Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Conversion From Nm3/h To KG/H For Hydrogen Gas From An Electrolyzer
Încărcat de
Mwl. Ngoma100%(3)100% au considerat acest document util (3 voturi)
12K vizualizări1 paginăHydrogen Electrolyser Model: 8.66 Nm3/h Hydrogen gas and 4.33 m3/h Oxygen gas
Titlu original
Conversion from Nm3/h to Kg/h for Hydrogen gas from an Electrolyzer
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentHydrogen Electrolyser Model: 8.66 Nm3/h Hydrogen gas and 4.33 m3/h Oxygen gas
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(3)100% au considerat acest document util (3 voturi)
12K vizualizări1 paginăConversion From Nm3/h To KG/H For Hydrogen Gas From An Electrolyzer
Încărcat de
Mwl. NgomaHydrogen Electrolyser Model: 8.66 Nm3/h Hydrogen gas and 4.33 m3/h Oxygen gas
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
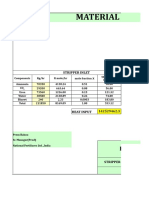
Hydrogen Electrolyser Model: 8.
66 Nm3/h Hydrogen
gas and 4.33 m3/h Oxygen gas
The ideal gas law demonstrates that: PV=nRT in which n=m/M
n= mole number
m= mass or mass flow (kg/h)
V= volume or volumetric flow (m3/hr)
M= molecular weight of the gas for example Molecular weight of hydrogen
(H2) = 2 kg/kg.mole
In Normal conditions according to the latest SI definition P=100 kPa (1 bar) and
T=00C or 273.15 K
R = gas constant =8.314 Pa.m3/mole.K
So, PV = (m/M)*R*T or m(kg/h) = (P*V*M)/(R*T)
At Normal conditions then we have:
m(kg/h) = M* 100* V (Nm3/h) / (8.314*273.15) or
m(kg/h) = 0.044 M* V (Nm3/h)
Production: 8.66 Nm3/h of hydrogen is equal to:
m = 0.044* 2 (molecular weight) * 8.66 (Nm3/h)
m = 0.762 kg/h.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 017 Hydrogen Generation PlantDocument4 pagini017 Hydrogen Generation PlantSubhasish mukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia Energy 2520 BalanceDocument7 paginiAmmonia Energy 2520 Balanceapi-3714811Încă nu există evaluări
- Steam Methane ReformerDocument3 paginiSteam Methane ReformerMuhammad FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen IcsDocument16 paginiHydrogen IcsVũ PhươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between Nm3 and Sm3Document1 paginăWhat Is The Difference Between Nm3 and Sm3jimx_101Încă nu există evaluări
- Reformer Technology For HydrogenDocument6 paginiReformer Technology For Hydrogensaleh4060Încă nu există evaluări
- CO2 Liquefaction PlantDocument21 paginiCO2 Liquefaction Plantshafique0442100% (2)
- Green Ammonia ShipmentDocument9 paginiGreen Ammonia ShipmentVedant ParabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia Slide Blok Diagram CV Nghjyujkm BNMC NDFHG NVBNBMGHDocument22 paginiAmmonia Slide Blok Diagram CV Nghjyujkm BNMC NDFHG NVBNBMGHR Kibik Sht100% (1)
- Electrochemical Reduction of CO To Oxalic Acid: V.S. Boor Thesis Defense 09-04-2020Document36 paginiElectrochemical Reduction of CO To Oxalic Acid: V.S. Boor Thesis Defense 09-04-2020Marcela FragozoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excess AirDocument10 paginiExcess AirjkaunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation of h2 Generation PlantDocument41 paginiPresentation of h2 Generation Plantmkchy12100% (1)
- HYSYS For Ammonia Plants Using Johnson Matthey Catalysts TechnologyDocument1 paginăHYSYS For Ammonia Plants Using Johnson Matthey Catalysts TechnologyAhmed Ali0% (2)
- Kres KBRDocument33 paginiKres KBRrenitadyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Heaters For Safe Startup ofDocument9 paginiElectric Heaters For Safe Startup ofSteve WanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PurifierDocument29 paginiPurifierRaghvendra Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Uhde Brochure Ammonia SCR PDFDocument28 paginiUhde Brochure Ammonia SCR PDFBaher ElsheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocument2 paginiPressure Swing AdsorptionaiensyafiqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Quencher DesignDocument8 pagini7 Quencher DesignJozsef Acs100% (1)
- Co2 RecoveryDocument10 paginiCo2 RecoveryvijayxmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Megan Pressure Swing Adsorption COMPLETEDocument27 paginiMegan Pressure Swing Adsorption COMPLETELeong CheaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia Storage and Filling FaciltyDocument24 paginiAmmonia Storage and Filling FaciltyRavian Lhr100% (1)
- Feasibility Analysis of Electrolysis PlantDocument13 paginiFeasibility Analysis of Electrolysis PlantSaswataChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia Design 2520of 2520equipmentsDocument32 paginiAmmonia Design 2520of 2520equipmentsapi-3714811100% (1)
