Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Perimeters Areas and Volumes
Încărcat de
wuratounDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Perimeters Areas and Volumes
Încărcat de
wuratounDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
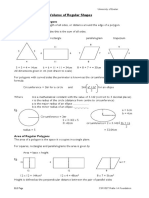
Perimeter, Area and Volume of Regular Shapes
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
Perimeter means the total length of all sides, or distance around the edge of a polygon.
For a polygon with straight sides this is the sum of all sides.
Eg. triangle rectangle parallelogram trapezium
8
11 9
5 5
6 6 7 7 4 4
4 11 8 3
5 + 5 + 4 = 14cm 6 + 6 + 11 + 11 = 34cm 8 + 8 + 7 + = 30cm 4 + 4 +9 + 3 = 20cm
All dimensions given in cm (not drawn to scale)
For polygons with curved sides the perimeter is known as the circumference and is given by the
formula
Circumference = 2πr for a circle and 2π√ a² + b² for an ellipse
2
Where π is a mathematical constant with the value of 3.142 (correct to 3 decimal places)
r is the radius of the circle (distance from centre to circumference)
a is the major radius of an ellipse …………….
b is the minor radius of an ellipse .._.._.._.._.._
Eg. a = 6cm
b = 4cm
Circumference = 2πr
2 x 3.142 x 5
31.42cm circumference = 2 x 3.142√ 36 + 16
2
radius = 5 = 32.04cm
Area of Regular Polygons
The area of a polygon is the space it occupies in a single plane.
For squares, rectangles and parallelograms the area is given by
Area = base x height
Eg.
12 4 ht = 7
12 12 8
12 x 12 = 144cm² 12 x 4 = 48cm² 8 x 7 = 56cm²
Height is defined as the perpendicular distance between the pair of parallel sides
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
All dimensions given in cm (not drawn to scale)
For Triangles area = ½ x base x height
Where height is distance from apex to meet base at right angle
Area = ½ x 12 x 3 = 18cm²
3 cm
12 cm
For Trapeziums area = ½ sum of parallel sides x height
8 cm
7 cm
Area = ½ x (8 + 14) x t = 77cm²
14 cm
For Circles area = π r²
Area = π r²
r=5
= 3.142 x 5² = 78.54cm²
For a sector of a Circle area = area of circle x sector angle
360
Area of sector = π r² x 60 = 13.1cm²
r=5
360
60°
For Ellipse area = π ab
Area = 3.142 x 10 x 5 = 157cm²
b=5
a=5
Complex shapes for which there are no formulas should be divided into simple shapes. The area
of each is then calculated and added together to determine the overall area.
Area = A1 + A2 + A3 + A4 + A5
A1 A4
A5
A3
A2
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
Volume of Regular Shapes
Volume is the amount of space in 3 dimensions occupied by a shape.
Prism
A prism is any shape where the cross-sectional area is constant.
For any prism: Volume = area of base x height
Rectangular Prism
area of base = length x breadth
volume = length x breadth x height
h
eg. calculate the volume of a block with a square base of side 6cm
and a height of 10cm
b
volume = 1 x b x h = 6 x 6 x 10 = 360cm³
I
Shaded area is the base
Triangular Prism
area of base = ½ x base x height
h1
h2 volume = ½ x base x h1 x h2
b
Shaded area is the base eg. determine the volume of a component 16cm long with a
triangular cross-section which has a base of 4cm and perpendicular
height of 5cm
area of base = ½x4x5
volume = ½ x 4 x 5 x 16
= 160cm³
Circular Prism
area of base = π r²
volume = π r² x height
h eg. calculate the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 5cm and a
height of 4cm.
r
volume = π r² x height
= 3.142 x 5² x 4 = 314.2cm³
Shaded area is the base
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
The volume of certain non-prismatic shapes can be determined by using the correct formula.
Sphere
volume of a sphere = 4 π r3
3
r
eg. determine the volume of a spherical component with the radius
of 7cm.
volume = 4 x 3.142 x 7³ = 1436.76cm³
3
Pyramid and cone
volume = 1 x base area x height
h 3
b
Pyramid
1 volume = 1x1xbxh
3
Cone
h volume = 1 x π r² x h
3
r
eg. calculate the volume of a cone with base radius of 6cm and perpendicular height of 10cm
Volume = 1 x 3.142 x 6² x 10 = 376.00cm³
3
Volumes of irregular shapes can be determined by calculation if the mass and density of the
material from which it is known or by displacement.
