Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Practice Problems Weeks 1 and 2
Încărcat de
SandeshChapagainDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Practice Problems Weeks 1 and 2
Încărcat de
SandeshChapagainDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Physics 112
Practice problems Covering Materials from Weeks 1 and 2
To the student:
Stars reflect the kind of the challenge you are likely to meet in each question, once you have
carefully reviewed your class notes and read the relevant sections of the textbook. Questions with one
star emphasize using physical laws to find their solutions, but it ought to be relatively clear which
physical laws are useful. On the other end of the spectrum, questions with three stars emphasize figuring
out which physical laws you can profitably use to find the solution, and how they apply.
1. Two identical -1 C charges are held 1 cm apart. How strong is the repulsive force between
them?
2. How many electrons are in the Earth? The mass of Earth is 6 ´10 24 kg, and you may assume
that, on average, every electron is accompanied by one proton and one neutron. One reliable
reference for the masses of subatomic particles is on-line at http://hyperphysics.phy-
astr.gsu.edu/hbase/tables/funcon.html. You are welcome to round all masses to 2 significant
figures.
3. In one common model of the hydrogen atom, a single electron revolves around a single
proton in an orbit of radius 5.3´10-11 m. What is the speed of the orbiting electron?
4. Two identically charged balls are suspended by 30 cm wires from a
common point, as shown, in a configuration known as "Coulomb's
pendulum". Coulomb's pendulum works in much the same way as an
electroscope. In this case, both balls have masses of 500 g. If the balls repel
one another so that the wires make an angle of 5° from the vertical, how much
5°
charge must each ball carry?
5. Electric charges are arranged in such a way so that whenever an
electron is placed at the origin, it speeds off to the right with an acceleration of
1´1012 m s-2 and leaves the system. What would be the acceleration of a
calcium ion (Ca++) placed at the origin?
Problem 4
6. A sodium ion (Na+) is held 500 pm to the left of a chlorine ion (Cl—). What
is the electric field vector midway between the two charges?
7. The hydrogen chloride molecule has equal and opposite charges separated from one
another, with product of charge and separation (i.e., qs) being 3.3´10-30 C m. If such a molecule
lies along the x-axis, centered at the origin with the H+ ion to the left of the Cl—, what is the electric
field vector 10 nm away along the y-axis?
8. Two parallel plates have equal and opposite charges. You measure the attractive force
between them when they are held 1 cm apart. How much weaker will the force be when they are
held 4 cm apart? Give your answer as a multiplicative factor, e.g., "20 times weaker."
9. A negatively charged macromolecule drifts through a gel electrophoresis apparatus with
a constant speed of 1 mm s-1. The drag force it feels due to the gel is 10 nN. The electric field at its
location has a magnitude of 100 N C-1. How many excess (i.e., unbalanced) electrons does the
molecule have?
10. The intracellular fluid, like other ionic solutions, is
a good conductor, with many mobile charges. Suppose a
large protein molecule, which we can think of as a spherical
ball of charge, carries 10−15 𝐶 of positive charge and is 8 nm 8 nm
outside a cell. Some positive or negative charges from
within the cell (shown in the sketch at right) must
redistribute themselves on the cell membrane. What will be
protein
the density of charge (i.e., charge per unit area) on the
membrane near the protein? Give magnitude and sign.
e
bran
11. What is the potential energy of repulsion when a proton
mem
and a helium nucleus (two protons and two neutrons) are 1
cell
nm apart? inside the cell
12. An electron is released from rest at a point in space Problem 10
where the electric potential is 5 V. How fast will it be
moving when it reaches a point in space where the electric potential is 9 V?
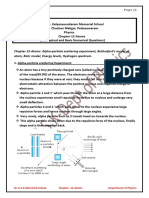
13. Ernest Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in an experiment in which he shot
helium nuclei at a gold foil, and saw that some of the projectiles bounced directly backwards. You
set out to re-do the experiment, shooting helium nuclei with a fixed speed at the gold. Your
projectiles reach a certain minimum distance from the gold nuclei before being repelled back. How
much nearer would they get if you tripled the speed of your projectiles?
14. Water molecules are electric dipoles, with dipole moment 6.0 ´10-30 C m. Cr+++
What is the potential energy (relative to infinite separation) when a
chromium ion (Cr+++) is 2 nm away from a water molecule, on the side
nearer the (negative) oxygen, as shown. Also, is the interaction attractive or
O 2 nm
repulsive?
H
15. Neutral carbon atoms have polarizability of 2.0 ´10-40 C2 m N-1 . H
An ion is brought near a neutral carbon atom and polarizes it, so that the ion Problem 14
and the atom attract one another. When the ion is 3 nm away from the
atom, the attractive force has a magnitude of 3 fN (i.e., 3´10-15 N). What is the magnitude of the
attractive force when the ion is moved back to 6 nm away from the carbon?
16. Potassium bromide (KBr) is a dipolar molecule, with dipole moment 3.4 ´10-29 C m . In an
electric field of magnitude 100 N C-1, how much more potential energy would a KBr molecule have
if it were antialigned with the field than if it were aligned?