- K-Green™: KBR'S Green Ammonia TechnologyDocument23 paginiK-Green™: KBR'S Green Ammonia Technologynixon manik100% (2)
- Sulfur Tank Heat LossDocument17 paginiSulfur Tank Heat LossAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casale Advanced Ammonia TechnologiesDocument35 paginiCasale Advanced Ammonia TechnologiesMaribel ParragaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia Training 1Document32 paginiAmmonia Training 1rohit100% (1)
- Design of Gas Absorber For The Exhaust Gases of Ammonia PlantDocument11 paginiDesign of Gas Absorber For The Exhaust Gases of Ammonia PlantVan LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slip Calcluation in Ammonia PlantDocument8 paginiSlip Calcluation in Ammonia PlantRajat Chauhan0% (1)
- PEM Water Electrolysis-Fundamentals Prof. TsiplakidesDocument37 paginiPEM Water Electrolysis-Fundamentals Prof. TsiplakidesfernandinhogmzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condenser DesignDocument7 paginiCondenser Designemesam100% (2)
- Green AmmoniaDocument13 paginiGreen AmmoniaUmar Saeed100% (2)
- Hydrogen Fired Steam Boilers IJERTCONV6IS10016Document5 paginiHydrogen Fired Steam Boilers IJERTCONV6IS10016rahuliitianluv100% (1)
- Calculation Nitrogen Consumption For Nitrogen BlanketingDocument1 paginăCalculation Nitrogen Consumption For Nitrogen Blanketingasep saefulloh100% (1)
- Material and Energy Balance of Urea Reactor and Stripper Saipem ProcessDocument20 paginiMaterial and Energy Balance of Urea Reactor and Stripper Saipem ProcessBalas43100% (1)
- Green Ammonia HughesDocument38 paginiGreen Ammonia Hughesahmed100% (1)
- Ammonia - Heat & Mat. BalanceDocument30 paginiAmmonia - Heat & Mat. BalanceRajeshkumar ElangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 2 2 Hydrogen FuelingDocument16 pagini2 2 2 Hydrogen Fuelingsbr4Încă nu există evaluări
- Study of Vapour Absorption System Using Waste Heat-F0283439Document6 paginiStudy of Vapour Absorption System Using Waste Heat-F0283439Anonymous NGXdt2BxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mollier Chart Methane PDFDocument1 paginăMollier Chart Methane PDFshivarajh8450% (2)
- LPG Leakage & DetectionDocument3 paginiLPG Leakage & DetectionSravan GopuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Considerations For Industrial Water Electrolyzer PlantsDocument17 paginiDesign Considerations For Industrial Water Electrolyzer PlantsMorteza MahdaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Boiler EfficiencyDocument43 paginiCalculation of Boiler EfficiencyTamer Abd ElrasoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon Hydrogen Ratio of Natural GasDocument10 paginiCarbon Hydrogen Ratio of Natural GasManish GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation of PEM Electrolyzer ModelingDocument15 paginiInvestigation of PEM Electrolyzer ModelingNabilah Mustafa100% (1)
- KBR Advanced Ammonia Process PlusDocument1 paginăKBR Advanced Ammonia Process PlusGajanan PadamwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmmoniaDocument17 paginiAmmoniaMohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co2 SpecificationDocument15 paginiCo2 SpecificationrkasiviswanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSFL ReportDocument56 paginiKSFL ReportAbhishek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4000 MTPD Ammonia Plant PaperDocument8 pagini4000 MTPD Ammonia Plant PaperJose DenizÎncă nu există evaluări
- BASF Oase Gas-TreatmentDocument12 paginiBASF Oase Gas-TreatmentSatria 'igin' Girindra NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 paginiUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Useful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowDocument3 paginiUseful Reference Mass, Volume and FlowAshok BaldaniyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- University Questions (Two Marks With Answers)Document17 paginiUniversity Questions (Two Marks With Answers)Uad100% (3)
