Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Proteus Lab Manual PDF
Încărcat de
Anie SaidTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Proteus Lab Manual PDF
Încărcat de
Anie SaidDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
LAB MANUAL
Prepared by
Prof. K. P. Paradeshi
Associate Professor,
Electronics Engineering,
kpparadeshi@pvpitsangli.edu.in
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 01
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
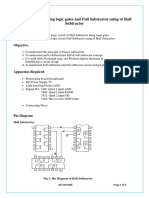
Design of Half Wave Rectifier using Proteus.
Aim:
Design & stimulate the half wave rectifier.
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of Half Wave Rectifier circuit.
• To understand the circuit arrangement of Half Wave Rectifier circuit.
• To understand the simulation procedure of ―Half Wave Rectifier‖ circuit
using proteus.
• To observe & analyze the output waveforms
Outcomes:
• Able to understand principal of working of Half Wave Rectifier circuit.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of Half Wave Rectifier circuit.
• Able to understand the simulaton procedure of Half Wave Rectifier circuit
using proteus.
• Able to observe & analyse the circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs.
• To enable to innovate, design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction:
The device which converts ac voltage into dc voltage is called rectifiers. In fact,
rectifiers produce unidirectional & pulsating voltage from ac source.
Rectifiers offers a low resistance to the flow of current in one direction & high
resistance to flow of current in opposite direction that is rectifier converts AC into DC. This
conversion is achieved by rectifier supplied with AC signal using step down transformer. The
output of contains pulsating DC (ripple voltage) which can be removed by using filter circuit.
we have to design the HWR using proteus. It is easy to design on the proteu
Circuit Diagram:
Half wave rectifier
Circuit arrangement:
The circuit arrangement of half wave as shown in fig. It uses one transformer for
providing step down operation as well as to provide electrical isolation. In this type of
arrangement diode D, load resistance RL are used, the output is taken across load resistance
as shown in figure.
Theory:
When a single rectifier unit is placed in series with the load across an ac supply, it
converts alternating voltage into uni-directional pulsating voltage, using one half cycles of
the applied voltage, the other half cycles being suppressed because it conducts only in one
direction. Unless there is an inductance or battery in the circuit, the current will be zero,
therefore, for half the time. This is called half-wave rectification. As already discussed, diode
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
is an electronic device consisting of two elements known as cathode and anode. Since in a
diode electrons can flow in one direction only i.e. from cathode to anode so the diode
provides the unilateral conduction necessary for rectification. This is true for diodes of all
types-vacuum, gas-filled, crystal or semiconductor, metallic (copper oxide and selenium
types) diodes. Semiconductor diodes, because of their inherent advantages are usually used as
a rectifying device. However, for very high voltages, vacuum diodes may be employed.
The half-wave rectifier circuit using a semiconductor diode with a load resistance R L
but no smoothing filter is given in figure. The diode is connected in series with the secondary
of the transformer and the load resistance RL, the primary of the transformer is being
connected to the ac supply mains.
A transformer has been added to provide the desired voltage into the rectifier. For
high voltage DC power supplies this would obviously be a step-up transformer,but with many
solid-state equipment application voltages of 4.5,6,9,22.5,40volts are used. Thus necessitating
a step-down transformer. Hence,in HWR the step-down transformer is used.
Working of a Half wave rectifier:
The ac voltage across the secondary winding changes polarities after every half cycle.
During the positive half-cycles of the input ac voltage i.e. when upper end of the secondary
winding is positive w.r.t. its lower end, the diode is forward biased and therefore conducts
current. When forward voltages crosses barrier potential (0.7v for silicon diode) the diode
works as closed switch,the large current flows through RL.This current produces dc voltage
across the load RL. If the forward resistance of the diode is assumed to be zero (in practice,
however, a small resistance exists) the input voltage during the positive half-cycles is directly
applied to the load resistance RL, making its upper end positive w.r.t. its lower end. The
waveforms of the output current and output voltage are of the same shape as that of the input
ac voltage.
During the negative half cycles of the input ac voltage i.e. when the lower end of the
secondary winding is positive w.r.t. its upper end, the diode is reverse biased and so does not
conduct that is diode D acts as open switch.Thus during the negative half cycles of the input
ac voltage the current through and voltage across the load remains zero if the reverse current,
being very small in magnitude, is neglected. Thus for the negative half cycles no power is
delivered to the load.
Thus the output voltage developed across load resistance R L (VL) is a series of positive
half cycles of alternating voltage, with intervening very small constant negative voltage
levels, It is obvious from the figure that the output is not a steady dc, but only a pulsating dc
wave. Since only half-cycles of the input wave are used, it is called a half-wave rectifier. The
output voltage is unidirectional,pulsating & intermittent.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
DC OUTPUT VOLTAGE:-
Vdc = Vm/3.14 (with no load)
Vm= maximum voltage
DC OUTPUT CURRENT:-
Idc = Im/3.14 Im=maximum current
Significance of half wave rectifier using proteus:
The most important characteristics which are required to be specified for a power supply
are given below :
1. The required output dc voltage.
2. The average and peak currents in the diode.
3. The peak inverse voltage (PIV) of each diode.
4. The regulation.
5. The ripple factor
Advantages:
• Simple circuit and low cost.
Disadvantages:
• The output current in the load contains, in addition to dc component, ac components
of basic frequency equal to that of the input voltage frequency. Ripple factor is high
and an elaborate filtering is, therefore, required to give steady dc output.
• The power output and, therefore, rectification efficiency is quite low. This is due to
the fact that power is delivered only half the time.
• Transformer utilization factor is low.
• DC saturation of transformer core resulting in magnetizing current and hysteresis
losses and generation of harmonics.
The type of supply available from a half-wave rectifier is not satisfactory for general
power supply. This type of supply can be satisfactory for some particular purposes such as
battery charging.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to pick device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right click and select edit properties to change the values.
5. Add voltage probe at input and output.
6. Select the ‗graph mode‘& choose analouge Analysis graph window.
7. Right click and select ‗add traces‘ (input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulation graph.
9. Observe and analyse input & output waveforms.
Circuit simulation
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
By using Proteus we can understand working of half wave rectifier. During the
negative half cycles of the input ac voltage, diode D acts as open switch. Thus for the
negative half cycles no power is delivered to the load. The input voltage during the positive
half-cycles is directly applied to the load resistance R L and waveforms appears across diode
D.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 02
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
To study bridge full wave rectifier.
Aim:
To design and simulate bridge full wave rectifier circuit using proteus and observe the
waveforms.
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of bridge full wave rectifier.
• To understand the circuit arrangement of bridge full wave rectifier.
• To understand the simulation procedure of bridge full wave rectifier circuit
using proteus.
• To observe & analyze the output waveforms
Outcomes:
• Able to understand principal of working of bridge FWR circuit.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of bridge FWR circuit.
• Able to understand the simulation procedure of bridge FWR circuit using
Proteus.
• Able to observe & analyze the circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied: 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs.
• To enable to innovate, design and develope a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction:-
The Full Wave Bridge Rectifier
Another type of circuit that produces the same output waveform as the full
wave rectifier circuit above is that of the Full Wave Bridge Rectifier. This type of single
phase rectifier uses four individual rectifying diodes connected in a closed loop "bridge"
configuration to produce the desired output. The main advantage of this bridge circuit is that
it does not require a special centre tapped transformer, thereby reducing its size and cost. The
single secondary winding is connected to one side of the diode bridge network and the load to
the other side as shown below.
Working of full wave bridge rectifier:
The circuit arrangement made for bridge FWR is as shown in fig. It uses one
transformer for providing step down operation as well as to provide electrical isolation. In
this type of arrangement, four diodes (D1, D2,D3,D4) are connected in such a way , to form
a bridge. Hence it is called as ―bridge FWR‖. Here, two diodes are conducting at a time and
remaining two diodes are non-conducting. The output is taken across load resistance as
shown in fig.
During positive half cycle of AC input, the diode D1 and D3 becomes forward
bias, at the same time, diodes D2 and D4 becomes reverse bias. Thus, current flows through
the path : diode D1, load resistance RL , diode D3, to the second end of transformer‘s
secondary winding. In this situation, current through RL flows from top to bottom producing
positive output voltage across it.
During negative half cycle of AC input, diode D2 and D4 becomes forward
biased, at the same time, diodes D1 and D3 becomes reverse bias. Thus, current flows
through the path : diode D2, load resistance RL , diode D4, to the second end of
transformer‘s secondary winding. In this situation, current flows in the same direction
producing positive output voltage across load resistance as shown in waveforms.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Theory:.
