Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MT Govt PDF
Încărcat de
jitendra sharmaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MT Govt PDF
Încărcat de
jitendra sharmaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Household consumes G&S produced by firms for which
MACROECONOMY they spent money.
Introduction
Banking sector is an integral part of economy. To better Next we can understand few economic terms with
understand banking sector, we must have an overview help of above model.
of economy. So let us have an idea how economy works?
In economics we mainly deals with, how production, Savings?
distribution and consumption of goods and services Let's introduce saving into our model
(G&S) takes place. We can understand broader As we know households does not spent their whole
functioning of an economy with the help of circular flow income but they also save a part of it in form of deposits
model. in banks, cash at hand, etc. As this money is not spent on
goods & services, so we can consider it as a leakage
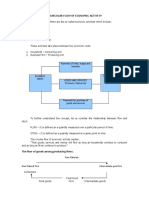
What is Circular flow model? from circular flow.
In economics, a circular flow model is used to
represent the monetary transactions in an economy. Savings – leakages Investments – injections
There are two flows present within the model Now let us consider three cases!
including flows of physical things (goods or labour) and If S>>I if savings are higher than investments means
flows of money (what pays for physical things). leakage is more money is not utilised in economy for
See table below for details production lesser production unemployment, …….
If S<<I I if savings are lesser than investments means
Production & consumption in an high investments more production in economy
employment…….
economy
If S = I everything in balance
Production
Who produces what & how?
Firms & factories produce goods and services. For Savings
Household
production firms requires land, labour, capital etc which
s
is provided by households. In return, households get
incomes(money) in form of salaries, rent, wages, Rent Land
Goods & Expenditure
interests.
Four factors of income and associated incomes Wages Labour
Services
Land -rent
Labour-wage
Capital-interest Firms Investments
Entrepreneurs-profits
Try yourself!
For above three cases Analyse effects on ? (↑↓)–
production - consumption - unemployment – inflation
Role of Banks?
Household Can banks help in channelizing money in economy by
s accepting savings from people and giving loans to
Rent Land
factories for investment & hence production!
Goods & Expenditure Clearly, banks have to encourage borrowers to borrow
Wages Labour more. Banks can do this by reducing the interest
Services rates they charge on loans
Firms Role of government in economy ?
As govt raise taxes on incomes of households, So this
Consumption part of money is not available for spending by
Who consumes what & how? households. So money not spent in economy is a kind of
leakage from circular flow.
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
But wait for a while & think, what govt do with this
money!
Govt spends on Subsidies --Transfer payments--Capital
investments (infrastructure, roads, railway, and dams)
One more crucial function of govt is -Redistribution of
income - by taxing rich higher & redistributing it in poor
by way of subsidies creating a balance!
Taxes
Household
s
Rent Land
Goods & Expenditure
Wages Labour
Services
Firms Govt Spending
Role of govt Taxation = leakage Govt spending =
injection
If G > T. if govt pending is much higher than money
received from taxation means govt 'running a
budgetary deficit‘
What is External sector?
If an Indian buy foreign G&S, than he is actually
spending money out of economy out of circular
flow Imports& investment by Indians abroad =
leakage
Exports& investment in India by foreigners (FDI, FII) =
injection
M = total money flowing out
X = total flow in
Import
Household
s
s
Rent Land
Goods & Expenditure
Wages Labour
Services
Firms Exports
M > X = Balance of Payments deficit.
We will discuss these concepts in separate chapters;
goal here is just to introduce you with economic
terms
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
To fill deficits government borrow from different
GOVERNMENT BUDGET sources.
Introduction
To properly understand govt budget, we must have
conceptual clarity of following two terms capital and
revenue.
Capital consists of anything (money-material) that can
be used in production. Capital is an input in the
production function.
Further, what we have finally produced using capital
can be taken as revenue.
See image below - imagine you establish a factory and
start production.
Now with the help of image below, try to understand
concept of INPUT money (capital) &OUTPUT Money
(revenue)
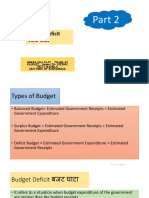
Important concepts about deficits
Revenue Deficit= revenue expenditure - revenue
receipts
Capital Deficit = Capital Expenditure– Capital Receipts
Govt budget is also divided on same lines, revenue Fiscal Deficit= Total Expenditure – (Revenue Receipts
side and capital side. + Non-debt Capital Receipts)
See diagram below and clearly observe following things Primary Deficit: fiscal deficit - interest payments.
