization of an
47. Large amount of cash is needed and cannot be raised organization.
through other sources
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
52 Comprehensive Exam
Selling
48. Retrenchment & divestiture failed Company’s
49. Only alternative is bankruptcy assets, in Liquidation Strategies
50. Minimize stockholder loss by selling firm’s assets parts, for their
tangible worth
Strategic Audit - ___________
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
53 Comprehensive Exam
Examples of symptoms and cases in marketing:
SYMPTOMS CAUSES
Declining market share Outdated product
New competition
Shifting demographics
Inappropriate pricing
Strategic Audit - ___________
Decline in profits Ineffective promotions
Escalating distribution costs
Improper channel structure
Inability to gain channel Lack of product differentiation
participation Misdirected promotions
Inferior product image
Heavy turnover in Lack of proper sales incentives
sales force Improper allocation of territories
Unrealistic sales quotas
Decline in company sales Decline in industry sales
Increased competition
# Symptoms plausible cause
1 ?Decline in sales Better price strategy of competitors
Better Varieties introduced by competitors
Changes in customer preferences
Decline in industry sales
2 ?Loss of market share Better promotion strategy of competitors
Up dated brands introduced by competitors
Changes in customer preferences
Lack of sales team effectiveness
3 ?High turn over in sales dpt In effective sales compensation package
Improper territories allocation
Unfavourable work conditions
4 ?Failure of New product launch In effective promotion strategy as
Improper advertising
Bad-Positioning
Lack of differentiation
Batter Available alternative in the market
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
54 Comprehensive Exam
5 Failure of newly opened outlet/ Improper selection of Location or area due
?branch : to
Area demographics
Area customers prefernces
Improper out let design
Improper out let Parking
Presence of strong competitor outlet
Strategic Audit - ___________
Student Name: Ali,Amr,Mostafa,Essam,Mostafa hosny
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Panchamrut DairyDocument52 paginiPanchamrut DairyAksha Khan50% (2)
- CFAP 3 - Study Manual (Final)Document243 paginiCFAP 3 - Study Manual (Final)danishjaved133841Încă nu există evaluări
- Mrc2213 Strategic ManagementDocument59 paginiMrc2213 Strategic ManagementDarylGamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFAC Guide To Quality Control For SMPsDocument162 paginiIFAC Guide To Quality Control For SMPsakosi LEIANÎncă nu există evaluări
- QTBH (3) - Sao ChépDocument60 paginiQTBH (3) - Sao ChépAnh KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- GM 323 Business Policy and Strategic Management FinalDocument56 paginiGM 323 Business Policy and Strategic Management FinalCastor MfugaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIS Management Information SystemsDocument89 paginiMIS Management Information SystemskareshmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attachment 2Document31 paginiAttachment 2Anna AkhayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aml CFT HandbookDocument107 paginiAml CFT HandbookBhavna Devi BhoodunÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Marketing 250 Feasibility Study: Tutor Name: Sean LeeDocument42 paginiInternational Marketing 250 Feasibility Study: Tutor Name: Sean LeeAshwine KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Dynamics & Work TeamsDocument29 paginiGroup Dynamics & Work TeamsbhavikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rohit Review CH 1-3Document46 paginiRohit Review CH 1-3IT'S SIMPLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estudio Australia 2010Document374 paginiEstudio Australia 2010Carlos Isla RiffoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Policy PFIRADocument66 paginiPolicy PFIRATauseefAhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business FundamentalsDocument329 paginiBusiness FundamentalsMohd Anas100% (1)
- HRM For Exit Exam - 1Document85 paginiHRM For Exit Exam - 1Malkamu Lobango100% (1)
- Commonwealth of Learning Executive MBA/MPA SCOM 4611: Quality ManagementDocument223 paginiCommonwealth of Learning Executive MBA/MPA SCOM 4611: Quality ManagementDeepak KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Training Report-MOHD JULAIHI BIN JAYADocument56 paginiIndustrial Training Report-MOHD JULAIHI BIN JAYAJULAI mjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adan FinalDocument32 paginiAdan FinalHamza JilaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAU 10 Years Strategic PlanDocument114 paginiAAU 10 Years Strategic PlanAbebe Tilahun100% (9)
