Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
Încărcat de
hallegendTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose
Încărcat de
hallegendDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
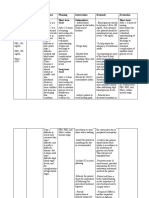
Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose
Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose: At risk for variation of blood glucose levels from the normal range that may
compromise health.
Risk factors
Inadequate blood glucose monitoring
Lack of adherence to diabetes management
Medication management
Deficient knowledge of diabetes management
Developmental level
Lack of acceptance of diagnosis
Stress
Sedentary activity level
Insulin deficiency or excess
Possibly evidenced by
[Not applicable for risk diagnosis. A risk diagnosis is not evidenced by signs and symptoms, as the
problem has not occurred and nursing interventions are directed at prevention.]
Desired outcomes
Patient has a blood glucose reading of less than 180 mg/dL; fasting blood glucose levels of less than
<140 mg/dL; and hemoglobin A1C level <7%.
May be related to
– lack of adherence to diabetes management
– inadequate blood glucose monitoring practices
– fluctuating physical activity level
– stress
As evidenced by
– blood glucose levels below or above normal levels
Desired Outcome
– identify factors that may lead to unstable blood glucose levels.
– verbalize understanding of balancing body and energy needs.
– verbalize plan in modifying identified risk factors to prevent shifts in glucose level.
– maintain blood glucose levels within normal range.
Tests:
• Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) • Hemoglobin A1c (A1c) test
• Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) • Random plasma (blood) glucose
Plasma glucose
Hemoglobin A
Fructosamine white blood cell (WBC) count and blood and urine cultures
beta-hydroxybutyrate level
urinary albumin (microalbumin), creatinine clearance, eGFR, CMP, BUN, creatinine, cystatin C
cholesterol and other lipids: cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, lipid profile
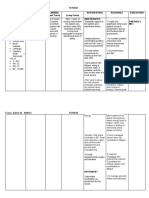
Nursing Interventions Rationale
Hyperglycemia results when there is an inadequate amount of
insulin to glucose. Excess glucose in the blood creates an
Assess for signs of hyperglycemia. osmotic effect that results in increased thirst, hunger, and
increased urination. The patient may also report nonspecific
symptoms of fatigue and blurred vision.
Blood glucose should be between 140 to 180 mg/dL. Non-
Assess blood glucose level before
intensive care patients should be maintained at pre-meal levels
meals and at bedtime.
<140 mg/dL.
Monitor patient’s HbA1c- This is a measure of blood glucose over the previous 2 to 3
glycosylated hemoglobin. months. A level of 6.5% to 7% is desirable.
Assess for anxiety, tremors, and
slurring of speech. Treat These are signs of hypoglycemia and D50 is treatment for it.
hypoglycemia with 50% dextrose.
Assess feet for temperature, pulses,
To monitor peripheral perfusion and neuropathy.
color, and sensation.
Assess the patient’s current
Nonadherence to dietary guidelines can result in hyperglycemia.
knowledge and understanding
An individualized diet plan is recommended.
about the prescribed diet.
Physical activity helps lower blood glucose levels. Regular
Assess the pattern of physical
exercise is a core part of diabetes management and reduces risk
activity.
for cardiovascular complications.
A patient with type 2 DM who uses insulin as part of the
treatment plan is at increased risk for hypoglycemia.
Manifestations of hypoglycemia may vary among individuals but
are consistent in the same individual. The signs are the result of
Monitor for signs of hypoglycemia.
both increased adrenergic activity and decreased
glucose delivery to the brain, therefore, the patient may
experienced tachycardia, diaphoresis, dizziness,
headache, fatigue, and visual changes.
Teach patient how to perform home Blood glucose is monitored before meals and at bedtime.
glucose monitoring. Glucose values are used to adjust insulin doses.
Monitor urine albumin to serum Renal failure causes creatinine >1.5 mg/dL. Microalbuminuria is
creatinine for renal failure. the first sign of diabetic nephropathy.