1. Reciepts and Expenditures on revenue side Interest payments reflect a consequence of past actions
2. Reciepts and Expenditures on Capital side of the government, namely, loans taken and given in
Govt reciepts always shortfall of its expenditures years prior to the one under consideration. Exclusion of
(Deficits). interest transactions enables us to see, how the
government is currently conducting its financial affairs.
Monetised Deficit:it indicates the level of support
extended by the Reserve Bank of India to the
government’s borrowing programme.
Effective Revenue Deficitis the difference between
revenue deficit and grants for creation of capital assets.
The definition of the revenue expenditure is that it must
not create any productive asset. However, There are
several revenue expenditures part of which do create
some assets MGNREGA, PMGSY. So ERD included in
budget.
Now we have an idea about govt deficits. Deficits are
calculated on a single year. Accumulation of deficits
over years leads to stock known as Debt
How govt fill its deficits - deficit
financing
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
1. External aids - generally developing and
underdeveloped countries take monetary help TAXATION
from developed countries. What is a tax?
2. External borrowings - borrow money from A tax is a financial charge on an individual or legal
other countries/banks/financial institutions entity by a state. Govt raise taxes for efficient
3. Internal borrowings - borrow from inside the administration of a country. Apart from that Govt
country- banks/financial institutions achieves redistribution of income & resources (by
4. Printing currency taxing rich more & poor less)
If govt has larger debts, it has to pay a lot in form of Methods of taxation
interests to lenders. Result is that govt remain with little Progressive taxation- increasing rate of tax with
money to spend on developmental works like infra, increasing value or volume. Ex -income tax in India.
education, health.. Which are more crucial for 30% taxes on rich with annual income more than 10
development of a country? lakhs. No taxation up to 2.5 lakhs of annual income
Regressive taxation- decreasing rate of tax with
What restrict govt from making large increasing value or volume. Taxation on essential goods.
borrowings/deficits Rich and poor have to pay equally while buying
FRBM act –2003 fiscal responsibility & budget toothpaste. But its burden on poor is more as 10 Rs
management act. matter a lot for poor & but 10 Rs nothing for a highly
The Act mandates the central government to take rich person.
appropriate measures to reduce fiscal deficit and
revenue deficits. If this is not achieved through tax Types of taxes
revenues, the necessary adjustment has to come from a To understand types of taxes, let us first have idea
reduction in expenditure about two basic concepts.
Incidence of tax –the point where tax looks being
Deficit Reduction imposed.
Government deficit can be reduced if govt increases it Burden of tax – the point where effect of tax being felt.
receipts while at the same time decreases its spending. Types of taxes
It is also known as fiscal consolidation. It can be Direct tax-
achieved in following ways 1. Person or entities pays it directly in the first
instance to the government.
Fiscal consolidation 2. Taxed on the income or profits.
Cutting down expenditure Increasing revenue receipts 3. On individual & legal entities.
↓Subsidies Tax reforms – GST 4. Incidence and burden at same point.
↓Salaries, pensions Disinvestment of PSUs Indirect tax
↓Interest burden 1. Paid indirectly to the government.
↓Defence spending
2. Put on goods and services (consumption rather on
↓Expenditure reforms
income)
3. Incidence and burden at different point.
Direct Tax Indirect Tax
Meaning Imposed on the Imposed on goods and
individual or legal services and on
entity. transactions.
Paid Directly to govt Paid indirectly to govt
income or profits Goods & services
Incidence Same points Different points
&Burden
Types Wealth Tax, Income Central Sales tax, VAT
Tax, Property Tax, (Value Added Tax), Service
Corporate Tax, Import Tax, STT (Security
and Export Duties. Transaction Tax), Excise
Duty, Custom Duty.
Evasion Tax evasion is possible. Tax evasion is hardly
possible
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
Inflation Reduces inflation. Promotes the inflation.
Nature Progressive Regressive
Let us understand about different types of taxeswith a
rough example. follow image below-
A farmer produces wheat sells it to Mill owner mill
owner manufacture bread out of it (excise duty on
manufacturing) wholesaler & retailer sells bread in
market (sales tax) if trader sales bread outside
country (customs duty for import/export)
Further bread factory makes profit (tax on profits-
corporate tax) employee in factory receives salary
(income tax) bread serves by a restaurant (service
tax for providing any service)
Various types of taxes by different
Governments
As per Indian constitution different governments have
separate domain and powers to levy taxes.
Let us see few examples
What is a VAT - Value added Tax
Vat is a kind of tax imposed on each stage of value
addition in a product. It is collected at every stage of
production and distribution
See example below
Assume tax rate is 10%. Suppose you are textile
manufacturer.
You as a buyer:
You buys cotton from farmer in Rs 100/- and paid Rs
10 as tax.
You as a seller:
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
When you sell a shirt to retailer you receive Rs 500/-
including a tax of RS 50/- EXTERNAL SECTOR
In the above two process, you as a buyer & as a seller Introduction
you collected net of Rs 40 (50-10) which govt finally The external sector is part of a country's economy that
collects from you. interacts with the economies of other countries. In
So Vat is a two way process, govt can verify transaction goods market, the external sector involves exports and
records from buyer as well as seller, therefore tax imports. In the financial market it involves capital
avoidance is difficult. flows.
Basis Sales Tax VAT What is balance of payment?
Meaning Tax charged on the VAT is a tax charged at each The Balance of Payment (BoP) records a country’s
total value of the level of the production and net of all transactions with the rest of the world. All
commodity, distribution chain whenever transaction include goods & services as well as
the value is added to the
product.
capital flows in/out of a country.
Nature Single point tax Multi point collection Therefore, BoP is a net of two accounts - current a/c &
collection capital a/c.
Tax Evasion Can be possible Cannot be possible See table below - various items are included in current
Cascading Yes No a/c & capital a/c. further revenue generated on capital
Levied on Total Value Value Added a/c is also included under Current a/c. (follow red
Tax Burden Falls on the Rationalized.
arrow in table)
consumer
Input Tax Unavailable Available Balance of Payment
Credit Capital FDI long-term capital Profits
A/c investment
Area Applies to the whole Applies within the FII purchase of shares and Incomes
country. jurisdiction of the state. bonds.
Loans – Any borrowing or Interests
ECB- govt lending in foreign
The Goods and Service Tax (GST) exchange
1. A new form of indirect tax property Immovable property, Rent
2. replace other indirect taxes like service tax, land
sales tax. Reserve a/c to buy and sell foreign
3. Dual tax- every supply of goods and services currencies by RBI
would be subjected to a Central GST (CGST) and Current balance of Goods (physical objects)
State GST (SGST) on intrastate supply. A/c trade (BoT)
Net of Services (invisibles)
4. A separate tax IGST for inter-state trade. ex/Im
5. states as well as the centre can tax services
6. GST will be available as input tax credit net primary Incomes from capital
7. Differential treatment for alcohol, tobacco and income a/c
petroleum products
Benefits net cash Remittances
1. Simplicity & increased compliance transfers
2. Less evasion -help to develop single market
Forex reserves
India’s foreign exchange reserves is made up of
1. Foreign currency assets (FCA) (US dollar, euro,
pound sterling, Canadian dollar, Australian dollar
and Japanese yen etc.)
2. gold
3. special drawing rights (SDRs) of IMF
4. Reserve tranche position (RTP) in the International
Monetary Fund (IMF)
In case of India: Capital a/c remains +ve due to high
flow of foreign capital (FDI/FII) inside India.
While current a/c remains -ve , given the more imports
over exports of goods and services by India.
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
So excess of capital a/c is used to finance our excess of
exports over imports. Remaining excess of capital a/c INFLATION
goes to forex reserve with RBI. See image below What is inflation?
Inflation is general rise in prices of goods & services.
Increase in prices caused by mismatch in demand &
supply side of an economy
Basis for FDI FII
Comparison
Meaning Long term FII is investments in the
investments in plant, share & stock market of a
machinary- productive country.
assets. Causes of inflation
Market Primary Secondary Factor causing inflation can be broadlycategorised in
two parts.
Entry and Difficult Easy If causes of inflation is on demand side (↑ consumption)
Exit ,it is known as Demand pull factors.
What it Long term capital Long/Short term capital
brings?
On the other hand if causes of inflation are on supply
Transfer of Funds, resources, Funds only. side it is known as Cost push factors. It occurs due to
technology, strategies, rise in input cost which ultimately reflect in price of
know-how etc. final goods and services
Economic Yes No
Growth Causes of inflation
Target Specific Company No such target, Demand pull factors Cost push factors (supply side)
investment flows into the
financial market. 1. Excess aggregate 1 Increasing raw material
demand. 1. Rising wage cost
2. Increase in disposable 2. Increased taxes
Control Yes No income 3. High profit margin
3. Increase in money supply 4. Rising import prices due to fall
(RBI) in exchange rate
Forex market- 4. Black money
1. The market in which buy, sell, exchange and
speculate on currencies .
2. Participants are made up of banks, commercial
Losers and gainers at time of inflation
companies, central banks,investment management Inflation = loss in value of money vs goods &
firms, hedge funds, and retail forex brokers and services
Losers Gainers
investors. The forexmarket is considered to be the
Creditors (lenders) Debtors(borrowers)
largest financial market in the world. Wage earners Businessmen
3. Exchange rate depends on three factors – Salaried persons Shareholders
i. Economic Activities Pensioners Govt
ii. GDP Bondholders
iii. Political stability
Related Terms
1. Deflation - continuous decrease in prices of goods
and services - inflation rate becomes negative
(below zero).
2. Stagflation - A condition of slow economic growth
and relatively high unemployment- a time of
stagnation- accompanied by inflation.
3. Disinflation- A slowing in the rate of price
inflation - when the inflation rate has reduced
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
marginally over the short term. It is used to
describe periods of slow inflation.
TERMS Rate of inflation
Deflation -ve
Stagflation +ve
Disinflation +ve
MOCKTIME.COM ONLINE TEST SERIES CORRESPONDENCE COURSE
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 18e Key Question Answers CH 38Document3 pagini18e Key Question Answers CH 38Kier Cayetano100% (1)
- 8.1 The Circular Flow of Income RSDocument22 pagini8.1 The Circular Flow of Income RSSyed HaroonÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Income and Related Aggregates: Dr. Roopali Srivastava Department of Management ITS, GhaziabadDocument30 paginiNational Income and Related Aggregates: Dr. Roopali Srivastava Department of Management ITS, GhaziabadniteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investment Models - Clear IASDocument6 paginiInvestment Models - Clear IASshahrachit91Încă nu există evaluări
- Govt Budger For Students of Xii - 2024Document33 paginiGovt Budger For Students of Xii - 2024bansaladitya1708Încă nu există evaluări
- Ecodev Midterm Notes 2Document3 paginiEcodev Midterm Notes 2Nichole BombioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiscal Policy 2023-24Document17 paginiFiscal Policy 2023-24priyanshu15678Încă nu există evaluări
- Macro CH 1 - NotesDocument12 paginiMacro CH 1 - NotesPrachi SanklechaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Eco Complete Ques+NotesDocument117 paginiMacro Eco Complete Ques+NotesPiyush ChhajerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics 1 A Unit 3 Notes Definition of A MarketDocument5 paginiEconomics 1 A Unit 3 Notes Definition of A MarketKathryn ParadisosÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Economy (Macroeconomy)Document37 paginiNational Economy (Macroeconomy)Irish Kate MantigueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circularflow of Nation IncomeDocument21 paginiCircularflow of Nation IncomeYograj PandeyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N Gregory Mankiw - Macroeconomics (2009, Worth Publishers) - Libgen - LC (084-088)Document5 paginiN Gregory Mankiw - Macroeconomics (2009, Worth Publishers) - Libgen - LC (084-088)Jose RizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting EquationDocument20 paginiAccounting Equationestherlorrainedioneencila00Încă nu există evaluări
- Michele Jaymalin-Dulay, PHD: College of Education 1 Sem 2020-2021Document21 paginiMichele Jaymalin-Dulay, PHD: College of Education 1 Sem 2020-2021MicheleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Flow of National IncomeDocument29 paginiCircular Flow of National IncomeRiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Circular Flow of Economic ActivityDocument13 paginiThe Circular Flow of Economic ActivityEng MatanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Flow of IncomeDocument15 paginiCircular Flow of IncomeSunny Deo BhaktaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L2 Basic Financial StatementsDocument41 paginiL2 Basic Financial StatementsSam TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lcci LV I TextDocument65 paginiLcci LV I TextPyin Nyar AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring National Income: GDP Calculation MethodsDocument13 paginiMeasuring National Income: GDP Calculation MethodsNoor EylianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Flow of Income: Closed and Open Economy ExplainedDocument23 paginiCircular Flow of Income: Closed and Open Economy Explainedrahul negiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Accounting Chapter 1 SummaryDocument38 paginiPrinciples of Accounting Chapter 1 SummaryAfsar AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Govt BudgetDocument38 paginiGovt BudgetRishab JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1586880280key Financial ReportsDocument13 pagini1586880280key Financial ReportsPhonepaxa PhoumbundithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 - Expenditure Multipliers PDFDocument53 paginiLecture 4 - Expenditure Multipliers PDFAhmed MunawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Flow of IncomesDocument9 paginiCircular Flow of IncomesMohammed NazeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco 102 (Chapter 2) NewDocument2 paginiEco 102 (Chapter 2) NewMA. FELICITI IGNACIOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statements - Basis of AnalysisDocument44 paginiFinancial Statements - Basis of AnalysisJasmine ActaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The EconomyDocument22 paginiWhat Is The EconomyMark Lester MagnayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to Accounting and FinanceDocument39 paginiIntro to Accounting and FinanceEngr Muhammad RohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- National-Economy-Marcoeconomy (Revised Edition)Document43 paginiNational-Economy-Marcoeconomy (Revised Edition)PehedenÎncă nu există evaluări
