Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Transaction Processing Systems
Încărcat de
Karla MaeDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Transaction Processing Systems
Încărcat de
Karla MaeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
Transaction Processing Systems
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) are computer-based versions of manual organization systems
dedicated to handling the organization’s transactions.
General requirements:
a. complete file structure
- normalized tables
- use of master and transaction file
b. incorporation of back-up, recovery and archiving features
c. complete data entry components
d. proper maintenance features
e. complete reports
f. data entry, validation and error trapping
g. validation, security, data accuracy and integrity features
Types of TPS:
1. Payroll System
A system designated to compute for the wage or salary due to each member in the organization
Important Considerations:
number of employee – at least 50 employees
types of employees (e.g. regular, contractual, part-time, consultant, etc.)
time keeping system
number of allowable absences/leaves, deductions (due to late, absences, under time, cash
advances, etc.)
cut-off period; frequency of payroll period
correctness and complexity of computations
pay slip generation
payroll summary report generation
existence of table of variables (e.g. SSS table, Tax table, etc.)
reports to other agencies (e.g. BIR, SSS, PAG-IBIG, etc.)
valid test data – 50 employees
2. Inventory System
A system designed to monitor the quantity of inventory items (raw materials, production materials,
and finished goods) to determine reorder or production point.
Important Considerations:
number of inventory items – at least 1,000 items
types of inventory items – 5 to 10 product lines
- 5 to 10 items per product line
acquisition of items from supplier
warehouse capacity
checking of critical levels (quantity ceiling and flooring), reorder point
generation of reports (backorder list, reorder list, stock adjustment, etc.)
frequency of reports (inventory summary)
January 2018 Page 1 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
suppliers
valid test data – 50 employees
3. Library System
A system designed to perform the processes involved in acquisition, catalog, and circulation of
books.
Important Considerations:
number of book titles – at least 2,000 books (CHED requirement)
total number of books
types of users
number of students/members – at least 500 students/members
borrowing system
returning system
reservation system
cataloguing system
computation of penalty
CHED reports (for school only)
Reports generated
Valid test data – 50 titles
- 50 borrowers
4. Accounting System
A system designed to monitor the inflow and outflow of cash, goods, and services of an
organization.
Important Considerations:
accounts receivables monitoring
accounts payable monitoring
incorporation of aging technique
posting of transaction on journal
frequency of report generation
valid test data – 30 accounts
5. Enrolment System
A system designed to perform the process involved in registration, advising, assessment and
payment of students as well as scheduling of classes.
Important Considerations:
number of students – at least 200 students
number of sections – at least 2 sections per year level
year levels (e.g. grades 1-6. 1st-4th year, etc.)
registration
assessment
payments
class schedule (scheduling/sectioning)
pre-requisites and co-requisites
view tuition/fees billing statement
courses and specializations (for Tertiary level)
January 2018 Page 2 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
student grades
reports generated
Students Information System (general information on student systems)
Faculty Information System
6. Hotel Reservation and Billing System
A system designated to manage information about rooms, reservations, customers, and customer
billing. The system provides functionality for making reservations, check in, and check out, in
addition to generating reports and displays.
Important Considerations:
Number of rooms – at least 20 rooms
Number of customers – at least 2 sections per year level
customer information
room information
services and facilities
check-in/out procedures
automatic billing system
reservation and cancellation
maintenance of fees
reports generated
valid test data – 50 customers
7. Patient Information and Billing System (Hospital System)
A system designed to perform process involved in admitting, diagnosing, medication, and boiling of
patients.
Important Considerations:
number of beds - at least 20 beds
total number of patients – at least 50 patients
patient history
medication
diagnosis
prognosis
physicians’ information
data recorded and monitored for each patient
automatic Billing system
maintenance of fees (e.g. room rates, medicines, services, laboratory fee, etc.)
valid test data – 50 patients
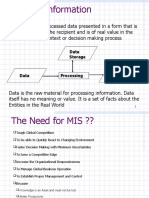
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS) are computer-based systems designed to provide standard
reports for managers about transaction data.
Important Considerations:
types of reports generated
- trend analysis report
January 2018 Page 3 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
- summary report
- exception report
- on-demand report
- ad-hoc report
- frequency report
- format of reports
Decision Support Systems
Decision Support Systems (DSS) are systems designed to help organization decision-makers make
decisions.
Important Considerations:
presence of three components
- database
- model base
- dialogue module
Geographical Information Systems
Geographical Information System (GIS) is a computer system capable of assembling, storing,
manipulating, and displaying geographically referenced information, i.e. data identified according to
their locations. GIS technology can be used scientific investigations, resource management, and
development planning. For example, a GIS might allow emergency planners to easily calculate
emergency response times in the event of natural disaster, or a GIS might be used to find wetlands that
need protection from pollution
Important Considerations:
Information retrieval
Topological modeling
Networks
Overlay (map layers)
Algorithms (e.g. shortest path algorithms, etc.)
