Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dashboard For Safety Related Items
Încărcat de
Richard Thodé JrTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dashboard For Safety Related Items
Încărcat de
Richard Thodé JrDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
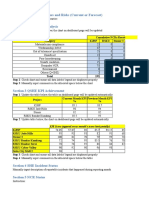
Safety Dashboard Questionnaire
Category Component Excellent Good Opportunity 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
Not Applicable 10 5 0 Points Comments Points Comments Points Comments Points Comments Points Comments
Members of management are
actively involved in the safety Members of management No evidence of management
management process through attend some safety meetings
Management Commitment Involvement being involved in the safety
participation in each meeting to and establish safety in process.
modeling and coaching safe correspodence to employees.
behavior.
Management has drafted and Management has signed the No evidence of management
Management Commitment Policy Statement stands behind the organization's safety policy statement. being involved with the safety
safety policy statement. policy statement.
Clear objectives are set on an
annual basis and communicated Objectives are written but no Management has not
Management Commitment Established objectives to the entire organization. metric developed to measure established safety objectives.
Metrics are established to efforts.
identify successes.
Funds are adequately allocated
for safety efforts. Individual Funds are allocated for safety
Management Commitment Safety Budget departments budget for safe on a request basis. There is no safety budget.
operations.
All levels of employment are
equally accountable for safe
operations. Safety Safety accountability written No evidence of accountability
Management Commitment Accountability for safety until mistakes are
accountability is written into job into job descriptions. made.
descriptions. Accountability
parameters are established.
Management hosts and Members of management No evidence of managers or
participates in risk management attend safety training given to
Management Commitment Supervisory / Management Training supervisors involvement in
and safety training on a employees on a scheduled safety training.
scheduled basis. basis.
Managers and supervisors have The safety coordinator provides No evidence of established
Management Commitment Employee Training a role in providing or arranging all safety training. safety training needs.
for job specific safety training.
Management and supervisors
are effective with timely
investigation of reported The safety coordinator conducts Investigations are not
incidents or accidents. Their all investigations and
Management Commitment Investigations recommends corrective action conducted. Only first reports of
report is documented with
recommendations for corrective to management. injury are completed.
action and established
completion dates.
Safety is an active agenda item Safety is occassionally on the No deliberate agenda for safety
Management Commitment Risk Management on Meeting Agendas in each management meeting. agenda in management in management meetings.
meetings.
Management is involed with all Management participates in
Management Commitment Facility Inspections safety inspections at least once Management is not involved
facility safety inspections. with facility safety inspections.
per year.
Management gives the Safety
Management always reviews Management isn't involved with
and signs off on approved Coordinator the responsibility approval of safety policies and
Management Commitment Approval of Safety Policies and Procedures
safety policies and procedures. to approve safety policies and procedures.
procedures.
Individual departments have
established metrics to identify Individual departments review The safety coordinator is
and address their safety
performance. Department their injury trends and are responsible for the
Management Commitment Safety Performance Responsibility responsible for addressing organization's safety
supervisors are held them. performance.
accountable to their safety
commitments.
Managers and supervisors are
actively involved in claims Human Resources and /or the
management through timely Safety Coordinator handles all The company lacks claims
Management Commitment Claims Management management.
investigations to serving on the claims management activities.
RTW Team
Managers and supervisors are
aware of claims costs and
trends specific to their Human Resources and/or the
department. They are charged Safety Coordinator generates
with implementing controls to No formal analysis of costs or
reports that are specific to each trends
Management Commitment Claims Costs and Claims Trends reduce or mitigate costs and department. The reports are of failures in safety is
trends related to safety failures. conducted.
reviewed with the respective
A charge back system or other manager or supervisor.
effective accountability process
is in place for each
department's performance.
Managers provide written The Safety Coordinator is There is no formal response to
responses to safety committee
Management Commitment Safety Recommendations responsible for all Safety safety committee
recommendations and follows Committee recommendations. recommendations.
through on completion items.
Supervisors complete the First
Report of Injury (FROI) and Injuries are reported to
Roles and Responsibilties submit to HR within 24 hour of supervisors, but HR or Safety
Management Roles Injury Reporting notice. Supervisors and Coordinator completes the FROI Injury reporting lags.
managers are accountable for timely.
accurate completion of FROI.
Supervisors thoroughly
complete an Incident
Investigation Report and submit HR or Safety Coordinator is
Roles and Responsibilties No incident investigations are
Incident Investigation to HR within 24 hours of notice. responsible for all incident
Management Roles completed.
Supervisors and managers are investigations.
held accountable for
incomplete investigations.
Provides recognition and
feedback for employee who Provides recognition and
Roles and Responsibilties deliberately work safely. coaching broadly to the No visible effort in cultivating
Management Roles Cultivates a Positive Culture Provides timely coaching to organization via email, in staff positive culture.
employees who are observed meetings, or other means.
working unsafely.
Ensures all employees receive
adequate safety orientation. Provides an employee
The orientation is completed handbook or other written New employees do not receive
Roles and Responsibilties New Employee Safety Orientation thoroughly by knowledgeable document for new employee to an adequate new employee
Human Resources Roles personnel. The orientation is review and sign in receipt of the orientation.
documented accurately with information.
topics and dates.
Works with supervisors and
Roles and Responsibilties management to address Assists employees with special
Accomodation documented requests for accomodation requests without No accomodations are made.
Human Resources Roles special safety needs of involving supervisor.
employees.
Roles and Responsibilties Safety standards are Safety standards are expected No safety standards are in
Human Resources Roles Job Profiles incorporated to job profiles. but not formally written. place.
Safety is incorporated into Safety is incorporated into
Roles and Responsibilties Safety is not incorporated into
Performance Evaluations performance evaluations for all performance evaluations only
Human Resources Roles performance evaluations.
levels of the organization. for line staff.
Reports all First Report of Timely submission of FROI lags
Injuries to the insurer within 24 Attempts to submit FROIs
Roles and Responsibilties within 24 hours, but often other by evidence of accident dates
Human Resources Roles Timely Reporting hours. Has designated a back tasks promote later reporting. and date received by insurance
up if out of the office. carrier.
Roles and Responsibilties Serves as the point of contact Supervisor, Safety Coordinator, No designated point of contact
Claims Communications for the insurer to begin and/or HR serves as initial point in place.
Human Resources Roles processing the claim. of contact.
Provides or arranges training for
supervisors on accurate Completes incomplete
Roles and Responsibilties completion of the FROI. Holds information on the FROI for the Supervisors are not involved in
Claims Training
Human Resources Roles supervisors accountable for supervisors. the FROI process.
incomplete reports.
Provides or arranges training for
supervisors on accurate
Roles and Responsibilties completion of the Incident Completes the Incident No incident investigations are
Incident Investigation
Human Resources Roles Investigation Report. Holds Investigation Report. completed.
supervisors accountable for
incomplete reports.
Reviews reports provided by the
insurance carrier and
communicates internally on Reviews reports from the Receives reports, but doesn't
Roles and Responsibilties status of claims and injury
Analysis insurance carrier, but no action know what to do with them or
Human Resources Roles trends. Works with is taken. doesn't receive reports.
management and Safety
Coordinator on identified
needs.
