Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Discounting Factoring and Forfiating
Încărcat de
Sachin0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări36 paginiThis document discusses various aspects of discounting, factoring, and forfeiting. It defines bill discounting as financing where a seller draws a bill on a purchaser who accepts it and returns it to the seller. The seller then discounts the bill at their bank. Factoring is defined as the selling of trade debts at a discount to a financial institution. It describes the modus operandi of factoring agreements and the functions performed by factors, including financing, sales ledger management, debt collection, and undertaking credit risk. The document also outlines different types of factoring such as full service, with recourse, and maturity factoring. It compares factoring to discounting and outlines the costs involved in factoring services.
Descriere originală:
Discounting and factorng
Titlu original
5. Discounting Factoring and Forfiating
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document discusses various aspects of discounting, factoring, and forfeiting. It defines bill discounting as financing where a seller draws a bill on a purchaser who accepts it and returns it to the seller. The seller then discounts the bill at their bank. Factoring is defined as the selling of trade debts at a discount to a financial institution. It describes the modus operandi of factoring agreements and the functions performed by factors, including financing, sales ledger management, debt collection, and undertaking credit risk. The document also outlines different types of factoring such as full service, with recourse, and maturity factoring. It compares factoring to discounting and outlines the costs involved in factoring services.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
1K vizualizări36 paginiDiscounting Factoring and Forfiating
Încărcat de
SachinThis document discusses various aspects of discounting, factoring, and forfeiting. It defines bill discounting as financing where a seller draws a bill on a purchaser who accepts it and returns it to the seller. The seller then discounts the bill at their bank. Factoring is defined as the selling of trade debts at a discount to a financial institution. It describes the modus operandi of factoring agreements and the functions performed by factors, including financing, sales ledger management, debt collection, and undertaking credit risk. The document also outlines different types of factoring such as full service, with recourse, and maturity factoring. It compares factoring to discounting and outlines the costs involved in factoring services.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 36
Discounting, Factoring & Forfeiting
Introduction Accounting System &
Procedure
Bill Discounting
Benefit
Factoring- Meaning &
Definition Factoring in India
Modus Operandi International Factoring
Terms of Agreement Types of Export Factoring
Functions Factoring in other Countries
Types of Factoring Forfeiting
Factoring Vs Discounting Factoring Vs Forfeiting
Cost of Factoring Advantages of Forfeiting
Format of Cost Sheet Forfeiting in India
Financial Services Chapter 07
Introduction
In India due to economic liberalisation & free
trade policy the financial service sector is
developing at a faster rate. Financial
institution try to extend their axis trace to
trading community through book debt
financing. In coming chapter we are going to
get information on three types of book debt
financing viz. Bill Discounting, Factoring &
Forfeiting.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Bill Discounting
This is a old & more usable type of book debt
finance in India. A Bill Discounting is type of
finance where seller draws bill on purchaser who
accept it & return to seller. Seller then goes to his
bank & discounted it. In this case seller gets
immediate cash, purchaser have not need to pay
immediately & Banks who pays the cash receives
interest for the period for which the bill is drawn.
So in short Bill discounting is a type of one of the
most quick liquid finance.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Bill Discounting
From the banking point of view Bill discounting
is very safe, secure & liquid finance. If in case of
emergency the bills which has been discounted
by seller, can be rediscounted with R.B.I. & Bill
discounting is again superior to traditional cash
credit in following ways:
a) Liquidity b) Quick Finance
c) The bills are always drawn with recourse so
all parties on instrument are liable till the bill is
finally discharged.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring – Meaning & Definition
The word factor has been derived from the
Latin word means ‘to make or to do’. In other
words ‘to get things done’. As we seen
invariably in small & medium scale companies
the problem of working capital. This is due to
large buyers procrastination. Factor plays
important role for these small & medium scale
companies.Factoring is nothing but selling of
trade debts at a discount to financial institution.
The definition of factoring according to V.A.
Avadhani, “factoring is a service of financial
nature involving the conversion of credit bills
into cash”. Financial Services Chapter 07
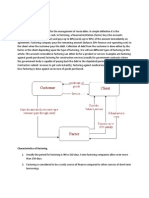
Modus Operandi
So factor provides finance to his client known
as factoring. The Modus operandi of factoring
scheme are:
There should be factoring agreement.
The client should prepares invoice in his usual way.
The goods are sent to buyers without Bill of
exchange but but Invoice.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Modus Operandi
The debt due by purchaser to client is
assigned to factor by advising the customer,
to pay to the factor.
The client hand over the invoices to factor
along with receipted delivery challans, or
copies of LR/PR etc.
Factor makes an immediate payment up to
80% of invoice value & the balance 20% after
realisation of debt.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Terms of Agreement
The important part of factoring is an
agreement between client & factor. Following
are some main points of the same.
Assignment of debt in favor of factor.
Selling limits for the client.
Condition of recourse.
Details of services offered by factor &
payment for same.
Interest to factor on the accounts where
credit allowed by seller to supplier.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Functions
The terms of agreement that lights on
functions of factor. The main function of factor
is to provide finance I.e. purchase & collection
of debts but along with that factor provides
other services those can be brief as below.
1. Sales Ledger Management: This is very
important function of factoring. Because when
factor offer service, it is his responsibility to
maintain sales ledger & keep track of payment
made by customer.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Functions
2. Purchase & Collection of Debts: Factor
provides immediate finance up to 80%. Thus
the collection of that invoice is his duty.
3. Undertaking of Credit Risk: This is also another
function which is very important. As you learn
factor provide spot finance, so he has to
closely monitor customer’s financial position,
his past performance and his honesty etc.
4. Provision of Finance: As stated earlier factor
provide immediate finance to client. The client
concentrate more on additional business
activities available.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Factoring
After seeing functions now lets see the
different types of factoring which varies on the
basis of the nature of transactions between
clients & his factor, volume of business.
following are some of the main types of
factoring.
1. Full Service Factoring: As the name suggest, it
is type where factor offers all services viz.
providing finance, administration of sales
ledger, collection of debts. This is called a
standard factoring practice.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Factoring
2. With Recourse Factoring: In this type factor
does not bear the credit risk. If debtors unable
to pay their dues & if the same is unpaid for
beyond a fixed period, the same is
automatically assigned back to client.
3. Bulk Factoring: It is also called as “Notified
Factoring” or “Disclosed Factoring” because
factor provides finance after disclosing the
fact of assignment of debts to the debtor
concerned. The management of sales ledger &
credit control has to be done by client himself.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Factoring
4. Maturity Factoring: Under this type factor does
not provide immediate cash payment to the
client. He undertakes to pay as & when
collection made from the debtor.
5. Invoice Factoring: In this type factor simply
provides finance against invoices without
undertaking any other function. The debtors
are not notified about finance so it is also
called as as “Undisclosed financing”.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Factoring
6. Agency Factoring: Under this type the work is
shared by both client & factor. The client has
to maintained sales ledger & collection work &
factor as to provide finances assuming credit
risk.
7. Invoice Factoring: As the name suggests it is
nothing but service of factor extended from
domestic market to international business.
this factoring is facilitated with the help of
import factor & export factors.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring Vs Discounting
As stated earlier the venture capital took roots
when comptroller of capital issues raised
guidelines for the same. The some of them are:
Point Factoring Discounting
Coverage Covers all debts Covers only those
debts
of a client. which are backed by
A.R.
Scope The scope is vast. The scope is limited
to
i.e.maintain sales provide finance against
ledger, credit risk, the discounted bills
provision of finance. Only.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring Vs Discounting
Point Factoring Discounting
Recourse Factor may extend It is always made
with
credit without any recourse to the client.
recourse.
Present- It is Known as It is Known as
ation “Off-B/s finance”. “In-B/s finance”.
Ownership Factor becomes The financer is an
the owner of value. agent not owner.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Cost of Factoring
Cost of factoring comprises of two aspects viz.
finance charges & service fees. Generally, the
factor charges a service fee on the total
turnover of the bills, it is around 1%. If the bills
paid earlier, the charges could be reduced.
Finance charges are normally same as interest
charged by bank. While the pricing of factoring
services, following components should be
taken into consideration. 1) Factoring Fees
2) Discount Charges Former comprises of
sales ledger, credit control & bad debts
administration. Later is for providing instant
credit to the client.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Format of Cost Sheet
The costing of factoring service is very important.
Following is the format of cost sheet for the
same.
A. Direct Cost
Per Invoice amount ……..
Per active account…….
Per Debtor account…….
Per Client account……. % of turnover
Bad debt provision……. % of turnover
Total of Direct Cost
B. Administrative Cost …….. % of turnover
C. Total Factoring Cost = A + B
D. Profit = ……% of turnover
E. Required factoring charges = ( C + D) x 100
Total turnover
Financial Services Chapter 07
Accounting System & Procedure
Normally factoring company keeps following
for accounts to record factoring transactions.
Sales Ledger Control A/c
Debt Purchase A/c
Client Current A/c
Bank A/c
Out of which A/c ‘a’ & ‘b’ must be maintained
separately for each customer. The accounting
procedure
involves following main entries at different stages.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Accounting System & Procedure
When Invoice are assigned
Sales ledger control A/c Dr.
To Debt Pur. A/c
When 80% Payment made
Client current A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
When Payment made by Debtors
Bank A/c Dr.
To Client Current A/c
Debt. Pur. A/c Dr.
To Sales Led. Control A/c
When Credit Note are assigned
Debt. Pur. A/c Dr.
To Sales Led. Control A/c
Financial Services Chapter 07
Benefits
1. Financial Service: In the current market situation &
payment trend, we often see many of the traders &
manufacturers being blocked their working capital
in trade debts. Factoring provides instant finance &
hence it gives opportunity to client to concentrate
on other business activities.
2. Collection Service: This is one of the best benefits
to client. It is found that total 60% of sales by SSI
sector is in the from of credit sale. So collection of
debts become vital for this sector. Now by
factoring this tension passes from client to factor,
leads to more time for client to concentrate on
production etc.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Benefits
3. Credit Risk Service: In the absence of factor, the
entire risk is on the shoulder of client. The bad
debts take away the profit of concern & in some
cases leads to winding up of organisation. But with
the factoring, now entire risk is borne by factor.
Client is assured of complete realisation of book
debts without tension.
4. ‘Sales Ledger Management Service’: Maintenance
of Sales Ledger is soul of business. It requires
expertise persons to do it, which the every client
may not have. Factoring helps client by sending
him monthly sales, collection analysis etc.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Benefits
5. Consultancy Service: Normally, factors are
professionals in offering management services.
They collects information about credit worthiness
of the customers, ascertain track record etc. Thy
also advice clients on import finance matters.
6. Economy Services: Factors are able to serve
economically as they have number of clients & so
they can spread their overheads between all of
them. So every client get service at lower cost. The
interest rate charged on 80% of amount so
factoring may considered cheap source of finance
compare to others.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Benefits
7. Off-Balance Sheet Financing: Factoring considered
as off - B/S finance. As this finance never appear in
liability side of B/S & this will improve current ratio
of company. Let’s take on example to make this
point clear.
Suppose the B/S of Well Pack shows: total of assets side 15
lakhs, comprises of debtors Rs.6,00,000, stock Rs.6,00,000
& other assets Rs.3,00,000. The debit side shows: loan
against stock Rs.4,00,000 & otter loan against Bills Rs.4,00,
000, other liability Rs.3,00,000 & Net working capital Rs.4,00,
000. From above,
The C.R. of the firm is 1.36 : 1
Now if debtors are purchase by factoring agent, he pays 80%
instantly so company gets Rs.4,80,000, which is used to pay
of bank loan. Now the revised position of Well Pack is as
below: Asset: stock Rs.6,00,000, debtors Rs.1,20,000.
The C.R. of company is 1.65 : 1
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring in India
In India the idea of factoring services was first
thought of by the Vaghul Working Group. The R.B.I.
Constituted study group in Jan. 1988 under
chairmanship of Mr. C. K. Kalyanasundaram & on
recommendation of the committee, the Banking
Act was amended in July 1990 with a view to
enabling commercial banks to take up factoring
services through their subsidiaries.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring in India
In Feb. 1994 R.B.I. Permitted all banks to enter
factoring business departmentally. In India the
factoring services firstly started by S.B.I. in
association with small Industries Development
Bank,Union Bank, State Bank of Sourashtra & State
Bank of Indore. The factoring company founded by
SBI called SBI- Factors & commercial services Pvt.
Ltd. (SBI- FACS) with capital of Rs.25 crores in
1991.
