Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Math 7 Worksheet - Properties of Numbers: of Addition or of Multiplication
Încărcat de
Chung Ek0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
28 vizualizări2 paginiProperties WS2
Titlu original
Properties WS2
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentProperties WS2
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
28 vizualizări2 paginiMath 7 Worksheet - Properties of Numbers: of Addition or of Multiplication
Încărcat de
Chung EkProperties WS2
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Math 7 Worksheet - Properties of numbers
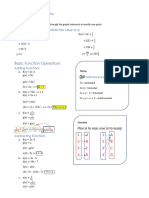
THE COMMUTATIVE PROPERTY OF ADDITION OR OF MULTIPLICATION:
You can switch the order of two terms in addition or two factors in multiplication
(but not in subtraction or division) [ examples: 2 + 3 = 3 + 2, 2 · 3 = 3 · 2, xy = yx ]
THE ASSOCIATIVE PROPERTY OF ADDITION OR OF MULTIPLICATION:
You can re-group three or more terms in addition or three or more factors in
multiplication
(but not in subtraction or division) [ examples: 2 + (3 + 5) = (3 + 2) + 5, 2 · (3 · 5)
= (3 · 2) · 5,
BUT 2 – (3 – 5) = 2 – 3 + 5, x – (y – z) = (x – y) + z, 20 ÷ (10 ÷ 2) = (20 ÷ 10) × 2]
THE DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY OF MULTIPLICATION OVER ADDITION OR
SUBTRACTION:
A number times a group of terms in parentheses can be “distributed”
(i.e. the number multiplied with each term separately), and the parentheses removed.
[ examples: 2(3 + 5) = (2 · 3 + 2 · 5), 2(x – 5) = (2x – 2 · 5), (x + 2)y = xy + 2y]
THE IDENTITY PROPERTY OF ADDITION OR OF MULTIPLICATION:
For addition: Adding 0 to something doesn’t change it (“keeps its identity”)
For multiplication: Multiplying 1 by something doesn’t change it (“keeps its
identity”)
[ examples: x + y + 0 = x + y, 5·1=5]
THE INVERSE PROPERTY OF ADDITION OR OF MULTIPLICATION:
For addition: Adding a number to its opposite gives 0. [example: 2 + (–2) = 0]
For multiplication: Multiplying a number by its reciprocal gives 1. [ 3 · ⅓ = 1, (–3) ·
(–⅓) = 1 ]
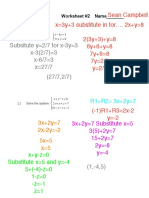
Name: _____________
Date ______ Per. __
Tell which property is being used:
a) 7 + a = a + 7
b) 7 + 0 = 7
c) 7 • 1 = 1
7
d) – 2 + 2 = 0
3 3
e) 3 • 2 = 1
2 3
f) 7 + (3 + 5) = (7 + 3) + 5
g) (3x)y = 3(xy)
h) – 2 + 0 = – 2
3 3
i) x + 4 = 4 + x
j) x(y + 2) = xy + 2x
k) 3(4 + 5) = 3 · 4 + 3 · 5
l) 3(a + 0) = 3a
m) (–7) + 7 = 0
n) –7(x + y) = (–7x) + (–7y)
o) 1 • 6 = 1
6
p) xy = yx
q) (7x)y = 7(xy)
r) a + (2 + c) = (a + 2) + c
s) (7x) + (–7x) = 0
t) x + (y + 3) = (y + 3) + x
u) x + (–x) + y = y
(two properties!)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- P6 Maths CA1 Worksheet - FractionsDocument6 paginiP6 Maths CA1 Worksheet - FractionsChung EkÎncă nu există evaluări
- P6 Maths CA1 Worksheet - FractionsDocument6 paginiP6 Maths CA1 Worksheet - FractionsChung EkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionDocument12 paginiChapter 2.3 - Relation and FunctionPoeil Sergio MoldezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addmath Form 4Document31 paginiAddmath Form 4Nor Hanina98% (40)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)De la EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Încă nu există evaluări
- La DerivadaDocument17 paginiLa DerivadaAndres Felipe Nuñez GraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen Math Week 1Document7 paginiGen Math Week 1France Dave Mercado MadrigalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilovepdf Merged (1) MergedDocument32 paginiIlovepdf Merged (1) MergedKeshav PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relation & FunctionsDocument7 paginiRelation & Functionsthesonofthewarrior123Încă nu există evaluări
- FactorizationDocument9 paginiFactorizationthesonofthewarrior123Încă nu există evaluări
- Math Lesson1 - 6Document1 paginăMath Lesson1 - 6cermatikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATH 11C Lecture 1.1. FunctionsDocument4 paginiMATH 11C Lecture 1.1. FunctionsChristian Claud Dominic PaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Increasing & Decresing FunctionsDocument4 pagini2 Increasing & Decresing FunctionsShivam LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 2 AlgebraDocument37 paginiUNIT 2 AlgebraDeneika MorganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Matek 1 - Muh. Zaid Iskandar - D091181006Document10 paginiTugas Matek 1 - Muh. Zaid Iskandar - D091181006MyazielÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONDocument9 paginiGeneral Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONLeopoldo MalicdemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ti 89 Titanium Exercise 5Document2 paginiTi 89 Titanium Exercise 5kalimbaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precal m2Document9 paginiPrecal m2RechelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA 411 Class Notes 1Document11 paginiMA 411 Class Notes 1Diana NjelesaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gen MathDocument3 paginiGen MathDaniel SolicitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical 1A: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations: CommandDocument2 paginiPractical 1A: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations: CommandPraveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths. SolutionsDocument8 paginiMaths. Solutionssabaa.shafeeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions Its OperationsDocument58 paginiFunctions Its OperationsGame AccountÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 JC1 Promo RevisionDocument477 pagini2012 JC1 Promo RevisionVincent SeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 7 Chapter 12 NcertDocument41 paginiClass 7 Chapter 12 NcertHimanshu JethwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM2 CW#34 U4L8 - Inverse Functions PracticeDocument2 paginiIM2 CW#34 U4L8 - Inverse Functions PracticeMakoto EnochsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q2, Gen MathDocument1 paginăQ2, Gen MathconsuelomariasofiatÎncă nu există evaluări
