Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DLP Boyles Law
Încărcat de
Jennifer MagangoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DLP Boyles Law
Încărcat de
Jennifer MagangoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Puerto Galera NHS-
School Grade Level 10
Dulangan Extension
DAILY
LESSON Teacher Mr. Herbert J. Magango Learning Area Science
PLAN Teaching Date January 16, 2019
Quarter Third
and Time 10:40-11:40 AM
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standard The learners demonstrate an understanding of…
how gases behave based on the motion and relative distances between
gas particles
B. Performance Standards The learners shall be able to demonstrate understanding of the gas laws.
C. Learning Competencies & The learners should be able to investigate the relationship between:
Code 1. volume and pressure at constant temperature of a gas;
II. CONTENT Properties of Gas – Boyle’s Law
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teaching Guide pp. 257-280
2. Leaners’ Material/
pp. 351-399
Textbook
3. Additional Materials from
LR portal
B. Other Learning Resources
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson or ELICIT:
presenting the new lesson 1. What are the properties or characteristics of gas?
B. Establishing a purpose for the ENGAGE:
lesson What happens to the lungs of a free diver during a deep dive, Boyle´s law
C. Presenting examples/ instances of in action?
the new lesson Show a video of an experiment with a liquid meter, open and turned upside
down. it plunged to -55 m with 1 liter of air inside. the water pressure push
up the air, compresing it to 154 ml at 55 m depth. the air expands while
climb back up to 1 liter.
D. Discussing new concepts and EXPLORE:
practicing new skills #1 Present a PowerPoint about Boyle’s Law
E. Discussing new concepts and Demonstrate solving problems on gas using the equation of Boyle’s Law.
practicing new skills #2
F. Developing mastery (leads to EXPLAIN:
Formative Assessment) Watch a video to clearly understand Boyle’s Law
G. Finding practical applications of ELABORATE:
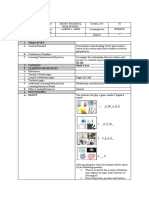
concepts and skills in daily living 1. For a cylinder containing helium gas indicate if cylinder A or cylinder B
represents the new volume for the following changes (n and T are
constant).
1) pressure decreases
2) pressure increases
2. A sample of helium gas in a balloon has a volume of 6.4 L at a pressure
of 0.70 atm. At 1.40 atm (T constant), is the new volume represented
by A, B, or C?
H. Making generalizations and SUMMARY of THE LESSON:
abstractions about the lesson Boyle’s Law relates the volume of the gas with its pressure at constant
temperature and amount of a gas.
He explained that as the pressure increases, it forces the gas particles
to move closer to each other. This causes a decrease in the spaces in
between and among them resulting to a decrease in the total volume of
the gas. Conversely, when the pressure is decreased, lesser force
controls the movements of the gas particles. This phenomenon can
make them move as far as possible from one another because they
have very weak intermolecular force of attraction. This will lead to an
increase in the total volume of the gas.
I. Evaluating learning EVALUATE: Use Boyle’s Law to solve the following problems.
1. A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 12.0 L at 600. mm Hg. What is the
new pressure when the volume changes to 36.0 L? (T and n constant).
a. 200. mm Hg
b. 400. mm Hg
c. 1200 mm Hg
2. If the sample of helium gas has a volume of 6.4 L at a pressure of 0.70 atm,
what is the new volume when the pressure is increased to 1.40 atm (T constant)?
a. 3.2 L
b. 6.4 L
c. 12.8 L
J. Additional activities for application EXTEND:
or remediation SOLVE:
If a sample of helium gas has a volume of 120 mL and a pressure of 850 mm
Hg, what is the new volume if the pressure is changed to 425 mm Hg ?
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
Prepared by:
HERBERT J. MAGANGO Checked by:
Subject Teacher
LOIDA P. VILLAS
Principal IV
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Boyle-s-Law-Lesson-Plan in ChemistryDocument3 paginiBoyle-s-Law-Lesson-Plan in ChemistryHavana Jabay SherrylynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Mr. Herbert J. Magango Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDocument2 paginiDaily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Mr. Herbert J. Magango Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyle's Law22 Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiBoyle's Law22 Lesson PlanMontesa Allana Ea82% (17)
- Boyles Law Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiBoyles Law Lesson PlanFany Fabia60% (5)
- Lesson Plan JUNIOR HIGHDocument3 paginiLesson Plan JUNIOR HIGHMyla BulalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COT Boyles LawDocument3 paginiCOT Boyles LawYvonne Regalado Parafina100% (1)
- Lesson-Boyles Law G10Document9 paginiLesson-Boyles Law G10Edie Lyn Catapang100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawDocument9 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawTeacher Derick Daet86% (7)
- Lesson Plan About Gay Lussacs Law 1Document10 paginiLesson Plan About Gay Lussacs Law 1Lyca Mae De Villa100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Log Boyle's LawDocument2 paginiDaily Lesson Log Boyle's LawANGELIQUE ANTONIO100% (6)
- Boyles LawDocument3 paginiBoyles Lawaiza larrozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Charles LawDocument6 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 Charles LawVaronessa MintalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Law. NewDocument5 paginiCharles Law. NewMarvin Agustin100% (1)
- Co1 Boyles LawDocument7 paginiCo1 Boyles LawTrisha Melrose Milanes100% (2)
- Charles Law Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiCharles Law Lesson PlanSigrid Amante100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: Charles' LawDocument6 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10: Charles' LawHaji Darell Bagtang95% (43)
- DLP - Properties of GasDocument2 paginiDLP - Properties of GasJennifer Magango100% (1)
- Charles Law Laboratory Activity DLLDocument5 paginiCharles Law Laboratory Activity DLLHeidie BalabboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles LawDocument5 paginiCharles Law기요나100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Document5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Richard Tañada Rosales74% (19)
- DLL Science 10 Gas Laws - Part 1Document4 paginiDLL Science 10 Gas Laws - Part 1kaycin Duzon100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Boyle's LawDocument4 paginiLesson Plan Boyle's LawQueencess Ara TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 GASSESDocument7 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 GASSESJenifer MacaraegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Laws Part 3 Charles LawDocument4 paginiGas Laws Part 3 Charles LawBuzz manzhjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyles Law Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiBoyles Law Lesson Planbernadeth barajasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyle's Law 7 E's Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiBoyle's Law 7 E's Lesson PlanGelCess Paroan75% (12)
- Boyles Law DLP DepedDocument8 paginiBoyles Law DLP DepedMarielle Trompeta II100% (4)
- Lesson Plan Exemplar APPLIED Chem. Cot#4: Topic/Title Time Allotment Learning Competencies/ObjectiveDocument4 paginiLesson Plan Exemplar APPLIED Chem. Cot#4: Topic/Title Time Allotment Learning Competencies/ObjectiveRosita Cayanan100% (3)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Document5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Yeng Santos100% (11)
- 7e For Observation Avogadros LawDocument6 pagini7e For Observation Avogadros LawRon Adrian Sarte SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Science 10Document4 paginiLesson Plan Science 10Glorylyn LacreÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ups and Downs of Population GrowthDocument2 paginiThe Ups and Downs of Population GrowthLaarni Faye SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Gas Law 7 E'sDocument5 paginiCombined Gas Law 7 E'sGelCess Paroan100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan On Charles LawDocument3 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan On Charles LawPrince Heuward100% (3)
- Grade 10 DLP in Properties of GasDocument9 paginiGrade 10 DLP in Properties of GasGel CabansagÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesDocument3 paginiThe Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesLørd Ken M. DilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Combined Gas LawDocument44 paginiFor Combined Gas LawApril Bartolome Flores100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 7e Combined Gas LawDocument7 paginiLesson Plan 7e Combined Gas LawYhen Fajarito Largueza100% (5)
- I. Objectives: Write The LC Code For EachDocument3 paginiI. Objectives: Write The LC Code For EachMICHAEL-JEFF GAGABEÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Lesson2 DLPDocument13 paginiG10 Lesson2 DLPAngeles, Mark Allen CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles' Law..Document7 paginiCharles' Law..Aira Villarin100% (2)
- LP 1 - Behavior of GasesDocument11 paginiLP 1 - Behavior of GasesArjean Ledesma100% (2)
- Effects of EM WavesDocument2 paginiEffects of EM WavesRosalyn Angcay Quintinita100% (2)
- GasDocument2 paginiGasLorraine Donio100% (1)
- Sample-Lesson PlanDocument7 paginiSample-Lesson PlanUy Yui100% (5)
- Protein Synthesis - DLPDocument4 paginiProtein Synthesis - DLPPristine Aila RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10, Quarter 4 PDFDocument45 paginiGrade 10, Quarter 4 PDFJe Lly Ann100% (20)
- Department of Education: Pply The Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionsDocument12 paginiDepartment of Education: Pply The Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionsCristina NobleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gay-Lussacs LawDocument6 paginiGay-Lussacs LawGarren Jude AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanDocument6 paginiCSE Grade 10 Science Lesson PlanJelly Marie Baya FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4TH Grading Science 10Document36 pagini4TH Grading Science 10Mary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-Cuadra50% (2)
- DLL November 23, 2017 - Endocrine DisordersDocument4 paginiDLL November 23, 2017 - Endocrine DisordersHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag100% (2)
- Lesson Plan - TocaDocument6 paginiLesson Plan - TocaAaron Asne100% (1)
- Combined Gas LawDocument7 paginiCombined Gas LawJoycel ComiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyle's Law Lesson PlanDocument14 paginiBoyle's Law Lesson PlanPristine Aila RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limiting Factors On Population DensityDocument2 paginiLimiting Factors On Population DensityLaarni Faye Sarmiento100% (1)
- Comprehensive Sexuality Education: Lesson Plan in Science 10 Quarter 3Document13 paginiComprehensive Sexuality Education: Lesson Plan in Science 10 Quarter 3contessa padonÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Chemistry 1 Week 5 6Document10 paginiGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 5 6Emmanuel ValenzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDLP Day Boyles LawDocument8 paginiSDLP Day Boyles LawAdan CaacbayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science: Quarter 4 - Week 1-2-Module 1 Behavior of GasesDocument28 paginiScience: Quarter 4 - Week 1-2-Module 1 Behavior of GasesPaul Bernard L. Aboguin100% (4)
- Stored Energy in CapacitorsDocument25 paginiStored Energy in CapacitorsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacific Intercontinental College (PIC)Document2 paginiPacific Intercontinental College (PIC)Patrick MorgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Problems 2Document3 paginiPerformance Problems 2Jennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Teacher'S Weekly PlanDocument1 paginăDepartment of Education: Teacher'S Weekly PlanJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPACITORS in PARALLELDocument18 paginiCAPACITORS in PARALLELJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learners Individual Class Home ProgramDocument1 paginăLearners Individual Class Home ProgramJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPSTDocument66 paginiPPSTJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Test - Electric Potential PDFDocument1 paginăChapter Test - Electric Potential PDFJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors With DielectricsDocument22 paginiCapacitors With DielectricsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Long TestDocument1 paginăChapter 2 - Long TestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Central Limit Theorem V2Document5 paginiDLP - Central Limit Theorem V2Jennifer Magango75% (4)
- Rubric NG Science ProjectDocument2 paginiRubric NG Science ProjectJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Test - Electric Potential PDFDocument1 paginăChapter Test - Electric Potential PDFJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Long TestDocument3 paginiChapter 3 - Long TestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument1 paginăSimple and Compound InterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument37 paginiElectric Forces and Electric FieldsJennifer Magango100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 - AREAS Under The Normal DistributionDocument37 paginiCHAPTER 2 - AREAS Under The Normal DistributionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound Interest More Than ONCEDocument24 paginiCompound Interest More Than ONCEJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coulomb's LawDocument24 paginiCoulomb's LawJennifer Magango50% (2)
- Electric Charges: Third QuarterDocument25 paginiElectric Charges: Third QuarterJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Business Mathematics: Simple NterestDocument12 paginiBasic Business Mathematics: Simple NterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template MAPEHDocument4 paginiTemplate MAPEHJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puerto Galera National High School Dulangan ExtensionDocument2 paginiPuerto Galera National High School Dulangan ExtensionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogDocument2 paginiPuerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP Compound InterestDocument3 paginiDLP Compound InterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Origin of The Solar SystemDocument1 paginăDLP - Origin of The Solar SystemJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionDocument3 paginiScience 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDocument2 paginiDaily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJennifer Magango100% (1)
- DLP PlanetsDocument2 paginiDLP PlanetsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Interior of The EarthDocument1 paginăDLP - Interior of The EarthJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alphabetic KnowledgeDocument8 paginiAlphabetic KnowledgejsdgjdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lightning Protection Measures NewDocument9 paginiLightning Protection Measures NewjithishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadDocument2 paginiEthical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadAvory0% (2)
- Neet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Document27 paginiNeet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Deev SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanDocument4 paginiSurvivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanGinnie Faustino-GalganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Akilas Mebrahtom ResumeDocument1 paginăAkilas Mebrahtom ResumeAnonymous lLpBfQÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Test Level 7 New Format 2019Document3 paginiFinal Test Level 7 New Format 2019fabian serranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)Document5 paginiAcetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)ddandan_2Încă nu există evaluări
- John Wren-Lewis - NDEDocument7 paginiJohn Wren-Lewis - NDEpointandspaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quanta To QuarksDocument32 paginiQuanta To QuarksDaniel Bu100% (5)
- A Case On Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi IndiaDocument39 paginiA Case On Marketing Strategy of Xiaomi IndiaSoumyajeet Rout0% (1)
- Hw10 SolutionsDocument4 paginiHw10 Solutionsbernandaz123Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2.3.3 History of Visual Arts Modernism Post ModernismDocument17 paginiChapter 2.3.3 History of Visual Arts Modernism Post ModernismKim Ashley SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychoanalytic Theory byDocument43 paginiPsychoanalytic Theory byjoy millano100% (1)
- Persuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person ParadigmDocument4 paginiPersuasive Speech 2016 - Whole Person Paradigmapi-311375616Încă nu există evaluări
- Xtype Power Train DTC SummariesDocument53 paginiXtype Power Train DTC Summariescardude45750Încă nu există evaluări
- EQ JOURNAL 2 - AsioDocument3 paginiEQ JOURNAL 2 - AsioemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMDocument8 paginiMasoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMNithyAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 35 Electrical Safety SamanDocument32 pagini35 Electrical Safety SamanSaman Sri Ananda RajapaksaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary FceDocument17 paginiVocabulary Fceivaan94Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic RegionDocument30 paginiNewsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic Regionapi-206643591100% (1)
- DCN Dte-Dce and ModemsDocument5 paginiDCN Dte-Dce and ModemsSathish BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drager Narkomed 6400 Field Service Procedure Software Version 4.02 EnhancementDocument24 paginiDrager Narkomed 6400 Field Service Procedure Software Version 4.02 EnhancementAmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Programming in Swift by Eidhof Chris, Kugler Florian, Swierstra Wouter.Document212 paginiFunctional Programming in Swift by Eidhof Chris, Kugler Florian, Swierstra Wouter.angloesamÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 7 (PE)Document2 paginiA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in MAPEH 7 (PE)caloy bardzÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationDocument29 paginiMS Lync - Exchange - IntegrationCristhian HaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- SavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015Document119 paginiSavannahHarbor5R Restoration Plan 11 10 2015siamak dadashzadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omnitron CatalogDocument180 paginiOmnitron Catalogjamal AlawsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Comma Rules Conversion 15 SlidesDocument15 paginiThe Comma Rules Conversion 15 SlidesToh Choon HongÎncă nu există evaluări
- IQAc 04-05Document10 paginiIQAc 04-05ymcacollegewebsiteÎncă nu există evaluări