Financial Services Chapter 07
International Factoring
Just like domestic suppliers, the exporters also
finds difficulty in receiving payments. That is why
factoring services not only popular in domestic
business but also they are gradually entering into
export business. the International factoring has
been define as, “an arrangement between
factor &his client which includes at least two of the
following services provided by factor. i) Finance ii)
Maintenance of A/cs iii) Collection of debts iv)
Protection against credit risk”. Although from
definition, the international factoring look same as
domestic factoring, it is different in respect of type
of export factoring & the arrangement made by the
exporter & factor.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Export Factoring
In the absence of export factoring all export
transactions are backed by letter of credit.
Factoring is done entirely on the basis of invoice
prepared by the exporter, so it is purely an “Invoice
based export finance” technique.
There are normally four types of export finance.
Two factor system: There are two factors.
One is in the exporter's country & other in
importer’s country. The exporter never sends
goods to importer before factoring
relationship established.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Types of Export Factoring
Single factor system: Under this system also
two factors involve. But the responsibility of
making payment maintaining books is with
export factor. To cover credit risk export
factor enter into agreement with import factor.
Direct export factor system: In this, the
agreement is made between the exporter &
the export factor-no other party involved. The
entire risk is to be borne by export factor.
Direct import factor system: This is just
opposite of the previous one. The agreement
made between exporter & import factor in the
import country. The import factor shoulders
all the risk.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring in Other Countries
Factoring in European countries have option to
finance both domestic & export business. but
though business condition & continued
recession have effected the factoring business.
Now more than 700 factoring companies are
operating in forty countries.
Italy occupies 1st position in terms of factoring
business volume, followed by USA. The U.K.
stands 3rd in the rank. Japan, Marico, France,
Netherlands join the suit after.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring in Other Countries
The world factoring turnover is explain in the
following table.
Name No.of Factoring Turnover % Share
Companies ($ billion) in world factoring
Italy 80 75.0 28.9
U.K. 30 28.5 11.0
U.S.A. 20 51.5 19.8
Mexico 70 18.5 7.1
Japan 43 16.5 6.4
France 17 15.0 5.8
Netherlands 5 11.0 14.2
Germany 14 10.1 3.9
South Korea 15 6.0 2.3
Sweden 20 5.0 1.9
Others - 22.9 8.8
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring in Other Countries
The year wise factoring turnover shows
consistent improvement in factoring. With the
help of following graph it is very much clear that
factoring has an upward trend in improvement,
both in domestic & international. In the last 6
years, the total of factoring have been improved
from 103.8$ Billion to 260.0$ Billion(estimated).
Which itself a clear indication of upward trend,
same the case with international factoring.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Forfeiting
As we are coming to end of the chapter, this is a
third type of financing against receivables like
factoring. This technique is helpful to exporter for
financing goods exported on medium term
deferred basis.
The term ‘Forfeit is French word means “to give
something” or “give up one’s right”. In Forfeiting,
exporter give up his right to receive payment in
future for immediate cash payment by forfeiter.
The definition says, “the non-recourse purchase
by a bank or any other financial institution, of
receivables arising from an export of goods &
services”.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Factoring Vs Forfeiting
Both factoring & forfeiting are tools of financing.
Some basic differences can be made as follows.
Points Factoring Forfeiting
Terms Short term financing Medium term financing
Scope Both domestic as well It is invariably employed
as International. In export business.
Services Not only arrangements of Only financial aspect that
finance but also sales ledger to only particular export
maintenance, consultancy. bill.
Finance 80% on the spot, balance 100% on the spot.
20% after receiving payment.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Advantages of Forfeiting
It is very clear from previous comparison, that
though forfeiting & factoring are tools for financing,
the actual use of them is made as per requirement.
Means if you want to export some goods, you
should go for forfeiting & not for factoring & vis-a-vis.
Following are some of the advantages of forfeiting.
Profitable & Liquid: From the point of view of
exporter as well as forfeiter, this is most liquid
& profitable because forfeiter not only get
immediate cash as from discount charges,
but he can sell the same in secondary market.
Financial Services Chapter 07
Advantages of Forfeiting
Simple & Flexible: From the point of view of
exporter, this tool of finance is simple &
flexible, as he & forfeiter can decide the term
according to the needs of each other.