- Gemechu FinalDocument49 paginiGemechu Finalmaheder wegayehuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jon M. Quigley (Author) - Shawn P. Quigley (Author) - Continuous and Embedded Learning For Organizations-Taylor & Francis (2020)Document295 paginiJon M. Quigley (Author) - Shawn P. Quigley (Author) - Continuous and Embedded Learning For Organizations-Taylor & Francis (2020)yayangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post-Harvest Loss Management StrategyDocument90 paginiPost-Harvest Loss Management StrategyAddisuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balanced Scorecard Case Study: Group AssignmentDocument40 paginiBalanced Scorecard Case Study: Group AssignmentFalak GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - MU Self-StudyDocument165 pagini1 - MU Self-StudyRougher Samonte BañaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSRs 2023 FInalDocument68 paginiNSRs 2023 FInalHenrique LeocádioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Social Responsibility and Access to FinanceDocument3 paginiCorporate Social Responsibility and Access to FinanceAlene Amsalu100% (1)
- MB 301 - Strategic Mgmt-Edit1-210 PagesDocument210 paginiMB 301 - Strategic Mgmt-Edit1-210 PagesManoj Kumar0% (1)
- Path Evaluation ReportDocument118 paginiPath Evaluation ReportLemonWizzFizz XDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Management, Corporate Social Responsibility and Customers: An Empirical InvestigationDe la EverandCorporate Management, Corporate Social Responsibility and Customers: An Empirical InvestigationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental and Social Management Framework (Esmf) Update - Women Entrepreneurship Development Project Additional FinancingDocument75 paginiEnvironmental and Social Management Framework (Esmf) Update - Women Entrepreneurship Development Project Additional Financingmichaele gobezieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jollibee Food Corporation Strategic Management PlanDocument99 paginiJollibee Food Corporation Strategic Management Planmichelle angela maramag100% (3)
- Turtle Project 2016-2018 PDFDocument50 paginiTurtle Project 2016-2018 PDFGuselsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 001 2018 4 Study-GuideDocument154 pagini001 2018 4 Study-GuideDINEO PRUDENCE NONGÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1 1 474 1692 PDFDocument115 pagini10 1 1 474 1692 PDFUsama WalyÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Marketing Final ReportDocument9 paginiInternational Marketing Final Reporteleas abidÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Report CabilDocument304 paginiFor Report Cabiltarun41873300Încă nu există evaluări
- Coca-Cola India Industry and Company ProfileDocument2 paginiCoca-Cola India Industry and Company ProfileBellapu Durga vara prasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Employee Retention Techniques of CompanyDocument87 paginiA Study On Employee Retention Techniques of CompanyRajesh BathulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitiveness and InnovationDocument40 paginiCompetitiveness and Innovationzuzka0120Încă nu există evaluări
- Tesla Strategy PDFDocument98 paginiTesla Strategy PDFvicente pochÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Useful is the Information Ratio to Evaluate the Performance of Portfolio Managers?De la EverandHow Useful is the Information Ratio to Evaluate the Performance of Portfolio Managers?Încă nu există evaluări
- GCM Pandemic Continuity of Operations 02.27.2020Document42 paginiGCM Pandemic Continuity of Operations 02.27.2020ohonestÎncă nu există evaluări
- (George Swartz CSP) Job Hazard Analysis A Guide T (BookFi) PDFDocument232 pagini(George Swartz CSP) Job Hazard Analysis A Guide T (BookFi) PDFOleg SlyussarevÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRD Press 50 Activities For Developing People Skills PDFDocument283 paginiHRD Press 50 Activities For Developing People Skills PDFSteve EvansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Practices of Flour Milling FirmsDocument102 paginiInventory Practices of Flour Milling FirmsatifamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summery Strategic MarketingDocument69 paginiSummery Strategic Marketingmohaawad2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Ronald SimiyuDocument86 paginiRonald SimiyuSimiyu RonaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- s192 - The Open Group Agile Architecture FrameworkDocument118 paginis192 - The Open Group Agile Architecture FrameworkFaqih ZulfikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business School Career of Administration and International BusinessDocument30 paginiBusiness School Career of Administration and International BusinessCaroline MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lippo Shop 18 Apr 01 BylippoDocument88 paginiLippo Shop 18 Apr 01 BylippoRizkyAufaS100% (1)
- PHD ThesisDocument256 paginiPHD ThesiscasaliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSRs Final 2020 Publication - Updated CoverDocument72 paginiNSRs Final 2020 Publication - Updated Coveramirkhakzad498Încă nu există evaluări
- Meta FacebookDocument101 paginiMeta Facebookmohamed saiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracon Trading PLCDocument61 paginiTracon Trading PLCRamon Colon100% (1)
- BBA ProjectDocument88 paginiBBA Projectjafir94Încă nu există evaluări
- Universal Jurisdiction Law and Practice in FinlandDocument35 paginiUniversal Jurisdiction Law and Practice in FinlandAchraf RabadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Awach HR Policies & Procedures Manual - Final VersionDocument48 paginiAwach HR Policies & Procedures Manual - Final VersionNoah Gunn100% (2)
- Strategy PDFDocument33 paginiStrategy PDFabraam100% (1)
- Internal and External Analysis with SWOT, TOWS, SPACE and Financial Statement SummaryDocument7 paginiInternal and External Analysis with SWOT, TOWS, SPACE and Financial Statement SummaryAhmed El-HashemyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA Exam StrategiesDocument97 paginiMBA Exam StrategiesabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Don't Forget - Amr PDFDocument24 paginiDon't Forget - Amr PDFabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saudi Steel Pipe Company - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Victor Sohmen Case Author: Salem Al-GhamdiDocument19 paginiSaudi Steel Pipe Company - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Victor Sohmen Case Author: Salem Al-GhamdiabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive FrameworkDocument4 paginiComprehensive FrameworkabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pestle PDFDocument26 paginiPestle PDFabubakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Ratios ComprehensiveDocument38 paginiFinancial Ratios ComprehensiveabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratio Analysis With Comment MOSTAFA HOSNY VERY GOOOODDocument21 paginiRatio Analysis With Comment MOSTAFA HOSNY VERY GOOOODabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arab Academy For Science, Technology & Maritime Transport Advanced Management Institute (AMI)Document10 paginiArab Academy For Science, Technology & Maritime Transport Advanced Management Institute (AMI)abraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study Strategic Audit: (XYZ Company Inc.)Document27 paginiA Case Study Strategic Audit: (XYZ Company Inc.)abraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gulf Upstream Manufacturing Company - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Victor Sohmen Case Author: C.P. RaoDocument19 paginiGulf Upstream Manufacturing Company - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Victor Sohmen Case Author: C.P. RaoabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- H.R Management SummaryDocument17 paginiH.R Management SummaryabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Egypt PEST AnalysisDocument11 paginiEgypt PEST Analysisabraam100% (1)
- Financial Analysis Case Study Key RatiosDocument1 paginăFinancial Analysis Case Study Key RatiosabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal and External Analysis with SWOT, TOWS, SPACE and Financial Statement SummaryDocument7 paginiInternal and External Analysis with SWOT, TOWS, SPACE and Financial Statement SummaryAhmed El-HashemyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 06 Merck CompanyDocument18 paginiCase 06 Merck CompanyabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 10 KPCDocument19 paginiCase 10 KPCabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 01 Moderna TextilesDocument20 paginiCase 01 Moderna Textilesabraam100% (1)
- Case 04 Kraft FoodsDocument18 paginiCase 04 Kraft FoodsKad Saad100% (2)
- Comprehensive OutlineDocument10 paginiComprehensive OutlineabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 07 Elsewedy ElectricDocument20 paginiCase 07 Elsewedy Electricabraam0% (2)
- Case 05 JohnsonDocument19 paginiCase 05 Johnsonabraam100% (1)
- Case 2: Nike, Inc. - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Mernoush Banton Case Author: Randy HarrisDocument20 paginiCase 2: Nike, Inc. - 2009 Case Notes Prepared By: Dr. Mernoush Banton Case Author: Randy HarrisabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 03 PepsiCoDocument16 paginiCase 03 PepsiCoabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 AssignmentDocument4 paginiChapter 9 AssignmentabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment CH5Document3 paginiAssignment CH5abraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 AssignmentDocument4 paginiChapter 9 AssignmentabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentDocument2 paginiAssignmentabraamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asian Paints - India's Largest Paint CompanyDocument4 paginiAsian Paints - India's Largest Paint CompanySam SpclÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile numbers of candidates by category and industryDocument419 paginiMobile numbers of candidates by category and industrysaraswatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proton's Supply Chain Management and Production ProcessDocument28 paginiProton's Supply Chain Management and Production ProcessKhairul PakhrudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- XXX Company Minutes of The MeetingDocument3 paginiXXX Company Minutes of The Meetingcreo williamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Compensation: Establishing Design PrinciplesDocument26 paginiSales Compensation: Establishing Design Principlessmoothy_14100% (1)
- Bond ValuationDocument12 paginiBond ValuationvarunjajooÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. & B. Beginning WIPDocument31 paginiA. & B. Beginning WIPChampy MadrigalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comment: (1) Sale' Defined: Art. 1458 Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocument3 paginiComment: (1) Sale' Defined: Art. 1458 Civil Code of The PhilippinesElla WeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format Man Mumbai Grahak Panchayat Case Study 2017 (1) (2) Final RevisedDocument20 paginiFormat Man Mumbai Grahak Panchayat Case Study 2017 (1) (2) Final RevisedImpact Journals0% (1)
- Evaluating A Company's External EnvironmentDocument47 paginiEvaluating A Company's External EnvironmentHong JunÎncă nu există evaluări
- House Number: CreativityDocument12 paginiHouse Number: Creativitykbreenbo1Încă nu există evaluări
- H-E-B Own Brands - Retail Case - 121590978Document21 paginiH-E-B Own Brands - Retail Case - 121590978Anuj SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Invty MgtORDocument36 paginiInvty MgtORkevin punzalan100% (1)
- Estee Lauder Beautiful Start Guide 2014Document165 paginiEstee Lauder Beautiful Start Guide 2014warpsbyherself100% (6)
- Tesco Financial Analysis Rap 8 PDFDocument36 paginiTesco Financial Analysis Rap 8 PDFSyed Irfan100% (1)
- Resume of Shashank SharmaDocument2 paginiResume of Shashank SharmaPrashant NehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Pair Trade With Some Sparkle - Long Signet Jewelers (SIG) /short Blue Nile (NILE)Document20 paginiA Pair Trade With Some Sparkle - Long Signet Jewelers (SIG) /short Blue Nile (NILE)PAA researchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Members: Cristopher Peña Mario RojasDocument23 paginiMembers: Cristopher Peña Mario RojasAnonymous GB2pLzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uncover Hidden Profits With Vwap Bands!: ProfitbandsDocument12 paginiUncover Hidden Profits With Vwap Bands!: ProfitbandsAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Doctrines 72-76Document1 paginăSales Doctrines 72-76Krishianne LabianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The US Airline Industry Case Study SolutionDocument6 paginiThe US Airline Industry Case Study SolutionGourab Das80% (5)
- Advanced AuditingDocument358 paginiAdvanced AuditingAnuj MauryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurship: Business Plan ProjectDocument61 paginiEntrepreneurship: Business Plan ProjectGigi SuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nes 124 - Quiz #6Document2 paginiNes 124 - Quiz #6PatrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Eleven StockDocument15 pagini7 Eleven StockChandra SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expedient Gun License AcquisitionDocument16 paginiExpedient Gun License AcquisitionyellahfellahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wetsown Hub BrochureDocument12 paginiWetsown Hub BrochureAbd Elmonem UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TANCET MBA Model Paper 2Document12 paginiTANCET MBA Model Paper 2TK5013Încă nu există evaluări
- Sample Final Semester Project ReportDocument37 paginiSample Final Semester Project ReportAditya SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit AnalysisDocument3 paginiCredit AnalysisLinus ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări