Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DLP - Combined Gas Law
Încărcat de
Jennifer MagangoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DLP - Combined Gas Law
Încărcat de
Jennifer MagangoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
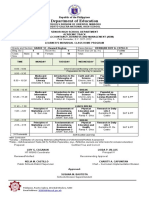
Puerto Galera NHS-
School Grade Level 10
Dulangan Extension
DAILY
LESSON Teacher Mr. Herbert J. Magango Learning Area Science
PLAN Teaching Date January 31, 2019
Quarter Third
and Time 10:40-11:40 AM
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standard The learners demonstrate an understanding of…
how gases behave based on the motion and relative distances between
gas particles
B. Performance Standards The learners shall be able to demonstrate understanding of the gas laws.
C. Learning Competencies & The learners should be able to investigate the relationship between:
Code 1. pressure and temperature at constant pressure of a gas;
II. CONTENT COMBINED GAS LAW
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teaching Guide pp. 257-280
2. Leaners’ Material/
pp. 351-399
Textbook
3. Additional Materials from
LR portal
B. Other Learning Resources
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson or ELICIT:
presenting the new lesson 1. What is the relationship between pressure and temperature
according to Gay Lussac?
2. How can it be expressed mathematically?
3. What is held constant in Gay Lussac Law?
B. Establishing a purpose for the ENGAGE:
lesson 1. Show the summary of equations of the three Gas Laws.
C. Presenting examples/ instances of 2. Ask the question, what is the relationship of volume to the pressure
the new lesson and temperature of gas?
D. Discussing new concepts and EXPLORE:
practicing new skills #1 Watch Combined Gas Law experiment
E. Discussing new concepts and Discuss the relationship of the 3 Gas Laws and its application in the
practicing new skills #2 experiments presented
Present and explain the equation of the Combined Gas law
F. Developing mastery (leads to EXPLAIN:
Formative Assessment) Demonstrate problem solving:
At the beginning of a journey, a truck tyre has a volume of 30 dm3 and
an internal pressure of 170 kPa. The temperature of the tyre is 160C.
By the end of the trip, the volume of the tyre has increased to 32 dm3
and the temperature of the air inside the tyre is 350C. What is the tyre
pressure at the end of the journey?
G. Finding practical applications of GROUP ACTIVITY:
concepts and skills in daily living Solve the following problems
1. A closed gas system initially has a volume of 8 L and a temperature of
100◦C. The pressure of the gas is unknown. If the temperature of the
gas decreases to 50◦C, the gas occupies a volume of 5 L. If the
pressure of the gas under these conditions is 1.2 atm, what was the
initial pressure of the gas?
2. A balloon is filled with helium gas at 27◦C and a pressure of 1.0 atm. As
the balloon rises, the volume of the balloon increases by a factor of 1.6
and the temperature decreases to 15◦C. What is the final pressure of
the gas (assuming none has escaped)?
3. 25 cm3 of gas at 1 atm has a temperature of 20◦C. When the gas is
compressed to 20 cm3, the temperature of the gas increases to 28◦C.
Calculate the final pressure of the gas.
H. Making generalizations and SUMMARY of the LESSON:
abstractions about the lesson In Combined Gas Law it states that,
The pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional to each
other, but are both directly proportional to the temperature of that gas.
𝑉𝑃 𝑘𝑇 𝑘𝑇 𝑉𝑃
𝑇= or 𝑉 = or 𝑃 = or 𝑘 =
𝑘 𝑃 𝑉 𝑇
The constant k in the equation above is known as the universal gas
constant. It is the result of the combination of the proportionality
constants in the three gas laws. Note that the formula is equal to a
constant, thus it is possible to compute for the change in volume,
temperature, or pressure using the following proportion:
𝑉1 𝑃1 𝑉2 𝑃2
= or 𝑉1 𝑃1 𝑇2 = 𝑇1 𝑉2 𝑃2
𝑇1 𝑇2
I. Evaluating learning Solve the following problems.
1. Helium gas has a volume of 250 mL at 0°C at 1.0 atm. What will be
the final pressure if the volume is reduced to 100 mL at 45°C?
2. The volume of a gas at 27°C and 700.0 mmHg is 600.0 mL. What
is the volume of the gas at -20.0°C and 500.0 mmHg?
3. A 2.5 L of nitrogen gas exerts a pressure of 760 mmHg at 473 K.
What temperature is needed to reduce the volume to 1.75 L at
1140 torr?
J. Additional activities for application
or remediation
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
Prepared by:
HERBERT J. MAGANGO Checked by:
Subject Teacher
LOIDA P. VILLAS
Principal IV
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gay-Lussacs LawDocument6 paginiGay-Lussacs LawGarren Jude AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP Boyles LawDocument2 paginiDLP Boyles LawJennifer Magango100% (1)
- Co1 Boyles LawDocument7 paginiCo1 Boyles LawTrisha Melrose Milanes100% (2)
- Boyles Law Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiBoyles Law Lesson PlanFany Fabia60% (5)
- Boyles LawDocument3 paginiBoyles Lawaiza larrozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Charles LawDocument2 paginiLesson Plan Charles LawQueencess Ara TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- C.O 4th QuarterDocument7 paginiC.O 4th QuarterOdessa Niña Pilapil Fernandez100% (1)
- DLP - Properties of GasDocument2 paginiDLP - Properties of GasJennifer Magango100% (1)
- LP - Charles LawDocument4 paginiLP - Charles Lawrichele rectoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson-Boyles Law G10Document9 paginiLesson-Boyles Law G10Edie Lyn Catapang100% (1)
- Boyle's Law22 Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiBoyle's Law22 Lesson PlanMontesa Allana Ea82% (17)
- Combined Gas LawDocument3 paginiCombined Gas Lawmarigold suarez0% (1)
- Charles LawDocument5 paginiCharles Law기요나100% (1)
- Department of Education: Pply The Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionsDocument12 paginiDepartment of Education: Pply The Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionsCristina NobleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Law. NewDocument5 paginiCharles Law. NewMarvin Agustin100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 Combined Gas LawDocument5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 10 Combined Gas LawJoriel Jordan CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Law Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiCharles Law Lesson PlanSigrid Amante100% (2)
- Boyles Law Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiBoyles Law Lesson Planbernadeth barajasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Law Laboratory Activity DLLDocument5 paginiCharles Law Laboratory Activity DLLHeidie BalabboÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 GASSESDocument7 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 GASSESJenifer MacaraegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles' Law..Document7 paginiCharles' Law..Aira Villarin100% (2)
- Boyles Law DLP DepedDocument8 paginiBoyles Law DLP DepedMarielle Trompeta II100% (4)
- DLL Science 10 Gas Laws - Part 1Document4 paginiDLL Science 10 Gas Laws - Part 1kaycin Duzon100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Behavior of GasesDocument5 paginiLesson Plan - Behavior of GasesDaryl CadanillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan JUNIOR HIGHDocument3 paginiLesson Plan JUNIOR HIGHMyla BulalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 paginiKinetic Molecular TheoryGarren Jude Aquino100% (1)
- Combined Gas LawDocument7 paginiCombined Gas LawJoycel ComiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COT Boyles LawDocument3 paginiCOT Boyles LawYvonne Regalado Parafina100% (1)
- Lesson Exemplar Dry RunDocument5 paginiLesson Exemplar Dry Runcristito inovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Boyle's LawDocument4 paginiLesson Plan Boyle's LawQueencess Ara TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan - TocaDocument6 paginiLesson Plan - TocaAaron Asne100% (1)
- DLL For COT4Document3 paginiDLL For COT4Abbie Gail CabatañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Gas Law 7 E'sDocument5 paginiCombined Gas Law 7 E'sGelCess Paroan100% (1)
- Grade 10 DLP in Properties of GasDocument9 paginiGrade 10 DLP in Properties of GasGel CabansagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explain The Relationship Between Population Growth and Carrying Capacity. 2. Suggest Ways To Minimize Human Impact On The EnvironmentDocument5 paginiExplain The Relationship Between Population Growth and Carrying Capacity. 2. Suggest Ways To Minimize Human Impact On The EnvironmentJaneth Miguel SatrainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan For Gas LawDocument7 paginiLesson Plan For Gas LawCherry CaspeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Avogaro's LawDocument2 paginiDLL Avogaro's LawHelen Grace Llemos Cabalag100% (1)
- GasDocument2 paginiGasLorraine Donio100% (1)
- Gas Laws Part 3 Charles LawDocument4 paginiGas Laws Part 3 Charles LawBuzz manzhjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Combined Gas LawDocument44 paginiFor Combined Gas LawApril Bartolome Flores100% (1)
- I - Objectives: S10Mt-Ive-G-23 S10Mt-Ivh-J-24Document4 paginiI - Objectives: S10Mt-Ive-G-23 S10Mt-Ivh-J-24JeanRachoPaynandosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boyle's & Charles' Law WorksheetDocument6 paginiBoyle's & Charles' Law WorksheetMary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-CuadraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Science 10Document12 paginiLesson Plan in Science 10Beryl Andal100% (1)
