Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
P 17
Încărcat de
selinaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
P 17
Încărcat de
selinaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
E UROCODES S PREADSHEETS S TRUCTURAL D ESIGN
S ECTION 1 E UROCODE 1 EN 1991-1-3
1.10 Verification tests
EN1991‐1‐3_(A).XLS. 6.00 MB. Created: 23 February 2013. Last/Rel.-date: 23
February 2013. Sheets:
— Splash
— CodeSec4-5
— CodeSec6.
EXAMPLE 1-A‐ Roof shape coefficients: Pitched roofs ‐ test 1
Given: Low wind velocities are sufficient to blow snow accumulations from a roof or to cause a
drift of snow which could lead to a local enhancement of the snow load. Roof shape
coefficients are needed for an adjustment of the ground snow load to a snow load on the
roof taking into account these effects. Assuming a geographical location where
exceptional snow falls are unlikely to occur but exceptional snow drifts may occur, find
the roof shape coefficients using the data given in tables below for angles of pitch of roof
equal to 1 = 30 and 2 = 40 .
Angle of pitch of roof : 0° < < 15° 15° < < 30° 30° < < 60° > 60°
1 = 0,8 0,8 + 0,4·( – 15)/15 1,2·(60 – )/30 0,0
Table 1.4 Drifted snow load shape coefficient for a duo-pitched roof(a).
(a). Manual for the design of building structures to Eurocode 1 and Basis of Structural Design April 2010. © 2010
The Institution of Structural Engineers.
Angle of pitch of roof : 0° < < 30° 30° < < 60° > 60°
1 = 0,8 0,8·(60 – )/30 0,0
Table 1.5 Undrifted snow load shape coefficient (from Table 5.2, EN 1991-1-3).
[Reference sheet: CodeSec4‐5]‐[Cell‐Range: A29:O29‐A63:O63].
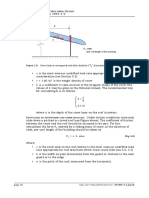
Solution: The most unfavourable load situation has to be chosen for the design. The undrifted and
drifted load arrangements which should be used are shown in Figure 1.9 below.
Using the given numerical data, we get:
(Case ii and iii) ‐ Drifted load arrangement (see Table 1.4 above):
1 = 30 , 1 1 = 0 8 + 0 4 1 – 15 15 = 0 8 + 0 4 30 – 15 15 = 1 20 ; 1 1 = 0 .
2 = 40 , 1 2 = 1 2 60 – 2 30 = 1 2 60 – 40 30 = 0 80 ; 1 2 = 0 .
(Case i) ‐ Undrifted load arrangement (see Table 1.5 above):
1 = 30 , 1 1 = 0 80 .
2 = 40 , 1 2 = 0 8 60 – 2 30 = 0 8 60 – 40 30 = 0 53 .
Topic: User’s Manual/Verification tests - EN1991-1-3_(a).xls page 17
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- EarthDocument1 paginăEarthselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Structural Drawings: Pared by Another Professional Engineer States The Following, "ClientsDocument1 paginăStructural Drawings: Pared by Another Professional Engineer States The Following, "ClientsselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlgebraDocument3 paginiAlgebraAbrahim A Verde AÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Stâlpi Din Beton ArmatDocument27 paginiStâlpi Din Beton ArmatselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- REBARSDocument1 paginăREBARSselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Geotechnical InformationDocument1 paginăGeotechnical InformationselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- S 2 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A A, A BDocument1 paginăS 2 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A A, A BselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- S 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A B: B Min 5h 5 MDocument1 paginăS 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A B: B Min 5h 5 MselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Structural Engineering Design Services For Buildings GuidelineDocument1 paginăStructural Engineering Design Services For Buildings GuidelineselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Case B: Case C:: S 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A BDocument1 paginăCase B: Case C:: S 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A BselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- S 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A B: SolutionDocument1 paginăS 2 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A A, A B: SolutionselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Eurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Section 1Document1 paginăEurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Section 1selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- p32 PDFDocument1 paginăp32 PDFselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- p35 PDFDocument1 paginăp35 PDFselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Structural Design Data MatrixDocument1 paginăStructural Design Data MatrixselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Eurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Annex C, Annex D: Section 3Document1 paginăEurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Annex C, Annex D: Section 3selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- 2.4 References (Section 2) : S S 4 67 0 60 2 80 KN / MDocument1 pagină2.4 References (Section 2) : S S 4 67 0 60 2 80 KN / MselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DDocument1 paginăS 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DDocument1 paginăS 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.3 Verification Tests: S 3 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A C, A DDocument1 pagină3.3 Verification Tests: S 3 E 1 EN 1991-1-3: A C, A DselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic LoadDocument1 paginăSeismic LoadselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- 1.3 Design