- Pengantar Teknik KimiaDocument6 paginiPengantar Teknik KimiabihaqibibiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gases Tutorial 2Document4 paginiGases Tutorial 2Idil WarsameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Chapter 3Document13 paginiSolutions Chapter 3JulianneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Air Pollution - WorkbookDocument10 paginiIntroduction To Air Pollution - Workbookrocky21stÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning About: The Ideal Gas Law: Read The Textbook, Pages 383 - 385, and Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 paginiLearning About: The Ideal Gas Law: Read The Textbook, Pages 383 - 385, and Answer The Following Questionscamilo atiluaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Dynamic Two-Fluid Model OLGA: Theory and ApplicationDocument18 paginiThe Dynamic Two-Fluid Model OLGA: Theory and ApplicationmgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH - 1 Basics of MeasurementDocument36 paginiCH - 1 Basics of MeasurementSusovan SensharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otc16561 Gas Compression A Future Option Sin CandadoDocument6 paginiOtc16561 Gas Compression A Future Option Sin CandadoErik Ferman AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sae J 2045 2012-11-01Document16 paginiSae J 2045 2012-11-01GT-LUCAS BARCI100% (1)
- Soalan Kimia Ujian 1Document8 paginiSoalan Kimia Ujian 1Liana JalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che323 Lecture 2 Humidification Wet BulbDocument19 paginiChe323 Lecture 2 Humidification Wet Bulbifiok100% (1)
- Kick Tolerance Paper 2Document8 paginiKick Tolerance Paper 2Diego AraqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial 2023 p4Document11 paginiTrial 2023 p4Marco MedhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ques 2Document3 paginiQues 2Falacy xenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Secondary 1 CheckpointDocument6 paginiCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpointigloo79100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document11 paginiChapter 1adlaborce7_821112170Încă nu există evaluări
- G2300 FR3 Operations and Procedures Guide 06-17 (English) - V5Document35 paginiG2300 FR3 Operations and Procedures Guide 06-17 (English) - V5Dominic Santiago100% (2)
- Full Exam Review #2Document14 paginiFull Exam Review #2ManmeetKalsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- R407C PDFDocument4 paginiR407C PDFNaufal LuthfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Authorised Gas Tester Training Level 1 Confined SpaceDocument38 paginiAuthorised Gas Tester Training Level 1 Confined SpaceTAHA GHORBELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weimer 1993Document11 paginiWeimer 1993Hana NisrinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norma Astm G76 18Document6 paginiNorma Astm G76 18Juancho CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xin Yang, Derek Ingham, Lin Ma, Hao Zhou, Mohamed PourkashanianDocument11 paginiXin Yang, Derek Ingham, Lin Ma, Hao Zhou, Mohamed Pourkashaniansattar aljabairÎncă nu există evaluări
- F4 Processes in FoamingDocument43 paginiF4 Processes in FoamingpadungekÎncă nu există evaluări
- L 70 MCC 8Document399 paginiL 70 MCC 8Adi FadilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling Simulation and Control of A Methanol Synthesis Fixed Bed ReactorDocument13 paginiModeling Simulation and Control of A Methanol Synthesis Fixed Bed ReactorAbdullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virial Equation of State 2Document7 paginiVirial Equation of State 2dnanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Introduction Phase BehaviourDocument62 pagini1 Introduction Phase BehaviourAli ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waste Heat Recovery BoilerDocument28 paginiWaste Heat Recovery Boilerapi-19908130100% (1)
- 05 MBE For Oil ReservoirsDocument20 pagini05 MBE For Oil ReservoirsFerdiNandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Questions MCqsDocument6 paginiThermodynamics Questions MCqsGoverdhan ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bond Graph Modeling of A Jet Engine With Electric Starter: Morteza Montazeri-Gh and Seyed Alireza Miran FashandiDocument18 paginiBond Graph Modeling of A Jet Engine With Electric Starter: Morteza Montazeri-Gh and Seyed Alireza Miran FashandiAsdewq LocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norsok M-506 (2005) - CO2 Corrosion Rate CalcDocument18 paginiNorsok M-506 (2005) - CO2 Corrosion Rate CalcAlina SmochinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer 1 Chemical Engineering Day 1Document13 paginiReviewer 1 Chemical Engineering Day 1Romevie Prado100% (2)
- Nptel Assignments & Solutions: Chapter 1: Introduction and Fundamental ConceptsDocument7 paginiNptel Assignments & Solutions: Chapter 1: Introduction and Fundamental ConceptsPanneer SelvamÎncă nu există evaluări