Instruct patient to take insulin as directed
Have an onset of action within 15 minutes of administration.
Rapid-acting insulin The duration of action is 2 to 3 hours for Humalog and 3 to 5
analogs: lisproinsulin hours for aspart.
(Humalog), insulin aspart
Intermediate and Premixed concentration has an onset of action similar to that of
rapid: 70% NPH/30% rapid-acting insulin and a duration of action similar to that of
intermediate-acting insulin.
regular.
Nursing Interventions Rationale
Priority 1: Assess risks and contributing factors to unstable blood glucose
levels1
Certain risk factors like family history of
diabetes, history of poor glucose control,
Determine the client’s factors that may
poor exercise habits, eating disorders and
contribute to unstable blood glucose
failure to recognize changes in glucose
levels.
needs can result in blood glucose stability
problems.
Determine influence of client’s cultural
and religious factors affecting dietary
These factors may need to be addressed in
practices, taking responsibility for own
creating client’s healthcare plan.
care and expectations of healthcare
outcome.
Age, developmental stage, maturity level
Determine client’s awareness or ability to
and current health status affect client’s
be responsible for own healthcare plans.
ability to adhere to treatment plans.
Priority 2: Assist client in creating preventive strategies for unstable blood
glucose levels
The blood glucose monitoring device is a
Ensure client is knowledgeable about handy and accurate way of assessing
using his own blood glucose monitoring blood glucose levels. Proper usage of this
device. device is essential in detecting unstable
blood glucose levels.
Educate about balancing food intake with Vital in preventing sudden increase or
physical activities. decrease in blood glucose levels.
Educate about adjusting home glucose
monitoring frequency depending on To quickly identify fluctuating blood
client’s risk factors like stress and poor
diet. glucose levels for immediate correction.
Blood glucose levels greatly depend on
Review and discuss client’s carbohydrate carbohydrate intake. It should be
intake. monitored and controlled closely when
stabilizing high blood glucose levels.
Essential in ensuring client’s
Discuss how the client’s anti-diabetic
understanding of his treatment regimen to
medications work.
ensure his compliance and adherence.
Priority 3: Ensure effective and safe treatment for clients on insulin therapy
It is important to regularly check for the
Emphasize importance of inspecting insulin’s expiration date,
client’s own insulin medication. cloudiness/clearness and storage to ensure
drug efficacy.
Different types of insulin have different
Discuss the different types of insulin as administration methods as well. Knowing
well as each type’s administration and following proper administration
method. method is important in ensuring drug’s
efficiency.
Insulin absorption is affected by the
integrity of injection sites. Insulin is less
Check injection sites.
absorbed in hypohypertropic or lumpy
tissues.
Priority 4: Promote wellness
Review client’s risk factors and provide
Ensures prevention of unstable blood
information on how to avoid
glucose levels in the future.
complications.
Refer client to a dietitian to plan specific
dietary needs based on complicated
To balance dietary intake with complicated
situations like pregnancy, growth spurt
body needs.
and change in activity level following an
injury.
Provide information about community
For client’s access to additional resources
resources, support groups and diabetic
for diabetes management.
