Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Reported Speech
Încărcat de
Juanita Rizqi Hadi SaputriDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Reported Speech
Încărcat de
Juanita Rizqi Hadi SaputriDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
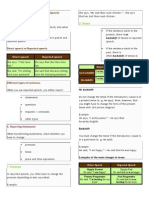
REPORTED (= INDIRECT) SPEECH
Is the reporting verb in the past form (said, told,...) you have to change the tense.
Direct speech Indirect speech Direct Speech Indirect speech
Present simple Past simple go went
Present progressive Past progressive am/is/are going was/were going
Past simple Past perfect went had gone
Past progressive Past perfect progressive was/were going had been going
Present perfect simple Past perfect has/have gone had gone
Present perfect progressive Past perfect progressive has/have been going had been going
Future Conditional I will go would go
Example:
Peter said, "Carol is a nice girl."
Peter said (that) Carol was a nice girl.
Don't change these verbs: might, could, would, should
Example:
He said, "I might arrive late."
He said (that) he might arrive late.
It isn't necessary to change the present tense into the past tense if the information in the direct
speech is still true or a general statement.
Examples:
Frank said, "My sister is a secretary."
Frank said (that) his sister is (was) a secretary.
He told us, "The sun rises in the east."
He told us that the sun rises (rose) in the east.
When you form the reported speech you have to pay attention that the pronouns refer to the correct
persons.
Examples:
Susan said, "My parents are clever scientists."
Susan said (that) her parents were clever scientists.
Tom said, "I like PE best."
Tom said (that) he liked PE best.
They said, "We went swimming with our friends."
They said (that) they had gone swimming with their friend.
Betty said, "Sam told me the truth."
Betty said (that) Sam had told her the truth.
Direct speech Indirect speech
She said I - my - me she - her - her
He said I - my - me he - his - him
They said we - our - us they - their - them
You and your:
They told her / him / me / them / us, "George likes you."
They told her / him / me / them / us (that) George liked her / him / me / them / us.
They told her / him / me / them / us,"George likes your sister."
They told her / him / me / them / us (that) George likes her / his / my / their / our sister.
They told her / him / me / them / us,"You are clever."
They told her / him / me / them / us (that) she / he / I / they / we was / were clever.
Expressions of time and place - we have to change them.
Direct speech Indirect speech
Time now then
today that day
yesterday the day before
tomorrow the next / following day
last week, month,... the previous week, month,... / the week, month,... before
next week, month,... the following week, month,...
a (week,...) ago a (week,...) before
Place here there
This that
these thos
Example:
She said, "I have already seen Carol today."
She said (that) she had already seen Carol that day.
Reported Questions
If there is a question word we keep it.
Examples:
They asked me, "Where is the next supermarket?"
They asked me where the next supermarket was.
She asked them, "How often do you play golf?"
She asked them how often they played golf.
If there is no question word we start the reported speech with if or whether
Examples:
She asked me, "Do you like some tea?"
She asked me if/whether I liked some tea.
We asked them, "Did she arrive in time?"
We asked them if/whether she had arrived in time.
Reported Requests
If someone asks you in a polite way use (not) to + infinitive
Examples:
He asked her, "Could you close the door, please?"
He asked her to close the door.
She asked them, "Help me, please."
She asked them to help her.
Reported Orders
If someone doesn't ask you politely or gives you an order use (not) to + infinitive
Examples:
He told me, "Be quiet!"
He told me to be quiet.
She told us, "Don't stay up too late!"
She told us not to stay up too late.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideDe la EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect SpeechDocument3 paginiIndirect SpeechlckjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument11 paginiReported Speechmis tarbiyatulmubtadiinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument8 paginiReported SpeechMAGDALENA MELANIA GHERGHEÎncă nu există evaluări
- USE FormDocument17 paginiUSE FormBernardo RochaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct & Indirect Spech RulesDocument9 paginiDirect & Indirect Spech RulesUmme AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 paginiDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6Încă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 paginiIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515Încă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech66Document14 paginiReported Speech66Harshita ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statements in Reported SpeechDocument6 paginiStatements in Reported SpeechZenmetsu No AkaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loi Noi Gian TiepDocument5 paginiLoi Noi Gian TiepNguyễn Bảo Gia HânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect Speech: StatementsDocument5 paginiDirect and Indirect Speech: StatementsЛеся ЧабаненкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofDocument6 paginiIndirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofMikael RanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocument6 paginiReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechHasib QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng GrammarDocument16 paginiEng GrammarChristine LlantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech - AdvancedDocument9 paginiReported Speech - Advancedomla2024pcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechNoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech RulesDocument4 paginiReported Speech RulesShaliza MardianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2º BachilleratoDocument4 paginiReported Speech 2º BachilleratoBlancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument8 paginiReported SpeechDoris Ana-MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)Document12 paginiDirect Indirect Speech (2 Mei 2014)A_IntaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoria Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiTeoria Reported SpeechasunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech BasicsDocument58 paginiReported Speech Basicskarakirkader094Încă nu există evaluări