Calculation of volume using density and mass.
eg. density of substance from which an irregular object is made is 8500kg/m³. if it has a mass of
425kg, calculate its volume.
Volume = mass = 425 = 0.05m³
density 8500
Measurement of volume using displacement
500cc 2nd reading
300cc 1st reading volume = 2nd reading – 1st reading
= 500 – 300 = 200cc
Measuring cylinder
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
Perimeter, Area and Volume of Regular Shapes Worksheet 1
Calculate the area of the following shapes
5 cm
1. 2. 3.
15 cm
9.5 cm
15 cm
4. 1.3 cm
3 cm
12 cm
5. 12 cm
3.5 cm
7.8 cm
47.5 cm
4.5 cm
1.3 cm
6 cm
2.5
cm 5 cm
24 cm
6. A water tank is a cuboid with a base of 1.2m by 0.8m. How deep is the water when the
tank contains 0.384m³ of water?
7. A classroom is 5m x 6m x 3m. Health regulations require that each student must have a
minimum of 5m³ of air. How many students can occupy the room?
Calculate the volume of the following shapes. All dimensions in cm.
8. 9. 2 10. Internal r = 0.75
External r = 1.00
2
12 8
2 15
2
6
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
Camborne School of Mines University of Exeter
Perimeter, Area and Volume of Regular Shapes Worksheet 2
Calculate the shaded area of the following shapes
1. 2. 3. 2 cm
5 cm 3 cm
6 cm 2.5 cm
9 cm 12 cm
12 cm 15 cm
all circles have a radius of 1.5cm
4. 5.
3.5 cm
4 cm
6 cm 16 cm
2 cm 9 cm
12 cm 12 cm
3 cm
32 cm radius of circle = 3cm
6. An ingot 80 x 10 x 300mm is cast into a cylinder 120mm diameter. Calculate its length.
7. A rivet has a hemispherical head 6mm radius and a stem of 6mm diameter and 15mm
length. Calculate the volume of 100 of the rivets.
8. What would be the volume of (a) air (b) plastic in a ball with 25cm diameter made from
plastic 2mm thick?
Calculate the volume of the following shapes. All dimensions in cm.
7
9. 10. 5
Normal ht = 6 Cylinder
14 radius = 1.5
Ken O’Brien 22/2/06
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- StudenttextDocument26 paginiStudenttextapi-195130729Încă nu există evaluări
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Shape, Space and Measures - Ages 8-11’ eBookDe la EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Shape, Space and Measures - Ages 8-11’ eBookÎncă nu există evaluări
- T12 Vectors II SolutionDocument7 paginiT12 Vectors II SolutionmengleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Counting Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookDe la EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Counting Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Maths Foundation Paper 1Document16 paginiMaths Foundation Paper 1KhasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mensuration ChapterDocument41 paginiMensuration ChapterBhumika DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Area and Perimeter of Rectangles 2Document3 paginiArea and Perimeter of Rectangles 2Ralen AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Mathematics Platinum Navigation PackDocument80 paginiGrade 10 Mathematics Platinum Navigation PackdithatolethaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound Measures 4 Worksheet DSTDocument2 paginiCompound Measures 4 Worksheet DSTDaniel DubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surface Area of Cube and Cuboid: Mrs. Rasiya Abdul SamedDocument14 paginiSurface Area of Cube and Cuboid: Mrs. Rasiya Abdul SamedKiran ARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsDocument28 paginiCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRADE 8 NOVEMBER 2022 FinalDocument11 paginiGRADE 8 NOVEMBER 2022 Finalnare100% (1)
- Argand Diagrams: Modulus, Argument and Polar FormDocument10 paginiArgand Diagrams: Modulus, Argument and Polar FormZazliana Izatti100% (1)
- Practice PaperDocument206 paginiPractice PaperTharshanth Bala100% (1)
- GCSE Maths Worksheet Standard Form AnswersDocument3 paginiGCSE Maths Worksheet Standard Form AnswersBrandon LarmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 9 History RevisionDocument6 paginiYear 9 History RevisionMenaga RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- DFMFullCoverage Surds PDFDocument10 paginiDFMFullCoverage Surds PDFMegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONDocument6 paginiGrade 7 Essential Lessons For 2020-2021-ONMatt LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths 1-6 Test QDocument7 paginiMaths 1-6 Test QNarissa PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Maths Book RATIOSDocument23 paginiGrade 10 Maths Book RATIOSMartin HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 4 Maths WorkshopDocument1 paginăYear 4 Maths WorkshopAnonymous BUQiN653Încă nu există evaluări
- Determining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5Document3 paginiDetermining Function Machine Rule: Sub 8 Add 8 Add 6 Sub 10 Sub 11 Add 4 Add 7 Sub 14 Sub 11 Sub 15 Add 13 Add 5api-288922072Încă nu există evaluări