- FABM2 Module 4Document7 paginiFABM2 Module 4Rhamyllia Kyla C. MaghanoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microeconomic AnalysisDocument32 paginiMicroeconomic AnalysisAbdin AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics, Govt BudgetDocument28 paginiEconomics, Govt BudgetRajinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Presentation On Government Budget and Economy: Prepared by Shiwali Agrawal (PGT Economics Sunbeam Suncity)Document18 paginiA Presentation On Government Budget and Economy: Prepared by Shiwali Agrawal (PGT Economics Sunbeam Suncity)Raj SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Australian Economy PowerPoint 2024Document176 paginiThe Australian Economy PowerPoint 2024cashspect.businessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block 1 MS 9 Unit 2Document18 paginiBlock 1 MS 9 Unit 2vinay kaithwasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Income Flow in 2, 3, and 4 Sector EconomiesDocument6 paginiCircular Income Flow in 2, 3, and 4 Sector EconomiesPrithivi RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Macroeconomics FundamentalsDocument20 paginiIntroduction to Macroeconomics Fundamentalssoumyadip p[aulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 10 MacroeconomicsDocument8 paginiChapter - 10 MacroeconomicsHiya MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peopleware Chapter 20Document14 paginiPeopleware Chapter 20Umar AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- F2Document8 paginiF2KAJOGBOLA FULLZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting ProcessDocument36 paginiAccounting ProcessYnnej GemÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5th Semester Economics Seleted Questions PDFDocument24 pagini5th Semester Economics Seleted Questions PDFAnil SonthaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate real cost of capitalDocument8 paginiCalculate real cost of capitalJiya RajputÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8: Introduction To Macroeconomics 1. IntroductionDocument12 paginiChapter 8: Introduction To Macroeconomics 1. IntroductionAishwaryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting 101 Chapter 1Document39 paginiAccounting 101 Chapter 1Md. Riyad Mahmud 183-15-11991Încă nu există evaluări
- Money and Income 2Document4 paginiMoney and Income 2YASEOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Accounting and Business FinanceDocument50 paginiFundamentals of Accounting and Business FinanceJomarie EmilianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Means Introduction of Income Into The FlowDocument3 paginiMeans Introduction of Income Into The FlowJaira AndanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Flow, NI & AggregatesDocument21 paginiCircular Flow, NI & AggregatesTanni BaruaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FoE Unit IVDocument31 paginiFoE Unit IVDr Gampala PrabhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 - Accounting and FinanceDocument21 paginiWeek 4 - Accounting and FinanceTharra ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBC2 - 18 Sem2Document28 paginiMBC2 - 18 Sem2Aref MaghmoumahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Economics AssignmentDocument20 paginiMacro Economics AssignmentSWAPNIL GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bfii Unit 2Document56 paginiBfii Unit 2Dhia. KhalloufiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cash flows for replacement project analysisDocument28 paginiCash flows for replacement project analysisNandhini NallasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ktu Studnts: Circular Flow of IncomeDocument12 paginiKtu Studnts: Circular Flow of IncomerichardhpdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument7 paginiChapter 2 NoteskhwaishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersDe la EverandFinancial Analysis 101: An Introduction to Analyzing Financial Statements for beginnersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faulty ParallelismDocument2 paginiFaulty Parallelismjitendra sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Hundred AntonymsDocument15 paginiThree Hundred Antonymsjitendra sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Route WordsDocument38 paginiLatin Route Wordsemiliow_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Quick Study - Spanish Verbs PDFDocument6 paginiQuick Study - Spanish Verbs PDFAirinHazelnutRaspberryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method of ProportionsDocument26 paginiMethod of Proportionsjitendra sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singapore EnglishDocument145 paginiSingapore EnglishtheurgliestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singapore DialectsDocument5 paginiSingapore Dialectsjitendra sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singapore EnglishDocument145 paginiSingapore EnglishtheurgliestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Match Point - BSC Magazine - June 2016Document2 paginiMatch Point - BSC Magazine - June 2016ashugkp1811Încă nu există evaluări