educators.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing Diagnosis For DKADocument6 paginiNursing Diagnosis For DKARhanne Bolante88% (24)
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument3 paginiRisk For Unstable Blood GlucoseMark Orcullo88% (8)
- Clinical Example:: What Additional Assessments Would The Nurse Want To Make To Plan Care For This Client?Document2 paginiClinical Example:: What Additional Assessments Would The Nurse Want To Make To Plan Care For This Client?Kim Kristine D. GuillenÎncă nu există evaluări
- (RP MPT Novice-Intermediate) 3x - Arms&DeltsDocument3 pagini(RP MPT Novice-Intermediate) 3x - Arms&Deltsmishka123Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 paginiNursing Care PlanLura Xstilice B. Galinato100% (1)
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPDocument5 paginiImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements - Diabetes - NCPJulie Ann Jimenez Manlangit50% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 paginiNursing Care PlanZerica Andaca83% (6)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument4 paginiNCP Activity IntoleranceKryza Dale Bunado Batican0% (1)
- Situation 1: Covina Is A 16-Year-Old Girl With Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. She IsDocument3 paginiSituation 1: Covina Is A 16-Year-Old Girl With Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes. She IsNicole GumolonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale EvaluationDocument5 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losanta100% (2)
- Project GymDocument12 paginiProject GymsatyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument6 paginiUnstable Blood Glucosetherese BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.Document8 paginiRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose Related To Unhealthy Lifestyle.eleinsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Document4 paginiRisk For Unstable Blood Glucose (DM)Ace Khiel Peralta50% (2)
- Nutrition NCPDocument3 paginiNutrition NCPMarielle Adrienne Bitancor100% (1)
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagini3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocument2 paginiRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 paginăActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 FatigueDocument2 paginiTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 FatigueSALMA M. TUANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- NCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument2 paginiNCP Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseNathalie kate petallar75% (8)
- NCP LeukemiaDocument3 paginiNCP LeukemiaLuige Avila100% (5)
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 paginiActivity IntoleranceMaze Reyes40% (5)
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPGimcy Dela Fuente100% (6)
- Electrical Safety (OSHS)Document25 paginiElectrical Safety (OSHS)hallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Glycolysis and The Catabolism of HexosesDocument65 pagini2 - Glycolysis and The Catabolism of HexosesEmily LukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bland DietDocument17 paginiBland DietAdade Solomon Yao-Say100% (1)
- Risk For Unstable Blood GlucoseDocument24 paginiRisk For Unstable Blood GlucoseFerreze Ann100% (1)
- NCP DMDocument4 paginiNCP DMStef Bernardo67% (3)
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPRachel PerandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP DMDocument2 paginiNCP DMAna Ramos LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lanjutan NCP DMDocument14 paginiLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 paginiCRF Fluid Volume Excess NCPchubbielitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument9 paginiNCPTracy Camille EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 paginiNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument7 paginiNCPChris Denver BancaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP (Fatigue)Document1 paginăNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- Malnutrition NCPDocument4 paginiMalnutrition NCPDenise Espinosa100% (3)
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 paginiNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia NCPDocument20 paginiAnemia NCPNursidar Pascual Mukattil80% (5)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChristine LebicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FatigueDocument3 paginiFatigueIande CornerÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For DehydrationDocument1 paginăNCP For Dehydrationjxhel63% (8)
- Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedDocument3 paginiNursing Diagnosis Ineffective Therapeutic Regimen Management RelatedbizzykenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument10 paginiNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Type IIChristine Karen Ang SuarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 paginiNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP DMDocument6 paginiNCP DMstara123Încă nu există evaluări
- Hiv NCPDocument2 paginiHiv NCPHeindrich Cardenas0% (1)
- NCP ShockDocument5 paginiNCP ShockJanina Patricia BuddleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument12 paginiNursing Care Plankeishaaa29100% (6)