Avoid Export Credit Risk: The exporter is
completely free from credit risk, that nay arise
out of possibility of interest rate fluctuations
etc.
Avoid Export Credit Insurance: If exporter
does not wish for forfeiting, he has to go for
export credit insurance. Which is sometime
involve very rigid procedure as well as costly.
But in case of forfeiting he need not bare any
such expenses. Financial Services Chapter 07
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?De la EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- BIll Discounting PDFDocument36 paginiBIll Discounting PDFharshithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unlocking Financial Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Establish Business CreditDe la EverandUnlocking Financial Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Establish Business CreditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring: Presented ByDocument24 paginiFactoring: Presented ByswatigouravÎncă nu există evaluări
- FACTORINGDocument6 paginiFACTORINGsadathnooriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring MBADocument9 paginiFactoring MBADilip SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debtors Financing-Factoring: Swayam Siddhi College of MGMT & ResearchDocument15 paginiDebtors Financing-Factoring: Swayam Siddhi College of MGMT & Researchpranjali shindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and ForfaitingDocument7 paginiFactoring and ForfaitingemildaraisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 12 Factoring and Bill DiscountingDocument13 paginiSession 12 Factoring and Bill DiscountingNeena TomyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FactoringDocument4 paginiFactoringjeganrajrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring 1Document15 paginiFactoring 1nikitaneha0603Încă nu există evaluări
- Alternate Source of Finance, Private and Social Cost-Benefit, Public Private PartnershipDocument20 paginiAlternate Source of Finance, Private and Social Cost-Benefit, Public Private PartnershipRewant MehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forfaiting PDFDocument20 paginiForfaiting PDFAditya Paul Sharma100% (1)
- Receivable ManagementDocument29 paginiReceivable Managementvini2710Încă nu există evaluări
- Submitted By: Vivek SharmaDocument18 paginiSubmitted By: Vivek SharmaVe1kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limitations of FactoringDocument12 paginiLimitations of Factoringkomalthorat50% (2)
- Factoring Project ReportDocument15 paginiFactoring Project ReportSiddharth Desai100% (3)
- Factoring Is A: Invoice DiscountingDocument5 paginiFactoring Is A: Invoice DiscountingnoushinesabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is FactoringDocument22 paginiWhat Is Factoringshah faisal100% (1)
- FactoringDocument36 paginiFactoringmaninder1419699Încă nu există evaluări
- Factoring in IndiaDocument6 paginiFactoring in IndiaAkash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On FactoringDocument32 paginiPresentation On Factoringjigs44100% (2)
- Factoring FSDocument13 paginiFactoring FSAvinaw KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FACTORING, Discounting& ForfaitingDocument22 paginiFACTORING, Discounting& ForfaitingamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring ServicingDocument25 paginiFactoring ServicingTanya JaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- FactoringDocument28 paginiFactoringsaimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IInd Unit - Factoring and Venture CapitalDocument28 paginiIInd Unit - Factoring and Venture Capitalguna57617Încă nu există evaluări
- M. Com IV Semester Paper: Financial Services Module: Factoring and ForfaitingDocument19 paginiM. Com IV Semester Paper: Financial Services Module: Factoring and ForfaitingAishwarya100% (1)
- MFS-IV Chapter - Factoring Factoring: The ConceptDocument9 paginiMFS-IV Chapter - Factoring Factoring: The ConceptAarya SinganiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Guide:-Submitted ByDocument13 paginiInternal Guide:-Submitted Byjitu247100% (2)
- Unit 19 Factoring, Forfaiting and Bill Discounting: ObjectivesDocument20 paginiUnit 19 Factoring, Forfaiting and Bill Discounting: ObjectivesmanishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring in IndiaDocument3 paginiFactoring in IndiachikuraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring Services: Submitted by Arulselvam.R 08-CO-455Document25 paginiFactoring Services: Submitted by Arulselvam.R 08-CO-455Arul SelvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring Study MaterialDocument2 paginiFactoring Study MaterialDr.G.H.KERINAB BEENUÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 6 Factoring & Forfaiting (M.Y.khan)Document32 paginiCH 6 Factoring & Forfaiting (M.Y.khan)mr_gelda6183Încă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)Document24 paginiPresented By: 1. Pravin Gavali 2. Vickram Singh MIT-MBA (Finance)shrikant_gaikwad100Încă nu există evaluări
- Domestic Factoring GuidelinesDocument32 paginiDomestic Factoring GuidelinesAnkitmehra8Încă nu există evaluări
- Factoring: BY: NOU Shin ESA BA REB ECC ADocument20 paginiFactoring: BY: NOU Shin ESA BA REB ECC AnoushinesabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and Invoice Discounting Working Capital Management OptionsDocument5 paginiFactoring and Invoice Discounting Working Capital Management OptionsKomal ParikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Services AssignmentDocument12 paginiFinancial Services AssignmentArpita TrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring: Factoring Is A New Financial Service That Is Presently Being Developed in IndiaDocument1 paginăFactoring: Factoring Is A New Financial Service That Is Presently Being Developed in IndiaCharu ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and IngDocument40 paginiFactoring and IngSajan VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- FactoringDocument48 paginiFactoringrajthapakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring, Forfeiting (Cir. 13.12.23)Document27 paginiFactoring, Forfeiting (Cir. 13.12.23)Sonali MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and ForfaitingDocument11 paginiFactoring and ForfaitingPriyanka MahawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FactoringDocument23 paginiFactoringYash KhonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Four Receivables Management Nature and Importance of ReceivablesDocument10 paginiChapter Four Receivables Management Nature and Importance of ReceivablesBenol MekonnenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap 06 REO Receivables - PDF 074431Document19 paginiAp 06 REO Receivables - PDF 074431Christian100% (1)
- Factoring NewDocument19 paginiFactoring NewParthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On FactoringDocument5 paginiAssignment On FactoringVISHNU. M. K MBA 2018Încă nu există evaluări
- Receivable & Payable Management PDFDocument7 paginiReceivable & Payable Management PDFa0mittal7Încă nu există evaluări
- Factoring 1Document21 paginiFactoring 1Sudhir GijareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1-LIABILITIES and PREMIUM LIABILITYDocument10 paginiModule 1-LIABILITIES and PREMIUM LIABILITYKathleen SalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factoring and IngDocument7 paginiFactoring and IngAnsh SardanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit PolicyDocument84 paginiCredit PolicyDan John Karikottu100% (6)
- Financial ManagementDocument24 paginiFinancial ManagementozalmistryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 ReceivablesDocument22 paginiChapter 3 ReceivablesCale Robert RascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM05 Working Capital & LiquidityDocument16 paginiLM05 Working Capital & LiquiditySYED HAIDER ABBAS KAZMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On The Financial Performance of Canara BankDocument7 paginiA Study On The Financial Performance of Canara BankAruna AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Economic Study MethodsDocument62 paginiChapter 3 Economic Study MethodsJohn Fretz AbelardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theodore E. Raiford - Mathematics of FinanceDocument500 paginiTheodore E. Raiford - Mathematics of FinanceHeru HermawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Chapter 1 ValuationDocument5 paginiNotes Chapter 1 ValuationArielle CabritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Project ReportDocument12 paginiMajor Project ReportAMAN SAXENAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business InfographicDocument1 paginăBusiness InfographicLuck BananaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Combination - ExercisesDocument36 paginiBusiness Combination - ExercisesJessalyn CilotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repos A Deep Dive in The Collateral PoolDocument7 paginiRepos A Deep Dive in The Collateral PoolppateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investment AppraisalDocument18 paginiInvestment AppraisalKwasi MmehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tax Calculator by Tax GurujiDocument4 paginiTax Calculator by Tax GurujiSunitKumarChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides Macroeconomics 1 - FTUDocument50 paginiSlides Macroeconomics 1 - FTUK60 Nguyễn Ái Huyền TrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Century Paper and Board Mills Limited - Case StudyDocument23 paginiCentury Paper and Board Mills Limited - Case StudyJuvairiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fintech Insights Q2 2022 Quarterly: FT Partners ResearchDocument110 paginiFintech Insights Q2 2022 Quarterly: FT Partners ResearchngothientaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xi Akl 3 - Lembar Kerja Memproses Entry JurnalDocument25 paginiXi Akl 3 - Lembar Kerja Memproses Entry JurnalKeshya MantovanniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Management-Kings 2012Document2 paginiFinancial Management-Kings 2012Suman KCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company Valuation MethodsDocument20 paginiCompany Valuation MethodsKlaus LaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Please DocuSign Agreement To Purchase Form - 20, Lorong Pending 2D Bandar Puteri Klang Selangor 2Document4 paginiPlease DocuSign Agreement To Purchase Form - 20, Lorong Pending 2D Bandar Puteri Klang Selangor 2Reena punithanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proforma Invoice Gilmar 003 02Document1 paginăProforma Invoice Gilmar 003 02diegomattaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Business Fundamentals Checking: Account SummaryDocument14 paginiYour Business Fundamentals Checking: Account Summaryabal67% (3)
- Topic 1 To 5 QuestionDocument7 paginiTopic 1 To 5 QuestionANIKET SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brea ch05 BMM 7e SGDocument85 paginiBrea ch05 BMM 7e SGSarosh Ata100% (1)