The Diode Bridge Rectifier
The four diodes labelled D1 to D4 are arranged in "series pairs" with only two
diodes conducting current during each half cycle. During the positive half cycle of the supply,
diodes D1 and D2 conduct in series while diodes D3 and D4 are reverse biased and the
current flows through the load as shown below.
The Positive Half-cycle
During the negative half cycle of the supply, diodes D3 and D4 conduct in series, but diodes
D1 and D2 switch "OFF" as they are now reverse biased. The current flowing through the
load is the same direction as before.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
The Negative Half-cycle
As the current flowing through the load is unidirectional, so the voltage
developed across the load is also unidirectional the same as for the previous two diode full-
wave rectifier, therefore the average DC voltage across the load is 0.637Vmax. However in
reality, during each half cycle the current flows through two diodes instead of just one so the
amplitude of the output voltage is two voltage drops ( 2 x 0.7 = 1.4V ) less than the input
VMAX amplitude. The ripple frequency is now twice the supply frequency (e.g. 100Hz for a
50Hz supply). Although we can use four individual power diodes to make a full wave bridge
rectifier, pre-made bridge rectifier components are available "off-the-shelf" in a range of
different voltage and current sizes that can be soldered directly into a PCB circuit board or be
connected by spade connectors.The image to the right shows a typical single phase bridge
rectifier with one corner cut off. This cut-off corner indicates that the terminal nearest to the
corner is the positive or +ve output terminal or lead with the opposite (diagonal) lead being
the negative or -ve output lead. The other two connecting leads are for the input alternating
voltage from a transformer secondary winding.
The Smoothing Capacitor
We saw in the previous section that the single phase half-wave rectifier
produces an output wave every half cycle and that it was not practical to use this type of
circuit to produce a steady DC supply. The full-wave bridge rectifier however, gives us a
greater mean DC value (0.637 Vmax) with less superimposed ripple while the output
waveform is twice that of the frequency of the input supply frequency.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Full-wave Rectifier with Smoothing Capacitor
The smoothing capacitor converts the full-wave rippled output of the
rectifier into a smooth DC output voltage. Generally for DC power supply circuits the
smoothing capacitor is an Aluminum Electrolytic type that has a capacitance value of 100uF
or more with repeated DC voltage pulses from the rectifier charging up the capacitor to peak
voltage. However, there are two important parameters to consider when choosing a suitable
smoothing capacitor and these are its Working Voltage, which must be higher than the no-
load output value of the rectifier and its Capacitance Value, which determines the amount of
ripple that will appear superimposed on top of the DC voltage.
Too low a capacitance value and the capacitor has little effect on the output
waveform. But if the smoothing capacitor is sufficiently large enough (parallel capacitors can
be used) and the load current is not too large, the output voltage will be almost as smooth as
pure DC. As a general rule of thumb, we are looking to have a ripple voltage of less than
100mV peak to peak.
The maximum ripple voltage present for a Full Wave Rectifier circuit is not only
determined by the value of the smoothing capacitor but by the frequency and load current,
and is calculated as:
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Bridge Rectifier Ripple Voltage
Where: I is the DC load current in amps, ƒ is the frequency of the ripple or twice
the input frequency in Hertz, and C is the capacitance in Farads.
The main advantages of a full-wave bridge rectifier is that it has a smaller AC ripple
value for a given load and a smaller reservoir or smoothing capacitor than an equivalent half-
wave rectifier. Therefore, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice that of the
AC supply frequency (100Hz) where for the half-wave rectifier it is exactly equal to the
supply frequency (50Hz).
The amount of ripple voltage that is superimposed on top of the DC supply
voltage by the diodes can be virtually eliminated by adding a much improved π-filter (pi-
filter) to the output terminals of the bridge rectifier. This type of low-pass filter consists of
two smoothing capacitors, usually of the same value and a choke or inductance across them
to introduce a high impedance path to the alternating ripple component.
Another more practical and cheaper alternative is to use an off the shelf 3-terminal
voltage regulator IC, such as a LM78xx (where "xx" stands for the output voltage rating) for
a positive output voltage or its inverse equivalent the LM79xx for a negative output voltage
which can reduce the ripple by more than 70dB (Datasheet) while delivering a constant
output current of over 1 amp.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
FWR Circuit Using Proteus
Components required:
Name Description Number of
components
required
RES Resistor(3.3K) 1
DIODE Diode 1N4007 4
TRAN Transformer 280-280) 1
Vac Ac voltage source 1
GND Ground 3
Procedure using proteus:
1. First of all, pick a bridge of diodes 1N4007 from the components list, and place it
properly on the screen
2. Pick the transformer having rating of 12-0-12 and place it as per the circuit diagram.
3. Pick a resistance of 3.3kilo ohm, and place it properly.
4. Connect the AC Source of 230V(freq.50Hz) volts source .
5. With the help of wires, connect all these components in a proper way, as shown in fig.
6. Connect voltage probes to the input & output positions.
7. open graph option and activate analogue analysis option to observe the output
waveforms.
8. By right clicking on the window, add the traces of each component. And then
simulate the graph. After that, you will get desired output waveforms of the bridge
FWR.
Advantages:
1.Smaller size of transformer is required due to higher value of transformer utilization factor.
2.The need of centre tap transformer is eliminated.
3.PIV rating of diode is less as compared to centre tap FWR.
4.There is no problem of transformer core saturation.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Disadvantages:
1. It requires two additional diodes as compared to centre tap FWR.
CIRCUIT SIMULATION
RESULT
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
By studying bridge FWR, we conclude that bridge FWR is most efficient
electronic circuit which converts AC signal into DC signal. As the current flowing through
the load is unidirectional, so the voltage developed across the load is also unidirectional the
same as for the previous two diode full-wave rectifier, therefore the average DC voltage
across the load is 0.637Vmax. However in reality, during each half cycle the current flows
through two diodes instead of just one so the amplitude of the output voltage is two voltage
drops ( 2 x 0.7 = 1.4V ) less than the input VMAX amplitude. The ripple frequency is now
twice the supply frequency (e.g. 100Hz for a 50Hz supply).
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 03
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title :
Low Pass Filter & High Pass Filter .
Aim :
To Study & simulate frequency response of low pass & high pass filter.
Objectives:
To understand principal of working of low pass & high pass filter.
To understand the circuit arrangement of low pass & high pass filter.
To understand the procedure of low pass & high pass filter using
capacitor& register circuit using proteus.
To observe the frequency response waveforms and analyze the circuit.
Outcomes:
Students will be able to study low pass & high pass filter using capacitor&
register.
Students will be able to understand the circuit arrangement of pass & high
pass filter
Students will be able to understand the procedure of pass & high pass filter
using capacitor & register circuit using proteus.
Students will be able to observe the simulation and analyse the working of
circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by
applying basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and
also be able to use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill
social needs
To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and
computer based components and system for applications including signal
processing , communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction
Low Pass Filter :
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals and attenuates
(reduces the amplitude of) signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The
actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes
called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter when used in audio applications. A low-pass filter is
the opposite of a high-pass filter. A band-pass filter is a combination of a low-pass and a
high-pass.
Low-pass filters exist in many different forms, including electronic circuits (such as
a hiss filter used in audio), anti-aliasing filters for conditioning signals prior to analog-to-
digital conversion, digital filters for smoothing sets of data, acoustic barriers, blurring of
images, and so on. The moving average operation used in fields such as finance is a particular
kind of low-pass filter, and can be analyzed with the same signal processing techniques as are
used for other low-pass filters. Low-pass filters provide a smoother form of a signal,
removing the short-term fluctuations, and leaving the longer-term trend.
An optical filter could correctly be called low-pass, but conventionally is described as
"longpass" (low frequency is long wavelength), to avoid confusion.
Electronic low-pass filters
Passive electronic realization
Passive, first order low-pass RC filter
One simple electrical circuit that will serve as a low-pass filter consists of a resistor in
series with a load, and a capacitor in parallel with the load. The capacitor exhibits reactance,
and blocks low-frequency signals, causing them to go through the load instead. At higher
frequencies the reactance drops, and the capacitor effectively functions as a short circuit. The
combination of resistance and capacitance gives the time constant of the filter
(represented by the Greek letter tau). The break frequency, also called the turnover frequency
or cutoff frequency (in hertz), is determined by the time constant:
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
or equivalently (in radians per second):
One way to understand this circuit is to focus on the time the capacitor takes to charge. It
takes time to charge or discharge the capacitor through that resistor:
At low frequencies, there is plenty of time for the capacitor to charge up to practically the
same voltage as the input voltage.