- LAS 2: Boyle's Law Pre-TestDocument4 paginiLAS 2: Boyle's Law Pre-TestSalve SerranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesDocument3 paginiThe Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Explains The Properties of Gases and Describes The Behavior of GasesLørd Ken M. DilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7e For Observation Avogadros LawDocument6 pagini7e For Observation Avogadros LawRon Adrian Sarte SebastianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avogadros LawDocument5 paginiAvogadros LawAgyao Yam FaithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Activity No. 1 Gas LawsDocument5 paginiLaboratory Activity No. 1 Gas LawsaerinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Science 10 - June 25Document2 paginiDLL Science 10 - June 25johann reyes50% (2)
- Properties of GasesDocument14 paginiProperties of GasesNeo EpeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily-Lesson-Log 7e '17-'18 Week 2Document3 paginiDaily-Lesson-Log 7e '17-'18 Week 2Michelle Gonzales Caliuag100% (1)
- G10 Lesson2 DLPDocument13 paginiG10 Lesson2 DLPAngeles, Mark Allen CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Chemical EquationsDocument4 paginiWriting Chemical EquationsGlenda Cate CanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Exemplar APPLIED Chem. Cot#4: Topic/Title Time Allotment Learning Competencies/ObjectiveDocument4 paginiLesson Plan Exemplar APPLIED Chem. Cot#4: Topic/Title Time Allotment Learning Competencies/ObjectiveRosita Cayanan100% (3)
- 4TH Grading Science 10Document36 pagini4TH Grading Science 10Mary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-Cuadra50% (2)
- 1.8 RNA Transcription and TranslationDocument8 pagini1.8 RNA Transcription and TranslationLadylee AcuñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Gay Lussac LawDocument6 pagini10 Gay Lussac LawDarryl Jean GeveroÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL-Observation On Combined Gas LawDocument3 paginiDLL-Observation On Combined Gas LawCALEB DEAREN G. BEMBO100% (1)
- SDLP-Charles'-Law 3Document6 paginiSDLP-Charles'-Law 3Jessica SudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- IDEA Lesson Exemplar CO2Document4 paginiIDEA Lesson Exemplar CO2Lourie Guerra LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stored Energy in CapacitorsDocument25 paginiStored Energy in CapacitorsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacific Intercontinental College (PIC)Document2 paginiPacific Intercontinental College (PIC)Patrick MorgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Problems 2Document3 paginiPerformance Problems 2Jennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Teacher'S Weekly PlanDocument1 paginăDepartment of Education: Teacher'S Weekly PlanJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPACITORS in PARALLELDocument18 paginiCAPACITORS in PARALLELJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learners Individual Class Home ProgramDocument1 paginăLearners Individual Class Home ProgramJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPSTDocument66 paginiPPSTJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Test - Electric Potential PDFDocument1 paginăChapter Test - Electric Potential PDFJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors With DielectricsDocument22 paginiCapacitors With DielectricsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Long TestDocument1 paginăChapter 2 - Long TestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Central Limit Theorem V2Document5 paginiDLP - Central Limit Theorem V2Jennifer Magango75% (4)
- Rubric NG Science ProjectDocument2 paginiRubric NG Science ProjectJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Test - Electric Potential PDFDocument1 paginăChapter Test - Electric Potential PDFJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Long TestDocument3 paginiChapter 3 - Long TestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple and Compound InterestDocument1 paginăSimple and Compound InterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocument37 paginiElectric Forces and Electric FieldsJennifer Magango100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 - AREAS Under The Normal DistributionDocument37 paginiCHAPTER 2 - AREAS Under The Normal DistributionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compound Interest More Than ONCEDocument24 paginiCompound Interest More Than ONCEJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coulomb's LawDocument24 paginiCoulomb's LawJennifer Magango50% (2)