Data output
Scientific and Office Information Systems
Scientific and Office Information Systems are systems used in the administration of organization or as a
support to specific functions:
Important Considerations:
quality of information
quantity of information
types of users
functions to support
available resources
January 2018 Page 4 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
Multimedia Systems
A software which encapsulates the reputation of various digital media – text, images, audio, video,
graphics, animation, music, etc.
Important Considerations:
incorporation of at least 4 media (text, graphics, audio, video)
incorporation of maintenance features
use of database(s) in storing information in various media
nature of data, purpose, source and users of data
search features, save and print functions
organizations/category of topics or information
users/beneficiaries of the system
user levels (e.g. systems administrator, viewers/researchers, etc.)
copyright of materials utilized for the system
Additional Reference
http://www.cs.cf.ac.uk/Dave/Multimedia/
Computer-Aided Instruction (CAI)
A software designed to facilitate learning. CAI utilizes multimedia integration to present lessons, give
exams/drills and provide necessary feedback.
Important Considerations:
multimedia system concepts
major categories – drills and practice, tutorials, simulation, games
2 to 3 methods of presenting the topics
identification of the target age bracket/users
organization of topic/discussions
source/basis of lessons/topics
level of difficulty of lessons and test items
valid test items – source/basis of questions
random generation of test items
analysis of results
feedback of user performance
testing – 50 items per topic
required analysis/design tools or methods – storyboarding, flowcharting, HIPO, others.
Additional Reference
January 2018 Page 5 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
Web Applications
Web Development focuses on using the latest technology to develop innovative and creative Web
Applications.
Important Considerations:
dynamic pages
multimedia concepts
incorporation of maintenance features
use of database(s) in storing information in various media
organization/category of topics or information
standard conformance, portability, and clear navigation
nature of data, purpose, source and users of data
meta tags
uploaded
security
required development tool/programming languages: HTML, VBScripts, JavaScripts, XML, PHP,
ASP, Perl and other web development programming languages
Note: Please refer to Thesis Seminar Series 3 hand-outs about Web Application Development for
important considerations for e-Business and e-Commerce application.
Additional Reference
http://teachers.net/manual/
http://harry.cciflorida.com/HTML3/hmer/work/opini/www/websiteplan.html
http://www.phpbuilder.com/columns/angus20010304.php3
http://www.w3.org/TR/WAI-WEBCONTENT/
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Types of AI:
1. Expert Systems (ES) – a computer-based system designed to mimic the performance of human
experts.
Important Considerations:
Database
Dialogue module
Inference engine
Knowledge acquisition technique
Expert system programming language
2. Neural Networks – a system modeled after neurons (nerve cells) in biological nervous system and
intended to simulate the way in which our brain processes information, learns and remember.
3. Robotics – the integration of computers and industrial robots, and is more often than not associated
with unmanned assembly lines.
4. Intelligent Agents
5. ICAI
January 2018 Page 6 of 7
Areas of Research
Thesis SY2018
Software Engineering
Software Engineering is the establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to obtain
economical software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines.
Focus of Research:
Paradigm of software engineering based on new approaches in programming
Cost models
Systems Software – a type of software that tells the CPU what to do
Example: Operating System, Compilers, Interpreters, Utilities, etc.
Other Software Packages
Example: Desktop Publishing, Graphics Editor, Word Processor, Spreadsheets, CAD,
Communications Software, etc.
Systems Analysis Design
System Analysis and Design and Implementation is a complex organizational process whereby computer-
based information system are developed and maintained.
Focus of Research: Automated Tool that combines both process and data views of systems
Networking
Networking is the process of connecting computer devices and circuits for transferring data from one
computer to another.
Focus of Research: Network topology implementation
Information Research Management
Management of information which evolves on the concept that information is a major corporate
resource that should be managed in the same manner as other assets such as land, people, etc., are
managed.
