Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
When Do We Use The Simple Past?: 1. Actions Finished in The Past (Single or Repeated)
Încărcat de
Samuel Rivas0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
15 vizualizări4 paginiThe Simple Past tense, also called the Past Simple, is used to talk about finished actions or situations that occurred in the past. It is formed by adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Irregular verbs have varied past forms. The Simple Past can describe single events, repeated actions, or a series of completed past actions. It is also used with the Past Progressive to describe interrupted past actions. Common time words like "yesterday" are used with the Simple Past.
Descriere originală:
asdasdasdasd asdasdasd asdasdasd asdasdasdasdasd as dasdasdasd
Titlu original
Simple Past
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe Simple Past tense, also called the Past Simple, is used to talk about finished actions or situations that occurred in the past. It is formed by adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Irregular verbs have varied past forms. The Simple Past can describe single events, repeated actions, or a series of completed past actions. It is also used with the Past Progressive to describe interrupted past actions. Common time words like "yesterday" are used with the Simple Past.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
15 vizualizări4 paginiWhen Do We Use The Simple Past?: 1. Actions Finished in The Past (Single or Repeated)
Încărcat de
Samuel RivasThe Simple Past tense, also called the Past Simple, is used to talk about finished actions or situations that occurred in the past. It is formed by adding "-ed" to regular verbs. Irregular verbs have varied past forms. The Simple Past can describe single events, repeated actions, or a series of completed past actions. It is also used with the Past Progressive to describe interrupted past actions. Common time words like "yesterday" are used with the Simple Past.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
Colegio Isaac Newton Prof.
Samuel Alberto Rivas
When do we use the Simple Past?
The Simple Past is used to talk about actions or situations in the past. It is also called Past Simple.
1. actions finished in the past (single or repeated)
I visited Berlin last week.
Andrew watched TV yesterday.
My friends went to Paris a week ago.
My parents ate a lot of junk food when they were young.
2. series of completed actions in the past
First I got up, then I had breakfast.
On Sunday my brother and I went to a nice lake. There we met our friends. We swam in the warm water
and played volleyball in the afternoon. Too bad that we had to go home in the evening.
We didn't want to go to school on Monday.
3. together with the Past Progressive/Continuous – the Simple Past interrupted an action
which was in progress in the past.
They were playing cards when the telephone rang.
1st action → Past Progressive → were playing
2nd action → Simple Past → rang
While Dennis was reading outside, it started to rain.
1st action → Past Progressive → was reading
2nd action → Simple Past → started
4. Signal words
yesterday
last week
a month ago
in 2010
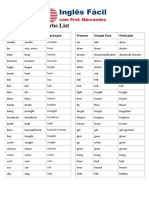
5. Form
regular verbs → infinitive + ed
irregular verbs → 2nd column of the table of the irregular verbs
6. Examples
6.1 Affirmative sentences in the Simple Past – regular verbs
Long forms Contracted forms
I cleaned my room.
You cleaned your room. not possible
He cleaned his room.
Colegio Isaac Newton Prof. Samuel Alberto Rivas
4.2. Affirmative sentences in the Simple Past – irregular verbs
Long forms Contracted forms
I went home.
You went home. not possible
He went home.
4.3. Negative sentences in the Simple Past
Do not negate a main verb in English. Always use the auxiliary did (Simple Past of to do) and
the infinitive of the verb for negations.
There is no difference between regular and irregular verbs in negative sentences.
Long forms Contracted forms
I did not clean the room. I didn't clean the room.
You did not clean the room. You didn't clean the room.
He did not clean the room. He didn't clean the room.
4.4. Questions in the Simple Past
You need the auxiliary did and the infinitive of the verb.
Long forms Contracted forms
Did I play football?
Did you play football? not possible
Did he play football?
How to pronounce -ed in the Simple Past
In the Simple Past we add -ed to regular verbs. Be careful pronuncing the verbs:
1. verbs ending in -ed preceded by a voiceless consonantt [p, k, f, ʃ, ʧ, s, θ] → speak [t].
The -e is silent.