Situations: S 1 E 1 EN 1991-1-3Document1 pagină1.3 Design Situations: S 1 E 1 EN 1991-1-3selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DDocument1 paginăS 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- S 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DDocument1 paginăS 3 e 1 en 1991-1-3: A C, A DselinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- P 16Document1 paginăP 16selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P 13Document1 paginăP 13selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hoadly 01Document12 paginiHoadly 01selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Section 1Document1 paginăEurocode 1 EN 1991-1-3: Section 1selinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Indian Standard: Application Guide For Voltage Transformers (Document16 paginiIndian Standard: Application Guide For Voltage Transformers (Pardeep KhosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efflux Time: TOGUN Iyanuoluwa JohnDocument24 paginiEfflux Time: TOGUN Iyanuoluwa JohnJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- POGIL Molecular GeometryDocument3 paginiPOGIL Molecular Geometryliza120750% (2)
- Full PDFDocument445 paginiFull PDFعلي مؤيد مطشر صدامÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock Test Paper NeetDocument28 paginiMock Test Paper NeetmayankÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCE 311 Lecture 1Document77 paginiBCE 311 Lecture 1francessichÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER ProblemsDocument3 paginiCHAPTER ProblemsOmarWaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 Daily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesDocument3 paginiGrade 7 Daily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesJanecil A. BonzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bond Under Cyclic LoadDocument5 paginiBond Under Cyclic LoadjeffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Additional Mathematics Project Work 2014 (Sabah)Document16 paginiAdditional Mathematics Project Work 2014 (Sabah)Shelyn HiewÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABAQUS Training PDFDocument114 paginiABAQUS Training PDFManuelDarioFranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Relay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnDocument9 paginiRelay: Relay Is Basically A Magnetism Based Switch. It Consists of A Coil Through Which Current Passes and OnAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer Final NehaDocument45 paginiHeat Transfer Final NehanighatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control of STATCOM by Using Optimal Reactive Power Flow SolutionsDocument5 paginiControl of STATCOM by Using Optimal Reactive Power Flow Solutionsshiks16Încă nu există evaluări
- D. Myers - Surfaces, Interfaces and Colloids - Principles and ApplicationsDocument520 paginiD. Myers - Surfaces, Interfaces and Colloids - Principles and ApplicationsAmairanyta Hernandez Zarate100% (4)
- EN2314 Hydraulics - Formula Sheet 30oct19Document3 paginiEN2314 Hydraulics - Formula Sheet 30oct19mohamedyahaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Operation of Power SystemDocument45 paginiEconomic Operation of Power SystemDogbey BrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esas ObjectivesDocument43 paginiEsas Objectivesbulatao allan50% (2)
- OATBooster Formula Sheet (July 2022) PDocument11 paginiOATBooster Formula Sheet (July 2022) PzainabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of 765kv Transmission LineDocument10 paginiDesign of 765kv Transmission LineNaveen SabbavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd PT Science 6Document14 pagini3rd PT Science 6Dhines CBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 - Graph MatchingDocument3 paginiLab 1 - Graph Matchingkitsune-nildeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity AssignmentDocument1 paginăElectricity AssignmentSHANKARJEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci 09 Sample QPDocument8 paginiSci 09 Sample QPkvindhraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Theory For Fatigue Failure Under Multiaxial Stress-Strain ConditionsDocument27 paginiA Theory For Fatigue Failure Under Multiaxial Stress-Strain ConditionsFabián Stark CatongaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robert Caldwell - Dark Energy CosmologyDocument21 paginiRobert Caldwell - Dark Energy CosmologyLopmazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Design Handbook - Hydrocarbon Processing - 1974Document96 paginiFoundation Design Handbook - Hydrocarbon Processing - 1974VS2712100% (4)
- Relativity VIC McqsDocument3 paginiRelativity VIC McqsLasnthaBandara75% (4)
- A .Nuclear Cross Section Hand Book PDFDocument292 paginiA .Nuclear Cross Section Hand Book PDFeric_rr_1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Origin of The Universe 101 - National GeographicDocument2 paginiOrigin of The Universe 101 - National GeographicColeen Jade CondinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDe la EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (64)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe la EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2193)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDe la EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDe la EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (51)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDe la EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDe la EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (20)