- Mosaic 1 Silver Edition: GrammarDocument7 paginiMosaic 1 Silver Edition: Grammaresya asmandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument7 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechDivya Rai SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech: Created by Gabriela Encheva 3 High School of Natural Sciences VarnaDocument29 paginiReported Speech: Created by Gabriela Encheva 3 High School of Natural Sciences VarnaEmiliya IvanovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2020Document17 paginiReported Speech 2020ekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReported SpeechJohn Alvin de LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect (Reported) Speech in StatementsDocument4 paginiIndirect (Reported) Speech in Statementssenthilr78Încă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument24 paginiReported SpeechjuliareveronraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)Document6 pagini8. REPORTED SPEECH (Lời nói gián tiếp)HangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech 2Document13 paginiReported Speech 2S Wladislaw NitreanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech RulesDocument14 paginiReported Speech RulessigiryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 SPEECH - Rules & ExerciseDocument32 pagini7 SPEECH - Rules & ExerciseHarunur RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 paginiEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocument7 paginiGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument8 paginiDirect and Indirect SpeechjankascottishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument17 paginiReported SpeechLisseth Andrea Ledesma GarriazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReported SpeechZaniShiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5Document35 paginiGroup 5Marta AtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocument3 pagini1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Grammar 0Document5 paginiReported Speech Grammar 0Katita VieraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Direct and Indirect 3 Pages OnlyDocument4 paginiLecture Direct and Indirect 3 Pages OnlyJuliet Orabiles MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Speech: Sibela EminovićDocument21 paginiIndirect Speech: Sibela EminovićAndjela TomovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pagini01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument4 pagini2-Tenses: Direct Speech Reported SpeechAbdelhadi Ait AllalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DestroyedDocument14 paginiDestroyedДильназ КожахметоваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument34 paginiReported SpeechCary Ortiz100% (3)
- Reported Speech 0Document6 paginiReported Speech 0Eva VillamedianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech Rules: StatementsDocument6 paginiReported Speech Rules: Statementsmnj_gautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReported SpeechalmurcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument28 paginiDirect & Indirect SpeechKaashvi AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported Speech.Document4 paginiReported Speech.reebot 666Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 - Language Focus - Reported SpeechDocument11 paginiUnit 3 - Language Focus - Reported SpeechNguyễn Minh KhôiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument8 paginiReported SpeechHienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statements, Questions, and Commands/requests.: Reported SpeechDocument7 paginiStatements, Questions, and Commands/requests.: Reported SpeechVanja Đorđevic100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument4 paginiReported SpeechIrina MargineanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morphology 5 DerivationDocument5 paginiMorphology 5 DerivationYuriatson JubhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1 5. (Textbook) Abstract Nouns PDFDocument4 pagini5.1 5. (Textbook) Abstract Nouns PDFUDAYAN SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Superlatives LessonDocument2 paginiSuperlatives LessondanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2 TestDocument3 paginiB2 TestJavier Alvarez RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Strong and Weak FormsDocument28 paginiChapter 7 Strong and Weak Formsaligamil9100% (1)
- InglésDocument3 paginiIngléscamila ruiz0% (1)
- RPT English Form 2Document8 paginiRPT English Form 2Hayati AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 Tense in English ClassDocument8 pagini16 Tense in English ClassRivaldy FirmansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Alphabet: Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 Row 4 Row 5 Row 6 Row 7 Row 8Document15 paginiThe Alphabet: Row 1 Row 2 Row 3 Row 4 Row 5 Row 6 Row 7 Row 8nguyenquyhoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ModuleDocument20 paginiSample ModuleJeremiah CalpaturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Makalah Tentang Adverb PresentasikanDocument11 paginiMakalah Tentang Adverb PresentasikanNila sari al fahryÎncă nu există evaluări
- French Grammar For BeginnersDocument3 paginiFrench Grammar For BeginnersMandar GogateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triumph Redong Vol 1Document112 paginiTriumph Redong Vol 1VINOTINIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Work For 13 April 2022 - Reported SpeechDocument6 paginiClass Work For 13 April 2022 - Reported SpeecharavindrnairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple: Affirmative Form Negative Form Interrogative FormDocument3 paginiPresent Simple: Affirmative Form Negative Form Interrogative Formvanda_mataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International Examinations: Bengali 3204/02 May/June 2017Document8 paginiCambridge International Examinations: Bengali 3204/02 May/June 2017Shadman ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Iii (English) Tejas Question Paper 2024Document4 paginiClass Iii (English) Tejas Question Paper 2024vinodsharmaupiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monroe 14 - Commas, Colons, and Semicolons PracticeDocument2 paginiMonroe 14 - Commas, Colons, and Semicolons PracticeJames HollomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi 1 Active & Passive Voice-1Document13 paginiMateri 1 Active & Passive Voice-1OktaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia4 - Inglés 10 - 2020Document7 paginiGuia4 - Inglés 10 - 2020miguel beltranÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUGAS - Bahasa Inggris UtDocument29 paginiTUGAS - Bahasa Inggris UtCahyani SiskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spanish English Verb Tenses 2015Document155 paginiSpanish English Verb Tenses 2015Fernando GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phrasal Verbs TesisDocument317 paginiPhrasal Verbs TesisEl Lauta100% (16)
- Learn Spanish - Speak Abroad AcademyDocument245 paginiLearn Spanish - Speak Abroad AcademyNina MOHAAMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Best A2 Unit 1 Reading TestDocument3 paginiPersonal Best A2 Unit 1 Reading Testmaru lozanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Worksheets PDFDocument4 pagini3 Worksheets PDFTeresa ValverdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of AdverbsDocument8 paginiTypes of AdverbsJeremy BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Passive Voice WorksheetsDocument7 paginiThe Passive Voice WorksheetsAzra IlyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises Remedial 08 11.04.2016Document21 paginiExercises Remedial 08 11.04.2016Admir100% (1)
- Your PDF - English Tenses For IELTSDocument9 paginiYour PDF - English Tenses For IELTSSofia Cristina Briones RamosÎncă nu există evaluări