Example: I stop – I stopped [stɒpt]
2. verbs ending in -ed preceded by a voiced consonant [b, g, v, ʒ, ʤ, z, ð, l, m, n] or a vowel → speak [d].
The -e is silent.
Example: I clean – I cleaned [kli:nd]
3. verbs ending in -ed preceded by [t] or [d] → speak [ɪd].
-e changes to [ɪ] (otherwise the ending could not be heard)
Example: I visit – I visited [vɪzɪtɪd]
Colegio Isaac Newton Prof. Samuel Alberto Rivas
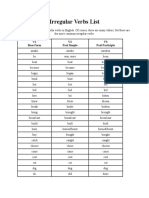
Irregular Verbs
be (is, am,are) was, were been
beat beat beaten
become became become
begin began begun
bend bent bent
bet bet bet
bite bit bitten
blow blew blown
break broke broken
bring brought brought
build built built
burn burned/burnt burned/burnt
buy bought bought
catch caught caught
choose chose chosen
come came come
cost cost cost
cut cut cut
dig dug dug
dive dove dived
do did done
draw drew drawn
dream dreamed/dreamt dreamed/dreamt
drive drove driven
drink drank drunk
eat ate eaten
fall fell fallen
feel felt felt
fight fought fought
find found found
fly flew flown
forget forgot forgotten
forgive forgave forgiven
freeze froze frozen
get got gotten
give gave given
go went gone
grow grew grown
hang hung hung
have had had
hear heard heard
hide hid hidden
hit hit hit
hold held held
hurt hurt hurt
Colegio Isaac Newton Prof. Samuel Alberto Rivas
keep kept kept
know knew known
lay laid laid
lead led led
leave left left
lend lent lent
let let let
lie lay lain
lose lost lost
make made made
mean meant meant
meet met met
pay paid paid
put put put
read read read
ride rode ridden
ring rang rung
rise rose risen
run ran run
say said said
see saw seen
sell sold sold
send sent sent
show showed shown
shut shut shut
sing sang sung
sit sat sat
sleep slept slept
speak spoke spoken
spend spent spent
stand stood stood
swim swam swum
take took taken
teach taught taught
tear tore torn
tell told told
think thought thought
throw threw thrown
understand understood understood
wake woke woken
wear wore worn
win won won
write wrote written
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Common Irregular Verbs in EnglishDocument4 paginiCommon Irregular Verbs in EnglishLoredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăIrregular VerbsGavriella LombardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Form Past Simple: Dreamed/dreamtDocument1 paginăBase Form Past Simple: Dreamed/dreamtEmanuel D. Bejarano LiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study / Studied / Studied: V1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleDocument5 paginiStudy / Studied / Studied: V1 Base Form of Verb V2 Past Simple V3 Past Participleelabozkurt054491Încă nu există evaluări
- Think Level Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăThink Level Irregular VerbsMaria JuneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think Level 3 Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăThink Level 3 Irregular VerbskaticatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think Level 3 Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăThink Level 3 Irregular VerbsЮлиана КриминскаяÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbs Regular e IrregularDocument4 paginiVerbs Regular e IrregularCristianMachucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs: V1 Base Form V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleDocument5 paginiIrregular Verbs: V1 Base Form V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleJamie Tan Ling SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs List: Present Simple Past Participle Present Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 paginiIrregular Verbs List: Present Simple Past Participle Present Simple Past ParticipleMônica BarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular VerbsDocument2 paginiIrregular VerbselizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Verbs in Past and Past Participle Form: Root Past Past Participle Root Past Past ParticipleDocument1 paginăList of Verbs in Past and Past Participle Form: Root Past Past Participle Root Past Past ParticipleAbigail V. AtienzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- So3 A2p SB Verb TableDocument1 paginăSo3 A2p SB Verb TabletkaczynskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument1 paginăIrregular Verbs ListR.Dario GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Irregular Verbs: Infinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleDocument3 paginiList of Irregular Verbs: Infinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleAndres OlivieriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs 2024Document1 paginăIrregular Verbs 2024Freddy jesus Soto castroÎncă nu există evaluări
- (B1) Irregular Verbs ListDocument2 pagini(B1) Irregular Verbs ListElena Caterev91% (11)