Information Systems Plan for an organization
January 2018 Page 7 of 7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Data and Information ManagementDocument6 paginiData and Information ManagementPraveen TrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Systems: Unit-VDocument24 paginiExpert Systems: Unit-VasarvigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social, Ethical, and Legal Issues in Information Systems: Chapter FourDocument39 paginiSocial, Ethical, and Legal Issues in Information Systems: Chapter FourRyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument11 paginiIntroduction To Managerial Economicssiva883Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Operate A Spreadsheet Application AdvanceDocument32 pagini2 Operate A Spreadsheet Application Advanceapi-247871582Încă nu există evaluări
- Create A Table in Microsoft WordDocument3 paginiCreate A Table in Microsoft WordSharmila SathiaselanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 03 - The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic EventsDocument143 paginiChapter 03 - The Accounting Cycle: Capturing Economic EventsElio BazÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Compelling Need For Data WarehousingDocument36 paginiThe Compelling Need For Data WarehousingAnonymous Ck9Og8UEqzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Word Processing Skills: Prepared By: Myrrha Michaela CascaroDocument25 paginiAdvance Word Processing Skills: Prepared By: Myrrha Michaela CascaroDaku Fureimu MasutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Warehouse Concepts PresentationDocument60 paginiData Warehouse Concepts PresentationThirumal Selvaraj100% (1)
- Systems Security-BIC3263 - Course OutlineDocument9 paginiSystems Security-BIC3263 - Course OutlineBorotho MolemoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting Information System Course SyllabusDocument10 paginiAccounting Information System Course Syllabusali alhussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYLLAB - 00accounting Information SystemDocument6 paginiSYLLAB - 00accounting Information SystemEfren100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveDocument18 paginiChapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveHarold Falip100% (1)
- MIS - Management Information SystemsDocument68 paginiMIS - Management Information SystemsRuchi Gupta100% (1)
- Module 1 Overview of Management ScienceDocument10 paginiModule 1 Overview of Management ScienceRaphael GalitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Based Information SystemDocument3 paginiComputer Based Information SystemLem TechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verona UniversityDocument1 paginăVerona UniversityMohammad Farhan SafwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 2 3Document41 paginiChapter 1 2 3Cathleen Ancheta NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office Automation Systems (OAS)Document12 paginiOffice Automation Systems (OAS)Abhishek Kumar100% (1)
- Ais Chapter 1 and 2 QuizletDocument63 paginiAis Chapter 1 and 2 QuizletVenice Espinoza100% (1)
- The Era of Big Data: Databases, Information Systems, & Artificial IntelligenceDocument63 paginiThe Era of Big Data: Databases, Information Systems, & Artificial IntelligenceRatri NugraheniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS449 - Syllabus-Algorithms & ComplexityDocument5 paginiCS449 - Syllabus-Algorithms & ComplexityLaura CraigÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Most Promising Big Data Solution ProvidersDocument2 pagini100 Most Promising Big Data Solution ProvidersInfo TrellisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Production and Supply Chain Management Information SystemsDocument57 paginiChapter 4 - Production and Supply Chain Management Information SystemsNHÂN NGUYỄN ĐỨCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Cost AccountingDocument5 paginiAdvanced Cost AccountingPrathamesh ChawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit Under Computerized Information System CISDocument59 paginiAudit Under Computerized Information System CISJohn David Alfred EndicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 - Actg Research Methods (Structure)Document13 paginiLecture 1 - Actg Research Methods (Structure)markÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study of Manual Voting System and E-Voting System For Supreme Student Government Council Election of Paso de Blas National High SchoolDocument27 paginiA Comparative Study of Manual Voting System and E-Voting System For Supreme Student Government Council Election of Paso de Blas National High SchoolLaura JadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch01-An Introduction To Information SystemsDocument53 paginiCh01-An Introduction To Information SystemsNoor Mohd EffendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Science Textbook Solutions - 11Document31 paginiComputer Science Textbook Solutions - 11acc-expertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 AccountingDocument11 paginiChapter 3 AccountingĐỗ ĐăngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15 - The Role of Communications in Labor-Management RelationsDocument23 paginiChapter 15 - The Role of Communications in Labor-Management RelationsANN ONYMOUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Xero: Cloud ComputingDocument17 paginiLesson 1 Introduction To Xero: Cloud ComputingLeah ManalangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computers: Topic 1Document37 paginiIntroduction To Computers: Topic 1Celyn Anne Jati EkongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bisdig - Week 2Document47 paginiBisdig - Week 2auliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance and Counseling Record Management SystemDocument7 paginiGuidance and Counseling Record Management SystemVelumani sÎncă nu există evaluări