Serves as coordinator for the
RTW process. Coordinates RTW
meetings and documents
Roles and Responsibilties results. Assists with finding Coordinates light duty with
Human Resources Roles Return to Work (RTW) Team supervisor and employee. RTW teams are not used.
light duty tasks. Documents
RTW job offers. Tracks
progressive healing process.
Actively participates in new Is not required to participate in
employee orientations. Asks Signs off on new employee
Employee Roles Safety Orientation new employee safety
questions andunderstanding is orientation. orientation.
evidenced.
Actively participates in job
Signs off on Job Safety Training. Is not required to participate in
Employee Roles Job Safety Training specific safety training. Job Safety Training.
Demonstrates understanding.
Reports injuries or incidents as Injury and incident reporting is Reports are only given if
Employee Roles Reporting Incidents and Injuries soon as possible and within the usually timely. medical treatment or property
same workday. damage occur.
Always wears the required PPE. Uses PPE when Safety
Employee Roles Personal Protection Equipment (PPE) Keeps PPE clean and well Coordinator or Supervisor is Does not wear PPE.
maintained. present.
Maintains good housekeeping
in work areas. Uses warning or Cleans work area when told to Housekeeping is generally not
Employee Roles General Housekeeping caution signs if work area will do so. maintained.
be disturbed.
Reports hazards to supervisor.
Takes initiative to address Reports hazard after incident or
Employee Roles Hazard Reporting hazard if within the employees Reports only serious hazards. injury.
control.
Plans work with safety
forecasting. Arranges work
process safely. Controls or Follows safety rules and No forethought put into safe
Employee Roles Safe Work Practices guidelines as they are written. work processes.
mitigates hazards before
starting task.
Helps coworkers work safely.
Openly communicates hazards Will work as a team and talk
safety as other employees do. Each employee is responsible
Employee Roles Teamwork and controls of tasks. Informs Does not address safety on for his/her own safety.
others as information is
available. his/her own.
Safety management is a full Safety management is a half Safety management is an
Safety Coordinator Appointed time position. time position. additional duty.
Can stop work if conditions or Works with supervisor on
Safety Coordinator Authority practices are unsafe. resolving safety issues. No visible authority.
Delegates projects, follows up Chairs committee and takes on Effective safety committee
Safety Coordinator Leads Safety Committee on completion. the committee work load. leadership is not visible.
Drafts, formalizes, and works to Proposes safety programs to
implement safety programs. management and waits for Safety programs are incomplete
Safety Coordinator Safety Programs Evaluates program effectiveness approval. Implements via email and not implemented.
annually. memo.
Reports quarterly to Executive Emails communications to No lines of communication with
Safety Coordinator Management Involvement Management on State of Safety. management as needed. coordinator and management.
Analyzes accident reports and
loss reports from insurance Reviews information and
carrier. Works to implement
Safety Coordinator Analysis effective corrective action. Has provides direction. Follow No formal analysis in place.
established metrics to identify through and metrics lack.
success.
Does not participate in the
Participates in the Emergency There is no Emergency Action
Safety Coordinator Emergency Action Team existing Emergency Action
Action Team. Team.
Team.
Organizes safety training Safety training is held at least Safety training is done as
programs at least quarterly.
Safety Coordinator Safety Training Establishes metric for results of annually. The training is needed and documentation is
safety training. documented. sporadic.
Provides or arranges ergonomic
assessments for new
employees, existing employees,
and injured employees. Follows Ergonomic assessments are
up with management to ensure conducted when requested. Ergonomics process is reactive
Safety Coordinator Ergonomics Training is conducted for new following reported problems.
recommendations have been employees.
implemented. Provides
ergonomic training to all
employees annually.
Poignant in self growth and
development in regard to safety Continues growing through
leadership. Attends at least one company experience. Does not
Safety Coordinator Continues Education have time or budget to attend No continuing education.
safety seminar or conference
per year. safety conferences or seminars.
Conducts an audit of the
organization's safety Conducts self audits on an
management program at least unscheduled basis. Compiles
annually. Formally
recommends improvement report of findings and
Safety Coordinator Self Audits communicates to management. No self audits.
needs to management and Awaits for management
promotes the identified needs direction.
be incorporated into annual
objectives.
Thoroughly understands
organizational risks. Has ability Spends 95% of time in an office
to visit field work and analyze setting. Understands risk by Does not understand or manage
Safety Coordinator Risk Management work practices. Incorporates description but has not the organization's risks.
risk mitigation measures into all thoroughly analyzed the risks.
job categories.
Conducted frequently and Conducted annually and No evidence of facility
Hazard Identification Facility Safety Inspections corrective action is corrective action is inspections being conducted.
documented. documented.
Conducted frequently and Conducted annually and No evidence of grounds
Hazard Identification Grounds Safety Inspections corrective action is corrective action is inspections being conducted.
documented. documented.
Pre-operational inspections No evidence of fleet
Hazard Identification Fleet Safety Inspections documented with timely Monthly inspections conducted. inspections.
corrective action.
Pre-operational inspections No evidence of heavy
Hazard Identification Heavy Equipment Safety Inspections documented with timely Monthly inspections conducted. equipment safety inspections.
corrective action.
Pre-operational inspections
Monthly inspections conducted. No evidence of ATV or UTV
Hazard Identification ATV or Utility Vehicle Inspections documented with timely
corrective action. inspections.
Pre-operational inspections
Hazard Identification Hand and Power Tool Inspections documented with timely Monthly inspections conducted. No evidence of inspections.
corrective action.
Pre-operational inspections
Hazard Identification Ladder Safety Inspections documented with timely Monthly inspections conducted. No evidence of inspections.
corrective action.
Work activities are reviewed on Work activites are addressed on
a scheduled interval with timely an unscheduled, as needed No evidence of behavioral
Hazard Identification Behavioral Safety Inspections feedback provided to safety inspections.
basis.
employees.
Company specific driving rules,
seat belt use, distraction
prevention, fleet inspection,
Hazard Identification and driver training in place. No formal fleet program is in
Hazard Specific Controls Fleet Safety Motor vehicle records are effect.
checked initially and annually
for persons regularly required
to drive a company vehicle.
Written program in place to
include new employee training,
list of hazardous chemicals,
employee access to safety data
sheets, defined labeling Written program in place with
Hazard Identification No written program or
Hazard Specific Controls Hazard Communication requirements, personal some missing elements. employee training in place.
protective equipment Employee training in place.
requirements, and additional
training should a new chemical
or process be introduced into
the workplace.
A written chemical hygiene plan
is in place: standard procedures
in place for handling and storing
hazardous chemicals, fume
hoods are adequately
maintained and verified
functioning. Certain procedures
require permission and
Hazard Identification oversight from the employer A necessary chemical hygiene
Hazard Specific Controls Chemical Hygiene plan is not in place.
prior to performing. Medical
monitoring program is in place
for affected employees if
applicable. Employee training is
conducted initially and annually.
The program is reviewed
annually to evaluate its
effectiveness.
Written respiratory protection
program is in place to include
Hazard Identification Respiratory hazards quantified program administrator, medical No written program, medical
Respiratory Protection and controlled by engineering questionnaire, fit testing, or
Hazard Specific Controls questionnaire, fit testing,
practices. training in place.
equipment inspection, and
training.
