Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The Alveoli
Încărcat de
makkosette0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
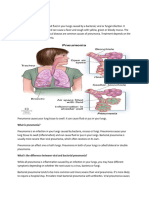
6 vizualizări3 paginiPneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs that affects the alveoli. It is usually caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection. Symptoms can include cough, chest pain, fever, trouble breathing, and confusion. Risk factors include other lung diseases, smoking history, diabetes, and a weak immune system. Pneumonia affects approximately 450 million people globally each year and results in around 4 million deaths annually. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures. Treatment depends on whether it was community-acquired or hospital-acquired and may include antibiotics, rest, and fluids.
Descriere originală:
hkhkhjkgj
Titlu original
Pneumonia is an Inflammatory Condition of the Lung Affecting Primarily the Alveoli
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentPneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs that affects the alveoli. It is usually caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection. Symptoms can include cough, chest pain, fever, trouble breathing, and confusion. Risk factors include other lung diseases, smoking history, diabetes, and a weak immune system. Pneumonia affects approximately 450 million people globally each year and results in around 4 million deaths annually. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures. Treatment depends on whether it was community-acquired or hospital-acquired and may include antibiotics, rest, and fluids.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6 vizualizări3 paginiPneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The Alveoli
Încărcat de
makkosettePneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs that affects the alveoli. It is usually caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection. Symptoms can include cough, chest pain, fever, trouble breathing, and confusion. Risk factors include other lung diseases, smoking history, diabetes, and a weak immune system. Pneumonia affects approximately 450 million people globally each year and results in around 4 million deaths annually. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, blood tests, and sputum cultures. Treatment depends on whether it was community-acquired or hospital-acquired and may include antibiotics, rest, and fluids.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of
the lung affecting primarily the alveoli.
-Symptoms include: productive or dry cough, chest
pain, fever, and trouble breathing, confusion may be the
most prominent sign. More severe signs and symptoms in
children may include blue-tinged skin, convulsions, vomiting,
extremes of temperature. Severity is variable.
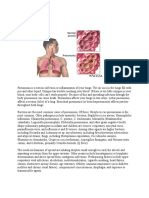
Pneumonia is usually caused by infection
with viruses, bacteria or fungi .
Pneumonia caused by Legionella may occur with abdominal
pain, diarrhea, or confusion. Pneumonia caused
by Streptococcus pneumoniae is associated with rusty
colored sputum. Pneumonia caused by Klebsiella may have
bloody sputum. Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma
pneumoniae may occur in association with swelling of the
lymph nodes in the neck, joint pain, or a middle ear
infection.
Commonly-implicated viruses
include rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, influenza
virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus,
and parainfluenza.
Risk factors include other lung diseases such as cystic
fibrosis, COPD, and asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a
history of smoking, a poor ability to cough such as following
a stroke, or a weak immune system, alcoholism, chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, chronic kidney
disease, liver disease, and old age
Pneumonia affects approximately 450 million people
globally (7% of the population) and results in about 4 million
deaths per year.
Diagnosis is often based on the : Chest X-ray, blood tests,
and culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis.
Imaging: X-ray presentations of pneumonia may be
classified as lobar pneumonia, bronchopneumonia (also
known as lobular pneumonia), and interstitial pneumonia.
Complications such as pleural effusion may also be found
on chest radiographs.
Pneumonia frequently starts as an upper respiratory tract
infection that moves into the lower respiratory tract. It is a
type of pneumonitis (lung inflammation). The normal flora of
the upper airway gives protection by competing with
pathogens for nutrients.
Pneumonia is most commonly classified by where or how it
was acquired: community-acquired, aspiration, healthcare-
associated, hospital-acquired, and ventilator-associated
pneumonia. It may also be classified by the area of lung
affected: lobar pneumonia, bronchial pneumonia and acute
interstitial pneumonia, may additionally be classified based
on signs and symptoms as non-severe, severe, or very
severe.
Prevention: Vaccination prevents against certain bacterial
and viral pneumonias both in children and adults.
Medications: amantadine or rimantadine may help prevent
the condition; Oral antibiotics, rest, simple analgesics, and
fluids usually suffice for complete resolution.
Treatment before culture results with amoxicillin is
recommended as the first line.