- NCP For LeukemiaDocument2 paginiNCP For Leukemiaخالد الغامديÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 paginiDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDocument7 paginiCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDocument4 paginiNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument7 paginiNCPJo Chiko FlorendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document1 paginăNCP - Patient For Electrocardiogram (ECG)SelwynVillamorPatenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiNursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationJobie CasipongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin Secretion and FunctionDocument8 paginiInsulin Secretion and FunctionWendy EscalanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiDiabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyG FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDharylle Cariño100% (3)
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesDocument5 paginiDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 NotesAimee Kaye DetablanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 116 Skills - Midterm NotesDocument20 paginiNCM 116 Skills - Midterm NotesmareginaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes InfoDocument24 paginiDiabetes Infoalle manoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelworks: Standard Hooks, Bends and Splice Locations: Research Work No. 2Document9 paginiSteelworks: Standard Hooks, Bends and Splice Locations: Research Work No. 2hallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Softening SystemsDocument1 paginăWater Softening SystemshallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inclined Surface LoadsDocument1 paginăInclined Surface LoadshallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filtration MechanismsDocument2 paginiFiltration MechanismshallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology: Water CycleDocument4 paginiHydrology: Water CyclehallegendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jose Rizal Movie ReviewDocument3 paginiJose Rizal Movie Reviewhallegend100% (1)
- Sugar Content of Popular Sweetened Beverages Based On Objective Laboratory Analysis: Focus On Fructose ContentDocument7 paginiSugar Content of Popular Sweetened Beverages Based On Objective Laboratory Analysis: Focus On Fructose ContentEgg BreadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery: ReviewDocument10 paginiThe Evolution of Metabolic/Bariatric Surgery: ReviewAlexandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 AssignmentDocument1 paginăUnit 1 Assignmentapi-249610248Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 To 20 Years: Girls Body Mass Index-For-Age Percentiles: Date Age Weight Stature Bmi CommentsDocument2 pagini2 To 20 Years: Girls Body Mass Index-For-Age Percentiles: Date Age Weight Stature Bmi CommentsTaha Mohammed TahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic-NeuropathyDocument4 paginiDiabetic-NeuropathyHaleelu Abdul JaleelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protein Intake Guide: Updated September 2020Document52 paginiProtein Intake Guide: Updated September 2020monlovi100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Disorders Stom 10-11Document61 paginiCarbohydrate Metabolism Disorders Stom 10-11Artem GrigoryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX 65 LeafletDocument2 paginiPX 65 LeafletrinthusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Funda (Course Audit)Document16 paginiFunda (Course Audit)Kath-Kath Cubillan RanayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lean Bulk Diet Plan (With PDF Meal Plans)Document1 paginăLean Bulk Diet Plan (With PDF Meal Plans)Joan Ruano RocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VadagDocument4 paginiVadagS A M I E L L E G A I L E N I N A C H A V E Z A R A D I L L O SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Rehabilitation: The Benefits of Aquatic TherapyDocument6 paginiTotal Rehabilitation: The Benefits of Aquatic TherapyAleCsss123Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Eso Final TestDocument3 pagini2 Eso Final TestMeyling Benavidez100% (1)
- Total AnabolismDocument48 paginiTotal AnabolismTswiglyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artigo Sobre Nutrigenômica e Nutrigenética PDFDocument18 paginiArtigo Sobre Nutrigenômica e Nutrigenética PDFDiogo JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix B Pathophysiology of DM Type 2Document20 paginiAppendix B Pathophysiology of DM Type 2Jennifer AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stretching ExercisesDocument5 paginiStretching ExercisesramyakarivedagmailcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Eating Workshops For ParentsDocument26 paginiHealthy Eating Workshops For ParentsNicu IancuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Article: MODULATORY EFFECT OF Drosera Peltata J.E.Sm ON Development of Metabolic Syndrome in Tumor Bearing MiceDocument8 paginiResearch Article: MODULATORY EFFECT OF Drosera Peltata J.E.Sm ON Development of Metabolic Syndrome in Tumor Bearing MiceElfiaNeswitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarcopenia and Obesity: ReviewDocument7 paginiSarcopenia and Obesity: ReviewPaula KissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy MCQsDocument11 paginiAnatomy MCQsEt LinnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocument81 paginiHypertensive Disorders in PregnancyarunshreerajendranÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emotional Eater The Ebook by Susan Albers PsyD 2Document23 paginiThe Emotional Eater The Ebook by Susan Albers PsyD 2Ana Elisa Araujo100% (2)
- The Lesbian Key Exposed: Keto Nutritional Supplements For Great Sex.Document2 paginiThe Lesbian Key Exposed: Keto Nutritional Supplements For Great Sex.noisespleen5Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz BeeDocument34 paginiQuiz BeeMhel DemabogteÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Dietary Restriction in Binge EatingDocument11 paginiThe Role of Dietary Restriction in Binge EatingSofie WiddershovenÎncă nu există evaluări