Equipment specific hazardous
energy control procedures are Locks and tags are available for
documented. Employees employees performing service No lockout tagout program is in
Hazard Identification Lockout Tagout receive training intially and or maintenance on equipment.
Hazard Specific Controls annually. Periodic inspections Training has been conducted for place.
are conducted and authorized employees.
documented.
Spaces are identified and
employees are trained to never
enter OR a written program is in
place. Entry occurs only by
permit. Atmospheres are Spaces are not identified but
monitored before and during employees may have an
Hazard Identification entry. Attendant always present occasional need to enter a No confined space entry
Confined Space Entry
Hazard Specific Controls without other assigned duties. confined space. Entry occurs program or training is in place.
Emergency rescue plans in with proper ventilation and an
place. Employees trained in attendant present.
confined space entry
procedures and rescue
procedures. An annual review
of the program is in place.
Noise is established safe
through engineering controls
OR a written hearing
conservation program is in Effective hearing protection is Noise exposures have not been
Hazard Identification place that includes baseline and required when working with or evaluated. Employees can wear
Hazard Specific Controls Hearing Conservation Program
annual audiograms, new around noisy equipment. ear plugs if they want to.
employee and annual training,
and properly chosen hearing
protection.
Equipment and power tools
with guards will not operate Machines and equipment are
Hazard Identification without the guards in place. guarded. The guards can be There is no verification of
Hazard Specific Controls Equipment / Machine Guarding Employees receive training on removed but only with a adequate machine guarding.
machine guarding lockout tagout process.
requirements.
Only qualified personnel work
on electrical systems. Electrical
systems are adequately
guarded. Cord powered Only qualified personnel work
equipment is inspected. Cords on electrical systems. Electrical
are not covered with tape and
ground pin is never removed. systems are adequately
Hazard Identification guarded. Cord powered No visible electrical safety
Electrical Safety Ground Fault Circuit
Hazard Specific Controls equipment is inspected and efforts in place.
Interuppters (GFCI) or ground
assurance program are in place. addressed appropriately. Safety
awareness program provided
Inspections look for electrical for all employees.
safety and needs for permanent
wiring. Safety awareness
program provided for all
employees.
Fall protection plans are in
Employees are protected by place. Employees are trained in Fall protection systems are not
Hazard Identification engineered fall protection
Fall Protection Systems use, maintenance, and
Hazard Specific Controls systems while working on requirements of personal fall provided.
elevated work surfaces. protection.
A certified hazard assessment Personal Protective Equipment
has been conducted.
Hazard Identification Employees are provided is available for use, but
Hazard Specific Controls Personal Protective Equipment decide when to use PPE is not provided.
appropriate PPE and are trained employees
it.
in its use.
A written EAP is in place and
addresses potential A written plan is in place.
emergencies at the specific Facility plans are posted.
Hazard Identification workplace. Employees receive
Emergency Action Plan (EAP) Employees are shown exits An EAP does not exist.
Hazard Specific Controls training initially and annually. when they begin their
Physical drills are performed employment
and evaluated on a scheduled
basis.
Hazard Identification A written fire prevention plan is The fire prevention plan is
Hazard Specific Controls Fire Prevention Plan in place and followed. known, but not written. No plans for fire prevention.
Workzones are established
following the Manual of
Uniform Traffice Control Devices
(MUTCD) guidelines. Internal
traffic control plans are
identified and followed. Site Construction zones are set up to
specific training occurs for control public motorists.
Hazard Identification No visible efforts are in place
Traffic Control Plan affected employees. Flaggers Awareness is discussed for
Hazard Specific Controls for traffic control plans.
are trained specifically for their internal traffic control.
duties. Reflective attire is worn Reflective attire is worn.
when onsite. Public service
announcements are provided to
the community. Law
enforcement is requested to
patrol the site.
An ergonomics process has
been established. Employees
are trained in risk factors and
prevention methods. Employees are trained initially
Engineering methods are used Ergonomics is addressed
and annually in ergonomics.
Hazard Identification to maintain anatomically reactively when discomfort or
Hazard Specific Controls Ergonomics correct postures while Symptoms of injury are cumulative injuries are
reported timely and action is
minimizing repetition and force. reported.
taken.
A reporting system is in place
for symptoms of cumulative
injury. High risk tasks are
analyzed for improvement.
Manual material handling is
minimized. Lifting policies are
in place. Mechanical No visible efforts are in place to
Hazard Identification equipment is available and used Back safety training is
Manual Material Handling address manual material
Hazard Specific Controls by qualified personnel. conducted once per year. handling.
Employees are trained in injury
prevention methods at least
annually.
All operators are trained and
authorized. The equipment is
inspected before operation and
the inspection is documented. All operators are trained and Employees who know how to
Hazard Identification Power Industrial Truck (PIT), often Forklift, Safety issues are addressed authorized. A pre-operational operate the PIT are encouraged
through the inspection process inspection is completed but
Hazard Specific Controls but could be other to pitch in. No inspections are
and a paper trail follows documentation lacks. Safe conducted.
identified issues to completion. operations are enforced.
Seat belts are required. Exhaust
issues, if applicable, are
effectively addressed.
Appropriate sloping, shoring, or
shielding used for 5' or deeper.
Competent person inspects the
trench daily and as conditions
change. Employees receive
Hazard Identification training initially, annually, and No evidence of excavation
Trenching and Excavation
Hazard Specific Controls site specific. Heavy equipment safety in place.
and spoil always kept at least 2
feet away from edge. Ladders
provided for access and exit.
Atmosphere is tested prior to
entry.
Full Exposure Control Program
implemented: Exposure group
identified, initial and annual
training, training records kept,
vaccines offerred and Program is written.
Hazard Identification Exposure Control Plan for Prevention of declinations documented, Improvements are necessary in A necessary exposure control
Hazard Specific Controls Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure engineering controls and safe program is not in place.
implementation.
work practices identified and
followed; decontamination
procedures in place.
Effectiveness is reviewed
annually.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Welding controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Compressed Gas controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Hand and Power Tool Program controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Consumer Aggression controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Violent Offenders controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Patient Handling controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Working with Livestock controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Working with Wildlife controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Unexploded Ordinance controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Handling Fire Arms or other weapons controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Handling Explosives controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Airplane Operations controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Helicoptor Operations controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Wildland Fire Fighting controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Structural Fire Fighting controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Working in or around waterways controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification:
Additional Worksite Hazards: [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Define the controls in place for each Print Press Operation controls here] controls here] controls here]
as applicable.