Cephazolin plus macrolide such as azithromycin or a
fluoroquinolones is recommended.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia include third- and fourth-
generation cephalosporins, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones,
aminoglycosides, and vancomycin.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Central Academy: Biology ProjectDocument12 paginiCentral Academy: Biology ProjectMastbleÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument5 paginiPneumoniasamtaynbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia, BronchiolitisDocument65 paginiPneumonia, BronchiolitisYemata HailuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaDocument21 paginiAddis Ababa University: Collage of Health Science Pediatrics and Neonatology On PneumoniaCheru DugaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400Document37 paginiCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Nelson 400fatima chrystelle nuñalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document30 paginiChapter 1Ayro Business CenterÎncă nu există evaluări
- W1 L2 PneumoniaDocument57 paginiW1 L2 PneumoniaAnas FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument3 paginiPneumoniaJAGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaDocument14 paginiWae'l Hayajneh: PneumoniaRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument10 paginiPneumoniaJohn Philip M. Lacas RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- S. Pneumoniae Produces Local Edema That Aids in The Proliferation of Organisms and TheirDocument7 paginiS. Pneumoniae Produces Local Edema That Aids in The Proliferation of Organisms and TheirKadek Soga Prayaditya PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratorydisease 170426125838Document69 paginiRespiratorydisease 170426125838Hayder MaqsadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification: PneumoniaDocument2 paginiClassification: PneumoniaAlbean DelojeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology:: Parasites (Parasitic Pneumonia)Document5 paginiMicrobiology:: Parasites (Parasitic Pneumonia)9t6vx7psm5Încă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedDocument7 paginiPneumonia: Pneumococcus. A Serious Complication of Pneumonia, Pneumococcal Meningitis, Is AssociatedHannah YtacÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument27 paginiPneumoniamohammedghassan53Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)Document58 paginiAcute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)api-19916399Încă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orDocument6 paginiPneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orOtrebron BatisanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument68 paginiPneumoniaJelmalyn Basali100% (1)
- Pneumonia 3Document8 paginiPneumonia 3janinecasilenÎncă nu există evaluări
- PNEUMONIA NotesDocument4 paginiPNEUMONIA NotesKate HizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument1 paginăPneumoniaJas PerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument3 paginiUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionmcvirgo014100% (1)
- Lect 8 Pneumonia PDFDocument68 paginiLect 8 Pneumonia PDFRaghad AbdullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia WrittenDocument12 paginiPneumonia WrittenFereli Joy SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument8 paginiPneumoniaNader Smadi100% (2)
- Pneumonia Is AnDocument9 paginiPneumonia Is Ansandro2000Încă nu există evaluări
- Name: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikDocument37 paginiName: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikChintiya PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia and GastroentiritisDocument3 paginiPneumonia and Gastroentiritismarie100% (5)
- URTIDocument2 paginiURTImetch isulatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap MRDocument7 paginiCap MRZachary CohenÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument13 paginiPneumoniaRobelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 paginiBroncho PneumoniamarkkkkkkkheeessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia Is An: ClinicalDocument13 paginiPneumonia Is An: ClinicaldfgsfsfssdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Argh 1Document3 paginiArgh 1acebanditsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument24 paginiGroup 2 Community Acquired PneumoniaalyanadayritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PNEUMONIADocument40 paginiCase Study PNEUMONIAHomework PingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Essentials: View Media GalleryDocument22 paginiPractice Essentials: View Media GalleryAza Patullah ZaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases ClinicalDocument57 paginiDiseases Clinicalsomayya wali100% (1)
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung, Especially ofDocument14 paginiPneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung, Especially ofNar Patrick PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WO Trpmed HHDocument26 paginiWO Trpmed HHWinona JenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases of Respiratory OrgansDocument72 paginiDiseases of Respiratory OrgansEdi Kerina SembiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- PBLDocument7 paginiPBLRobelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System DisordersDocument9 paginiRespiratory System Disordersasop06Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 9 Respiratory Disorders Part 2Document11 paginiLec 9 Respiratory Disorders Part 2iam2117Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Pathophysiology: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati College of NursingDocument12 paginiRespiratory Pathophysiology: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati College of NursingDoc JacqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17Document19 paginiChapter 17Patricia VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Nelson 20 EdDocument43 paginiPediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Nelson 20 EdRazel Kinette AzotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia With Pleural EffusionDocument24 paginiPneumonia With Pleural EffusionMund CheleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Borne DiseasesDocument3 paginiAir Borne DiseasesMuhammad Anwar GulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 Restrictive DisordersDocument212 paginiWeek 4 Restrictive Disordersdelrosariojm87Încă nu există evaluări