- 6 Budget in Brief English 2021 22Document55 pagini6 Budget in Brief English 2021 22Dawndotcom100% (2)
- Sovereign Risk and Natural Disasters in Emerging MarketsDocument17 paginiSovereign Risk and Natural Disasters in Emerging MarketsAgnes DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECOXII201920Document70 paginiECOXII201920Payal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Economic Policy 1991 Upsc Notes For Economy 0f484a72Document6 paginiNew Economic Policy 1991 Upsc Notes For Economy 0f484a72aryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study KhushiDocument9 paginiCase Study KhushiKhushi VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomic Theory and Policy for an Open EconomyDocument61 paginiMacroeconomic Theory and Policy for an Open EconomySayan MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acca f9 Revision Kit Acca 24 Old Past Paper Solved Old Professional Scheme - CrackedDocument237 paginiAcca f9 Revision Kit Acca 24 Old Past Paper Solved Old Professional Scheme - CrackedAlex SemusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Murray - Lindo ControllershipDocument27 paginiMurray - Lindo ControllershipMichella ManlapigÎncă nu există evaluări
- President Marcos' SONA to focus on economy, agriculture, pandemic recoveryDocument3 paginiPresident Marcos' SONA to focus on economy, agriculture, pandemic recoveryChristine April BrillantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- West Africa Regional Economic Outlook 2020-FinalDocument90 paginiWest Africa Regional Economic Outlook 2020-Finaladewunmi olufemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of Foreign Trade and Exchange - Economic Education..Document30 paginiThe Basics of Foreign Trade and Exchange - Economic Education..William FanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foreign Trade of PakistanDocument3 paginiForeign Trade of PakistanZuhair Naqvi0% (1)
- FIN 30220: Macroeconomic Analysis: Capital MarketsDocument66 paginiFIN 30220: Macroeconomic Analysis: Capital MarketsPushpa KamatÎncă nu există evaluări
- BraunDocument79 paginiBraunSally SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Macroeconomics Chapter 3: Open Economy Macroeconomics - Exchange Rates and The Balance of PaymentsDocument9 paginiInternational Macroeconomics Chapter 3: Open Economy Macroeconomics - Exchange Rates and The Balance of PaymentsdkwlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepal COSDocument45 paginiNepal COSLeo KhkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics 4th Edition Krugman Test BankDocument34 paginiMacroeconomics 4th Edition Krugman Test Bankdencuongpow5100% (24)
- UntitledDocument69 paginiUntitledJonathan OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aggregate Supply and the Phillips Curve: Exploring the Relationship Between Inflation and UnemploymentDocument68 paginiAggregate Supply and the Phillips Curve: Exploring the Relationship Between Inflation and UnemploymentPrateek BabbewalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget Deficit ExplainedDocument20 paginiBudget Deficit ExplainedAyushÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1001 Questions For Last Moment Banking PreparationsDocument35 pagini1001 Questions For Last Moment Banking PreparationsAparajito SethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dec10 AfcatDocument4 paginiDec10 Afcatsandyjawale18Încă nu există evaluări
- Foreign Currency Transaction: Factors Cause Foreign Currency Exchange Rates To ChangeDocument13 paginiForeign Currency Transaction: Factors Cause Foreign Currency Exchange Rates To ChangeJeska QuirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bank Management Financial Services Rose 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument23 paginiBank Management Financial Services Rose 9th Edition Solutions Manualkevahuynh4vn8d100% (27)
- ALAN STOLEROFF - 2013 - Employment Relations and Unions in Public Administration in Portugal PDFDocument15 paginiALAN STOLEROFF - 2013 - Employment Relations and Unions in Public Administration in Portugal PDFManuel MenezesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dayag Chapter 4Document17 paginiDayag Chapter 4Clifford Angel Matias71% (7)
- Unit 4 - EIC AnalysisDocument29 paginiUnit 4 - EIC AnalysisjineshshajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 1: Fiscal Policy FormulationDocument9 paginiGroup 1: Fiscal Policy Formulationaige mascodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Budget Summary CaliforniaDocument248 paginiFull Budget Summary CaliforniaLairdhÎncă nu există evaluări