Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
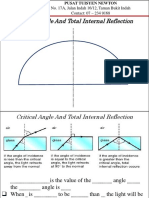
Periscope To Binocular
Încărcat de
sylent gohTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Periscope To Binocular
Încărcat de
sylent gohDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Additional question 5.
4 Lenses
[1]
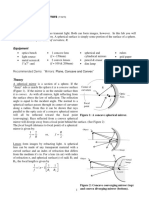
1. [SBP Trial 2006 P2 (A) Q7 (a)]
Figure shows an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment.
The objective and the eyepiece of the telescope have powers of + 2 D and + 20 D respectively.
The objective lens also has a diameter that is larger than the diameter of the eyepieces.
Objective Eye piece
(a) (i) Explain why the objective of the telescope needs to have a larger diameter. [1 mark]
Menumpukan lebih banyak cahaya dari objek supaya imej lebih terang
To collect more light from the object [produce brighter image]
(ii) Calculate the length of the telescope. [2 marks]
Calculate the focal length correctly
1
f0 = m/ 0.5 m / 50 cm
2
1
f0 = m/ 0.05 m / 5 cm
20
length of the telescope = 50 + 5 = 55 cm
2. [PERAK 2007 P2 Part B Q9 (c) (i)]
Suggest modifications to be made to convert the periscope to binoculars [4]
object convert
Right angle prisms
image
observer
image observer
First prism:
Total internal reflection occurs twice (2 kali) [1]
periscope Second prism: total internal reflection occurs twice [1]
Binocular
5.4 Telescope & binoculars, light phenomenon 1
3. [SPM 1998 P2 (A) Q2]
Symbol Observation
P Fish in an aquarium seems closer from its real position
Q When right hand is brought up in front of a mirror, image shows left hand being brought up
R Shot aim at a fish from the bank of river into clear river does not hit its target
S On a hot day, a pool of water is seen on a dry road
T The wall of the intestine can be seen by doctor through endoscope made by fiber optic
U Moon’s image can be seen at the surface of water at night
Table 1 shows an objective found in a research about the phenomenon of light
(a) State three light wave phenomenal involved in observation P, Q,R, S, T and U.
(b) Categorize the given observations into a few group according to light wave phenomenal
by using the given symbol.
(c) (i) Explain why observation R happened.
(ii) State one suitable way to shoot a fish so that the shot hit the target.
4. Draw the ray diagram to show that the water in a deep pool appears less deep that
it really is.
[3 marks]
5.4 Telescope & binoculars, light phenomenon 2
Suggested answer [1998 P2 (A) Q2]
(a) Refraction, reflection and total internal reflection.
(b) Refraction = P, and R
Reflection = Q and U
Total internal reflection = S and T
(c) (i) Light ray from fish that travels towards water-air boundary is refracted away from normal.
Shooter view light ray as a straight line.
Apparent position of the fish is higher than the real position of the fish.
Shot fired only moves towards the fish’s image.
(ii) Apparent position of the fish is higher than the real position of the fish,
So that the shooter will have to shoot lower than the apparent position of the fish.
Summary : The construction rays of Astronomical Telescope
1. The objective lens (convex) of a telescope 2. The eyepiece lens (convex) acts a magnifying glass for
produces a real image of the distant object looking at this small real image.
It is usual to have the real image exactly at the focus of
the eyepiece lens. This is called normal adjustment.
Objective lens Eye piece lens
5.4 Telescope & binoculars, light phenomenon 3
Real image
Parallel rays
from top of
distant object I
To the top of
virtual image
(at infinity)
first image, I1 formed by the objective lens is final image, I2 is virtual, inverted and (magnified)
real, inverted and diminished much larger than the object.
The first image, I1 becomes the object for the
eyepiece
Parallel rays f0 fe
from top of
distant object
fe, fo
Objective lens
Top of image
appears
to be here Eye piece
(kanta mata)
comparison between fo and fe [for focal length]
f0 > fe focal length of objective lens > focal length of the eye piece
comparison between mo and me [focal linear magnification]
Linear magnification linear magnification of
m0 < me of objective lens < of the eye piece
Power of lens,
Astronomical telescope 1
= focal length
Formula,
1
P= f
5.4 Telescope & binoculars, light phenomenon 4
M0 < Me
f0 > fe
Figure 20
1. An astronomical telescope is an optical instrument that is used
to view objects at a great distance, such as planets and stars.
2. An astronomical telescope consists of two convex lenses.
(a) The power of objective lens is low because the objective lens has a long focal length, f0.