At high frequencies, the capacitor only has time to charge up a small amount before the
input switches direction. The output goes up and down only a small fraction of the
amount the input goes up and down. At double the frequency, there's only time for it to
charge up half the amount.
Another way to understand this circuit is with the idea of reactance at a particular frequency:
Since DC cannot flow through the capacitor, DC input must "flow out" the path marked
(analogous to removing the capacitor).
Since AC flows very well through the capacitor — almost as well as it flows through
solid wire — AC input "flows out" through the capacitor, effectively short circuiting to
ground (analogous to replacing the capacitor with just a wire).
The capacitor is not an "on/off" object (like the block or pass fluidic explanation above). The
capacitor will variably act between these two extremes. It is the Bode plot and frequency
response that show this variability.
Active electronic realization
An active low-pass filter
Another type of electrical circuit is an active low-pass filter.
In the operational amplifier circuit shown in the figure, the cutoff frequency (in hertz) is
defined as:
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
or equivalently (in radians per second):
The gain in the passband is −R2/R1, and the stopband drops off at −6 dB per octave (that is
−20 dB per decade) as it is a first-order filter.
Discrete-time realization
Many digital filters are designed to give low-pass characteristics. Both infinite impulse
response and finite impulse response low pass filters as well as filters using fourier
transforms are widely used.
Simple infinite impulse response filter
The effect of an infinite impulse response low-pass filter can be simulated on a
computer by analyzing an RC filter's behavior in the time domain, and then discretizing the
model.
A simple low-pass RC filter
Finite impulse response
Finite impulse response filters can be built that approximate to the ideal sinc time
domain response. In practice the time domain response must be time truncated and is often of
a simplified shape; in the simplest case, a running average can be used giving a square time
response.[3]
High Pass Filter
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter that passes high-frequency
signals but attenuates (reduces the amplitude of) signals with frequencies lower
than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency
varies from filter to filter. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-
invariant system. It is sometimes called a low-cut filter or bass-cut filter.[1] High-
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
pass filters have many uses, such as blocking DC from circuitry sensitive to non-
zero average voltages or RF devices. They can also be used in conjunction with a
low-pass filter to make a bandpass filter.
First-order continuous-time implementation
Figure 1: A passive, analog, first-order high-pass filter, realized by an RC circuit
The simple first-order electronic high-pass filter shown in Figure 1 is
implemented by placing an input voltage across the series combination of a
capacitor and a resistor and using the voltage across the resistor as an output.
The product of the resistance and capacitance (R×C) is the time constant (τ); it
is inversely proportional to the cutoff frequency fc, that is,
where fc is in hertz, τ is in seconds, R is in ohms, and C is in farads.
Figure 2: An active high-pass filter
Figure 2 shows an active electronic implementation of a first-order high-pass
filter using an operational amplifier. In this case, the filter has a passband gain
of -R2/R1 and has a corner frequency of
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Because this filter is active, it may have non-unity passband gain. That is, high-
frequency signals are inverted and amplified by R2/R1.
Advantages:
Low pass filter
1. The gain of integrater decreases with frequency whereas gain of differentiator increases
linearly with frequency,so it is easier to stabilize the output of integrators.
2. Due to limited B.W,integrator are less sensitive to noise voltage than differentiators.
3.It is more convenient to introduce the initial conditions in an integrator circuit.
Disadvantages:
For lower frequency reactance offered by capacitor C is very high & hence these frequencies
are not passed at output.
Low pass filter circuit using proteus:
Procedure using Proteus:
10. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to pick device from library.
11. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
12. Place the all components on the Proteus screen.
13. Right click and select edit properties to change the values.
14. Add voltage probe at input and output.
15. Select the ‗graph mode‘ & choose analouge Analysis graph window.
16. Right click and select ‗add traces‘(input & output trace).
17. Right click & activate simulation graph.
18. Observe and analyse input & output waveforms.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
High pass filter using proteus
Result
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Low pass filter using proteus:
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Result
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
We can understand working of low pass & high pass filter. By using proteus
we can observe simulation of circuit & analyses the waveform taken across capacitor
C1.
In Low pass filter the frequency is passes below cut off region And in high
pass filter the frequency passes above the cut off region.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 04
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
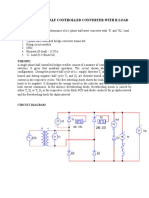
Title:
Design ± 5V and ±12V regulated power supply using Proteus.
Aim:
Design and simulate the ± 5V and ±12V regulated power Supply.
Objectives:
To understand principal of working of regulated power supply.
To understand the circuit arrangement regulated power supply.
To understand the procedure of regulated power supply circuit using proteus.
To observe the simulation of circuit.
Outcomes:
Able to understand principal of working of regulated power supply circuit.
Able to understand the circuit arrangement of regulated power supply circuit.
Able to understand the procedure of regulated power supply.‖ circuit using
proteus.
Able to observe the simulation of circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs.
• To enable to innovate, design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Principle:
7805 is a 5V fixed three terminal positive voltage regulator IC. The IC has features
such as safe operating area protection, thermal shut down, internal current limiting which
makes the IC very rugged. Output currents up to 1A can be drawn from the IC provided that
there is a proper heat sink. A 9V transformer steps down the main voltage, 1A bridge rectifies
it and capacitor C1 filters it and 7805 regulates it to produce a steady 5voltDC.
Introduction:
The stepdown transformer, down-converts the high voltage AC input (230V,50Hz) to
a 9V,2A; because the transformer we used here having a specification of 9V/A. The
alternating voltage from secondary terminal of the transformer is given to a bridge rectifier.
The bridge rectifier converts alternating voltage to unidirectional voltage with the switching
action of diodes. This voltage is finally fed to a 5V regulator IC through a 470uF,50v
electrolytic capacitor, which eliminates the ripples and make the output stable. After
regulation we get a 5V DC voltage at the output of 7805 IC.
Circuit Diagram:
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Circuit arrangement:
The circuit arrangement of IC 7805 is as shown in fig. It uses one IC 7805 to generate
+5V output . In this type of arrangement two resistors and two capacitors are used, the output
is taken across pin no 3 of IC 555 as shown in figure.
Theory:
Theory of IC 78XX
Transformer:-
A bridge rectifier coupled with a step down transformer is used for our design. The
voltage rating of transformer used is 0-12V and the current rating is 500mA. When AC
voltage of 230V is applied across the primary winding an output AC voltage of 12V is
obtained. One alteration of input causes the top of transformer to be positive and the bottom
negative. The next alteration will temporarily cause the reverse.
Rectifier:-
In the power supply unit, rectification is normally achieved using a solid state diode.
Diode has the property that will let the electron flow easily at one direction at proper biasing
condition. Bridge rectifiers of 4 diodes are used to achieve full wave rectification. Two
diodes will conduct during the negative cycle and the other two will conduct during the
positive half cycle.
Filtering unit:-
Filter circuit which is usually a capacitor acts as a surge arrester always follows the
rectifier unit. This capacitor is also called as a decoupling capacitor or a bypass capacitor, is
used not only to short the ripple with frequency to ground but also leave the frequency of the
DC to appear at the output.
Regulators:-
The voltage regulators play an important role in any power supply unit. The primary
purpose of a regulator is to aid the rectifier and filter circuit in providing a constant DC
voltage to the device. Power supplies without regulators have an inherent problem of
changing DC voltage values due to variations in the load or due to fluctuations in the AC line
voltage. With a regulator connected to DC output, the voltage can be maintained within a
close tolerant region of the desired output. IC 7805 and 7812 regulators are used in this
project for providing a DC voltage of +5V and +12V respectively.
Technical Details:-
Transformer: 230/12 volts step down transformer, 1 ampere
Diodes: IN 4007
7805: The 7805 supplies 5 volts at 1 amp maximum with an input of 7-25 volts
Electrolytic Capacitors: 100pF, 330pF and 100μF, power rating of 25V.
Features:-
· Gives a well regulated +12V and +5V output voltages
· Built in overheating protection shuts down output when regulator IC gets too hot.
· Very stable output voltages, reliable operation
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
· The circuit has overload and thermal protection.
ADVANTAGES:
78xx series ICs do not require additional components to provide a constant, regulated
source of power, making them easy to use, as well as economical and efficient uses of
space. Other voltage regulators may require additional components to set the output
voltage level, or to assist in the regulation process. Some other designs (such as
a switched-mode power supply) may need substantial engineering expertise to
implement.