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- AQA - Physics - Unit 1Document3 paginiAQA - Physics - Unit 1sashabelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsDocument26 paginiPhysicsAlbert ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Electricity and MagnetismDocument7 paginiUnit 5 Electricity and MagnetismareejÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Basic PhysicsDocument51 pagini1 - Basic PhysicsSsassy RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3Document2 paginiLesson 3Genesis PalangiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY167 1 Electrostatics PDFDocument11 paginiPHY167 1 Electrostatics PDFAljhon MarajuniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys-FRCR Vol 1Document113 paginiPhys-FRCR Vol 1Anonymous oQtve4o100% (1)
- Van Der Graff Electrostatic Fisica ElectricaDocument15 paginiVan Der Graff Electrostatic Fisica ElectricaComunicaciones DreamJobsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiconductor Materials: A) Energy Bands in A Solid:: Consider The Atomic Structure of Cu-AtomDocument4 paginiSemiconductor Materials: A) Energy Bands in A Solid:: Consider The Atomic Structure of Cu-AtomAmit ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument16 paginiElectric Charges and FieldsPRACHI GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDocument83 paginiFundamentals of Electrical and ElectronicsDr Narayana Swamy Ramaiah100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Document71 paginiINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Part 3Triphon Gyle BalidiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eec 124Document29 paginiEec 124Adetayo Salawu100% (3)
- 1 - Electronics 1 Lecture 1Document11 pagini1 - Electronics 1 Lecture 1alazawekokoÎncă nu există evaluări
- P 62Document25 paginiP 62JohnnardBelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics - Direct Current PDFDocument76 paginiElectrostatics - Direct Current PDFRita UmutoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric ChargeDocument10 paginiElectric ChargeAmethyst0% (1)
- Lesson 1 Electric Charge Coulombs Law Electric Fields and Electric Flux2 PDFDocument10 paginiLesson 1 Electric Charge Coulombs Law Electric Fields and Electric Flux2 PDFAjzÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 paginiCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureahumanbeinginearthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Note - 1-Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument3 paginiLecture Note - 1-Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawThe NocturnalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureDocument6 paginiCIE Chemistry A Level: 2: Atomic StructureMyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsslive-XII-Physics-1. ELECTROSTATICSDocument16 paginiHsslive-XII-Physics-1. ELECTROSTATICSСука ЛазаньяÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveDocument16 paginiXii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju Hssliveapi-3487796590% (1)
- Chapter 12-Atoms-NewDocument26 paginiChapter 12-Atoms-NewTeamDRxBeRliNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ella Brown - Video Questions - Electric Charge Crash Course Physics #25Document4 paginiElla Brown - Video Questions - Electric Charge Crash Course Physics #25Ella BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Physics PaperDocument2 paginiApplied Physics PaperSabeeh HasnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFDocument11 pagini9 Science Ncert ch4 PDFSeenu SÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBI 1 - Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument10 paginiCBI 1 - Fundamentals of ChemistryRianna NÎncă nu există evaluări
- General+Physics+2+ +week+1Document6 paginiGeneral+Physics+2+ +week+1senpai notice meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts: Chapter Overview 1. Nature of ElectricityDocument22 paginiBasic Concepts: Chapter Overview 1. Nature of ElectricityGunadevan ChandrasekaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2Document10 paginiImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2PriyanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Nature of ElectricityDocument14 paginiModule 1 - Nature of ElectricityEd Carlo RamisÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialDocument63 paginiPPT-Course 1-2-Charge Force Field Gaus PotentialRaul AtofaneiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Grade 11 - September 16 - Electric Forces, Fields & PotentialDocument27 paginiPhysics - Grade 11 - September 16 - Electric Forces, Fields & Potential川贝林Încă nu există evaluări
- Chem3420 Topic3 5 New2Document28 paginiChem3420 Topic3 5 New2justinhadinata283Încă nu există evaluări
- Atom and NecluiDocument11 paginiAtom and NecluithinkiitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1.1 ChemistryDocument7 paginiUnit 1.1 ChemistryHumoon AfsardeirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Structure of Atom Telegram PDFDocument8 paginiOpen Structure of Atom Telegram PDFnimarsharma7Încă nu există evaluări
- ch1 PDFDocument99 paginich1 PDFsamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Physics NotesDocument80 paginiA Level Physics NotesAsghar Abbas100% (2)
- Unit 3 - MSCDocument22 paginiUnit 3 - MSCAndroid DotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thomson Atom Model: Physics NotesDocument13 paginiThomson Atom Model: Physics NotesEs EÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Structure of MatterDocument3 paginiThe Structure of MatterFull StudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Transport in SolidsDocument130 paginiElectrical Transport in SolidsSaroshan DeshapriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (2087) Lecture Notes 1 Atomic Structure eDocument53 pagini(2087) Lecture Notes 1 Atomic Structure eRamJiPandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SemiconductorDocument6 paginiSemiconductordksingh369Încă nu există evaluări