- Pneumonia: Related Diagnostic TestsDocument2 paginiPneumonia: Related Diagnostic TestsBenj VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument15 paginiPneumoniaJawahir Gomez100% (1)
- 17 PneumoniaDocument30 pagini17 PneumoniaCabdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction BronchoPneumoniaDocument2 paginiIntroduction BronchoPneumoniaJanna FavilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhino PharyngitisDocument27 paginiRhino PharyngitisinriantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - PneumoniaDocument6 pagini3 - PneumoniaAmmar AlnajjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumoniaDocument2 paginiPneumoniaMargaret EricksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesDe la EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physio Zone - Best Physiotherapist in Pimple Saudagar, Physiotherapist in Pimple SaudagarDocument13 paginiPhysio Zone - Best Physiotherapist in Pimple Saudagar, Physiotherapist in Pimple SaudagarGaurav MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk and HazardDocument22 paginiRisk and HazardRamirJanice Gulle MonjeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surehands LMNDocument1 paginăSurehands LMNapi-383151067Încă nu există evaluări
- CV RUGS Format TZMTJ 18022014Document6 paginiCV RUGS Format TZMTJ 18022014Nor LiyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSNDocument1 paginăBSNAnonymous 75TDy2yÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Medical Association Declaration of HelsinkiDocument5 paginiWorld Medical Association Declaration of Helsinkiapi-3711862Încă nu există evaluări
- Group 4 - Accomplishment ReportDocument5 paginiGroup 4 - Accomplishment ReportMa. Millen PagadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing CareDocument4 paginiNursing CareNdupan PandoersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation4 PDFDocument36 paginiPresentation4 PDFKARISHMA PATHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Call To Reexamine Quality of Life Through Relationship-Based FeedingDocument7 paginiA Call To Reexamine Quality of Life Through Relationship-Based FeedingLauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Venous CatheterDocument2 paginiCentral Venous CatheterErick ToHuÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPPE-FPPE ToolkitDocument71 paginiOPPE-FPPE ToolkitHosi Pba100% (1)
- Analisis Pengendalian Persediaan Obat-Obatan Instalasi FarmasiDocument20 paginiAnalisis Pengendalian Persediaan Obat-Obatan Instalasi Farmasitri handayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication Flow Chart For Symptomatic Personnel: TTMF-Temporary Treatment and Monitoring FacilityDocument7 paginiCommunication Flow Chart For Symptomatic Personnel: TTMF-Temporary Treatment and Monitoring FacilityBrynard GarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health and Fitness Vocab (6799)Document2 paginiHealth and Fitness Vocab (6799)yoanaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Galvano-Spa-Bath and HealthDocument2 paginiGalvano-Spa-Bath and HealthDeu na telha com Janaína BensdorpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Cardiology PDF 3vl DR NotesDocument709 paginiPractical Cardiology PDF 3vl DR NotesRemzi BoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Prescribing Guidelines For Geriatric PatientsDocument41 paginiGeneral Prescribing Guidelines For Geriatric PatientsBharath Gowda100% (1)
- Measurement of EpidiologyDocument45 paginiMeasurement of EpidiologyMuhammad AneesÎncă nu există evaluări
- OBK RON v2Document9 paginiOBK RON v2Ernest Rice-BeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM No. 524 S. 2022 2022 GLOBAL HANDWASHING DAY CELEBRATIONDocument7 paginiDM No. 524 S. 2022 2022 GLOBAL HANDWASHING DAY CELEBRATIONEhlee Eton TubalinalÎncă nu există evaluări
- HA-RLE-WS # 6 Assessing PainDocument3 paginiHA-RLE-WS # 6 Assessing PainAshley Blaise JoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hematology Course SyllabusDocument2 paginiHematology Course Syllabusmohamedali991706Încă nu există evaluări
- Instructions For Use: Cryo 6Document48 paginiInstructions For Use: Cryo 6Hussein Abo aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- QR Management of Breast Cancer (3rd Ed)Document8 paginiQR Management of Breast Cancer (3rd Ed)Jye yiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proper Pet Care in BangladeshDocument2 paginiProper Pet Care in BangladeshNoshin NawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- JWC Convatec Wound-Hygiene-28pp 14-Feb CA Web-LicDocument28 paginiJWC Convatec Wound-Hygiene-28pp 14-Feb CA Web-LicAjeng Kania100% (1)
- A Study On Assessment of Effect of Samyoga Viruddha Ahara Consumption On Metabolic Syndrome in 35 - 50 Year Old Men and Women of MumbaiDocument11 paginiA Study On Assessment of Effect of Samyoga Viruddha Ahara Consumption On Metabolic Syndrome in 35 - 50 Year Old Men and Women of MumbaiIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development PlanDocument2 paginiDevelopment Planapi-531834240Încă nu există evaluări
- Glenmark Unveils Its Strategic Blueprint For Transition Into An Innovation ) Led Global Pharmaceutical Organization in The Next Decade (Company Update)Document31 paginiGlenmark Unveils Its Strategic Blueprint For Transition Into An Innovation ) Led Global Pharmaceutical Organization in The Next Decade (Company Update)Shyam SunderÎncă nu există evaluări