78xx series ICs have built-in protection against a circuit drawing too much power. They
have protection against overheating and short-circuits, making them quite robust in most
applications. In some cases, the current-limiting features of the 78xx devices can provide
protection not only for the 78xx itself, but also for other parts of the circuit.
DISADVANTAGES:
The input voltage must always be higher than the output voltage by some minimum
amount (typically 2 volts). This can make these devices unsuitable for powering some
devices from certain types of power sources (for example, powering a circuit that requires
5 volts using 6-volt batteries will not work using a 7805).
As they are based on a linear regulator design, the input current required is always the
same as the output current. As the input voltage must always be higher than the output
voltage, this means that the total power (voltage multiplied by current) going into the
78xx will be more than the output power provided. The extra input power is dissipated as
heat. This means both that for some applications an adequate heatsink must be provided,
and also that a (often substantial) portion of the input power is wasted during the process,
rendering them less efficient than some other types of power supplies. When the input
voltage is significantly higher than the regulated output voltage (for example, powering a
7805 using a 24 volt power source), this inefficiency can be a significant issue.
Even in larger packages, 78xx integrated circuits cannot supply as much power as many
designs which use discrete components, and are generally inappropriate for applications
requiring more than a few amperes of current.
Each specific model of 78xx is designed to produce only one fixed voltage output, so
they may not be suitable for applications requiring a configurable or varying output (For
such applications, the LM317 series of ICs are available, which are similar to 78xx ICs
but can produce a configurable voltage).
± 5V and ±12V regulated power supply using Proteus.
Component:
230V ac transformer, diodes, capacitor and IC 7805.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Then place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right click the component properties to change the required value
5. Add voltage probe at input and output of diagram.
6. Select the graph mode & choose AC sweep analysis option
7. Right click in the graph window and select add traces(input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulate graph
9. Observe input & output waveforms and analysis the results.
CIRCUIT SIMULATION
Result
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
By using ± 5V and ±12V regulated power supply using Proteus; we
understand that the voltage regulators play an important role in any power supply unit. The
primary
purpose of a regulator is to aid the rectifier and filter circuit in providing a constant DC
voltage. To avoid variations in the load or due to fluctuations in the AC
line voltage, IC 7805 and 7812 regulators are used.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 05
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
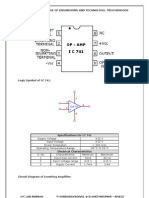
Study and Analysis of Non inverting amplifier.
Aim:
Design, simulate and analyze non inverting amplifier using IC 741 using following
tools
1) Analogue analysis
2) Frequency analysis
3) Noise analysis
4) Distortion analysis
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of Non inverting amplifier
• To understand the circuit arrangement of Non inverting amplifier
• To understand the simulation procedure of Non inverting amplifier circuit
using proteus.
• To observe & analyze the output waveforms using different analysis tools.
Outcomes:
• Able to understand principal of working of Non inverting amplifier circuit.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of Non inverting amplifier circuit.
• Able to understand the simulation procedure Non inverting amplifier circuit
using Proteus.
• Able to observe & analyse the circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
• To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction:
Non-inverting amplifier is one of the most popular op amp circuits similar to Op amp
inverting amplifier circuit. It provides a gain to the input signal without any change in the
polarity. If a sine wave is fed to the input of this op amp non inverting amplifier, the output
will be an amplified sine wave with zero phase shift.
Here the input is applied to the non inverting terminal of the op amp. The non
inverting amplifier gain is given by the expression A=1+R3/R2 where R2 is the feedback
resistance and R3 is the input resistance. The input impedance of non-inverting amplifier is
extremely large, typically 100MΩ.
Working of Non- inverting Amplifier:-
The second basic configuration of an operational amplifier circuit is that of a Non-
inverting Amplifier. In this configuration, the input voltage signal, (Vin ) is applied
directly to the non-inverting ( + ) input terminal which means that the output gain of
the amplifier becomes "Positive" in value. The result of this is that the output signal is
"in-phase" with the input signal.
Feedback control of the non-inverting amplifier is achieved by applying a small part
of the output voltage signal back to the inverting ( - ) input terminal via a R3- R2
voltage divider network, again producing negative feedback. This closed-loop
configuration produces a non-inverting amplifier circuit with very good stability, a
very high input impedance, R1 approaching infinity, as no current flows into the
positive input terminal, (ideal conditions) and a low output impedance, Rout as shown
below.
The working of non inverting amplifier is similar to that of inverting amplifier except
that the output has no phase shift here.
The resistors R2 and R3 form a voltage divider network.
A negative feedback is provided by applying a little of output voltage to the inverting
input terminal through the potential divider network R2 and R3.
The voltage gain of the amplifier is determined by the ratios of R3 and R2 since Gain,
A=1+R3/R2
So the amplitude of the output voltage signal can be varied by varying either of the
resistors R2 or R3
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Theory:-
• Closed loop configuration
1) Non-inverting amplifier
2) Inverting amplifier
3) Differential amplifier
1. Non-inverting amplifier
Non-inverting amplifier is voltage series feedback amplifier. The input signal is
given to the non-inverting terminal of op-amp & output signal is in same phase with input. So
it is called as non inverting amplifier.
• Closed loop voltage gain
The closed loop voltage gain is given by,
Af=Vo/Vin . . . . . . . . . . . .(1)
The output voltage Vo is given by,
Vo=A*(Vid)
=A*(V1-V2) . . . . . . . . . (2)
where V1=Vin
V2=Vf
Therefore feed back voltage Vf is given by,
Vf=(R2/R2+Rf)*Vo . . . . . . . . . . (3)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Therefore output voltage Vo is given by,
Vo=A*(Vin-Vf)
Vo=A*(Vin-R2*Vo/R2+Rf)
Vo(1+AR2/R2+Rf)=AVin
Vo/Vin=A/(R2+Rf+AR2/R2+Rf)
Af=A(R2+Rf)/(R2+Rf+AR2) . . . . .(4)
Generally A is very large.
Therfore AR2>>R2+Rf &
R2+Rf+AR2=AR2
Therefore Af=(R2+Rf)/R2
Af=1+Rf/R2 . . . . . . . . . . .(5)
The gain of voltage seriers feedback amplifier is determined by the two resistances R2& Rf.
• Closed loop voltage gain (Af) in terms of open loop gain(A)
The feedback voltage is given by,
Vf=(R2/R2+Rf)*Vo
Vf/Vo=R2/R2+Rf
Vf/Vo=B=R2/R2+Rf . . . . . . . . . . . .(6)
The closed loop gain (Af) is expressed as follows from Eq (4)
Af=A(R2+Rf)/(R2+Rf+AR2) . . . . . . (7)
Rearranging Eq (7),we get,
Af=A/(1+AB)
where B=R2/R2+Rf
• Input resistance with feedback
Input resistance of op-amp with feedback is the equivalent resistance which
observed from the non-inverting input.
Let Rf is the feedback resistance & Ri is the input resistance of op-amp.So the input
resistance of op-amp with feedback is given by,
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Rif=Vin/Iin . . . . . . . . . . . . . .(8)
where Iin=Vid/Ri
Rif=Vin/(Vid/Ri) . . . . . . . . .(9)
However,
Vid=Vo/A & Vo=(A/1+AB)*Vin . . . . . .(10)
substitute the Eq (10) in Eq (9), we get,
Rif=Vin/(Vo/ARi)
=Ri*Vin/(Vo/A)
=Ri*Vin/((A/1+AB)*(Vin/A))
=Ri*(1+AB) . . . . . . . . .. . . (11)
So from Eq (11), we conclude that the input resistance of non-inverting amplifier with
feedback is (1+AB) times Ri.
• The output resistance (Ro) with feedback
The output resistance (Ro) wiyh feedback is the resistance that is observed backward
from the output terminal.
The analysis is done by using thevenin's theorem of circuit. In this the independant
source is reduced to zero and apply external voltage Vo and current Iois calculated.