- GROUP - 4 - Payroll SystemDocument35 paginiGROUP - 4 - Payroll SystemCharian Andojar PendicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT Application Tools in Business Course Content PDFDocument2 paginiIT Application Tools in Business Course Content PDFCabatan, Jenevie D.Încă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Basic AccountingDocument5 paginiReviewer For Basic AccountingSVTKhsiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting Information Systems, 10th Edition: James A. HallDocument35 paginiAccounting Information Systems, 10th Edition: James A. HallAlexis Kaye DayagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3-Production and Cost AnalysisDocument24 paginiUnit 3-Production and Cost AnalysisSri HimajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Credit Investigation or Background Investigation PDFDocument4 paginiCredit Investigation or Background Investigation PDFjoan100% (3)
- Businees Logic RevisedDocument9 paginiBusinees Logic RevisedSandra DandingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Systems Operations and MaintenanceDocument8 paginiInformation Systems Operations and MaintenanceJOMAR FERRERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical Analysis With Software Application PDFDocument145 paginiStatistical Analysis With Software Application PDF2B MASIGLAT, CRIZEL JOY Y.Încă nu există evaluări
- File Management System of Deseo Boarding HouseDocument39 paginiFile Management System of Deseo Boarding HouseAlfred Roi Ballatan100% (3)
- Case Study 2 Carlson Department StoreDocument2 paginiCase Study 2 Carlson Department StoreMaricar PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Chapter 1 Data Warehousing and ManagementDocument11 paginiAssignment On Chapter 1 Data Warehousing and ManagementAnna BelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computerized Enrollment System of Lasam AcademyDocument19 paginiComputerized Enrollment System of Lasam AcademyViernesCacholaRovelyn100% (1)
- CISM SyllabusDocument4 paginiCISM SyllabusBirhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Transaction ProcessingDocument20 paginiIntroduction To Transaction ProcessingSatrio MangkunegoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter: 4.2 Word Processing Concepts Topic: 4.2.1 Introduction To Word ProcessingDocument44 paginiChapter: 4.2 Word Processing Concepts Topic: 4.2.1 Introduction To Word ProcessingETL LABSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: San Pedro CampusDocument6 paginiPolytechnic University of The Philippines: San Pedro CampusJemh VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1 Ia2Document4 paginiQuiz 1 Ia2Angelica NilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting The Study of Accounting in Nigerian UniversitiesDocument8 paginiFactors Affecting The Study of Accounting in Nigerian UniversitiesDheetMonsterLiuchaoshinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Billing System PresentationDocument29 paginiWater Billing System PresentationJasper BernalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web-Based Student Identification Card System An Alternative For School On-Site ProcessingDocument6 paginiWeb-Based Student Identification Card System An Alternative For School On-Site ProcessingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Name: Course Code: Credit: 5 Credit (Document53 paginiCourse Name: Course Code: Credit: 5 Credit (Kritika AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ais lý thuyếtDocument13 paginiAis lý thuyếtAnh Trần ViệtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Just For Fun: Perspective: More Than 100 Fun and Simple Step-By-Step Projects... // PDF MZ3JEW1UMUDocument1 paginăJust For Fun: Perspective: More Than 100 Fun and Simple Step-By-Step Projects... // PDF MZ3JEW1UMUKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MadlyDocument10 paginiMadlyKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BenDocument2 paginiBenKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn Filipino BK I Chap 1Document30 paginiLearn Filipino BK I Chap 1v5romero100% (1)
- Mass Readings February 2020 PDF DownloadDocument3 paginiMass Readings February 2020 PDF DownloadKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar For Writing 1 An Editing Guide To WritingDocument29 paginiGrammar For Writing 1 An Editing Guide To WritingKarla Mae0% (1)
- Ikaw Pa RinDocument9 paginiIkaw Pa RinKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument1 paginăReadmeKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Position Track Name ArtistDocument10 paginiPosition Track Name ArtistKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imahe Mo Mahal KoDocument9 paginiImahe Mo Mahal KoKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImaheDocument5 paginiImaheKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eb 5 D 1 Fa 4 Ca 1053 C 1 C 7723 e 30 e 8 F 563Document2 paginiEb 5 D 1 Fa 4 Ca 1053 C 1 C 7723 e 30 e 8 F 563Karla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImaheDocument5 paginiImaheKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imahe Mo Mahal KoDocument5 paginiImahe Mo Mahal KoKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Korean IdiomsDocument6 paginiKorean IdiomsKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03.midterm Examination Key To CorrectionDocument3 pagini03.midterm Examination Key To CorrectionKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHILGOVDocument5 paginiPHILGOVKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To E-CommerceDocument3 paginiIntroduction To E-CommerceKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03.midterm Examination Answer Key ITEC 101Document3 pagini03.midterm Examination Answer Key ITEC 101Karla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book Pls Upload HeheDocument1 paginăBook Pls Upload HeheKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tagalog Malay Similar WordsDocument15 paginiTagalog Malay Similar WordsKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02.final Examination Answer KeyDocument2 pagini02.final Examination Answer KeyKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visitor Log and Monitoring SystemDocument7 paginiVisitor Log and Monitoring SystemKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seizure and Forfeiture ProceedingsDocument20 paginiSeizure and Forfeiture ProceedingsBadong SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karla MaeDocument1 paginăKarla MaeKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Event Management An Android Application: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Cience, Ngineering and EchnologyDocument5 paginiEvent Management An Android Application: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Cience, Ngineering and EchnologyKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 1 1 893 2799 PDFDocument101 pagini10 1 1 893 2799 PDFKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled Spreadsheet PDFDocument1 paginăUntitled Spreadsheet PDFKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument13 paginiChapter 3 PDFKarla MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-CHS LM Module4 Q3-Q4decDocument130 paginiE-CHS LM Module4 Q3-Q4decHari Ng Sablay91% (11)