- Electric Charges: Third QuarterDocument25 paginiElectric Charges: Third QuarterJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Business Mathematics: Simple NterestDocument12 paginiBasic Business Mathematics: Simple NterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template MAPEHDocument4 paginiTemplate MAPEHJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puerto Galera National High School Dulangan ExtensionDocument2 paginiPuerto Galera National High School Dulangan ExtensionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogDocument2 paginiPuerto Galera National High School: Daily Lesson LogJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP Compound InterestDocument3 paginiDLP Compound InterestJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Origin of The Solar SystemDocument1 paginăDLP - Origin of The Solar SystemJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionDocument3 paginiScience 10: Department of Education Division of Oriental Mindoro Puerto Galera Nhs Dulangan ExtensionJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDocument2 paginiDaily Lesson Plan School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJennifer Magango100% (1)
- DLP PlanetsDocument2 paginiDLP PlanetsJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP - Interior of The EarthDocument1 paginăDLP - Interior of The EarthJennifer MagangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 5 Science L-11Essential For Life Air and WaterDocument5 paginiClass 5 Science L-11Essential For Life Air and WaterAnshu SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengembangan Bahan Ajar Kimia Rintisan Sma Bertaraf Internasional Kelas Xi Materi Laju ReaksiDocument12 paginiPengembangan Bahan Ajar Kimia Rintisan Sma Bertaraf Internasional Kelas Xi Materi Laju ReaksiazizahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJC - H2 - Chem P3 - MSDocument10 paginiMJC - H2 - Chem P3 - MSclarissa yeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesDocument4 paginiExperiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesTAIMUR NASIRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument3 paginiAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501Încă nu există evaluări
- Recreational Drugs - Proffessor Buzz (Ebook)Document161 paginiRecreational Drugs - Proffessor Buzz (Ebook)Jim Hosein84% (56)
- Lesson 8 - SolutionsDocument13 paginiLesson 8 - SolutionsscientistgenerosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Flake BehavioursDocument12 paginiHydrogen Flake BehavioursAlex AjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Chemistry - D&F Block Elements - 12 Classes PDFDocument42 pagini2 - Chemistry - D&F Block Elements - 12 Classes PDFkrishna mohan G0% (1)
- 3 - Classification of ElementsDocument10 pagini3 - Classification of ElementsV̶a̶i̶s̶h̶n̶a̶v̶Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit Operations 1 Set BDocument4 paginiUnit Operations 1 Set BJeoh SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxygen USPDocument2 paginiOxygen USPMartha Lucia Roa FonsecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cape Physics U1 P1 2013Document11 paginiCape Physics U1 P1 2013C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Radiation Crosslinking of Polyamide 610Document4 paginiRadiation Crosslinking of Polyamide 610ecclesiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Chemical Education Volume 74 Issue 1 1997Document2 paginiJournal of Chemical Education Volume 74 Issue 1 1997Hector LeytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- KIMIA K2 SkimaDocument7 paginiKIMIA K2 SkimaTay Poh Leng0% (1)
- Tutorial CondensationDocument5 paginiTutorial CondensationKusmakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 10Document4 paginiA Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 10Anthony AndyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metallization, Back-End Technology (BEOL)Document65 paginiMetallization, Back-End Technology (BEOL)Celia ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Law of Definite Composition - Answer SHeetDocument2 paginiLaw of Definite Composition - Answer SHeetFrank Anthony SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bimbel 2Document6 paginiBimbel 2Wibowo Sugandi, S.T.Încă nu există evaluări
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper-II PDFDocument46 paginiMECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper-II PDFVISHESH JAISWALÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Chemistry Course OverviewDocument2 paginiAP Chemistry Course OverviewHorizonAcademyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hess's Law LabDocument9 paginiHess's Law LabPooyan Sharifi91% (35)
- Using Cyanex 923 For Selective Extraction in A High Concentration Chloride Medium-Part II-LarssonDocument8 paginiUsing Cyanex 923 For Selective Extraction in A High Concentration Chloride Medium-Part II-LarssonDaiana NavarreteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate of Evaporation of Different Liquids: CertificateDocument14 paginiRate of Evaporation of Different Liquids: CertificateAmandeep KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctDocument60 paginiBS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctRamiAl-fuqahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Null 2Document31 paginiNull 29153am735443Încă nu există evaluări
- TASKDocument1 paginăTASKDaniiarÎncă nu există evaluări