Hazard Identification [type additionally identified hazards specific [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Other Worksite Hazards: to your organization here] controls here] controls here] controls here]
Hazard Identification [type additionally identified hazards specific [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Other Worksite Hazards: to your organization here] controls here] controls here] controls here]
Hazard Identification [type additionally identified hazards specific [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Other Worksite Hazards: to your organization here] controls here] controls here] controls here]
Hazard Identification [type additionally identified hazards specific [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Other Worksite Hazards: to your organization here] controls here] controls here] controls here]
Hazard Identification [type additionally identified hazards specific [type your current hazard [type your current hazard [type your current hazard
Other Worksite Hazards: to your organization here] controls here] controls here] controls here]
Open positions are advertised in multiple
Hiring & Onboarding Practices venues for a standardized amount of time. Always Sometimes Never
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Job postings include the job requirements. Always Sometimes Never
Job postings include the requirement to
Hiring & Onboarding Practices pass a drug screen before employment. Always Sometimes Never
A formal application process is in place.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
The application has been approved by legal Always
Hiring & Onboarding Practices counsel. Sometimes Never
Application is reviewed and content is
Hiring & Onboarding Practices verfied by appointed personnel. Always Sometimes Never
References are provided by the candidate
Hiring & Onboarding Practices and checked by the employer. Always Sometimes Never
Written job desciptions are in place for all
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
positions.
Job descriptions outline the physcial
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
requirements of the job.
Job descriptions include expectations of
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
safe work practices.
Potential candidates are screened by
Hiring & Onboarding Practices meeting the minimum qualifications which Always Sometimes Never
have been defined.
Interviews are conducted by both human
Hiring & Onboarding Practices resources and the supervisor to whom the Always Sometimes Never
candidate would report to.
Hiring managers have received training on
appropriate interview techniques and legal
Hiring & Onboarding Practices issues that may involve the interview Always Sometimes Never
process.
During the interview process the candidates
Hiring & Onboarding Practices are requested to elaborate on their work Always Sometimes Never
history and experience.
During the interview process the candidates
Hiring & Onboarding Practices are requested to explain gaps in Always Sometimes Never
employment.
During the interview process the candidates
are asked if they can perform the essential Always
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Sometimes Never
functions of the job with or without
accomodations.
Interview questions about prior workers
Hiring & Onboarding Practices compensation injuries are avoided. Always Sometimes Never
Questions regarding the candidates
Hiring & Onboarding Practices perception of safety are included in the Always Sometimes Never
interview process.
Post job offer background checks are
Hiring & Onboarding Practices conducted on potential hires with their Always Sometimes Never
consent.
Post offer credit checks are conducted on
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
potential hires with their consent.
Job offers are made contingent upon the
candidate passing applicable post offer drug
Hiring & Onboarding Practices test, physical, background check, motor Always Sometimes Never
vehicle check, etc.
Pre-employment/ post offer drug testing
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
follows a lawful chain of custody process.
Candidates who fail the post offer drug test
Hiring & Onboarding Practices have opportunity to retest at their own Always Sometimes Never
expense.
Job offers are made contingent upon
Hiring & Onboarding Practices passing a pre-employment / post offer Always Sometimes Never
physical.
Pre-employment physicals are designed to
Hiring & Onboarding Practices simulate the physical requirements of the Always Sometimes Never
job.
Post offer physicals are medical
Hiring & Onboarding Practices certifications as required by a regulatory Always Sometimes Never
agency.
Clean motor vehicle records are required for
Hiring & Onboarding Practices those who have or may have the duty to Always Sometimes Never
drive as part of their job.
E-verify is used to confirm lawful working
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
status.
Job offers are provided in writing and
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
accepted by the candidate's signature.
A probationary period is established,
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
communicated, and adhered to.
Medical benefits are provided to the
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
employee by the company.
Medical benefits are affordable, measured
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Always Sometimes Never
by most employees participating.
New employees are eligible for medical
Hiring & Onboarding Practices benefits within the first 90 days of Always Sometimes Never
employment.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Proper employment documents are signed Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations by the employee and turned in timely.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices A point person reviews company policies
Clear Expectations with the new hire. Always Sometimes Never
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Company commitment to safety and
employee accountability toward success is Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations verbalized.
Emergency procedures are discussed and
Hiring & Onboarding Practices the new employee is provided a facility tour
Clear Expectations to effectively identify exit routes, fire Always Sometimes Never
extinguishers, and shelters in place.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Injury reporting procedures are provided in Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations written and oral format.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices The Return to Work program and Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations expectations are provided.
If employees supply their own tools, the
Hiring & Onboarding Practices safety requirements/conditions of the tools Always
Clear Expectations Sometimes Never
are provided in written and oral format.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Employees are informed of their Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations empowerment to stop an unsafe job.
Employees are paired with a mentor who
Hiring & Onboarding Practices provides on the job training and observes Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations the new employee.
Performance expectations are
Hiring & Onboarding Practices
Clear Expectations communicated to the employee during the Always Sometimes Never
orientation process.
Employee performance is measured and
Hiring & Onboarding Practices reviewed with the employee at pre-
Clear Expectations determined intervals, such as 1 month, 3 Always Sometimes Never
months, and 6 months.
Hiring & Onboarding Practices Performance issues are addressed Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations immediately through coaching.
A progressive disciplinary action process is
Hiring & Onboarding Practices established and described to address non- Always Sometimes Never
Clear Expectations performers.
Workstations are verified to be
Hiring & Onboarding Practices ergonomically correct for the new
Clear Expectations Always Sometimes Never
employee.
New Employee Training for All
Training Always Sometimes Never
New Employee orientation conducted orally Always
Training and written Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Accident Reporting Procedures Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Hazard Reporting Procedures Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Emergency Procedures Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Fire Prevention Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation First Aid Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Ergonomics Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Back Injury Prevention Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Slip and Fall Prevention Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Introduction of Safety Committee Members Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Safety Accountability Always Sometimes Never
Training
Employee Orientation Return to Work Program Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Personal Protective Equipment Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Worksite Specific Hazards Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Hazardous Chemicals Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Equipment Operations Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Fall Protection Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Safe Use of Ladders Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Electricity Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Fleet Operations Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Workzone Safety Always Sometimes Never
Training
Job Specific Training Excavation / Trenching Always Sometimes Never
Training Felling / Bucking Trees Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Power Tools Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Lockout Tagout Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Hearing Conservation Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Confined Space Entry Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Respiratory Protection Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Machine Guarding Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Lone Work Procedures Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Training conducted by knowledgable person Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training on topic
Training Regular Refresher Training Scheduled Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Additional training in areas of major loss Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training sources
Training Training conducted when new hazards Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training identified
Training Job Transfer Training Always Sometimes Never
Job Specific Training
Training Safety is on the agenda in staff meetings Always Sometimes Never
Awareness
Training Safety materials are posted Always Sometimes Never
Awareness
Training
Awareness Safety advertisements are done Always Sometimes Never
Training
Awareness Safety fairs or Safety days are used Always Sometimes Never
Training
Awareness Safety incentive programs exist Always Sometimes Never
Training
Awareness Safety newsletters are established Always Sometimes Never
Training Safety Goals and Objectives are
Awareness Communicated Always Sometimes Never
Training Safety Committee notifies the company of
Awareness meeting minutes availability Always Sometimes Never
Training Accident analysis is shared with company
Awareness employees Always Sometimes Never
Training Hazard Alerts communicated with company Always
Awareness employees Sometimes Never
Training
Awareness Safety recognition programs are in place Always Sometimes Never
Training Employees and staff are informed of safety
Awareness committee members Always Sometimes Never
A written incident management policy has
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
been developed and implemented.
A formal Return to Work program has been Always
Incident Management Sometimes Never
developed.
