Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 2 Central Processing Unit and Execution of Programs MCQ 1: Register Which Is Used To Store Values of Arithmetic and L
Încărcat de
Saad0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
12 vizualizări3 paginifundamental of computer mcqs best
Titlu original
Fundamental of computer
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentfundamental of computer mcqs best
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
12 vizualizări3 paginiChapter 2 Central Processing Unit and Execution of Programs MCQ 1: Register Which Is Used To Store Values of Arithmetic and L
Încărcat de
Saadfundamental of computer mcqs best
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
Chapter 2 Central Processing Unit and Execution of
Programs MCQ 1: Register which is used to store values of arithmetic and l
ogical opera- tions is termed as A. Arithmetic register B. accumulator C.
logical register D. controller MCQ 2: Built-
in set of machine code instructions of computer are called A. instruction
set B. transfer of data C. logical operations D. logical
set MCQ 3: Specific purpose storage location is termed as A. register B.
executed register
C. timed register D. sequenced
register MCQ 4: Two main types of branch instructions are A. conditional
branch B. unconditional branch C. logical branch D. both a and
b MCQ 5: Most of the time, computer instructions are divided into A.
function code B. instruction code C. operand D. both A and
C MCQ 6: Counter that holds instruction fetched from store during decoding
and execution is called A. current instruction register B. program instruction
counter C. sequence instruction register D. programming
register MCQ 7: Ordered set of instructions that are carried out by a compute
r is called A. programs B. machine C. machine code D. programming
languages MCQ 8: Binary code which gives an actual instruction is called A.
instruction code B. logical code C. function code D.
address MCQ 9: In instruction format, address of any data location is said to
be A. function code B. instruction code C. operand
D. logical code MCQ 10: Sequence control register is also known as A.
program counter B. instruction counter C. sequence register D. controlling
register MCQ 11: Counter that holds addresses of next fetched instruction is
called A. sequence control register B. program counter C. temporary
register D. both A and
B MCQ 12: Instructions that are programmed to make decisions are termed a
s A. branch instructions B. programmed instructions C. logical
instructions D. arithmetic instructions
MCQ 13: Branch instruction 'JUMP TO SUBORDINATE' is an example of
A. unconditional branch B. arithmetic branch C. transferring branch D.
conditional branch MCQ 14: Built-
in set of codes in a computer are called as A. machine B. machine code C.
programming languages D.
programs MCQ 15: Control unit timed sequence that fetches instructions fro
m the com- puter main store is classified as A. the fetch execute cycle B. the
timed cycle C. the sequenced cycle D. the execution cycle
MCQ 16: Branch instruction 'JUMP IF ZERO' is an example of A.
transferring branch B. conditional branch C. unconditional branch D.
arithmetic branch MCQ 17: Branch instruction is also known as A. jump
instruction B. logical instruction C. arithmetic instruction D. programmed
instructions Answers
Key: 1. B 2. A 3. A 4. D 5. D 6. A 7. A 8. C 9. C 10. A 11. D 12. A 13. A 14. B 15. A 16. B 17
.A
Chapter 3 Communications Hardware - Terminals and
Interfaces MCQ 1: Processing which is carried out by the use of remote ter
minal proces- sors is called A. teleprocessing B. digital processing C. logical
processing D. manual
processing MCQ 2: Technique of using two buffers as interface between two
devices is called A. double digitalizing B. single buffering C. double
interfacing D. double
buffering MCQ 3: Network in which data is in the form of packets is called a
s A. packet switching
B. logical packets C. packaged switching D. none of the
above MCQ 4: Transmission in which all bits are sent at the same time for ea
ch char- acter is called A. parallel transmission B. wide transmission C. local
transmission D. serial
transmission MCQ 5: Speed of transmitted data is measured by A. baud B.
band C. hertz D.
seconds MCQ 6: Process of communicating data over relatively larger distan
ces is called
A. digital communication B. optical communication C. analog
communication D.
telecommunications MCQ 7: IO devices which enable user to communicate
with computer system are called A. terminals B. telecommunication C.
buses D. communication
devices MCQ 8: Terminal which has its own processor and without linking t
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Plc&Scada MergedDocument823 paginiPlc&Scada Mergedmarathi sidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 6075523113284535298Document67 pagini5 6075523113284535298Akash PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization Questions and Answers - Basic OrganizationDocument27 paginiComputer Organization Questions and Answers - Basic Organizationmeenakshi singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer: C: Department of Information Technology UNIT-III-CAO-MCQ B.Tech 4 SEMDocument4 paginiAnswer: C: Department of Information Technology UNIT-III-CAO-MCQ B.Tech 4 SEMVaishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer: C: Department of Information Technology UNIT-I-CAO-MCQ B.Tech 4 SEMDocument5 paginiAnswer: C: Department of Information Technology UNIT-I-CAO-MCQ B.Tech 4 SEMVaishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture McqsDocument10 paginiComputer Architecture McqsSatsshhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Systems Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 paginiComputer Systems Multiple Choice QuestionsAckena CaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- 501 Mcqs TextDocument31 pagini501 Mcqs TextAkram KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CA&ODocument12 paginiCA&OMohammad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Sample Problems 05Document6 paginiElectronics Sample Problems 05Genesis PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 paginiMultiple Choice QuestionsSravanthi Gelley0% (1)
- Codmcq 1Document17 paginiCodmcq 1Yash Gupta Maurya100% (1)
- Micro ReviewerDocument33 paginiMicro ReviewerPatrick GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Fundamentals MCQDocument8 paginiComputer Fundamentals MCQangelo_lopez1993Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture MCQs From Latest Books EditionDocument7 paginiComputer Architecture MCQs From Latest Books EditionMoiz Saif FAST NU LHRÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS501 SOLVED MCQs FINAL TERM BY JUNAIDDocument51 paginiCS501 SOLVED MCQs FINAL TERM BY JUNAIDMuhammad AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONSDocument9 paginiCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONSAshish AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture and OrganizationDocument5 paginiComputer Architecture and OrganizationPriyanka PardeshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz- Computer Architecture Components FunctionsDocument6 paginiQuiz- Computer Architecture Components FunctionsBảo Lê MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC0040 Computer Organization and Architecture Paper 2Document15 paginiBC0040 Computer Organization and Architecture Paper 2SeekEducationÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQs For SComputerDocument15 paginiMCQs For SComputerzawiyartariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examinations For 2005 - 2006 / Semester 1: Module: Computer Fundamentals Module Code: Duration: 2 HoursDocument8 paginiExaminations For 2005 - 2006 / Semester 1: Module: Computer Fundamentals Module Code: Duration: 2 HoursAmani UrassaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Diploma & Engineering Classes Register Transfer Language (RTL) GuideDocument22 paginiReal Diploma & Engineering Classes Register Transfer Language (RTL) Guidejayonline_4u0% (1)
- MCQs Chapter no7 Computer ArchitectureDocument9 paginiMCQs Chapter no7 Computer ArchitectureCh Adnan AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sna Bullet 8 McqsDocument12 paginiSna Bullet 8 McqsMursaleen UmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- CaoDocument13 paginiCaoragavendharÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS501 Advance Computer Architecture - MCQS From Quiz #3Document3 paginiCS501 Advance Computer Architecture - MCQS From Quiz #3Muhammad AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Which of The Following Is NOT A Hardware of A Computer?: A. Windows B. Monitor C. Central Processing Unit D. Key BoardDocument16 paginiWhich of The Following Is NOT A Hardware of A Computer?: A. Windows B. Monitor C. Central Processing Unit D. Key BoardLeo SaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- TwinCAT 2 Manual v3.0.1Document412 paginiTwinCAT 2 Manual v3.0.1Vladimir Friz100% (2)
- Computer Fundamentals MCQs For IBPS IT Officer Guide4XamDocument113 paginiComputer Fundamentals MCQs For IBPS IT Officer Guide4Xambhaskarsw86100% (2)
- computer-networks [set 1]Document21 paginicomputer-networks [set 1]ali abbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cs501 Quiz 2 by Vu Topper RMDocument49 paginiCs501 Quiz 2 by Vu Topper RMAli AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelim ComarchDocument7 paginiPrelim ComarchRodrigo CalapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture Exam QuestionsDocument7 paginiComputer Architecture Exam QuestionsRodrigo CalapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPUTER FUNDAMENTAL QUESTIONSDocument47 paginiCOMPUTER FUNDAMENTAL QUESTIONSLovelle Belaca-olÎncă nu există evaluări