- Base Past Simple Past Participle Translation/ Example Base Past Simple Past Participle Translation/ ExampleDocument1 paginăBase Past Simple Past Participle Translation/ Example Base Past Simple Past Participle Translation/ ExampleDannika SaavedraÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Irregular Verbs IntDocument1 paginăList of Irregular Verbs IntNelson Carrasco FragaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tense Split View and Grammar PointsDocument5 paginiTense Split View and Grammar PointstinÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Irregular Verbs ListDocument5 paginiEnglish Irregular Verbs ListpeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regular & Irregular Verbs PDFDocument4 paginiRegular & Irregular Verbs PDFDANADANIKA107998100% (1)
- Think l5 Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăThink l5 Irregular VerbsRita LopesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs Laser A2Document3 paginiIrregular Verbs Laser A2Ane GaroñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 paginiInfinitive Past Simple Past Participle Infinitive Past Simple Past ParticiplemarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Most Common Irregular Verbs List: Exercises and PDF WorksheetsDocument1 paginăThe Most Common Irregular Verbs List: Exercises and PDF WorksheetsNaveenkumar AÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Irregular Verbs ListDocument2 paginiEnglish Irregular Verbs List04Aretta Widanie Lia HapsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs 1Document1 paginăIrregular Verbs 1Gloriada LetiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IrregularvbsDocument2 paginiIrregularvbsVasilica RaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs - Easy - Page 1Document2 paginiIrregular Verbs - Easy - Page 1Brayan StivenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Most Common Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăMost Common Irregular Verbspibenoh703Încă nu există evaluări
- Lista de Verbos IrregularesDocument1 paginăLista de Verbos IrregularesJahazelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument1 paginăIrregular Verbs: Base Form Past Simple Past Participlejoan LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs List: V1 Base Form V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticipleDocument4 paginiIrregular Verbs List: V1 Base Form V2 Past Simple V3 Past ParticiplemovieseekerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Form Past Tense Past ParticipleDocument44 paginiBase Form Past Tense Past ParticiplebaharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Form Simple Past Simple Form Simple Past: Past Participle Past ParticipleDocument1 paginăSimple Form Simple Past Simple Form Simple Past: Past Participle Past ParticipleEdgar Omar Diaz MoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument4 paginiIrregular Verbs Listtom100% (1)
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument2 paginiList of Irregular VerbsdanahansttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verb ListDocument6 paginiIrregular Verb ListFelipe Nobre BianchiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs List: Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument5 paginiIrregular Verbs List: Base Form Past Simple Past Participlehayati2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs Simple Present Simple Past Past ParticipleDocument6 paginiIrregular Verbs Simple Present Simple Past Past ParticipleVanessa SibayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Sinif 8 Unite Bookworms Konu Anlatimi 2 Irregular Verbs ListDocument1 pagină6 Sinif 8 Unite Bookworms Konu Anlatimi 2 Irregular Verbs ListGonca RamogluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbos Irregulares1252684196413Document1 paginăVerbos Irregulares1252684196413octavioimilan2324Încă nu există evaluări
- Irregular VerbsDocument5 paginiIrregular Verbsalmendracontrera68Încă nu există evaluări
- Present Simple Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 paginiPresent Simple Past Simple Past ParticipleЖеня СувороваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purdue OWL - Irregular VerbsDocument2 paginiPurdue OWL - Irregular Verbseiad-mahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăIrregular VerbsmimepasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument1 paginăIrregular Verbs ListPACHAS CONTRERAS ADRIAN JOSUEÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument4 paginiList of Irregular Verbsulises2007mentaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument1 paginăIrregular Verbs: Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleLéa Denise Simões AlvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Form Past Simple Past ParticipleDocument2 paginiBase Form Past Simple Past Participleralf kenjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs ListDocument1 paginăIrregular Verbs ListMariajosé MartínezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infinitive English VerbsDocument5 paginiInfinitive English VerbsCristian EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verb