(b) The power eyepiece lens is high because the eyepiece lens has a short focal length, fe.
focal ength focal ength
f0 > fe
3. The distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece is (f0 + fe ),
it is the principal focus of the objective lens, F0 is coincident with the principal focus of the eyepiece, Fe.
Both lens have the same focal plane/[or at principal axis]
4. Parallel rays of light from the distant object converge at the focal plane of the objective lens to form the
first image, I1, which is real, inverted and diminished.
( objectivel ns) (ey piec )
5. The first image, I1 becomes the object for the eyepiece.
6. The first image, I1 is at the focal plane of the eyepiece.
The final image, I2 is virtual, inverted and magnified.
7. The final image I2 is formed at infinity (object at very far distance).
8. The magnification of the telescope in a normal adjustment (pelarasan normal), it is with image formed at infinity,
is given by:
M= f0
or M=
Focal length of objective lens, f 0 fe
Focal length of eyepiece, f e
Exams Tip
Method of drawing a ray diagram for an astronomical telescope.
5.4 Telescope & binoculars, light phenomenon 5
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesDocument14 paginiTopic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesNorhisham Mohamed SobriÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksDe la EverandI Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Part 34 StudentsDocument24 paginiLight Part 34 StudentsSharvinder SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics116 L20 InstrumentsDocument17 paginiPhysics116 L20 InstrumentsSånśkār Sıñģh RåńåÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 paginiLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Phyiscs LensesDocument10 paginiIGCSE Phyiscs LensesneelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Uses of Lenses in Optical DevicesDocument6 paginiThe Uses of Lenses in Optical DevicesAin NadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Science Lab Manual X Expt 47Document5 paginiNCERT Science Lab Manual X Expt 47Samarth AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 30 Optical Instrument - EQSDocument3 paginiChapter 30 Optical Instrument - EQSAnson LchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightDocument9 paginiChapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightHHK88893% (15)
- Determination of The Focal-Length.Document11 paginiDetermination of The Focal-Length.mohammed1998Încă nu există evaluări
- Simple MicroscopeDocument10 paginiSimple MicroscopeHabimana HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTL TNVLDocument8 paginiBTL TNVLNguyên Nguyễn XuânÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound MicroscopeDocument7 paginiCompound Microscopeaman100% (1)
- Igcse Phy 07Document2 paginiIgcse Phy 07Kamrul Hasan SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aberrations of TelescopeDocument14 paginiAberrations of Telescopelighttec21Încă nu există evaluări
- Module Science Week 7 10Document2 paginiModule Science Week 7 10Joe CrisologoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics of Convex LensesDocument29 paginiPhysics of Convex LensesEdu 4 UÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity #11: Lens Lab Part 1. Image FormationDocument4 paginiActivity #11: Lens Lab Part 1. Image FormationJuan Carlos Mejia MaciasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics PART3Document39 paginiPhysics PART3Thene Truthe NoweÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Thin Lenses 2Document7 pagini05 Thin Lenses 2HelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 paginiLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple MicroscopeDocument9 paginiSimple MicroscopeAlyan Ashraf100% (2)
- 0490f1d4-6cb3-4dfa-b85d-9087d2d549c5Document10 pagini0490f1d4-6cb3-4dfa-b85d-9087d2d549c5Rafiya95z MynirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Instruments Part 2 - Compund MicroscopeDocument14 paginiOptical Instruments Part 2 - Compund MicroscopeSolomon Peter SunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light PDFDocument1 paginăLight PDFsatish dongardiyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optics Lab: Forming Images with Lenses and MirrorsDocument10 paginiOptics Lab: Forming Images with Lenses and MirrorsGabriel Eyapan100% (1)
- Activity 13Document11 paginiActivity 13shreyamohanty298Încă nu există evaluări
- To Study Nature and Size of ImageDocument11 paginiTo Study Nature and Size of ImageUnknown???Încă nu există evaluări
- Refraction LensesDocument42 paginiRefraction LenseswhybangadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module P7 L4Document13 paginiModule P7 L4geth jonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes: Questions To Think AboutDocument10 paginiSection 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes: Questions To Think Aboutsamyak jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument18 paginiReflection and Refraction Notessundeepika2008Încă nu există evaluări