Employees have been trained in incident
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
reporting procedures.
All Incidents are reported, regardless of
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
severity / property damage.
An incident investigation program has been Always
Incident Management Sometimes Never
developed.
Injured employees are involved in the
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
incident review process.
Incident reviews lead to causation factors
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
and drive corrective action.
Incidents are managed to ensure prompt
Incident Management medical care to injured employees. Always Sometimes Never
Incidents are managed to ensure all injuries
Incident Management are reported within 24 hours. Always Sometimes Never
OSHA recordkeeping reports are completed
Incident Management immediately. Always Sometimes Never
Temporary transitional jobs are designated
Incident Management so RTW can begin immediately. Always Sometimes Never
Employer sends RTW information to the
Incident Management Always Sometimes Never
doctor with the injured employee.
Employer requires employee to return
Incident Management medical status forms following every doctor Always Sometimes Never
visit.
Temporary duty status is reviewed following
Incident Management every visit to the doctor. Always Sometimes Never
All injuries are considered for participation
Incident Management in RTW. Always Sometimes Never
Employees on transitional duty are
Incident Management managed to ensure they are not working Always Sometimes Never
outside their restrictions.
Corrective actions are taken to prevent the
Incident Management reoccurrance of the injury. Always Sometimes Never
Employees are re-trained in any changes
Incident Management made because of an incident. Always Sometimes Never
Management instills a positive, cooperative
Return to Work (RTW) culture for Return to Work within the Always Sometimes Never
Management Components company.
A transitional duty team coordinator (TDTC)
Return to Work (RTW) has been assigned to facilitate transitional Always Sometimes Never
Management Components duty team meetings and manage the
workers' compensation claim process.
All injured employees immediately notify
Return to Work (RTW)
Management Components their supervisor, human resources or the Always Sometimes Never
TDTC when injured.
The First Report of Injury is submitted to the
Return to Work (RTW) workers compensation carrier within 24
Management Components hours following notification from the Always Sometimes Never
employee of an injury.
The medical status form is provided to the
Return to Work (RTW) employee to take to their first and
Management Components subsequent visits with their health care Always Sometimes Never
provider.
When the medical status form is received
and the injured employee is released to
work, a transitional duty team meeting is
scheduled and held between human
Return to Work (RTW) resources (HR) and or the TDTC, the Always Sometimes Never
Management Components supervisor and the injured employee; to
review medical restrictions listed on the
medical status form and to collectively
develop transitional duty.
The employee provides the medical status
form after every medical visit to the TDTC.
Return to Work (RTW) The TDTC then schedules a meeting with the Always Sometimes Never
Management Components transitional duty team to discuss updates to
those restrictions and make adjustments to
the employee's RTW Plan.
If the employee is not released, the
supervisor and or TDTC makes weekly
Return to Work (RTW) contact with employee and ensures the Always Sometimes Never
Management Components contact log is updated.
The return to work plan is documented
Return to Work (RTW) using the transitional duty tracking form (or
Management Components other form of documentation) after every Always Sometimes Never
transitional duty team meeting.
A copy of the transitional duty tracking form
Return to Work (RTW) is provided to the employee to provide at Always Sometimes Never
Management Components the next health care provider's visit.
The return to work progress of injured
Return to Work (RTW) employees is regularly communicated to the Always Sometimes Never
Management Components workers compensation carrier.
HR/TDTC keeps in contact with the claims
examiner throughout the process. HR/TDTC
Return to Work (RTW) stays informed on severity, lost time, and Always Sometimes Never
Management Components duration. TDTC ensures contact is
maintained between the examiner and the
employee.
HR Specialist/TDTC monitors the claim until
Return to Work (RTW) employee reaches maximum medical
Management Components improvement (MMI); HR/TDTC asks claims Always Sometimes Never
examiner to close the claim.
Medical Status Forms, transitional duty
Return to Work (RTW) tracking forms, contact logs, FROI are filed Always Sometimes Never
Management Components for each injured worker.
The physical/mental demands of the
Return to Work (RTW)
Management Components department's positon are listed in the job Always Sometimes Never
profile.
Return to Work (RTW) Return to work training is provided to all Always Sometimes Never
Management Components employees.
Return to Work (RTW) Return to work training is provided to all Always Sometimes Never
Management Components supervisors.
Return to Work (RTW) Regular RTW training and updates are
incorporated into safety committee Always Sometimes Never
Management Components meetings or other staff meetings.
RTW responsibilities are incorporated into
Return to Work (RTW) position descriptions and performance
Management Components Always Sometimes Never
appraisals.
The number of transitional duty team
Return to Work (RTW) meetings are monitored and the outcome of Always Sometimes Never
Management Components the RTW effort is tracked.
A safety committee has been created.
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
The safety committee has some employees
Safety Committee from each workgroup. Yes Maybe No
The safety committee has members from
Safety Committee both management and employee groups. Yes Maybe No
Employees have been selected based on
Safety Committee their interest in safety, or their ability to Yes Maybe No
help lead change.
A written Committee Charter has been
Safety Committee developed. Yes Maybe No
Employees have been given permission to
Safety Committee fully participate in the safety committee Yes Maybe No
activities.
The committee has been funded.
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
Recommendations made by the committee
Safety Committee are considered by management and drive Yes Maybe No
change.
The committee meets regularly.
Safety Committee (Monthly) (Quarterly) (Less)
The committee has clear goals and
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
objectives.
Meeting minutes are kept and posted where Yes
Safety Committee Maybe No
all employees can see them.
The committee spreads safety awareness
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
throughout the company.
Safety Committee The committee performs incident reviews. Yes Maybe No
The committee makes recommendations
Safety Committee from incident reviews to prevent future Yes Maybe No
incidents from occurring.
The committee performs hazard
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
assessments.
Committee members have training in hazard Yes
Safety Committee Maybe No
identification.
The committee has a designated
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
chairperson.
Committee members review safety
Safety Committee programs and make suggestions for Yes Maybe No
revisions.
Safety Committee members hold toolbox
Safety Committee meetings with their workgroups. Yes Maybe No
Safety committee members bring safety
Safety Committee committee information back from meetings Yes Maybe No
to their workgroup.
Safety committee members bring concerns
Safety Committee and issues to the safety committee Yes Maybe No
meetings from their workgroups.
The safety committee tracks its successes
Safety Committee and shares them throughout the Yes Maybe No
organization.
The safety committee hosts safety events to
Safety Committee raise awareness and education. Yes Maybe No
Safety committee members are the eyes and Yes
Safety Committee ears of the company. Maybe No
The safety committee is viewed as a
Safety Committee resource and trusted group by the Yes Maybe No
employees.
The committee members are renewed or
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
replaced on a scheduled basis.
Safety Committee members are rewarded
Safety Committee Yes Maybe No
for their participation on the committee.
New employee orientation
Recordkeeping Yes No
Task specific training
Recordkeeping Yes No
Date, topic, and sign in sheet for safety
Recordkeeping trainings Yes No
Safety committee minutes
Recordkeeping Yes No
Date of safety inspections
Recordkeeping Yes No
Date of corrective items applicable to safety
Recordkeeping inspection Yes No
Recordkeeping Progressive discipline for safety violations Yes No
Written safety program
Recordkeeping Yes No
Preventative maintenance
Recordkeeping Yes No
Repair logs
Recordkeeping Yes No
Incident investigation forms
Recordkeeping Yes No
First Report of Injury
Recordkeeping Yes No
Recordkeeping OSHA 300 Logs (current and five years prior) Yes No
Employer Experience Reports, also known
Recordkeeping Yes No
as, Loss Runs
Recordkeeping Safety Data Sheets (SDS), formerly MSDS Yes No
Fire extinguisher inspections
Recordkeeping Yes No
Snow removal logs
Recordkeeping Yes No
Return to Work Program
Recordkeeping Yes No
Offers of Light Duty
Recordkeeping Yes No
Claims notes
Recordkeeping Yes No
Emergency drill evaluations
Recordkeeping Yes No
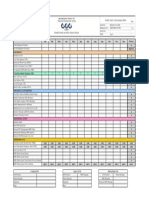
Safety Dashboard Summary
Hazard Identification Hiring & Onboarding Practices Incident Management
Total Possible Total Possible Total Possible
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 49 49 2014 0 0 0 47 47 2014 0 0 0 18 18
2015 0 0 0 49 49 2015 0 0 0 47 47 2015 0 0 0 18 18
2016 0 0 0 49 49 2016 0 0 0 47 47 2016 0 0 0 18 18
2017 0 0 0 49 49 2017 0 0 0 47 47 2017 0 0 0 18 18
2018 0 0 0 49 49 2018 0 0 0 47 47 2018 0 0 0 18 18
Excellent
2014 2015 2014 2015 2014 2015
Always Always
Good
Sometimes Sometimes
Opportunity
Never Never
Not Answered
Not Answered Not Answered
2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018
Management Commitment Recordkeeping Return to Work Management
Total Possible Total Possible Total Possible
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Points Year Yes No Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 15 15 2014 0 0 21 21 2014 0 0 0 20 20
2015 0 0 0 15 15 2015 0 0 21 21 2015 0 0 0 20 20
2016 0 0 0 15 15 2016 0 0 21 21 2016 0 0 0 20 20
2017 0 0 0 15 15 2017 0 0 21 21 2017 0 0 0 20 20
2018 0 0 0 15 15 2018 0 0 21 21 2018 0 0 0 20 20
2014 2015 2014 2015 2014 2015
Excellent Yes Always
Good Sometimes
Opportunity No Never
Not Answered Not Answered Not Answered
2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018
Roles and Responsibilities Safety Committee Safety Coordinator
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Total Possible Year Yes Maybe No Not Answered Total Possible Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Total Possible
Points Points Points
2014 0 0 0 21 21 2014 0 0 0 27 27 2014 0 0 0 12 12
2015 0 0 0 21 21 2015 0 0 0 27 27 2015 0 0 0 12 12
2016 0 0 0 21 21 2016 0 0 0 27 27 2016 0 0 0 12 12
2017 0 0 0 21 21 2017 0 0 0 27 27 2017 0 0 0 12 12
2018 0 0 0 21 21 2018 0 0 0 27 27 2018 0 0 0 12 12
2014 2015 2014 2015 2014 2015
Excellent Yes Excellent
Good Maybe Good
Opportunity No Opportunity
Not Answered Not Answered Not Answered
2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018 2016 2017 2018
Training and Awareness
Total Possible
Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 48 48
2015 0 0 0 48 48
2016 0 0 0 48 48
2017 0 0 0 48 48
2018 0 0 0 48 48
2014 2015
Always
Sometimes
Never
Not Answered
2016 2017 2018
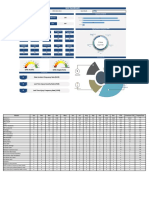
Safety Dashboard Summary
Hazard Identification Hiring & Onboarding Practices Incident Management
Total Possible Total Possible Total Possible
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 49 49 2014 0 0 0 47 47 2014 0 0 0 18 18
2015 0 0 0 49 49 2015 0 0 0 47 47 2015 0 0 0 18 18
2016 0 0 0 49 49 2016 0 0 0 47 47 2016 0 0 0 18 18
2017 0 0 0 49 49 2017 0 0 0 47 47 2017 0 0 0 18 18
2018 0 0 0 49 49 2018 0 0 0 47 47 2018 0 0 0 18 18
2018 2018 2018
2017 2017 2017
Excellent
Always Sometimes Always Sometimes
2016 Good 2016 2016
Opportunity
Never Not Answered Never Not Answered
2015 2015 2015
Not Answered
2014 2014 2014
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Management Commitment Recordkeeping Return to Work Management
Total Possible Total Possible Total Possible
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Points Year Yes No Not Answered Points Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 15 15 2014 0 0 21 21 2014 0 0 0 20 20
2015 0 0 0 15 15 2015 0 0 21 21 2015 0 0 0 20 20
2016 0 0 0 15 15 2016 0 0 21 21 2016 0 0 0 20 20
2017 0 0 0 15 15 2017 0 0 21 21 2017 0 0 0 20 20
2018 0 0 0 15 15 2018 0 0 21 21 2018 0 0 0 20 20
2018 2018 2018
2017 2017 2017
Excellent Always
Yes
2016 Good 2016 2016 Sometimes
No
Opportunity Never
Not Answered
2015 2015 2015 Not Answered
Not Answered
2014 2014 2014
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Roles and Responsibilities Safety Committee Safety Coordinator
Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Total Possible Year Yes Maybe No Not Answered Total Possible Year Excellent Good Opportunity Not Answered Total Possible
Points Points Points
2014 0 0 0 21 21 2014 0 0 0 27 27 2014 0 0 0 12 12
2015 0 0 0 21 21 2015 0 0 0 27 27 2015 0 0 0 12 12
2016 0 0 0 21 21 2016 0 0 0 27 27 2016 0 0 0 12 12
2017 0 0 0 21 21 2017 0 0 0 27 27 2017 0 0 0 12 12
2018 0 0 0 21 21 2018 0 0 0 27 27 2018 0 0 0 12 12
2018 2018 2018
2017 2017 2017
Excellent Excellent
Yes Maybe
2016 Good 2016 2016 Good
Opportunity Opportunity
No Not Answered
2015 2015 2015 Not Answered
Not Answered
2014 2014 2014
0 5 10 15 20 25 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Training and Awareness
Total Possible
Year Always Sometimes Never Not Answered Points
2014 0 0 0 48 48
2015 0 0 0 48 48
2016 0 0 0 48 48
2017 0 0 0 48 48
2018 0 0 0 48 48
2018
2017
Always
2016 Sometimes
Never
2015
Not Answered
2014
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Safety Dashboard Questionnaire: Category Component Excellent Good Opportunity 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Not ApplicableDocument9 paginiSafety Dashboard Questionnaire: Category Component Excellent Good Opportunity 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 Not ApplicableAbd el-hamid SeleimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolDocument105 paginiSHEQXel Performance Monitoring ToolEmil50% (2)
- Site EHS Budget Forecast - Rev BDocument2 paginiSite EHS Budget Forecast - Rev BDeepak100% (1)
- PT - Jel KPI & Calender Compliance 2019Document10 paginiPT - Jel KPI & Calender Compliance 2019adventmanurung100% (1)
- Incident and Injuries DashboardDocument4 paginiIncident and Injuries DashboardImam Hasan IdrisiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Statistics (Monthly) - Package I November-2016Document182 paginiHSE Statistics (Monthly) - Package I November-2016makdelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Man Power Total Man Hour Lagging Indicator: Hse Performance MonitoringDocument2 paginiTotal Man Power Total Man Hour Lagging Indicator: Hse Performance MonitoringRezza FahleviÎncă nu există evaluări
- SafetyDocument6 paginiSafetyrodrigo_gon57100% (1)
- QHSE Dashboard TemplateDocument8 paginiQHSE Dashboard TemplateDavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Master-Incidents-and-HSE-StatisticsDocument10 paginiProject Master-Incidents-and-HSE-StatisticsTina CoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Inspection Report 2nd Week April 2015Document5 paginiHSE Inspection Report 2nd Week April 2015adi50% (2)