- Bohr and Rydberg - Atomic Spectra ProblemsDocument13 paginiBohr and Rydberg - Atomic Spectra ProblemssubstitutescribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHS 304 (Modern)Document179 paginiPHS 304 (Modern)Eniibukun Keji-ayodejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 Revision NotesDocument5 paginiAS Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1 Revision NotesTheMagicCarpetÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Document11 paginiAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric CurrentDocument20 paginiElectric CurrentBik WodeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Physics NotesDocument81 paginiA Level Physics NotesJames Chong100% (1)
- Principios de Radiacion Goaz 1Document15 paginiPrincipios de Radiacion Goaz 1Alejo UrreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Level Physics NotesDocument93 paginiA Level Physics NotesAdam BaldwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryDe la EverandElementary Particles: The Commonwealth and International LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- What is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionDe la EverandWhat is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesDe la EverandThe Enigmatic Electron: Electron Behaviour and How It Influences Our LivesÎncă nu există evaluări
- JNTUA B Tech 2018 1 2 May R15 ECE 15A54201 Mathematics IIDocument2 paginiJNTUA B Tech 2018 1 2 May R15 ECE 15A54201 Mathematics IIMRUDULA KULAKARNIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultra Petronne Interior Supply Corp.: Manufacturer of Light Metal FramesDocument1 paginăUltra Petronne Interior Supply Corp.: Manufacturer of Light Metal Framesjun vincint geleraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SQ Presentation 2021-r2Document43 paginiSQ Presentation 2021-r2nadeem4ahmed-805026Încă nu există evaluări
- BSR NH Circle Jaipur 2016Document103 paginiBSR NH Circle Jaipur 2016vikash kumar50% (4)
- Experiment 5 DACDocument3 paginiExperiment 5 DACABHISHEK SHARMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21-3971-CLA - DisenŞo Preliminar Cimentacion - Normal SoilDocument4 pagini21-3971-CLA - DisenŞo Preliminar Cimentacion - Normal SoilJose ManzanarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cif Purge Plug Systems en 3Document3 paginiCif Purge Plug Systems en 3abdeljalil elbadrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whirlpool Duet HTDocument96 paginiWhirlpool Duet HTdanny85901100% (2)
- Using Dapper Asynchronously inDocument1 paginăUsing Dapper Asynchronously inGiovani BrondaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASADocument3 paginiVibration - Electrical or Mechanical - EASAGilbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil & Gas Asset Integrity IssuesDocument15 paginiOil & Gas Asset Integrity Issuesyogolain100% (2)
- ZF CAT EBook Oil-Filters-Construction-Agricultural-Machinery-Transmissions 50114 201806 V02 IN PDFDocument142 paginiZF CAT EBook Oil-Filters-Construction-Agricultural-Machinery-Transmissions 50114 201806 V02 IN PDFdeisy ortegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Dice Using LEDs Electrical Engineering ProjectDocument16 paginiElectronic Dice Using LEDs Electrical Engineering Projectprakhar agarwal33% (3)
- Air-Bag: (1) Connector InformationDocument34 paginiAir-Bag: (1) Connector InformationbakriramziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Examination System For AndroidDocument7 paginiOnline Examination System For AndroidSri Sai UniversityÎncă nu există evaluări
- SdccmanDocument126 paginiSdccmanGustavo A. Sarache MillanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tube Well Design Project SolutionDocument5 paginiTube Well Design Project SolutionEng Ahmed abdilahi IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell Hazardous Area Classification FundamentalsDocument30 paginiShell Hazardous Area Classification Fundamentalsthekevindesai100% (17)
- Ex-Cell XR2750 Pressure Washer Operation ManualDocument16 paginiEx-Cell XR2750 Pressure Washer Operation Manualj_wilson85Încă nu există evaluări
- EN 1991-1-4 NA enDocument4 paginiEN 1991-1-4 NA enanuj3936100% (1)
- Eramus Bridge PDFDocument10 paginiEramus Bridge PDFBabaO.Riley100% (1)
- Waqas Riaz: Total Years of Experience: 2 Years ObjectiveDocument2 paginiWaqas Riaz: Total Years of Experience: 2 Years ObjectiveIrfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8th ICCIT - 2005 - 564Document5 pagini8th ICCIT - 2005 - 564Amit BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feasibility Study of Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Energy Systems For Rural Villages of Ethiopian Somali Region (A Case Study of Jigjiga Zone)Document7 paginiFeasibility Study of Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Energy Systems For Rural Villages of Ethiopian Somali Region (A Case Study of Jigjiga Zone)ollata kalanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTE Maintenance Inspection For Grinding Eng WebDocument2 paginiOTE Maintenance Inspection For Grinding Eng WebjadetorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valve Body PDFDocument9 paginiValve Body PDFTimur TOT100% (2)
- ElectronicsDocument3 paginiElectronicsashishkumar218Încă nu există evaluări
- Eje Delantero BMW F10Document94 paginiEje Delantero BMW F10Daniel Muñoz SotomayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Is Electrical Energy MeasuredDocument4 paginiHow Is Electrical Energy MeasuredSonya ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări