Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Braden Skala - De.en
Încărcat de
Khamra SalahuddinDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Braden Skala - De.en
Încărcat de
Khamra SalahuddinDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.dekubitus-pflege.
info
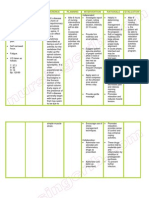
Braden scale for assessing a pressure ulcer risk
1 point 2 points 3 points 4 points
Sensory sentience is missing highly limited slightly limited available
Ability to adequately respond to
• no response to painful stimuli possible • a reaction takes place only on strong pain • Reaction to speech or commands • Reaction to speech, complaints can be
pressure-related discomfort reasons: loss of consciousness, sedation or stimuli uttered or
• Complaints can hardly be expressed (eg by • However, complaints can not always be
moaning or restlessness) or expressed (eg that the position should be
changed) or
• Disorder of pain sensation by paralysis • no fault of pain sensation
affecting the largest part of the body (for
example, high cross-section) • Disturbance of the pain sensation due to • disorder of pain sensation due to paralysis,
of which one or two extremities are affected
paralysis, half of the body is affected
humidity constantly moist often wet sometimes wet rarely humid
Extent to which the skin is exposed to moisture
• the skin is constantly wet by urine, sweat • the skin is often damp, but not always • the skin is sometimes wet, and about once a • the skin is usually dry
day, new underwear is required
or feces • new laundry is rarely needed
• always when the patient is turned, it lies in • bedding or linen must be changed per
shift at least once
the wet
activity bedridden sits on is little is regularly
Level of physical activity
• bedridden • can run something using • goes a day alone, but rarely and only short • is regularly 2-3 times per shift
distances
• its own weight can not bear alone • regularly moves
• need for longer distances • Help spends the
most time in bed or chair
• needs help to sit up (bed, chair, wheelchair)
mobility completely immobile Mobility severely limited Low mobility restricted mobile
Ability to change the position and to keep
• sometimes slightly moves (body or
• can also perform any slight change of extremities) • regularly makes small position change of the • can only change its position
body and extremities comprehensively
position without help • but can not regularly migrate alone is
sufficient
nutrition very poor diet moderate diet adequate nutrition Good nutrition
eating habits
• never eats on small portions, but • rarely eats a normal portion of food, but • eats more than half of the normal • always eats the offered meals
eating in general, about half of the food food portions
only 2/3
offered
• eats only two or less servings of protein • takes four protein servings to be • takes 4 or more servings of
protein to be
(dairy products, fish, meat) • occasionally refused a meal, but will
supplement food to him or
• eat about 3 servings of protein • sometimes eats between meals
• drinking too little • regularly supplement food for themselves or
• assumes no supplementary food to him or • can take the most nutrients across probe or • does not need supplementary food
infusions
• not receive enough nutrients through tube
• must orally do not take food to him or feedings or infusions
• only clear liquids or
• receives infusions longer than 5 days
Friction and shear forces problem potential problem no problem at the time
• takes a lot to massive support postural • something moves alone or need some • moving in bed and chair alone
help
• has enough strength to rise
• Lifting is not possible without loops over the • when pulling grinds the skin only slightly • may hold a position for a long time without
sliding down
sheets above the sheets (can, recover)
• slips kept falling in bed or in roll / chair, has to
be pulled up again • may be in a position hold for a long time
(chair, wheelchair)
• has spastic contractures or • is very restless • rarely slides down
(scrubs on the sheets)
Source: Angelika Zegelin, 1997
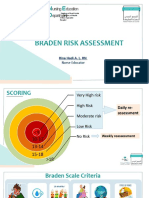
Decubitus hazard: low risk > 18 points
General risk 18-15 points
Average risk 14-13 points
High risk 12-10 points
Very high risk <9 points
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Screenshot 2020-09-29 at 11.57.53 AMDocument2 paginiScreenshot 2020-09-29 at 11.57.53 AMLorraine PadsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumble VibeDocument6 paginiTumble Vibedumdum2Încă nu există evaluări
- HerzinsuffizienzDocument10 paginiHerzinsuffizienzMagdalena PokusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Ulangan Harian Bahasa Inggris Kelas 7Document11 paginiSoal Ulangan Harian Bahasa Inggris Kelas 7indah safitri0% (1)
- PDF Muang NaDocument54 paginiPDF Muang NaCee005100% (1)
- Decubitus UlcerDocument8 paginiDecubitus UlcerDanilo EspinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Sss Use: Member'S Data Amendment Form (DEC. 96)Document2 paginiFor Sss Use: Member'S Data Amendment Form (DEC. 96)rosevannieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keperawatan Holistik - Ranah KopleenterDocument18 paginiKeperawatan Holistik - Ranah KopleenterPhiioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caring For Elderly Patients With Dementia Nursing PDFDocument11 paginiCaring For Elderly Patients With Dementia Nursing PDFElla OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taking The Medical HistoryDocument2 paginiTaking The Medical HistoryPaf VenancioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication in Hospital B1 - B2 - p2Document1 paginăCommunication in Hospital B1 - B2 - p2ayoubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Respiratory Rates by AgeDocument2 paginiNormal Respiratory Rates by AgeDanhil RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Working in TeamsDocument2 paginiAdvantages and Disadvantages of Working in TeamsvikasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note Note: PFLEGE A1 (3hrs/day) Week 1Document3 paginiNote Note: PFLEGE A1 (3hrs/day) Week 1Annamae Perez100% (2)
- 3.B1. 8x2 Vocabulary Flash Card Template.Document5 pagini3.B1. 8x2 Vocabulary Flash Card Template.Franz CaytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vital Sign CoversationDocument2 paginiVital Sign CoversationDelisa IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore Risk: ScoreDocument1 paginăBraden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore Risk: ScoreCristina GrozavuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Q Scale PDFDocument1 paginăBraden Q Scale PDFsholihatul fuadahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Pressure Ulcer Risk AssessmentDocument1 paginăBraden Pressure Ulcer Risk AssessmentNatasha BhasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument1 paginăBraden ScaleAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument1 paginăBraden ScaleYzabel BorjeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Q Scale:: Intensity and Duration of Pressure ScoreDocument1 paginăBraden Q Scale:: Intensity and Duration of Pressure Scoresholihatul fuadahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskDocument1 pagină4 Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskAdrianna BarnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale and ChaptersDocument1 paginăBraden Scale and ChaptersHall reverb Effect songs Bass boostedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale Homecare2Document1 paginăBraden Scale Homecare2muhammad al ihsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument2 paginiBraden ScaleFrancis Alfred Escaran100% (1)
- Lecture 12 - Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore RiskDocument1 paginăLecture 12 - Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore RiskjemalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale FillableDocument1 paginăBraden Scale FillablelkervinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore RiskDocument2 paginiBraden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore RiskPiper ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument3 paginiBraden Scalejackson wong100% (1)
- Braden ScaleDocument26 paginiBraden ScaleElessawey AbdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskDocument1 paginăBraden Scale For Predicting Pressure Ulcer RiskJian CarloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brad en ScaleDocument1 paginăBrad en ScalechantellghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument1 paginăBraden ScaleMohRozaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument1 paginăBraden ScaleRatus BornÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden RAChartDocument2 paginiBraden RAChartJerome CidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gordon'S Pattern of Functioning: Functional Health Pattern Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization InterpretationDocument4 paginiGordon'S Pattern of Functioning: Functional Health Pattern Before Hospitalization During Hospitalization Interpretationhotstars20Încă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar NCPDocument2 paginiBipolar NCPweehdinga89% (9)
- Braden Scale FormDocument1 paginăBraden Scale FormJILL ANGELESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment The Braden Scale: Deepesh Bhardwaj Associate ProfessorDocument13 paginiPressure Ulcer Risk Assessment The Braden Scale: Deepesh Bhardwaj Associate ProfessorLaly ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Distrubed Sleeping PatternDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Distrubed Sleeping Patternferrerjohnoliver86% (59)
- Sleep Rest PatternDocument4 paginiSleep Rest PatternCindy DelfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocument2 paginiNCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping Patternkaye040390% (30)
- Braden Scale Risk Assessment SheetDocument2 paginiBraden Scale Risk Assessment SheetAmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Conscious ExperienceDocument9 pagini6 Conscious ExperienceBARNUEVO HONEY MARIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore Risk: Christian Home Health CareDocument4 paginiBraden Scale For Predicting Pressure Sore Risk: Christian Home Health CareAntoinette Cowart RogersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Disturbed Sleeping Pattern Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan: Disturbed Sleeping Pattern Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveKryza CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screenshot 2022-11-06 at 6.53.08 PMDocument1 paginăScreenshot 2022-11-06 at 6.53.08 PMdina AbdelmoatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactDocument4 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactJennifer ArdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping Pattern Sleep ScienceDocument1 paginăNCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping Pattern Sleep ScienceYanejoulce SacanleÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.S Scale: Skala Braden Versi Indonesia Skala Braden Faktor DeskripsiDocument5 paginiS.S Scale: Skala Braden Versi Indonesia Skala Braden Faktor DeskripsiDIAN EKASOSIAWATIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ujian Praktikum Blok Sistem Integumen Prodi S1 Keperawatan Fikkes-UnimusDocument4 paginiUjian Praktikum Blok Sistem Integumen Prodi S1 Keperawatan Fikkes-UnimusFebri Adi PrasetyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Document18 pagini5 Prioritized Problems Bipolar 1Joseph D. Wang100% (30)
- Cga 1Document37 paginiCga 1UDDE-E MARISABELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Risk AssessmentDocument19 paginiBraden Risk AssessmentRina LestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 98 Painad PDFDocument2 pagini98 Painad PDFmaKitten08Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP PostpartumDocument3 paginiNCP Postpartumglocel88% (16)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plankehyrie100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Redemittel FÃ R Schriftliche Wissenschaftliche Texte - De.enDocument11 paginiRedemittel FÃ R Schriftliche Wissenschaftliche Texte - De.enKhamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden Skala - De.enDocument1 paginăBraden Skala - De.enKhamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- German Medical VocabularyDocument2 paginiGerman Medical VocabularyKhamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- German Medical Vocabulary PDFDocument4 paginiGerman Medical Vocabulary PDFKhamra Salahuddin100% (2)
- Perfekt Separaple InseparableDocument3 paginiPerfekt Separaple InseparableKhamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perfect Tense 2Document2 paginiPerfect Tense 2Khamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modes of Ventilation Chart - 1Document5 paginiModes of Ventilation Chart - 1Khamra SalahuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Paleo PloyDocument2 paginiThe Paleo PloyRaquel Spiegel VieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceptability of Avocado Mousse Cake Product of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in San Policarpo National High SchoolDocument10 paginiAcceptability of Avocado Mousse Cake Product of Grade 12 Senior High School Students in San Policarpo National High SchoolTing Ka100% (2)
- Muscle Spasm CrampsDocument3 paginiMuscle Spasm Crampsscribd_doc_filesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meal Plan #1: Meal Food Calories Protein Carbs FATDocument12 paginiMeal Plan #1: Meal Food Calories Protein Carbs FATPradeep ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boom Brand Creative Book - Donald Delahaye PDFDocument16 paginiBoom Brand Creative Book - Donald Delahaye PDFDonald Damjd DelahayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Owner's ManualDocument104 paginiAnimal Owner's Manualabubu19Încă nu există evaluări
- Slash Your Risk of AlzheimersDocument26 paginiSlash Your Risk of AlzheimersMihaela-Elena Pletea100% (3)
- Tesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSDocument24 paginiTesis vITAMIN C CONTENT IN FRUITSHema JothyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usmc FitnessDocument69 paginiUsmc FitnessJakeWillÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Blood Sugar MiracleDocument63 paginiThe Blood Sugar MiracleRick Swartz80% (5)
- Integrative Medicine and PhitotherapyDocument72 paginiIntegrative Medicine and PhitotherapyLibAmauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition & Nutritional AssessmentDocument57 paginiNutrition & Nutritional Assessmentmridul mithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition LabelsDocument8 paginiNutrition LabelsShubhangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health 2Document8 paginiHealth 2Joniele Angelo AninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giant Arms and LegsDocument22 paginiGiant Arms and LegsBlack Jackals100% (2)
- Fibersol 2Document4 paginiFibersol 2I. Murali KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 STD Test Fee - Rev2 - Feb 4 2015 PDFDocument17 pagini2014 STD Test Fee - Rev2 - Feb 4 2015 PDFDon King EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Nutrition MCQ PDFDocument3 paginiBasic Nutrition MCQ PDFMuhammad Azam100% (1)
- 10 Nutritional Guidelines For FilipinosDocument5 pagini10 Nutritional Guidelines For FilipinosJoyVee Pillagara-De Leon100% (1)
- Healthy Diet Plans (Anemia)Document21 paginiHealthy Diet Plans (Anemia)Rohan GulavaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Meal RevolutionTHE-LIST-A4Document2 paginiReal Meal RevolutionTHE-LIST-A4fridayschild2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Offi Cial Methods of Analysis: 19th Ed. (2012)Document3 paginiOffi Cial Methods of Analysis: 19th Ed. (2012)ImmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaffin - Diverticulosis Case StudyDocument24 paginiChaffin - Diverticulosis Case StudymollychaffinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Weight-Loss Smoothie Recipes - Liezl Jayne PDFDocument17 pagini3 Weight-Loss Smoothie Recipes - Liezl Jayne PDFSonia CorredorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braden ScaleDocument1 paginăBraden ScalePopa Niculina100% (1)
- Research Proposal Chapter 1-3Document37 paginiResearch Proposal Chapter 1-3Merryo Setyawan100% (8)
- Federal University of Agriculture, Makurdi College of Food Science and Technology Department of Food Science and TechnologyDocument13 paginiFederal University of Agriculture, Makurdi College of Food Science and Technology Department of Food Science and Technologyalyeabende moses msenÎncă nu există evaluări
- RENAL DIALYSIS - Nutrition, Imbalanced, Less Than Body RequirementsDocument3 paginiRENAL DIALYSIS - Nutrition, Imbalanced, Less Than Body Requirementsmakyofrancis20Încă nu există evaluări
- BenfotiamineDocument5 paginiBenfotiaminekether.thipharet5601Încă nu există evaluări