Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lecture IX (Riveted Joint - Eccentric Loading)
Încărcat de
Dangol Rupesh0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
60 vizualizări17 paginiRiveted joint
Titlu original
Lecture IX (Riveted Joint_Eccentric Loading) - Copy
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentRiveted joint
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
60 vizualizări17 paginiLecture IX (Riveted Joint - Eccentric Loading)
Încărcat de
Dangol RupeshRiveted joint
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPSX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 17
Machine Element Design & Process - I
MEEG 315
Module VIII : Riveted, Screw Threaded and Welded
Connections
Lecture 9 : Eccentric Loading
DISCLAIMER
The presentation contains extraction of contents from books, technical paper,
studies and other public domain.
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 2
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Line of force doesn’t pass through the centre of
gravity (CG) of the joint
• Has an offset of
distance ‘e’
• Structural joints are
commonly eccentrically
loaded joints
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 3
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Forces on riveted joints due to eccentric load
Axial Force (Primary)
Torsion Force
(Secondary)
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 4
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Primary / Direct Shear Force
P
Ps
n
acting parallel to the
direction of P
n = no of rivets
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 5
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Secondary / Torsion Force
• Moment tries to
rotate the joint
about CG
Moment (M) = P.e
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 6
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Secondary / Torsion Force
• Force due to moment
Fm α l
l = radial distance
from CG
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 7
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Secondary / Torsion Force
• Force due to moment
Fm α l
Fm = k.l
Fm
k
l
k = proportionality
constant
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 8
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Secondary / Torsion Force
• Force due to moment
M = Fm.l
= (k.l).l
= k.l2
Total M = Σ k.l2
= k.Σl2
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 9
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Secondary / Torsion Force
• Force due to moment
Total M = (Fm/l). Σ l2
M = P.e
Fm
P.el
l 2
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 10
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Total forces acting on the joint
P
Fs Ps
n
Fm
P.el
l 2
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 11
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Resultant Force
R P F 2Ps FmCos
s
2 2
m
= angle between Ps and Fm
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 12
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
• Resultant Force
Which rivet is more
vulnerable?
Rivet 1 / 2 / 3 / 4?
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 13
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
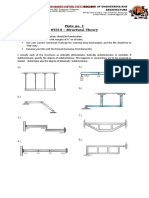
Exercise 6.1
The bracket as shown in figure, is to
carry a load of 45 kN.
Determine the size of the rivet if the
shear stress is not to exceed 40
MPa.
Assume all rivets of the same size.
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 14
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
Exercise 6.1
The bracket as shown in figure, is to
carry a load of 45 kN.
Determine the size of the rivet if the
shear stress is not to exceed 40
MPa.
Assume all rivets of the same size.
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 15
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
Exercise 6.2
A bracket is to be attached to a wall with the help of 6 rivets. The
different arrangements in which the brackets can be attached to
the wall, with these rivets are shown in the figure. The maximum
allowable stress in shear is 60N/mm2.
The bracket is required to support a load of 90 kN with an
eccentricity of 200mm.
Determine the way in which the rivets should be arranged so that
the design is economical. Also determine the size of the rivet.
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 16
Welded Joints
Eccentric Loaded Joints
12/24/2015 Lecture 9: Eccentric Loading 17
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- MATH Final PreboardDocument8 paginiMATH Final PreboardKristelle V. TorrealbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Blasthole Drilling PDFDocument64 paginiIntroduction To Blasthole Drilling PDFSawadogo100% (3)
- Bolted ConnectionsDocument59 paginiBolted ConnectionsTusharRanjan100% (5)
- Review Module 45 (RCD 5) - May 2022Document2 paginiReview Module 45 (RCD 5) - May 2022Team EsperanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspection of Steel Penstocks & Pressure Conduits Vol2-8Document43 paginiInspection of Steel Penstocks & Pressure Conduits Vol2-8Manmohit Singh67% (3)
- 02 STRUCTURAL STEEL DESIGN IntroDocument21 pagini02 STRUCTURAL STEEL DESIGN IntroRi MarkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Seminar 2015 PDFDocument196 paginiAnnual Seminar 2015 PDFWai TszYanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diamec Brochure PDFDocument12 paginiDiamec Brochure PDFDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board Exam SyllabusDocument7 paginiBoard Exam SyllabusRegin Adrian LansangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bmat Physics Formula Sheet InverseDocument2 paginiBmat Physics Formula Sheet Inverseeneagu3349Încă nu există evaluări
- All DesignDocument45 paginiAll Designchandan kumar c gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Column Lateral TiesDocument36 paginiShort Column Lateral TiesMark Gerald Oreiro100% (2)
- 1 Steel Penstock: 1.1 Location and ArrangementDocument7 pagini1 Steel Penstock: 1.1 Location and ArrangementDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- HTTP WWW Mathalino Com Reviewer Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Energy and HeadDocument13 paginiHTTP WWW Mathalino Com Reviewer Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Energy and HeadYel Carla Sovill100% (3)
- Inspection of PenstockDocument9 paginiInspection of PenstockDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battery Room Ventilation and SafetyDocument62 paginiBattery Room Ventilation and SafetyingatvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Hammer KSB PumpsDocument34 paginiWater Hammer KSB Pumpsfuji6500100% (12)
- Centrifugal Fan Design: Design of Inlet Duct and ImpellerDocument9 paginiCentrifugal Fan Design: Design of Inlet Duct and ImpellerTanish VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992De la EverandComputational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992S. MurakamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Sets For MECHANICS OF MACHINESDocument11 paginiProblem Sets For MECHANICS OF MACHINESzxzxzx207Încă nu există evaluări
- Merge Fluid MechanicsDocument221 paginiMerge Fluid Mechanicsbigorno12333% (3)
- 4.) RCD - Midterm Library Work Quiz - Concept and Solutions (1-Way Slab)Document8 pagini4.) RCD - Midterm Library Work Quiz - Concept and Solutions (1-Way Slab)Penuel G. Bantog100% (1)
- PDF Simplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPDocument200 paginiPDF Simplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPMeverlyn RoqueroÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCD CompanyDocument21 paginiPCD CompanyPaolo ManansalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Bridge StructuresDocument158 paginiAnalysis and Design of Reinforced Concrete Bridge StructuresINARQ1979Încă nu există evaluări
- Timber and Steel Design IntroductionDocument40 paginiTimber and Steel Design IntroductionCloe Dianne SillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swot Analysis On The Development of Cold Chain Logistics in ChinaDocument4 paginiSwot Analysis On The Development of Cold Chain Logistics in ChinaIJIRIS - INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE RESEARCH IN INFORMATION SECURITYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Compression Members Lec #1Document5 paginiModule 3 Compression Members Lec #1k. NotujÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE144 Q2 AnswersDocument2 paginiCE144 Q2 AnswersMike SyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge ComponentsDocument58 paginiBridge Componentsradhakrishnang100% (1)
- Plate No. 1 ST314 - Structural Theory: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument4 paginiPlate No. 1 ST314 - Structural Theory: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityRamil T. TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- A) Ability To Function On Multidisciplinary Teams B) Ability To Communicate EffectivelyDocument24 paginiA) Ability To Function On Multidisciplinary Teams B) Ability To Communicate EffectivelyJulian DeleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Types of Water Distribution NetworkDocument5 pagini4 Types of Water Distribution Networkjuan dela cruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Structure I Sesi 10Document21 paginiSteel Structure I Sesi 10sagokkantangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp-9 Bending Test On Wooden BeamDocument8 paginiExp-9 Bending Test On Wooden BeamsushilkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hinges PDFDocument2 paginiHinges PDFKirstenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 013 - ForewordDocument2 pagini013 - ForewordMark Roger II HuberitÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOS 2 - 3 Moment EquationDocument5 paginiTOS 2 - 3 