- Elevator Control System Project PDFDocument11 paginiElevator Control System Project PDFBruno RussellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linsn-Led-Control-System-Manual English PDFDocument37 paginiLinsn-Led-Control-System-Manual English PDFLaza UrosevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of ComputerDocument18 paginiEvolution of Computerkeitch jonh SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIS Paps 1002Document6 paginiCIS Paps 1002Marvin Anglacer100% (1)
- G7-Pretechnical Studies Notes AdsDocument7 paginiG7-Pretechnical Studies Notes AdsMartin Thumbi100% (1)
- Notation Material and Form, Ramati, FreemanDocument7 paginiNotation Material and Form, Ramati, FreemanLila Lila100% (1)
- Perform Computer Operations QuizDocument2 paginiPerform Computer Operations QuizArt Dollosa100% (1)
- CS1100 - Introduction To ProgrammingDocument42 paginiCS1100 - Introduction To ProgrammingRashmi SahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument146 paginiPDFOm BurhadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itt Questions 1Document156 paginiItt Questions 1Deepak TamboliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who Invented The ComputerDocument6 paginiWho Invented The ComputerParker Girl100% (3)
- Lesson Plans: Dr. Muhammad NafeesDocument11 paginiLesson Plans: Dr. Muhammad NafeesMah Rukh QadriÎncă nu există evaluări
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 EditionDocument52 paginiWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 6 EditionRahmat RafliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Pic16F877A Microcontroller: Equipments RequiredDocument7 paginiStudy of Pic16F877A Microcontroller: Equipments RequiredPriyadharshini TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get Appy Design FolioDocument25 paginiGet Appy Design FolioChok Wai Philbert LayÎncă nu există evaluări
- BARC (AutoRecovered)Document6 paginiBARC (AutoRecovered)VasudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Levels of AutomationDocument3 paginiLevels of AutomationProcurement PardisanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Input and Output Device PaperDocument8 paginiInput and Output Device PaperRISKI SAPUTRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer HistoryDocument12 paginiComputer Historyapi-295973659Încă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)Document18 paginiQuarter 3 - Module 1-W1&W2: Computer Systems Servicing (CSS)AC Balio100% (5)
- Chess King Manual 201512Document339 paginiChess King Manual 201512Song Jin100% (3)
- Earth Unmasked - Cosmic Synchronicity RPGDocument151 paginiEarth Unmasked - Cosmic Synchronicity RPGstellapolare19721100% (1)
- C SolutionsDocument158 paginiC SolutionsOnkar GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Hardware and SoftwareDocument229 pagini1.3 Hardware and SoftwarehussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- AKNU-B. Com (CA) - 20-21-2feb21Document65 paginiAKNU-B. Com (CA) - 20-21-2feb21Subha SarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download New Perspectives On Computer Concepts 2014 Comprehensive 17th Edition Parsons Test BankDocument34 paginiFull Download New Perspectives On Computer Concepts 2014 Comprehensive 17th Edition Parsons Test Bankgraysonchvego100% (26)
- VMware Shortlist For Online TestDocument40 paginiVMware Shortlist For Online TestArushi ParasharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Control System ENGDocument27 paginiCentral Control System ENGsuriwaitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 - Week 7 and 8 - Platform Technologies PDFDocument46 paginiModule 5 - Week 7 and 8 - Platform Technologies PDFRonald Bautista Rivera50% (4)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityDe la EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItDe la EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (66)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeDe la EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (36)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsDe la EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (722)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyDe la EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (111)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldDe la EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDe la EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldDe la EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (55)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyDe la EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (51)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe la EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldDe la EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (107)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDe la EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyDe la EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (24)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderDe la EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (398)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesDe la EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumDe la EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (12)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootDe la EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyDe la EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andDe la EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (709)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterDe la EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDe la EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDe la EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (228)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansDe la EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialDe la EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (238)