- Area of Plane ShapesDocument5 paginiArea of Plane ShapesNanettePascualÎncă nu există evaluări
- N Convert Recurring Decimals To Fractions PDFDocument3 paginiN Convert Recurring Decimals To Fractions PDFMusaib BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformation Geometry: Mark Scheme 1Document6 paginiTransformation Geometry: Mark Scheme 1anwar hossainÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE ICT Mark SchemeDocument10 paginiIGCSE ICT Mark Schemeanon_977221299100% (1)
- Test 1B Scatter Plots and Data AnalysisDocument2 paginiTest 1B Scatter Plots and Data Analysisahmed5030 ahmed5030Încă nu există evaluări
- Bidmas-Review-Questions 3 PDFDocument2 paginiBidmas-Review-Questions 3 PDFId Tawheed KolajoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebraic Expressions WorksheetDocument4 paginiAlgebraic Expressions Worksheeth8alfredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry-Edexcel GCSEDocument16 paginiTrigonometry-Edexcel GCSEMoli CaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.4b Solving Absolute Value Equations WorksheetDocument1 pagină1.4b Solving Absolute Value Equations WorksheetR ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 Level 1 Mathematics and Statistics AS91027 CAT ADocument8 pagini2017 Level 1 Mathematics and Statistics AS91027 CAT ABenjamin HongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 6-8Document28 pagini2005 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 6-8carmenÎncă nu există evaluări
- StudenttextDocument29 paginiStudenttextapi-195130729Încă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics SPM Chapter 6 Math ReasoningDocument12 paginiMathematics SPM Chapter 6 Math ReasoningSamsiah MustaffaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unitary MethodDocument18 paginiUnitary MethodanilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice P2 Higher Edexcel 2Document23 paginiPractice P2 Higher Edexcel 2rsendhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 Cpe Maths QPDocument16 pagini2014 Cpe Maths QPDefimediagroup LdmgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Year 7 Group ProjectDocument26 paginiMaths Year 7 Group ProjectfarhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.14 Quadratic Graphs - QP HardDocument5 pagini2.14 Quadratic Graphs - QP HardLyShan TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ict Igcse Paper 3 Revision WebauthoringDocument8 paginiIct Igcse Paper 3 Revision WebauthoringPrayrit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questionpaper Paper3F November2018 PDFDocument20 paginiQuestionpaper Paper3F November2018 PDFMontaha ToohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Studies Financial MathsDocument7 paginiMath Studies Financial MathsGirish MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numbers - PercentagesDocument6 paginiNumbers - PercentagesLajwanthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambDocument2 paginiAnswers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambJetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factorization Worksheet PDFDocument2 paginiFactorization Worksheet PDFtakiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathemania QuesDocument11 paginiMathemania QuesRhythm's Pathak0% (1)
- Percentage Problems QDocument4 paginiPercentage Problems QParveen DagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Square Cubes and Their Roots PDFDocument2 paginiSquare Cubes and Their Roots PDFgururajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- StudenttextDocument15 paginiStudenttextapi-195130729Încă nu există evaluări
- Powerpoint Angles in TrianglesDocument52 paginiPowerpoint Angles in TrianglesNguyen DuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Manipulatives in Mathematics EducationDocument7 paginiVirtual Manipulatives in Mathematics EducationCrystal WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Pure Mathematics A J Sadler PDFDocument2 paginiUnderstanding Pure Mathematics A J Sadler PDFgwagsiglenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monday 7 January 2019: Mathematics BDocument20 paginiMonday 7 January 2019: Mathematics BNar NarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4024 s02 QP 1Document16 pagini4024 s02 QP 1Anas ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 710 SyllabusDocument195 paginiMathematics 710 Syllabusazhari7ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse/O Level Add Maths Vectors (Constant Velocity) Past PapersDocument13 paginiIgcse/O Level Add Maths Vectors (Constant Velocity) Past PapersKiefer Ansel OBBOHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third Space Learning Upper and Lower Bounds GCSE Worksheet 1Document11 paginiThird Space Learning Upper and Lower Bounds GCSE Worksheet 1erin zietsman0% (1)