- Niosh Training ScheduleDocument20 paginiNiosh Training Scheduleakula100% (2)
- Safety Statistic (Apr 2012)Document3 paginiSafety Statistic (Apr 2012)Nacorn Panchanawaporn50% (2)
- Workplace Health and Safety Assessment FormDocument9 paginiWorkplace Health and Safety Assessment Forms9n9Încă nu există evaluări
- Sheqxel Kpi Dashboard TemplateDocument15 paginiSheqxel Kpi Dashboard TemplatebergenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2a.. HSE Program & Performance CPI Project 2016Document4 pagini2.2a.. HSE Program & Performance CPI Project 2016NurAjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Documentation Audits: - Project Name - Quality Dashboard ForDocument2 paginiDocumentation Audits: - Project Name - Quality Dashboard Forfadli100% (1)
- QHSE Dashboard TemplateDocument10 paginiQHSE Dashboard TemplateAli AlahmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Safety Report For ContractorsDocument1 paginăMonthly Safety Report For ContractorsNowfal Habeeb100% (1)
- QSHE Dashboard GBU 2018.09Document218 paginiQSHE Dashboard GBU 2018.09Syerifaizal Hj. MustaphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 29 03 16 - Internal Audit Checklist - UpdatedDocument83 pagini29 03 16 - Internal Audit Checklist - Updatedhoanam2009Încă nu există evaluări
- H-F-07 EHS Monthly Performance Report REV#01Document28 paginiH-F-07 EHS Monthly Performance Report REV#01Mohamed ThowfeekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Safety Report February 2019Document2 paginiMonthly Safety Report February 2019Anonymous eFF9uwuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Dashboard 2Document4 paginiSafety Dashboard 2victorÎncă nu există evaluări
- She Performance Measurement and Monitoring RegisterDocument12 paginiShe Performance Measurement and Monitoring RegisterGcinumuzi SibandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Dashboard For Single SiteDocument23 paginiHSE Dashboard For Single SiteFOZCAN100% (2)
- Hse Monthly ReportDocument1 paginăHse Monthly Reportpunnyakumar100% (1)
- Weekly Safety ReportDocument5 paginiWeekly Safety ReportrajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Performance Report 01Document2 paginiHSE Performance Report 01Cywoo UDEHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Dashboard: Total Employees Trained Number of Internal TrainingsDocument25 paginiTraining Dashboard: Total Employees Trained Number of Internal TrainingsSajid Shah100% (2)
- QSHE Dashboard GBU 2018.08Document207 paginiQSHE Dashboard GBU 2018.08Syerifaizal Hj. MustaphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Details: HSE Action Tracker-Data Filter CreteriaDocument18 paginiProject Details: HSE Action Tracker-Data Filter CreteriaNexar GendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Safety Activity Plan of UAIL Site, Rev.-03Document1 paginăAnnual Safety Activity Plan of UAIL Site, Rev.-03Sheikh AshfaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Management Form: Project Monthly SHEQ Wall Activity PlannerDocument3 paginiSite Management Form: Project Monthly SHEQ Wall Activity PlannerParashuram PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ltifr Trir: Target Actual Performance TrendsDocument2 paginiLtifr Trir: Target Actual Performance TrendsCustomer Service0% (1)
- CCW Action Plan - GAP ANALYSIS ON SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMDocument14 paginiCCW Action Plan - GAP ANALYSIS ON SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMVinod GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osh PlanDocument11 paginiOsh PlanjookapleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- New HSE Monthly Report Statistic 2015Document47 paginiNew HSE Monthly Report Statistic 2015IchsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- QHSE Dashboard - Leading IndicatorDocument4 paginiQHSE Dashboard - Leading IndicatorAryful yahdi0% (1)
- Monthly Report - Health, Safety & Environmental GET - XXX - X - HSE Monthly Report - S397 - OPR - RPT - C - 1010Document5 paginiMonthly Report - Health, Safety & Environmental GET - XXX - X - HSE Monthly Report - S397 - OPR - RPT - C - 1010NiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Safety Observation Report For 2012Document6 paginiMonthly Safety Observation Report For 2012Ariel Dela Cruz100% (5)
- HSE Infographic Annual ReportDocument11 paginiHSE Infographic Annual Reportthinkpad100% (2)
- Initial & Re-CertificationDocument107 paginiInitial & Re-CertificationSatya PrabhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Hse Kpi ReportDocument35 paginiMonthly Hse Kpi Reportutam0% (1)
- Prequalification Checklist - (Coastline Geophysical Saudi Arabia) 2nd ReviewDocument9 paginiPrequalification Checklist - (Coastline Geophysical Saudi Arabia) 2nd ReviewShafie ZubierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phoenix H10 Weekly HSE Report 10-04-2019 To 16-04-2019Document6 paginiPhoenix H10 Weekly HSE Report 10-04-2019 To 16-04-2019Bhaskar RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAFETY Statistics AprDocument1 paginăSAFETY Statistics AprSantos RexÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Training HistoryDocument1 paginăHSE Training HistorysubhanmusadiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Monthly Report Mei 2020Document19 paginiHSE Monthly Report Mei 2020Rendi SeptiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monthly Health and Safety Statistic ReportDocument1 paginăMonthly Health and Safety Statistic Reportsubhanmusadiq100% (6)
- Qhse Dashboard: OHS Audits OHS InspectionsDocument2 paginiQhse Dashboard: OHS Audits OHS InspectionsMazhar Kaleem0% (1)
- Key Performance Indicator: Date ManpowerDocument1 paginăKey Performance Indicator: Date ManpowerAsad Awan0% (1)
- Safety Report Sample FormatDocument16 paginiSafety Report Sample FormatgomertweeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Templates Package 2 ContentDocument6 paginiTemplates Package 2 ContentMansyur NasutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Profile Sheet: Assessor (S) Labor Posture ActivityDocument70 paginiAssessment Profile Sheet: Assessor (S) Labor Posture ActivityDave Labberton92% (13)
- Assessment Profile Sheet: Assessor (S) Labor Posture ActivityDocument70 paginiAssessment Profile Sheet: Assessor (S) Labor Posture ActivityAnonymous iI88Lt100% (1)
- Monthly OHSE ReportDocument4 paginiMonthly OHSE ReportMutee MustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSE Statistics PDFDocument5 paginiHSE Statistics PDFRashid100% (1)
- General Power Tools Safety Inspection ChecklistDocument3 paginiGeneral Power Tools Safety Inspection ChecklistMobin Thomas AbrahamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lms Leading IndicatorsDocument3 paginiLms Leading IndicatorsAlvin AlfiyansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SR Calc SheetDocument5 paginiSR Calc SheetRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazmat ImanualDocument9 paginiHazmat ImanualRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Guide 1.01.001Document3 paginiInstallation Guide 1.01.001Richard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heavyjet - 328-310Document2 paginiHeavyjet - 328-310Richard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson ThemeDocument15 paginiLesson ThemeRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- OHS Policies and Procedures ManualDocument13 paginiOHS Policies and Procedures Manualismailines100% (2)
- Rescue Chart F70 F100Document2 paginiRescue Chart F70 F100Richard Thodé Jr100% (1)
- Ecbc Guide MassCasualtyDecontam 0813 PDFDocument135 paginiEcbc Guide MassCasualtyDecontam 0813 PDFRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazmat by LSUDocument240 paginiHazmat by LSURichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daniel Karnak yDocument26 paginiDaniel Karnak yRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Service PresentationDocument41 paginiCustomer Service PresentationIkin Solihin100% (2)
- Daniel Karnak yDocument26 paginiDaniel Karnak yRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Muslimah Sex Manual - A Halal Guide To Mind Blowing SexDocument65 paginiThe Muslimah Sex Manual - A Halal Guide To Mind Blowing SexRichard Thodé Jr77% (53)
- Install La Ti On - READ MEDocument2 paginiInstall La Ti On - READ MEKanagaraj PetchimuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO Audit ChecklistDocument21 paginiISO Audit Checklistghostghost12380% (5)
- Arizona HazmatDocument86 paginiArizona HazmatRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is UI Builder Worth Calculator For All Excel TipesDocument4 paginiWhat Is UI Builder Worth Calculator For All Excel TipesRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is UI Builder Worth Calculator For All Excel TipesDocument4 paginiWhat Is UI Builder Worth Calculator For All Excel TipesRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Front-End Loader TrainingDocument27 paginiFront-End Loader TrainingOmosigho Osaro0% (1)
- Model Indentifiction For Cars TestsDocument454 paginiModel Indentifiction For Cars TestsRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Leave SampleDocument14 paginiAnnual Leave SampleRichard Thodé Jr100% (1)
- Action ItemsDocument4 paginiAction ItemsRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist Audit Voor Supervisors ISO 9001Document2 paginiChecklist Audit Voor Supervisors ISO 9001Richard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Issue Management TemplateDocument4 paginiIssue Management Templatejindalyash1234Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Ract 20140411Document33 pagini2 Ract 20140411Richard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modifiable Skills MatrixDocument82 paginiModifiable Skills MatrixRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Climbing Up and Down On MachinesDocument18 pagini8 Climbing Up and Down On MachinesRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn To Know : The No-ZoneDocument20 paginiLearn To Know : The No-ZoneRichard Thodé JrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SQA Plan TemplateDocument106 paginiSQA Plan TemplatedtsharpieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Dust PDFDocument4 paginiCoal Dust PDFhoathai1112Încă nu există evaluări
- Override Bypass ControlDocument26 paginiOverride Bypass ControlRajesh Krishnamoorthy100% (2)
- SPARK - HSE ManualDocument183 paginiSPARK - HSE ManualXtian Anes100% (1)
- NFCC Specialised Housing GuidanceDocument342 paginiNFCC Specialised Housing GuidanceAaron FillisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Control ManualDocument78 paginiQuality Control ManualRajeshSekar100% (3)
- Cold Front - Vol. 10 No. 2, 2010 NewsletterDocument8 paginiCold Front - Vol. 10 No. 2, 2010 NewsletterAshfaq Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AB-524 Pressure Relief Devices Requirements Specification PDFDocument55 paginiAB-524 Pressure Relief Devices Requirements Specification PDFkhaireddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atlas Copco - Roto Xtend Duty Fluid - SDSDocument14 paginiAtlas Copco - Roto Xtend Duty Fluid - SDSEloany Batista da SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Firefighting EquipmentsDocument4 paginiList of Firefighting EquipmentsR Cube Infratech Pvt Ltd100% (1)
- Bdo Unibank Osha ImplementationDocument9 paginiBdo Unibank Osha ImplementationAbegail TorremochaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Honda Hornet 2004 - CB600F - ServicemanualDocument247 paginiHonda Hornet 2004 - CB600F - ServicemanualGeorge Calin0% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet BIOC16975A: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDocument9 paginiSafety Data Sheet BIOC16975A: Section: 1. Product and Company IdentificationJosé Eduardo Narváez CampechanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GMP+ B1 - ENm 9234Document40 paginiGMP+ B1 - ENm 9234Julio Cesar Valle ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Register-QatarDocument62 paginiLegal Register-QatarRamasubramanian Sankaranarayanan80% (5)
- Example Health and Safety Policy: Setting The SceneDocument4 paginiExample Health and Safety Policy: Setting The SceneFuzail AyazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exxsol D60Document10 paginiExxsol D60Adi WiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kurebwa and Mushiri 1-S2.0-S2351978919309795-MainDocument15 paginiKurebwa and Mushiri 1-S2.0-S2351978919309795-MainJoseph KurebwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dasar ToksikologiDocument47 paginiDasar ToksikologiAmirul Rahmat AlfaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod9 Confined Spaces QuizDocument16 paginiMod9 Confined Spaces QuizMhanna AYÎncă nu există evaluări
- F&E0003 - Fire & Evacuation PlanDocument3 paginiF&E0003 - Fire & Evacuation PlanStephenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety in GPR Prospecting: A Rarely-Considered IssueDocument2 paginiSafety in GPR Prospecting: A Rarely-Considered Issuerahmaan perkasa alamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Asses 41-Blasting and Painting ControlDocument3 paginiRisk Asses 41-Blasting and Painting ControlRochdi Bahiri100% (2)
- HAZMAT Management Program PlanDocument105 paginiHAZMAT Management Program PlanMansoor AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4 Draft University Safety Policy v2Document18 paginiP4 Draft University Safety Policy v2Deil L. NaveaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emulsogen Epn 287-MSDSDocument10 paginiEmulsogen Epn 287-MSDSMohamed HalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Paper Information Security Risk ManagementDocument19 paginiWhite Paper Information Security Risk ManagementPryn SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review On Health and SafetyDocument7 paginiLiterature Review On Health and Safetyeygyabvkg100% (1)
- Task Based Risk MG T FormDocument3 paginiTask Based Risk MG T FormNur Hanim Abd GhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precast Concrete Stormwater Management Technical BrochureDocument12 paginiPrecast Concrete Stormwater Management Technical BrochureDodecccahedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology and Livelihood Education Agriculture 9: Quarter 3, Wk.5 Module 5: Common OHS HazardsDocument11 paginiTechnology and Livelihood Education Agriculture 9: Quarter 3, Wk.5 Module 5: Common OHS HazardsJay Aldin RoseteÎncă nu există evaluări