- Moody's Seminars: Corporate Credit Rating AnalysisDocument3 paginiMoody's Seminars: Corporate Credit Rating AnalysisDevon JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabm2 - Q2 - M3Document14 paginiFabm2 - Q2 - M3Christopher AbundoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection 2-Capital Markets VideoDocument2 paginiReflection 2-Capital Markets Videojonald almazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- $20K Per Day Ecom Secrets - Adrian Morrison PDFDocument30 pagini$20K Per Day Ecom Secrets - Adrian Morrison PDFAlexandru ArbanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMFG India Credit Company LimitedDocument9 paginiSMFG India Credit Company Limitedvatsal sinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- National CPI: (April 2015 = 100) (یرو)Document25 paginiNational CPI: (April 2015 = 100) (یرو)Sakhi AhmadyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample MCQsDocument6 paginiSample MCQsRubal GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pymnts Reinventing b2b Payments ReportDocument27 paginiPymnts Reinventing b2b Payments ReportTimmy O' CallaghanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neighborhood 3 B29 L19Document4 paginiNeighborhood 3 B29 L19Kate CastañaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistDe la EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindDe la EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (276)
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoDe la Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (25)
- Summary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: Dotcom Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Growing Your Company Online with Sales Funnels by Russell Brunson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffDe la Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (19)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveDe la EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (154)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItDe la EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (152)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleDe la EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (48)
- Summary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your Stuff by Alex Hormozi: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (6)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldDe la EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Storytelling: A Guide on How to Tell a Story with Storytelling Techniques and Storytelling SecretsDe la EverandStorytelling: A Guide on How to Tell a Story with Storytelling Techniques and Storytelling SecretsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (72)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetDe la EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"De la EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (164)
- How to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorDe la EverandHow to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (33)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeDe la EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (88)
- Understanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationDe la EverandUnderstanding Digital Marketing: Marketing Strategies for Engaging the Digital GenerationEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (22)
- Summary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert B. Cialdini Ph.D.: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Ca$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneDe la EverandCa$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (114)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeDe la EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (278)
- Summary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (10)
- Visibility Marketing: The No-Holds-Barred Truth About What It Takes to Grab Attention, Build Your Brand, and Win New BusinessDe la EverandVisibility Marketing: The No-Holds-Barred Truth About What It Takes to Grab Attention, Build Your Brand, and Win New BusinessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (7)
- The Lean Product Playbook: How to Innovate with Minimum Viable Products and Rapid Customer FeedbackDe la EverandThe Lean Product Playbook: How to Innovate with Minimum Viable Products and Rapid Customer FeedbackEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (82)
- Invisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorDe la EverandInvisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (131)
- Summary: The Intelligent Investor: The Definitive Book on Value Investing by Benjamin Graham: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: The Intelligent Investor: The Definitive Book on Value Investing by Benjamin Graham: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessDe la EverandMarketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (203)
- The Culture Code: An Ingenious Way to Understand Why People Around the World Live and Buy As They DoDe la EverandThe Culture Code: An Ingenious Way to Understand Why People Around the World Live and Buy As They DoEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (28)
- The Power of Experiments: Decision-Making in a Data Driven WorldDe la EverandThe Power of Experiments: Decision-Making in a Data Driven WorldÎncă nu există evaluări