- KRISHNENDU GUIN - Assignment 2Document20 paginiKRISHNENDU GUIN - Assignment 2Krishnendu GuinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz - 06 Von Neumann ArchitectureDocument8 paginiQuiz - 06 Von Neumann Architecturebehruzoralov.richÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uu Tien 1Document180 paginiUu Tien 1Tran Quang Khoa (K18 HCM)Încă nu există evaluări
- Esas ReviewDocument48 paginiEsas ReviewSPARK TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- D. Capture Tshark Log by Multiple Split File With 150M File SizeDocument6 paginiD. Capture Tshark Log by Multiple Split File With 150M File SizeAriakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Question Bank: Objective QuestionsDocument8 paginiComputer Question Bank: Objective QuestionsrashmiameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontroller MCQ Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Microcontrollers with 20 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 paginiMicrocontroller MCQ Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Microcontrollers with 20 Multiple Choice QuestionsDeepika SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer FundamentalDocument28 paginiComputer FundamentalParashar Das100% (1)
- Computer ArchitecureDocument150 paginiComputer ArchitecurediÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETI All MCQDocument601 paginiETI All MCQParth ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNADocument12 paginiCCNAkwame AyewÎncă nu există evaluări
- NETWORK 621 CA TEST 1 MCQsDocument60 paginiNETWORK 621 CA TEST 1 MCQsKeshia MullerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Analysis: Computer Architecture FundamentalsDocument10 paginiAssignment Analysis: Computer Architecture FundamentalsRoohul BayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture Assignment AnalysisDocument15 paginiComputer Architecture Assignment AnalysisRoohul BayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemDe la EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded C Programming: Techniques and Applications of C and PIC MCUSDe la EverandEmbedded C Programming: Techniques and Applications of C and PIC MCUSEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (3)
- PIC Projects and Applications using C: A Project-based ApproachDe la EverandPIC Projects and Applications using C: A Project-based ApproachEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Networked Control System: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDe la EverandNetworked Control System: Fundamentals and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Course for Advanced Computer StudiesDe la EverandFoundation Course for Advanced Computer StudiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ms Word Mcqs Top FiveDocument1 paginăMs Word Mcqs Top FiveSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 To 115 To Best Word McqsDocument5 pagini101 To 115 To Best Word McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 171 To 180 Word Mcqs Best McqsDocument2 pagini171 To 180 Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 151 To 160 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsDocument2 pagini151 To 160 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Other Mcqs BetDocument3 paginiSecurity Other Mcqs BetSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Find Format Painter Tool on Formatting ToolbarDocument3 paginiFind Format Painter Tool on Formatting ToolbarSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security McqsDocument4 paginiSecurity McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Other Mcqs BetDocument3 paginiSecurity Other Mcqs BetSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 161 To 170 Word Mcqs BestDocument2 pagini161 To 170 Word Mcqs BestSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 121 To 135 Top Word Mcqs BestDocument3 pagini121 To 135 Top Word Mcqs BestSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 100 Word McqsDocument19 paginiTop 100 Word McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 To 120 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsDocument4 pagini101 To 120 Ms Word Mcqs Best McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 20 Data Structure McqsDocument8 paginiTop 20 Data Structure McqsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Resignation From FFTTC Service: TH THDocument1 paginăSubject: Resignation From FFTTC Service: TH THSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Units of ComputerDocument2 paginiDifferent Units of ComputerSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text and Memo Data TypesDocument3 paginiText and Memo Data TypesSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Law & Justice Minister of Pakistan Is Mr. Zahid Hmaid As at May 10, 2016Document2 paginiThe Law & Justice Minister of Pakistan Is Mr. Zahid Hmaid As at May 10, 2016SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
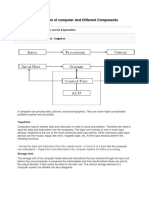
- Q.No.1 Block Diagram of Computer and Different ComponentsDocument1 paginăQ.No.1 Block Diagram of Computer and Different ComponentsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSI Model Layer FunctionsDocument2 paginiOSI Model Layer FunctionsSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBPS SO OS Study NotesDocument23 paginiIBPS SO OS Study NotesSaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iai Msel-Pc PG CatalogDocument11 paginiIai Msel-Pc PG CatalogElectromateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newsfeed - Nextdoor 2Document1 paginăNewsfeed - Nextdoor 2Mary MacLellanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outreach NetworksDocument15 paginiOutreach NetworksKaustav BhattacharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buyers Guide For MDUDocument18 paginiBuyers Guide For MDUjatinrastogi28Încă nu există evaluări
- Hello Service Using Corba Hello - IdlDocument13 paginiHello Service Using Corba Hello - IdlSobhan DasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atm&Ip Dual Stack (Ran16.0 - 01)Document54 paginiAtm&Ip Dual Stack (Ran16.0 - 01)hekriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usermanual Omnik Wifi Kit en 20130626 v2.4Document27 paginiUsermanual Omnik Wifi Kit en 20130626 v2.4nelson_grandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- QIG+NV412A+Video+Encoder 1013 PDFDocument12 paginiQIG+NV412A+Video+Encoder 1013 PDFSdiri OùMaimàÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umesh Kumar Gupta: Educational QualificationsDocument2 paginiUmesh Kumar Gupta: Educational Qualificationsvikram_908116002Încă nu există evaluări
- WCDMA, LTE, Wireless LAN and Satellite, MobileDocument82 paginiWCDMA, LTE, Wireless LAN and Satellite, MobileterdpongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apigee Edge API Services Brief 0Document5 paginiApigee Edge API Services Brief 0Corina SerbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 209Document1 pagină12 209Adeel Mirza100% (1)
- Replacement Guidelines: Controllogix 5560/5570 To Controllogix 5580Document74 paginiReplacement Guidelines: Controllogix 5560/5570 To Controllogix 5580NixiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bca Semester-Vi 2019-20 PDFDocument6 paginiBca Semester-Vi 2019-20 PDFAnmolÎncă nu există evaluări
- CXZOSAdminGuide en PDFDocument354 paginiCXZOSAdminGuide en PDFCassio CristianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC 800M 6.0 Communication Protocols PDFDocument258 paginiAC 800M 6.0 Communication Protocols PDFToni BaenkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debian-Ubuntu Hardening GuideDocument87 paginiDebian-Ubuntu Hardening GuideadhieimoetzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies v1.0 (CLCOR)Document56 paginiImplementing Cisco Collaboration Core Technologies v1.0 (CLCOR)SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- DeployingF5LoadBalancerswithCiscoISE Techalk Security Dec04 2014Document208 paginiDeployingF5LoadBalancerswithCiscoISE Techalk Security Dec04 2014Phyo Min TunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Engineer Resume SummaryDocument4 paginiNetwork Engineer Resume SummaryYogesh ArasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orabbix Install v0.6Document11 paginiOrabbix Install v0.6aguiberto539Încă nu există evaluări
- Certificate Renewal Global Task Guide: Information ClassificationDocument11 paginiCertificate Renewal Global Task Guide: Information ClassificationVenkata SureshÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2000 Northbound MML Command Interface Developer GuideDocument39 paginiM2000 Northbound MML Command Interface Developer GuideWidagdho WidyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Gprs & Edge: E W E SDocument56 paginiIntroduction To Gprs & Edge: E W E SAmine InpticÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAMILDocument58 paginiTAMILTamil VananÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3U en M F005 ANSI Web PDFDocument364 paginiP3U en M F005 ANSI Web PDFRoberto Su100% (1)
- Belden Fieldbus CablesDocument4 paginiBelden Fieldbus CablesprogradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 600-35ns01-a_honeywell 35 series nvr network security guide-0728Document25 pagini600-35ns01-a_honeywell 35 series nvr network security guide-0728conrradoegmÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNMP Cli Show Cli AlcatelDocument20 paginiSNMP Cli Show Cli Alcatelfalberto08Încă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Quarter Exam in Media and Information LiteracyDocument2 pagini3rd Quarter Exam in Media and Information LiteracyWilson Dela Cruz100% (4)






























![computer-networks [set 1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/721359975/149x198/d7eeef8fbb/1712635462?v=1)