List - Intermediate EnglishDocument2 paginiIrregular Verb List - Intermediate EnglishEls TreviñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar - Irregular Verbs (Most Common) : Infinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleDocument4 paginiEnglish Grammar - Irregular Verbs (Most Common) : Infinitive Simple Past Past ParticipleDrum_GRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs (Short List)Document2 paginiIrregular Verbs (Short List)BreederÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irregular Verbs (Bang Dong Tu Bat Quy Tac) PDFDocument2 paginiIrregular Verbs (Bang Dong Tu Bat Quy Tac) PDFHân NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Most Common Irregular VerbsDocument1 paginăMost Common Irregular VerbsNarges AhmadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teza b2 Sem 1, Units 10-12Document2 paginiTeza b2 Sem 1, Units 10-12ali_nusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Content A1-BusinessDocument28 paginiCourse Content A1-BusinessYerai Sanchez MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thinking About Pronouns PDFDocument2 paginiThinking About Pronouns PDFNiña Alyanna Babasa Marte100% (1)
- Interactive Student Book 1 Start UpDocument1 paginăInteractive Student Book 1 Start UpcelezavirtualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Grammer RulesDocument14 paginiBasic Grammer RulesSyaz AmriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Old English GrammarDocument14 paginiOld English GrammarCristina IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument13 paginiParts of SpeechCherish PimmaengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Adverbs Multimedia Flashcard PPT (N.t. Barodi)Document25 paginiTypes of Adverbs Multimedia Flashcard PPT (N.t. Barodi)Norminy Tan Barodi100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Parts of SpeechDocument18 paginiLesson 2 Parts of Speechangel_soshi100% (1)
- ExamenDocument12 paginiExamenjavier felipe marquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phrasal Verbs - GrammarDocument24 paginiPhrasal Verbs - GrammarRosalba Bryan100% (1)
- Practice Exam Examen I Los Verbos ReflexivosDocument3 paginiPractice Exam Examen I Los Verbos ReflexivoslzeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Language Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryDocument2 paginiLanguage Functions and Forms: A Brief SummaryJujuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masculine and Feminine Nouns: Cenar Is The Rough Equivalent of "To Dine" or "To Eat Dinner" and Refers Specifically ToDocument5 paginiMasculine and Feminine Nouns: Cenar Is The Rough Equivalent of "To Dine" or "To Eat Dinner" and Refers Specifically ToRobin KhatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Nominative and VocativeDocument10 paginiLesson 1 Nominative and VocativeSeijuro HikoÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument18 paginiList of Irregular VerbsAlexandru D. GateaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic English GrammerDocument5 paginiBasic English GrammerhashcedarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sertifikat TOEFL ITP 2Document1 paginăSertifikat TOEFL ITP 2BambangrestuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career Point: Pre-Foundation DivisionDocument18 paginiCareer Point: Pre-Foundation DivisionVanidevi Mani100% (1)
- Present Progressive Story 1 PDFDocument7 paginiPresent Progressive Story 1 PDFЕлена КосенкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOCABULARY NotesDocument26 paginiVOCABULARY Notesbhargav tanguduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveDocument3 paginiPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ProgressiveAnca MorosanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Possessives PraticeDocument1 paginăPossessives PraticeMarleny Rojas CcariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument8 paginiSubject Verb Agreementsarah rasydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future WillDocument7 paginiFuture WillSamuel Tafur BustamanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curso de Inglês Conversação Aplicada Class 1 - Names: Rui VenturaDocument15 paginiCurso de Inglês Conversação Aplicada Class 1 - Names: Rui VenturaHello i am GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Kalaam (Speech/Words) Is Only of Three Kinds:: A Noun A Verb A ParticleDocument10 paginiThe Kalaam (Speech/Words) Is Only of Three Kinds:: A Noun A Verb A Particleias1969Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning English With MisterduncanDocument12 paginiLearning English With Misterduncanhungndo100% (1)
- Summary English 2 With Exercises-3Document41 paginiSummary English 2 With Exercises-3Cindy paulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Makalah Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument11 paginiMakalah Tugas Bahasa InggrisMamat SuhendarÎncă nu există evaluări