- III SEM - EC31 - Unit - IVDocument49 paginiIII SEM - EC31 - Unit - IVJoash Clavin John ClaytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gif - PrmoDocument6 paginiGif - PrmoapocalypticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Functions ReviewDocument8 paginiInverse Functions ReviewMay JayyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 GEN MATHDocument7 paginiModule 3 GEN MATHVenice CalimutanÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument7 paginiUntitledChetan GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centro de Bachillerato Tecnológico, Industrial y de Servicios N° 137Document19 paginiCentro de Bachillerato Tecnológico, Industrial y de Servicios N° 137Melissa Janeth Muñoz EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAT2DMX Assessment1Document9 paginiMAT2DMX Assessment1sureshni fernandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebraic Expressions FactorizationDocument39 paginiAlgebraic Expressions Factorizationthinkiit100% (3)
- TEST 2. Derivatives (2016)Document2 paginiTEST 2. Derivatives (2016)2sqxh64p5zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support Vector Machine SVMDocument58 paginiSupport Vector Machine SVMHeenal MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)Document11 pagini7 Quadratic Expressions: 7.1 Expansion (Multiplication)tamleduc1810dnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 2Document1 paginăWorksheet 2api-353953546Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Operations On FunctionDocument4 pagini2 Operations On FunctionJan Zennif DomanicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Legal Basis of Math-1Document5 paginiThe Legal Basis of Math-1hartati100% (1)
- The Legal Basis of Math-1Document5 paginiThe Legal Basis of Math-1hartatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignmnet # 03: A. Implicit DerivativesDocument4 paginiAssignmnet # 03: A. Implicit DerivativesAbraham Mallari MacapagalÎncă nu există evaluări
- LP General-Mathematics Week-3Document6 paginiLP General-Mathematics Week-3nicole MenesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 1.7Document28 paginiDay 1.7Teacher JAY-AR LAGMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation On FunctionDocument5 paginiOperation On FunctionRandy MaltoÎncă nu există evaluări
- D091201012 - Muhammad Ziyad Faiz AminDocument9 paginiD091201012 - Muhammad Ziyad Faiz AminNicola InzaghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zca 110 Fe 0607Document12 paginiZca 110 Fe 0607G11 Lee Yan HangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations On Polynomials (Revised)Document6 paginiOperations On Polynomials (Revised)Elvin PrestoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia de Observación Jun. - 2019: Lógico MatemáticoDocument2 paginiGuia de Observación Jun. - 2019: Lógico MatemáticoJesús DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Mathematics Ncert Ch02 Polynomials Ex 2.5 Ans MaxDocument12 pagini09 Mathematics Ncert Ch02 Polynomials Ex 2.5 Ans MaxJohn RajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Assignment - 1 - FunctionsDocument7 paginiMathematics Assignment - 1 - Functionsmohit24031986Încă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical Methods For Business, Economics & FinanceDocument67 paginiMathematical Methods For Business, Economics & FinanceHareen JuniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Std09-II-Maths-EM 8Document1 paginăStd09-II-Maths-EM 8bagmassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zeros of Polynomial FunctionsDocument11 paginiZeros of Polynomial FunctionsRhoda LuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.0 Review of FunctionsDocument5 pagini1.0 Review of FunctionsAlvin Louie DiataÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Chain RuleDocument4 paginiThe Chain RuleDaiszyBarakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3Document5 paginiLab 3untrustedusageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integral Calculus Math AssignmentDocument7 paginiIntegral Calculus Math AssignmentDipon AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemh114 PDFDocument14 paginiHemh114 PDFhoneygarg1986Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Answers KeyDocument1 paginăMCQ Answers KeyJomari MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penyelesaian Latihan3 Q9Document2 paginiPenyelesaian Latihan3 Q9Chung EkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discover Your Preferred Learning StyleDocument6 paginiDiscover Your Preferred Learning StyleChung EkÎncă nu există evaluări