Moment EquationAndrei AlidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR 410110 Prestressed ConcreteDocument8 paginiNR 410110 Prestressed ConcreteSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- LOCAL BUCKLING2 VisualBeeDocument24 paginiLOCAL BUCKLING2 VisualBeeMart Brevin BitonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clave, Artemio John C./ 1512117 CE513/ Prestresessed Concrete Design Bsce/ 5 Year/ CE52S2/ Assignment No. 2 Engr. Adams Royce A. DionisioDocument3 paginiClave, Artemio John C./ 1512117 CE513/ Prestresessed Concrete Design Bsce/ 5 Year/ CE52S2/ Assignment No. 2 Engr. Adams Royce A. DionisioDaniel DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Global Analysis EquationsDocument54 paginiChapter 3 - Global Analysis EquationsCarl Chester RagudoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceDocument4 paginiA. Read The Following Book Chapters and Other Readings For ReferenceJomar LampitokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 4 - QuantityDocument12 paginiModule 4 - QuantityKimberly Wealth Meonada MagnayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionDocument26 paginiIrregular Section of Beams Reinforced For TensionMadelyn Escaner MorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Mensuration ProblemsDocument2 paginiSolid Mensuration ProblemsAven MharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Manual For Structural Analysis PDFDocument17 paginiSolutions Manual For Structural Analysis PDFMugiwara SparrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis ManuscriptDocument177 paginiThesis ManuscriptMaevin WooÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPM Cost Crashig-3Document17 paginiCPM Cost Crashig-3John Rennekien Mateo0% (1)
- ECS448 - Topic 5 (Deformation - Virtual Work For Frame & Truss)Document33 paginiECS448 - Topic 5 (Deformation - Virtual Work For Frame & Truss)darwishshahrir__Încă nu există evaluări
- Indetermine StructureDocument8 paginiIndetermine Structuremaloy100% (1)
- History of Reinforced Concrete ConstructionDocument8 paginiHistory of Reinforced Concrete ConstructionBlueeeMoonZiahGraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH Activity 7Document3 paginiMATH Activity 7EurydiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMDocument16 pagini2160607-Elementary Structural Design 09012017 040945AMAydinAkhtarpour100% (1)
- Assignment Traffic EngineeringDocument9 paginiAssignment Traffic EngineeringNadeem YousafzaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- C 9 - Long ColumnsDocument29 paginiC 9 - Long ColumnsRekanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Document2 paginiFA NO. 7 (Problem Set)Peter Adrian Ngo100% (1)
- T Beams 1Document27 paginiT Beams 1Jonniel De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Appendix For Structural Steel DesignDocument36 paginiDesign Appendix For Structural Steel DesignridzwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chpater 01Document3 paginiChpater 01Emersson Baltazar Aguilar HuamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydraulicsDocument1 paginăHydraulicsJerry Jake June HayaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Quiz - Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument1 paginăFinal Quiz - Mechanics of Deformable BodieschbarcenalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hollow Blocks PiceDocument4 paginiHollow Blocks PiceCharlyn FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No. 5 Reflection On Virtual Plant Visits - Concrete and Rebars Rehabilitations and Webinar - Tunneling (Tunnel Boring Machine) v.2Document1 paginăAssignment No. 5 Reflection On Virtual Plant Visits - Concrete and Rebars Rehabilitations and Webinar - Tunneling (Tunnel Boring Machine) v.2John Rhey Almojallas BenedictoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Columns Subject To Axial Load and BendingDocument10 paginiDesign of Columns Subject To Axial Load and BendingWilbert ReuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FootingsDocument24 paginiFootingsLester Corvera OlaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Fluids: Sample Problems BDocument4 paginiProperties of Fluids: Sample Problems BFronda Jerome BlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch-6 One Way SlabDocument12 paginich-6 One Way SlabameerÎncă nu există evaluări
- River NavigationDocument7 paginiRiver NavigationIntan MadiaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus 2017 Numerical Methods For Civil EngineeringDocument3 paginiSyllabus 2017 Numerical Methods For Civil EngineeringNyikolajev100% (1)
- Design of Purlins: With Engr. Mark Lehi P. Palmes Faculty-RMMC Civil Engineering Program Review LecturerDocument5 paginiDesign of Purlins: With Engr. Mark Lehi P. Palmes Faculty-RMMC Civil Engineering Program Review LecturerMohammad Taha PumbayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985De la EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture VII (Riveted Joint - Eccentric Loading)Document17 paginiLecture VII (Riveted Joint - Eccentric Loading)Bikalpa khadkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Lift Gate PartsDocument2 paginiVertical Lift Gate PartsDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rupesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDocument4 paginiRupesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDocument2 paginiMDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDocument4 paginiRupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swaechchha Dahal: Electrical EngineerDocument1 paginăSwaechchha Dahal: Electrical EngineerDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDocument4 paginiRupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDocument4 paginiRupadadsadadadaddadsdaesh Dangol: Mechanical EngineerDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vidyut PDFDocument112 paginiVidyut PDFDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGM FutsalDocument7 paginiAGM FutsalDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling and Optimizing Hydraulic Transients in WaterDocument8 paginiModeling and Optimizing Hydraulic Transients in WaterDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metodos NumericosDocument226 paginiMetodos NumericosEVCYÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Toe THC-1 Drilling Machine. Document Number C76: Power Unit 2 Sets Double Cylinder Diesel EngineDocument8 paginiFrom Toe THC-1 Drilling Machine. Document Number C76: Power Unit 2 Sets Double Cylinder Diesel EngineDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Method of Characterstics in Water HammerDocument12 paginiApplication of Method of Characterstics in Water HammergouthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pen StockDocument7 paginiPen StockDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill LiDocument5 paginiDrill LiDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specifications For DrillingDocument9 paginiSpecifications For DrillingDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specifications For DrillingDocument9 paginiSpecifications For DrillingDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018-9-20 Chinese Class DAY-2Document11 pagini2018-9-20 Chinese Class DAY-2Dangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand List RupeshDocument2 paginiDemand List RupeshDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drill LiDocument5 paginiDrill LiDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018-9-17 Chinese Class DAY-1Document14 pagini2018-9-17 Chinese Class DAY-1Dangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018-9-20 Chinese Class DAY-2Document11 pagini2018-9-20 Chinese Class DAY-2Dangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground Freezing For Tunnel Cross PassagesDocument39 paginiGround Freezing For Tunnel Cross PassagesDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpurDocument57 paginiSpurDangol RupeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Organiser: Properties of Waves Sound Waves HearingDocument1 paginăKnowledge Organiser: Properties of Waves Sound Waves HearingLuisGamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS Iec-Ieee 62271-37-082-2012Document24 paginiBS Iec-Ieee 62271-37-082-2012Lugo EngenhariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16Document43 paginiChapter 16Kashan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFDocument6 paginiProblem Solving Questions (Part I) PDFclainÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME201 WorkHeatDocument5 paginiME201 WorkHeatsamar sultanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FFF SolutionsDocument152 paginiFFF SolutionsMohammedAL-AthariÎncă nu există evaluări
- UFAZ M2 Advanced Transfers Part IDocument19 paginiUFAZ M2 Advanced Transfers Part Ifidan muradovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions 2 PHYSICS 2Document6 paginiSolutions 2 PHYSICS 2MARIAMA SILLAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Project For Advanced Fluid MechanicsDocument15 paginiFinal Project For Advanced Fluid MechanicsMohammed SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Loading of A Forklift Truck Lifting InstallationDocument4 paginiDynamic Loading of A Forklift Truck Lifting Installationmiroslav11Încă nu există evaluări
- Wep ExerciseDocument25 paginiWep ExercisePankaj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 paginiمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter 11Document18 paginiPhysics Chapter 11cryptachrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No.7 Thermodynamics-I by Engineer Noor RahmanDocument54 paginiLecture No.7 Thermodynamics-I by Engineer Noor RahmanHassan MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (NORSOK) - 3Document5 paginiPages From DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES (NORSOK) - 3dunglxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiphysics Topology Optimization of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow SystemsDocument7 paginiMultiphysics Topology Optimization of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Systemslqwang20Încă nu există evaluări
- Kelompok 40 - Impact FIXDocument29 paginiKelompok 40 - Impact FIXDewi Puspa NingrumÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP350 Classical MechanicsDocument3 paginiMP350 Classical Mechanicsfree_progÎncă nu există evaluări
- BM QN Paper Nov Dec 2021Document3 paginiBM QN Paper Nov Dec 2021ShubhashreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure - IV CE 3251Document63 paginiStructure - IV CE 3251Abbdullah RayhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harony P2 CLS Final 2024Document452 paginiHarony P2 CLS Final 2024Muhammed RafelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANC20LA059 Structures Rudder Study-RelDocument16 paginiANC20LA059 Structures Rudder Study-RelFRRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y0405 2 md1Document6 paginiY0405 2 md1hthaier4062Încă nu există evaluări