- Perimeter, Area and Volume of Regular ShapesDocument6 paginiPerimeter, Area and Volume of Regular ShapesMohsin Raza MaitlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Trigonometric Ratios Mark SchemeDocument12 paginiChapter 9 Trigonometric Ratios Mark Schemeanwins46Încă nu există evaluări
- SPM Matematik K1 2019 PahangDocument17 paginiSPM Matematik K1 2019 PahangMat HuzainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- JdjudjdDocument1 paginăJdjudjdJulius BaniquedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 8 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument11 paginiModule 8 - Rotation of Rigid BodiesAllen Simon BaulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - Law of Sines and CosinesDocument8 paginiNotes - Law of Sines and CosinesLong NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotating Reference Frames and Relative Motion: MEAM 211Document13 paginiRotating Reference Frames and Relative Motion: MEAM 211manoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid AngleDocument9 paginiSolid AngleDimitrios Christos SarvanisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re-Profiling Tripper Conveyors ...Document2 paginiRe-Profiling Tripper Conveyors ...Srini KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRICHARAN SRIDHAR 20MIA1014 - PSOOP - Java - IPS9Document9 paginiSRICHARAN SRIDHAR 20MIA1014 - PSOOP - Java - IPS9Sricharan SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class XI All Jee Mains Rakhi Ass PDFDocument48 paginiClass XI All Jee Mains Rakhi Ass PDFprateek amrawanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSLC Model Examination, February - 2023 Mathematics ME 231: Each Questions From 1 To 4 Carries 2 ScoresDocument4 paginiSSLC Model Examination, February - 2023 Mathematics ME 231: Each Questions From 1 To 4 Carries 2 ScoresSree ammuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fowles 08Document18 paginiFowles 08jjmaldonisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions 12 (A) 1 Complete Solutions To Exercise 12 (A)Document4 paginiSolutions 12 (A) 1 Complete Solutions To Exercise 12 (A)الحسن المالح المزينىÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Points, Lines, Planes and AnglesDocument4 paginiChapter 1 - Points, Lines, Planes and AnglesJoseph Anthony EngallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Einstein Theory of RelativityDocument26 paginiEinstein Theory of RelativityPrince JurynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulas and Theorems For ReferenceDocument11 paginiFormulas and Theorems For ReferenceLulabu BubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 System of ParticlesDocument25 paginiCH 7 System of ParticlesazeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Motion and Work EnergyDocument78 paginiCircular Motion and Work EnergyPortia A. EgkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- KinematicsDocument83 paginiKinematicsKartik KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Measurement of Areas & Volumes of Solid FiguresDocument0 paginiSLC - Compulsory Math - Measurement of Areas & Volumes of Solid Figureswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDocument25 paginiMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 3: The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesAndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rumus Baru Math pt3Document2 paginiRumus Baru Math pt3farhan naaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch9 Volume and Surface Area of Pyramids Cones and SpheresDocument16 paginiCh9 Volume and Surface Area of Pyramids Cones and SpheresJKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8B Test Review: Find The Measure of The Arc or Angle IndicatedDocument6 paginiUnit 8B Test Review: Find The Measure of The Arc or Angle IndicatedVincent GiuntaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Identities Quiz Review March 2016Document4 paginiTrig Identities Quiz Review March 2016Psalm Palero SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 6 Igcse - Ariyan Palit - Term II ProjectDocument4 paginiClass 6 Igcse - Ariyan Palit - Term II ProjectKanika Sinha RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Surveying 1: Horizontal CurvesDocument30 paginiEngineering Surveying 1: Horizontal CurvesMuhammad Sajid100% (1)
- Area Under The Torque vs. RPM Curve: Average PowerDocument22 paginiArea Under The Torque vs. RPM Curve: Average PowerAdah BumboneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics P ME KNM 10-11-12Document3 paginiKinematics P ME KNM 10-11-12Raghav MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Activity Worksheets #3 Mathematics 7Document5 paginiLearning Activity Worksheets #3 Mathematics 7GINALYNROSE ROSIQUEÎncă nu există evaluări