- Vansh Srivastava Physics Class 12 ProjectDocument36 paginiVansh Srivastava Physics Class 12 ProjectOm Tiwari PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session5&6 - HK NEWTONDocument48 paginiSession5&6 - HK NEWTONDenny Febian SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirror Physics: Dinda Ayu Rahmi Firda Thalika Madina Rizqia Pravitasari Anjani Puspita Lysti VaniaDocument27 paginiMirror Physics: Dinda Ayu Rahmi Firda Thalika Madina Rizqia Pravitasari Anjani Puspita Lysti VaniaDinda YumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFDocument7 pagini6.3 Images Formation by Lens Answer PDFAin NadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensDocument9 paginiPhysics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensNamdeo JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Document22 paginiCH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Mohammad MujtabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Light Microscopy: Understanding the Key Components and CapabilitiesDocument52 paginiIntroduction to Light Microscopy: Understanding the Key Components and CapabilitiesJan Marlon GoritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 9 (L.O 3,6 Part 3)Document33 paginiLecture 9 (L.O 3,6 Part 3)ab4943409Încă nu există evaluări
- 15 AQA Physics Final PDFDocument67 pagini15 AQA Physics Final PDFKafka LukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of LightDocument10 paginiProperties of LightKesanam SpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Physics PDF ShubhamDocument13 paginiFinal Physics PDF ShubhamShubham Swami100% (1)
- (L2) Ray Optics - Optical Instruments 28th SepDocument55 pagini(L2) Ray Optics - Optical Instruments 28th SepRahul Kumar SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Chapter On Optical and Surveying InstrumentsDocument23 paginiSample Chapter On Optical and Surveying Instrumentshaider100% (4)
- LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 paginiLIGHT Physics Form 4Amrita KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Practical Experiment Class 12 (2022 Term 2)Document24 paginiPhysics Practical Experiment Class 12 (2022 Term 2)Arghyadeep DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnalysisDocument3 paginiAnalysisLAXMI NUNIAÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPTICAL INSTRUMENT Main Note - RevisedDocument15 paginiOPTICAL INSTRUMENT Main Note - RevisedOlasupo MowaninuolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedDocument52 paginiChapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedST4Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document3 paginiModule 2Princess ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument11 paginiCBSE Test Paper-01 Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refractionshubham sehgalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 2010Document12 paginiChapter 5 2010Agnes YaoYaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 3Document2 paginiActivity 3Kabir AgnihotriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format of Exp - Grade XIIDocument5 paginiFormat of Exp - Grade XIISheetal TrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Find Focal Length of Convex Mirror LabDocument6 paginiFind Focal Length of Convex Mirror LabAkshat GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Find Focal Length of Convex Mirror LabDocument19 paginiFind Focal Length of Convex Mirror LabRishiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.Document8 paginiRefraction 10TH Class Physics Important Questions SSC Abyasa Deepika.prakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSP Physics F4 2019Document40 paginiHSP Physics F4 2019sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulit 3 4531/2 Essay Question Chapter 5.4 Application of LensesDocument3 paginiSulit 3 4531/2 Essay Question Chapter 5.4 Application of Lensessylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- One Day Trip To TAIPEI CITYDocument3 paginiOne Day Trip To TAIPEI CITYsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Cell Organisation SDocument10 pagini2.2 Cell Organisation Ssylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 巨人和裁缝Document1 pagină巨人和裁缝sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016Document19 pagini2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malleable - Able To Hammered or Pressed Into Shape Without Breaking at Cracking Ductile - Able To Be Drawn Out Into A Thin WireDocument1 paginăMalleable - Able To Hammered or Pressed Into Shape Without Breaking at Cracking Ductile - Able To Be Drawn Out Into A Thin Wiresylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- C9 Space WeatherDocument7 paginiC9 Space Weathersylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodDocument4 paginiName: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested Foodsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systematic Error Random Error: AccuracyDocument1 paginăSystematic Error Random Error: Accuracysylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Cell 2016 HOTS StructureDocument6 paginiChapter 2 Cell 2016 HOTS Structuresylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHC AluminiumDocument2 paginiSHC Aluminiumsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 2.1 ExerciseDocument2 paginiChap 2.1 Exercisesylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Cell Organisation TranspDocument12 pagini2.2 Cell Organisation Transpsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- FORM 4: CHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganizationDocument4 paginiFORM 4: CHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organizationsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organisation NotesDocument15 paginiCell Organisation Notessylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organisation in PlantsDocument11 paginiCell Organisation in Plantssylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells AbudantlyDocument11 paginiCells Abudantlysylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Class: - Chap 2.2 Cell OrganizationDocument10 paginiName: - Class: - Chap 2.2 Cell Organizationsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016Document19 pagini2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variation 2017Document15 paginiVariation 2017sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structured Questions (Cell Organisation)Document3 paginiStructured Questions (Cell Organisation)sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatta Lakkhana SuttaDocument8 paginiAnatta Lakkhana Suttasylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genes Chromosomes 2017Document15 paginiGenes Chromosomes 2017sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- TwinDocument7 paginiTwinsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chanting ThaiDocument13 paginiChanting Thaisylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pressure MRSM 2008 P3BDocument6 paginiWater Pressure MRSM 2008 P3Bsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- PBHP Handbook of Buddhist Chanting ServiceDocument104 paginiPBHP Handbook of Buddhist Chanting ServiceBro. Oh Teik BinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Majjhima Nikaya 133-134Document5 paginiMajjhima Nikaya 133-134sylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organization and Management SyllabusDocument8 paginiOrganization and Management SyllabusArianne100% (6)
- Research Method Syllabus-F14Document6 paginiResearch Method Syllabus-F14kanssaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABC Game Plan: Guaranteed SuccessDocument1 paginăABC Game Plan: Guaranteed SuccessΚωνσταντίνος ΛοϊζίδηςÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Approach to Optimizing Reservoir ManagementDocument7 paginiAn Approach to Optimizing Reservoir ManagementRicci FGÎncă nu există evaluări
- III ReviewerDocument15 paginiIII ReviewerChristian CalauadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Legacy ExerciseDocument2 paginiThe Legacy Exerciseariskendell15Încă nu există evaluări
- Argumentative-Essay CounterargumentDocument2 paginiArgumentative-Essay CounterargumentVũ ĐỗÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yaksha PrasnamDocument9 paginiYaksha PrasnamYSRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law of Explosive GrowthDocument2 paginiLaw of Explosive GrowthEmm GheorghiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter I The Self From Various PersDocument45 paginiChapter I The Self From Various PersMavyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yes! Ok! Colour Coded LyricsDocument72 paginiYes! Ok! Colour Coded LyricsAccount 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Self Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisDocument57 paginiSelf Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisHarby Ongbay Abellanosa100% (1)
- John Dewey and Experiential Learning, Developing The Theory of Youth WorkGroverDocument18 paginiJohn Dewey and Experiential Learning, Developing The Theory of Youth WorkGroverGroverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. ObjectivesDocument2 paginiLesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. Objectivesrosemarie fortaleza100% (3)
- Implementasi Pembelajaran Berbasis Hots Dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Analisis Mata Kuliah Pembelajaran Ips Di Sekolah DasarDocument9 paginiImplementasi Pembelajaran Berbasis Hots Dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Analisis Mata Kuliah Pembelajaran Ips Di Sekolah DasarMuhajir HajirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lakshana Appear To Have Been Derived From The Natya-Sastra. The IndianDocument8 paginiLakshana Appear To Have Been Derived From The Natya-Sastra. The IndianPrantik GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 - Ingrid Johanne Moen - Marriage and Divorce in The Herodian Family. A Case Study of Diversity in Late Second Temple JudaismDocument385 pagini2009 - Ingrid Johanne Moen - Marriage and Divorce in The Herodian Family. A Case Study of Diversity in Late Second Temple Judaismbuster301168Încă nu există evaluări
- KamagariDocument31 paginiKamagariNicholai DiNardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- In The Spirit of Total Resistance Miller PDFDocument7 paginiIn The Spirit of Total Resistance Miller PDFRichard DodsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Should You Believe in The Trinity ?Document8 paginiShould You Believe in The Trinity ?api-26605500100% (1)
- BC MC P1ansDocument17 paginiBC MC P1anssharon cha100% (1)
- Dutch: Introductory CourseDocument13 paginiDutch: Introductory CourseLeanderson SimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astha Koota Matching HoroscopesDocument4 paginiAstha Koota Matching HoroscopesastrosanthoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bite-Sized Training - Mentoring - HelenaDocument15 paginiBite-Sized Training - Mentoring - HelenageorjalynjoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Four Functions of ManagementDocument3 paginiThe Four Functions of ManagementMark Elben100% (1)
- Voltaire and The Problem of EvilDocument23 paginiVoltaire and The Problem of EvilSeyf Eddin100% (1)
- JFL Volume 3 Issue 11 Pages 79-90Document12 paginiJFL Volume 3 Issue 11 Pages 79-90imaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improve subject-verb agreement skillsDocument6 paginiImprove subject-verb agreement skillsOjje Fauzi Hukum67% (3)
- Presuppositional Apologetics Paper 2412Document4 paginiPresuppositional Apologetics Paper 2412Amy Green BradleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Change Approaches: Framework PrimerDocument20 pagini6 Change Approaches: Framework PrimerLuis Alberto Lamas LavinÎncă nu există evaluări