Rof=Vo/Io . . .. . . . . . . .(12)
By applying kirchoff's current law,
Io=Ia+Ib . . . . . . . . .. . (13)
since (Rf+R2)||Ri>>Ro & Ia>>Ib
Therefore by applying kirchoff's voltage law for output loop,
vo-RoIo-AVid=0
Io=Vo-AVid/Ro . . . . . . . .(14)
However, Vid=V1-V2
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
where V1=0
V2=Vf
therefore Vid=-Vf
=-(R2/R2+Rf)*Vo
=-BVo . . . . . . . . . . . . . (15)
substituting the value of Vid in Eq (14), we get,
Io=Vo-A(-BVo)/Ro
Io=Vo+ABVo/Ro . . . . . . . . (16)
substitute the value of Io from Eq (16) in Eq (12),
Rof=Vo/(Vo+ABVo/Ro)
=Ro/1+AB . . . . . . . . . . (17)
From Eq (17), we can conclude that the output resistance of voltage series
feedback amplifier is 1/1+AB times Ro.
Non-inverting amplifier circuit using Proteus
Components Required :
Name Description Number of components
required
IC IC 741 1
Multi cell Multi cell 2
battery battery(12V)
RES Resistor(10K) 3
PULSE As Input 1
GND Ground 1
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
Step 1:-Selection of components
1) Selection of OP-AMP:-
Activate component mode
Go to pick components (click on ‗P‘)
Type 741 in search section
Select IC 741
Place the component in circuit
2) Selection of Resistors:-
Again go to pick component section
And select three generic resistors
Place these 3 resistors in circuit at required place
Then go to edit properties by right clicking on that component
Set each resistor to 10 kilo ohm
3) Selection of batteries:-
Again go to pick component section
Then go to Miscellaneous
And select multi cell batteries
Place those batteries in circuit
Choosing edit properties option set batteries to 12V
4) Select sine generator from generator section
5) Do the connections (wiring)as per circuit diagram
6) Add voltage probe at the 6 th and pin of operational amplifier (741)
Step 2:-Simulation
Graph Analysis:-
Go to graphs option and select analogue
Drag that graph in circuit section
Insert voltage probe in graph section
Go to ‗add trace‘ and add the traces of input and output
Right click and activate simulate graph option
Repeat the same steps for noise , frequency , distortion analysis.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
we have studied operation of non-inverting amplifier. We have observed input and
output waveforms for the given gain parameter. Also with the help of analogue, frequency,
noise and distortion options and different graphs we have analysed the noninverting
amplifier.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 06
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Transient response analysis using RLC components.
Aim:
Design a simple circuit using RLC Component to observe transient response using
Proteus.
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of Transient Response of RLC Circuit
• To understand the circuit arrangement of Transient Response of RLC Circuit
• To understand the procedure of Transient Response of RLC Circuit circuit
using proteus.
• To observe the simulation of circuit
Outcomes:
• Able to study Transient Response of RLC Circuit.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of Transient Response of RLC
Circuit.
• Able to understand the procedure of Transient Response of RLC Circuit in
proteus.
• Able to observe the simulation of circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
• To enable to innovate ,design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction-
An RLC circuit (or LCR circuit or CRL circuit or RCL circuit) is an electrical circuit
consisting of a resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor, connected in series or in parallel. The
RLC part of the name is due to those letters being the usual electrical symbols for resistance,
inductance and capacitance respectively. The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current
and will resonate in a similar way as an LC circuit will. The main difference that the presence
of the resistor makes is that any oscillation induced in the circuit will die away over time if it
is not kept going by a source. This effect of the resistor is called damping. The presence of
the resistance also reduces the peak resonant frequency somewhat. Some resistance is
unavoidable in real circuits, even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. A
pure LC circuit is an ideal which really only exists in theory.
There are many applications for this circuit. They are used in many different types
of oscillator circuits. Another important application is for tuning, such as in radio receivers or
television sets, where they are used to select a narrow range of frequencies from the ambient
radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can
be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning
application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as
a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by
a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis
Circuit diagram –
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Circuit arrangement:
The circuit arrangement of An RLC circuit as shown in fig. It uses one Resistor,
Inductor and Capacitor connected in series or in parallel. Output is taken across the capacitor
of 10uF.
Theory:
Transient response-
a transient response or natural response is the response of a system to a change from
equilibrium. The transient response is not necessarily tied to "on/off" events but to any event
that affects the equilibrium of the system. The impulse response and step response are
transient responses to a specific input (an impulse and a step, respectively
Plot showing underdamped and overdamped responses of a series RLC circuit. The critical
damping plot is the bold red curve. The plots are normalised for L=1, C=1 and
The differential equation for the circuit solves in three different ways depending on the value
of . These are underdamped ( ), overdamped ( ) and critically damped ( ). The
differential equation has the characteristic equation.
The roots of the equation in s are,[6]
The general solution of the differential equation is an exponential in either root or a linear
superposition of both,
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
The coefficients A1 and A2 are determined by the boundary conditions of the specific problem
being analysed. That is, they are set by the values of the currents and voltages in the circuit at
the onset of the transient and the presumed value they will settle to after infinite time.[7]
Properties-
Typical second order transient system properties
Rise time
Rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value
to a specified high value. Typically, these values are 10% and 90% of the step height.
Overshoot
Overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It is often associated with
ringing.
Settling time
Settling time is the time elapsed from the application of an ideal instantaneous step
input to the time at which the output has entered and remained within a specified error
band.
Delay time
The delay time is the time required for the response to reach half the final value the
very first time.
Peak time
The peak time is the time required for the response to reach the first peak of the
overshoot.
RLC circuit using Proteus
Components required:
Name Description Number of components
required
RES Resistor 1
CAP Capacitor 1
INDUC Inductor 1
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
PULSE As Input 1
GND Ground 1
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to pick device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right click and select edit properties to change the values.
5. Add voltage probe at input and output.
6. Select the ‗graph mode‘ & choose analouge Analysis graph window.
7. Right click and select ‗add traces‘ (input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulation graph.
9. Observe and analysis input & output waveforms.
Circuit Stimulation Using Proteus
RESULT
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
We understand the transient response using RLC circuit in proteus software. We
observe the simulation of circuit & study the transient response.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 07
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Simulation of Astable Multivibrator using transistor using Proteus.
Aim:
Design & simulate the Astable Multivibrator using transistor.
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of Astable Multivibrator.
• To understand the circuit arrangement of Astable
Multivibrator
• To understand the procedure of Astable Multivibrator using transistor circuit
using proteus.
• To observe the waveforms and analyze the circuit
Outcomes:
• Able to study Astable Multivibrator using transistor.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of Astable Multivibrator
• Able to understand the procedure of Astable Multivibrator using transistor
circuit using proteus.
• Able to observe the simulation and analysis of circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
• To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Introduction:
An astable multivibrator is a regenerative circuit consisting of two amplifying
stages connected in a positive feedback loop by two capacitive-resistive coupling networks.
The amplifying elements may be junction or field-effect transistors, vacuum tubes,operational
amplifier or other types of amplifier. The example diagram shows bipolar junction transistors.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
The circuit is usually drawn in a symmetric form as a cross-coupled pair. Two
output terminals can be defined at the active devices, which will have complementary states;
one will have high voltage while the other has low voltage, (except during the brief
transitions from one state to the other)
Circuit Diagram:
Theory:
Operation:
The circuit has two stable states that change alternatively with maximum transition
rate because of the "accelerating" positive feedback. It is implemented by the coupling
capacitors that instantly transfer voltage changes because the voltage across a capacitor
cannot suddenly change. In each state, one transistor is switched on and the other is switched
off. Accordingly, one fully charged capacitor discharges (reverse charges) slowly thus
converting the time into an exponentially changing voltage. At the same time, the other
empty capacitor quickly charges thus restoring its charge (the first capacitor acts as a time-
setting capacitor and the second prepares to play this role in the next state). The circuit
operation is based on the fact that the forward-biased base-emitter junction of the switched-
on bipolar transistor can provide a path for the capacitor restoration
State 1 (Q1 is switched on, Q2 is switched off):
In the beginning, the capacitor C1 is fully charged (in the previous State 2) to the
power supply voltage V with the polarity shown in Figure 1. Q1 is on and connects the left-
hand positive plate of C1 to ground. As its right-hand negative plate is connected to Q2 base,
a maximum negative voltage (-V) is applied to Q2 base that keeps Q2 firmly off. C1 begins
discharging (reverse charging) via the high-value base resistor R2, so that the voltage of its
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
right-hand plate (and at the base of Q2) is rising from below ground (-V) toward +V. As Q2
base-emitter junction is backward-biased, it does not conduct, so all the current from R2 goes
into C1. Simultaneously, C2 that is fully discharged and even slightly charged to 0.6 V (in the
previous State 2) quickly charges via the low-value collector resistor R4 and Q1 forward-
biased base-emitter junction (because R4 is less than R2, C2 charges faster than C1). Thus C2
restores its charge and prepares for the next State 2 when it will act as a time-setting
capacitor. Q1 is firmly saturated in the beginning by the "forcing" C2 charging current added
to R3 current; in the end, only R3 provides the needed input base current. The resistance R3
is chosen small enough to keep Q1 (not deeply) saturated after C2 is fully charged.
When the voltage of C1 right-hand plate (Q2 base voltage) becomes positive and
reaches 0.6 V, Q2 base-emitter junction begins diverting a part of R2 charging current. Q2
begins conducting and this starts the avalanche-like positive feedback process as follows. Q2
collector voltage begins falling; this change transfers through the fully charged C2 to Q1 base
and Q1 begins cutting off. Its collector voltage begins rising; this change transfers back
through the almost empty C1 to Q2 base and makes Q2 conduct more thus sustaining the
initial input impact on Q2 base. Thus the initial input change circulates along the feedback
loop and grows in an avalanche-like manner until finally Q1 switches off and Q2 switches on.
The forward-biased Q2 base-emitter junction fixes the voltage of C1 right-hand plate at 0.6 V
and does not allow it to continue rising toward +V.
State 2 (Q1 is switched off, Q2 is switched on):
Now, the capacitor C2 is fully charged (in the previous State 1) to the power supply
voltage V with the polarity shown in Figure 1. Q2 is on and connects the right-hand positive
plate of C2 to ground. As its left-hand negative plate is connected to Q1 base, a maximum
negative voltage (-V) is applied to Q1 base that keeps Q1 firmly off. C2 begins discharging
(reverse charging) via the high-value base resistor R3, so that the voltage of its left-hand plate
(and at the base of Q1) is rising from below ground (-V) toward +V. Simultaneously, C1 that
is fully discharged and even slightly charged to 0.6 V (in the previous State 1) quickly
charges via the low-value collector resistor R1 and Q2 forward-biased base-emitter junction
(because R1 is less than R3, C1 charges faster than C2). Thus C1 restores its charge and
prepares for the next State 1 when it will act again as a time-setting capacitor...and so on...
(the next explanations are a mirror copy of the second part of Step 1).
Output pulse shape
The output voltage has a shape that approximates a square waveform. It is
considered below for the transistor Q1.
During State 1, Q2 base-emitter junction is backward-biased and the capacitor C1 is
"unhooked" from ground. The output voltage of the switched-on transistor Q1 changes
rapidly from high to low since this low-resistive output is loaded by a high impedance load
(the series connected capacitor C1 and the high-resistive base resistor R2).
During State 2, Q2 base-emitter junction is forward-biased and the capacitor C1 is "hooked"
to ground. The output voltage of the switched-off transistor Q1 changes exponentially from
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
low to high since this relatively high resistive output is loaded by a low impedance load (the
capacitance C1). This is the output voltage of R1C1 integrating circuit.
To approach the needed square waveform, the collector resistors have to be low resistance.
The base resistors have to be low enough to make the transistors saturate in the end of the
restoration (RB < β.RC).
Astable Multivibrator using transistor circuit using proteus.
Component:
Name Description Number of
components required
RES Resistor 4
CAP Capacitor 2
VDC Dc voltage 1
source
TRANS. Transistor 2
GND Ground 1
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Then place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right clik the component properties to change the required value
5. Add voltage probe at input and output of diagram.
6. Select the graph mode & choose AC sweep analysis option
7. Right click in the graph window and elect add traces(input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulate graph
9. Observe input & output waveforms and analysis the results.
CIRCUIT SIMULATION USING PROTES
RESULT
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
We can understand the working of Astable Multivibrator . By using proteus we
can observe the simulation of circuit & analyse the waveforms taken across capacitor C2.
Astable multivibrator has no stable state. It generates square wave of predetermined
frequency. Hence it is a square wave generator.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 08
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Simulation of Astable Multivibrator using 555 using Proteus.
Aim:
Design & stimulate the Astable Multivibrator using 555.
Objectives:
To understand principal of working of Astable Multivibrator.
To understand the circuit arrangement of Astable
Multivibrator
To study Astable Multivibrator using IC 555.
To understand the procedure of ―Astable Multivibrator using IC 555‖ circuit
using proteus.
To observe the simulation of circuit.
Outcomes:
Able to study Astable Multivibrator using IC 555.
Able to understand the circuit arrangement of Astable Multivibrator
Able to understand the procedure of ―Astable Multivibrator using IC 555‖
circuit using proteus.
Able to observe the simulation of circuit.
Programme Education Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing ,
communication , computer network and control system.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Introduction:
Astable Multivibrator can be designed by using 555 timer IC, Op Amps and also
using transistors. The 555 IC provide accurate time delay from mille seconds to hours. The
frequency of oscillation can be controlled manually by simple modification. It suitable for
circuit designers with a relatively stable, cheap, and user-friendly integrated circuit for both
monostableandAstableapplications.
The 555 timer IC was first introduced around 1971 by the Signetics Corporation as the
SE555/NE555. This is a simple 555 timer circuit project.
Astable Multivibrator is simply an oscillator circuit that produces continuous pulses. The
frequency can be controlled by changing the values of R1, R2 and C1. You can construct
Astable multivibrator using transistors also, but the 555 circuit is comparatively simple.
we have to design the Astable Multivibrator using proteus. It is easy to design on the
proteus.
The Astable multivibrator generates a square wave, the period of which is
determined by the circuit external to IC 555. The Astable multivibrator does not require any
external trigger to change the state of the output. Hence the name free running oscillator. The
time during which the output is either high or low is determined by the two resistors and a
capacitor which are externally connected to the 555 timer.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Circuit Diagram:
INTERNAL DIAGRAM OF IC 555
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Circuit arrangement:
The circuit arrangement of Astable Multivibrator as shown in fig. It uses one IC
555 as an Astable multivibrator. In this type of arrangement two resistors and two capacitors
are used, the output is taken across pin no 3 of IC 555 as shown in figure.
Theory:
The circuit diagram for the Astable multivibrator using IC 555 is shown here.
The astable multivibrator generates a square wave, the period of which is determined by the
circuit external to IC 555. The Astable multivibrator does not require any external trigger to
change the state of the output. Hence the name free running oscillator. The time during which
the output is either high or low is determined by the two resistors and a capacitor which are
externally connected to the 555 timer.
The above figure shows the 555 timer connected as an Astable multivibrator.
Initially when the output is high capacitor C starts charging towards Vcc through RA and RB.
However as soon as the voltage across the capacitor equals 2/3 Vcc ,
comparator1 triggers the flip-flop and the output switches to low state.
Now capacitor C discharges through RB and the transistor Q1. When voltage
across C equals 1/3 Vcc, comparator 2‘s output triggers the flip- flop and the output goes high.
Then the cycle repeats. The capacitor is periodically charged and discharged between 2/3 Vcc
and 1/3 Vcc respectively. The time during which the capacitor charges from 1/3 Vcc to 2/3 Vcc
is equal to the time the output remains high and is given by
Tc =0.693(RA+RB)C
Where, RA and RB are in ohms and C is in Farads. Similarly the time during which
the capacitor discharges from 2/3 Vcc to 1/3 Vcc is equal to the time the output is low and is
given by
td =0.693(RB) C
Thus the total time period of the output waveform is
T=td+td=0.693(RA+2RB) C
Therefore the frequency of oscillation
f=1/T=1.45/ (RA+2RB) C
The output frequency, f is independent of the supply voltage Vcc
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Working of Astable Multivibrator:
Principle of working:
The Astable multivibrator generates a square wave, the period of which is determined by
the circuit external to IC 555. The Astable multivibrator does not require any external trigger
to change the state of the output. The time during which the output is either high or low is
determined by the two resistors and a capacitor which are externally connected to the 555
timer.
Consider the flip flop is initially cleared, when the power is switched on, then the
output of inverter will be HIGH.
Now the capacitor C1 starts charging through R1 and R2. (Discharge transistor Q1 is
OFF)
When the capacitor voltage exceeds 2/3 Vcc, the upper comparator output will be
High, it Reset the control flip flop.
So the Q output of control flip flop will be LOW and Q‘ will be High. So the final
output from Inverter is LOW
At the same time, the discharge transistor Q1 turns ON and the capacitor starts
discharge through R2
When the capacitor voltage less than 1/3 Vcc, the lower comparator output will be
high, then the control flip flop get set to High. (Q=1, Q‘=0, Final output=1)
Now the discharge transistor Q1 if OFF and then capacitor starts charging. This
process continues.
The LED connected at the output will glows according to the output status.
4th pin is Reset pin, a Low voltage at this pin resets the IC. The Low signal is applied
to the base terminal of reset transistor Q2. Then it turns ON followed by Discharge
capacitor Q1 and capacitor discharges.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Charging Discharging
Resetting
Advantages and Disadvantages of Astable Multivibrator:
(i)Advantages:
1. It is easy and quick to design an Astable using a 555 (also easy to troubleshoot).
2. The 555 timer can source or sink large amounts of current (some handle200mA).
3. It may require fewer devices or connections (1 IC, a cap and two resistors).
4. The 555 may have less frequency drift with temperature changes.
5. Some 555 timers have a wide input voltage range (3.5 to 18V).
555s have a large frequency range.
(ii)Disadvantages:
1.A disadvantage of the 555 is a poor rise and fall time which may cause problems for some
edge-triggered devices.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Astable Multivibrator using IC 555 circuit using proteus.
Component:
Name Description Number of
components required
RES Resistor 2
CAP Capacitor 2
555 Timer 1
VDC Dc voltage 1
source
GND Ground 3
Specifications:
The most important characteristics which are required to be specified for a circuit are
given below :
Supply voltage (VCC) 4.5 to 15 V
Supply current (VCC = +5 V) 3 to 6 mA
Supply current (VCC = +15 V) 10 to 15 mA
Output current (maximum) 200 mA
Maximum Power dissipation 600 mW
Operating temperature 0 to 70 °C
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Then place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right clik the component properties to change the required value
5. Add voltage probe at input and output of diagram.
6. Select the graph mode & choose AC sweep analysis option
7. Right click in the graph window and elect add traces(input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulate graph
9. Observe input & output waveforms and analysis the results.
CIRCUIT SIMULATION
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Result
Conclusion:
We can understand the working of Astable Multivibrator as well as the
detailed circuit of IC 555.By using proteus we can observe the simulation of circuit & study
the waveforms taken across pin no.3 of IC 555.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 09
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Simulate simple RC circuit using AC sweep analysis.
Aim:
To simulate RC circuit (low pass filter) using Ac sweep analysis.
Objectives:
• To understand principal of working of RC circuit.
• To understand the circuit arrangement of RC circuit.
• To study simple RC circuit using Ac sweep analysis.
• To understand the procedure of simple RC circuit using Ac sweep circuit
using proteus.
• To observe the simulation of circuit.
Outcomes:
• Able to understand principal of working of simple RC circuit.
• Able to understand the circuit arrangement of simple RC circuit.
• Able to study simple RC circuit using Ac sweep analysis.
• Able to understand the procedure of simple Rc circuit using Ac sweep analysis
circuit using proteus.
• Able to observe the simulation of circuit.
Program Education Objective(s) (PEO) Satisfied: 2, 3
• To enable student to analyse solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to
use modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
• To enable to innovate, design and develop a variety of electronic and computer
based components and system for applications including signal processing,
communication, and computer network and control system.
Principle:
An simple RC circuit in which output taken across capacitor ‘c’. At low frequencies capacitor
will occur maximum reactance hence acts as an open circuit. Resulting in transferring low
frequency signal to the output at high frequencies capacitive reactance is negligible hence it
act as an short transfer to the output.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Circuit Diagram:
Circuit arrangement:
The circuit arrangement of simple RC circuit as shown in fig. it consists of resister
and capacitor. Output taken across capacitor as shown in fig. in these circuit Vr is voltage
across resister and Vc is voltage across capacitor.
Theory:
A capacitor is a device for storing charge. The ability of a capacitor to hold a charge is
measured by its capacitance C. For a capacitor, Q = CV, where Q is the charge on one of the
capacitor plates, C is the capacitance of the capacitor, and V is the potential difference
maintained across the capacitor plates. The unit of capacitance is the Farad (F), where one
Farad equals one Coulomb per volt (1F = 1C/V).
If a capacitor is connected to a battery, it will cause a charge +Q to develop on one plate and
a charge -Q to develop on the other. If the battery is removed from the circuit the capacitor is
connected to a resistor, then the capacitor will discharge through the resistor. The voltage
across the resistor is given by V = IR, where I is the current through the resistor at a given
time, and R is the resistance of the resistor. Since V = Q/C, = we can also write
I = V/R = Q/RC
As the capacitor discharges, Q becomes smaller, and I also become smaller.
The current at any time t is given by:
I = I0e-t/RC = I0e-t/τ
Where I0 = initial value of the current, ti = time elapsed in seconds since the discharging
began τ = RC = capacitive time constant for the RC circuit, and e = 2.71828... .
AC Sweep:
In simple RC circuit we can apply AC sweep. For Ac sweep analysis is nothing but it is
going to calculate to frequency response of the circuit. over range of frequencies the
frequency response is nothing but the magnitude Vs frequency and phase Vs frequency. If
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
the frequency is double it is called an octave. If the frequency is increased by the factor of
10 it is called as decay increase. The decade increase in frequency the magnitude changes by
-20 and the slope of magnitude block is -20db/dc there are different type of sweep analysis.
We have to consider following certain parameter in the frequency sweep. i.e. starting
frequency and ending frequency. We have to specify the scale both linear, octave and
decade.
• Linear sweep :
The frequency is sweep linearly from the starting frequency to the
ending frequency with a step (number of step) the next frequency generated by a
constant to a present value.
• Octave sweep :
The frequency is sweep logarithmically by octave the next frequency is
generated by octave the next frequency is generated by multiplying a present value
by a constant the larger than the unity octal sweep is use when frequency range is
wide.
• Decade sweep :
The frequency is sweep logarithmically by decade. Decade is used if
frequency range is widest.
How to do the AC Sweep Analysis using Proteus Simulation Tool?
Introduction:
• AC sweep analysis is nothing but a frequency response analysis.
• It is a linear analysis (small-signal analysis).
• It means it only considers the gain and phase response of the circuit; it does not limit
voltages or currents.
• The non linear devices (like transistor amplifier) must be liberalized to run the
analysis. To do this conversion, we have to
a. Compute the DC bias point for the circuit
b. Compute the complex impedance and/or transconductance values for each value for
each device at this bias point.
c. Perform the linear circuit analysis at the frequencies of interest by using simplifying
approximations.
• The Proteus tool will take care of all these activities.ie,
• The Proteus tool calculates the small-signal response of the circuit to a combination of
inputs by transforming it around the bias point and treating it as a linear circuit.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Working of a Simple RC Circuit:
When the toggle switch is in the open position shown in the diagram, the capacitor is
not connected the Electromotive Force, emf, and, unless the capacitor was previously
charged, there will be no charges stored in the capacitor (i.e., q = 0) and the potential
difference between the plates of the capacitor will correspondingly be zero as well.
If the switch is toggled so that it connects the capacitor to the Electromotive Force,
charges will tend to accumulate on the plates of the capacitor, + on one plate, _ on the
other. This will continue until the accumulated charge creates a potential difference
(Vc) between the two plates that is numerically equal to the electromotive force. That
is, when:
Vc = ,
Current flow through the connecting wires will cease (i.e., I = 0).
When the switch is toggled to its alternate position, (i) the emf is bypassed, (ii) the
two plates of the capacitor are connected, and (iii) the charges stored on the capacitor
will tend to pass through the connecting wire to the opposite plate. In other words,
the charged capacitor will discharge.
There are 2 important things to remember about the electrical properties of R-C
circuits:
1. When the capacitor (C) is fully charged, the following relationship
holds:
q = C Equation 1a
Where q is the total amount of charge stored by the capacitor, C is the capacitance of
the capacitor, and is the electromotive force that is actually charging the capacitor.
Note that q = 0 when the capacitor is discharged. Also note that the equation may be
rearranged thus:
q/C = = Vc Equation 1b
Meaning that placing excess + on one plate of the capacitor and excess – on the other
plate will generate a potential difference between the plates.
2. Because of the presence of a resistance (R) in the circuit, current flow through the
circuit is slowed. As a result, changing the amount of charge stored on the plates of
the capacitor requires time. For example, if you were to start with a completely
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
discharged capacitor (i.e., q = 0 and Vc = 0) and connect it to a battery, the charging
of the capacitor would be described by an exponential equation,
qt = C(1 e-t/RC) Equation 2a
And if C = 1, = 10 and R = 1, the graph of qt vs. time would look like this:
Simple RC Circuit using AC sweep circuit using proteus.
Component:
Name Components Used Description Number of
components required
RES RC05 Resistor 2
CAP CAP Capacitor 2
GND SMB_SPL0 Ground 3
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
• From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
• In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
• Place the all components on the Proteus screen.
• Right click and select edit properties & select the proper value.
• Add voltage probe at input and output of circuit.
• Select the graph mode then add trace in graph window.
• Right click & select add traces (input & output trace).
• Right click & activate simulation graph
• Observe the input & output waveforms.
CIRCUIT SIMULATION USING PROTEUS
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
We can conclude that ac sweep analysis is a linear analysis; it only considers
the gain and phase response of the circuit. It gives linear frequency response. The
frequency is swept linearly from the starting frequency to the ending frequency with
a step the next frequency generated by a constant to a present value.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 10
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Fourier and Audio analysis using Proteus
Aim:
To study Fourier & Audio analysis using Proteus.
Objectives:
To understand principal of working of Fourier Transform
To understand the circuit arrangement of Fourier Transform
To understand the concept of Fourier Transform using proteus.
To observe the simulation of circuit and analyze using Fourier Transform.
Outcomes:
Students will be able to study Fourier Transform.
Students will be able to understand the concept of Fourier Transform
Students will be able to observe the simulation of circuit using Fourier Transform and
its application.
Programme Educational Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
To enable student to analyse, solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to use
modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and computer based
components and system for applications including signal processing , communication
, computer network and control system.
Theory:-
Development of Fourier Transform From Fourier Series:-
The exponential form of Fourier series representation of a periodic signal is given by,
+∞ 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x(t)= −∞ 𝑐 n𝑒 ....1
Where,
1 𝑇
2 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x(t)= 𝑇 −𝑇 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 d(t) ….2
2
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
In the Fourier representation using equation (1), the Cn for various values of
n are the spectral components of the signal x(t), located at intervals of fundamental frequency
𝛺. Therefore the frequency spectrum is discrete in nature.
The Fourier representation of a signal using equation (1) is applicable for
periodic signals. For Fourier representation of non periodic signals, let us consider that the
fundamental period tends to infinity, the fundamental frequency Ω tends to zero or becomes
very small. Since fundamental frequency Ω is very small, the spectral components will lie
very close to each other and so the frequency spectrum becomes continuous.
In order obtain the Fourier representation of non -periodic signal let us
consider that the fundamental frequency Ω0 is very small.
Let,
Ω0→ ∆ Ω0 .
On replacing Ω0 by ∆ Ω0 in equation (1) we get,
+∞ 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡
x(t)= −∞ 𝑐 n𝑒
On substituting for Cn in the above equation (2). (By taking Ƭ as dummy variable for
integration ) .
we get,
1 𝑇
+∞ 2 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x(t)= 𝑛=−∞. [𝑇 −𝑇 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 d(t)] 𝑒 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡 ……(3).
2
We know that,
2𝜋 1 Ω
Ω0 =2𝜋f0= ; ∴ = …(4)
𝑇 𝑇 2𝜋
Since,
1 Ω
Ω0→ ∆ Ω0 . = 2𝜋
𝑇
1
On substituting for from equation (4) in equation (3) we get ,
𝑇
1 𝑇
+∞ 2 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x(t)= 𝑛=−∞. [𝑇 −𝑇 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 d(t)] 𝑒 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡 .
2
1 1 𝑇
+∞ 2 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x(t)=2𝜋 𝑛=−∞. [𝑇 −𝑇 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 d(t)] 𝑒 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡 ∆ Ω.
2
Ω The fundamental period T tends to infinity. On letting limit T tends
to infinity in the above equation we get,
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
𝐿𝑡 1 1 𝑇
+∞ 2 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡
x (t)= 𝑡 ∞ 2𝜋 𝑛=−∞. [𝑇 −𝑇 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 d(t)] 𝑒 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡 ∆ .
2
When T ∞;Σ ∫; ∆Ω Ω.
+∞ +∞
x (t)= −∞
( −∞ 𝑥(Ƭ) 𝑒 −𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡 dƬ ) 𝑒 𝑗𝑛𝛺𝑡 dΩ. …..(5)
+∞
x(t)= −∞
𝑥(𝑗 Ω) 𝑒 𝑗𝑛 ∆𝛺𝑡 dΩ.
+∞
X(jΩ)= −∞
𝑥 (𝑡)𝑒 −𝑗𝑛 ∞𝑡 dƬ …(6)
The equation (6) Fourier transform of x (t) and equation (5) is inverse
Fourier transform of x (t).
Since the equation (6) extracts the frequency component of the signal ,
transformation using equation (6) is also called as analysis of the signal x (t).Since the
equation (5) combines frequency components of the signal , the inverse transformation using
equation (5) is also called as synthesis of the signal x (t).
Definition of fourier transform :_-
Let, x (t) = Continuous time signal
X (jΩ) = Fourier transform of x(t)
The Fourier transform of continuous time signal, X(t) is defined as,
+∞
X(jΩ)= −∞
𝑥 𝑡 𝑒 −𝑗 Ωt 𝐷𝑡
Also, x(jΩ) is denoted as F{x(t)} where ―F‖ is symbol used to denote the Fourier transform
operation.
+∞
𝐹{𝑥(𝑡)} = −∞
𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 −𝑗 Ωt dt
Note:-Sometimes the Fourier Transform is expressed as a function of cylic frequency F,
rather than radian frequency Ω .The Fourier transform as a function of cyclic frequency F, is
defined as,
+∞
X(jF)= −∞ 𝑥(𝑡) 𝑒 −𝑗 2FПt dt
Condition for Existence of Fourier Transform :-
The Fourier transform of x(t) exists if it satisfies the following Dirichlet condition.
1.The x(t) be absolutely integrable .
+∞
i.e. −∞
𝑥 𝑡 < ∞
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
2.The x(t) should have a finite number of Maxima and minima within any finite interval.
3. The x(t) can have a finite number of discontinuities within any interval.
Definition of inverse Fourier Transform:-
The inverse fourier transform of X(j )is defined as,
1 +∞
X(t)=F-1 X jΩ = 2П −∞
𝑋 𝑗Ω 𝑒 𝑗 Ω𝑡 𝑑 Ω
The signals x(t) and X(j) are called Fourier Transform pair and can be expressed as shown
below,
𝐹
x(t) 𝑋(𝑗Ω)
Note:-
When Fourier transform is expressed as a function of cyclic frequency F,the inverse Fourier
transform is defined as,
+∞
X(t)=𝐹 −1 𝑋 𝑗Ω = −∞ 𝑥(𝑗𝐹) 𝑒 𝑗 2FПt dF
Frequency spectrum using Fourier Transform:-
The X(jΩ) is a complex function of Ω .Hence it can be expressed as a sum of real part and
imaginary part as given below.
X(jΩ)=𝑋𝑟 𝑗Ω + 𝑗𝑋 𝑗Ω
where ,
𝑋𝑟 𝑗Ω = 𝑅𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑋(𝑗Ω)
𝑋𝑖 𝑗Ω = 𝐼𝑚𝑎𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑟𝑦 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑋(𝑗Ω)
The magnitude of X(jΩ) is called Magnitude Spectrum.
Magnitude Spectrum, 𝑋 𝑗Ω = 𝑋𝑟 2 (𝑗Ω) + 𝑋𝑖 2 (𝑗Ω)
Or
Magnitude spectrum , 𝑋(𝑗Ω) = 𝑋 𝑗Ω 𝑋 ∗ (𝑗Ω)
where , 𝑋 ∗ 𝑗Ω = 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑗𝑢𝑔𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑋(𝑗Ω)
The phase of X(jΩ) is called Phase spectrum.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
𝑋 𝑗Ω
Phase spectrum=<𝑋 𝑗Ω = tan−1 𝑋 𝑖
𝑟 𝑗Ω
The magnitude spectrum will always have even symmetry and phase spectrum will
have Odd symmetry .The magnitude and phase spectrum together called Frequency spectrum.
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right click the component properties to change the required value
5. Add voltage probe at input and output circuit points.
6. Select the graph mode & choose Fourier & Audio analysis option.
7. Right click in the graph window and select add traces (input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulate graphs.
9. Observe output waveforms and analysis the results.
Circuit Simulation
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Fourier analsis:-
Audio analysis:-
Conclusion:
We have understood the concept of Fourier Transform and audio analysis.We
can observe from waveforms that Fourier Transform is useful to find out major spectral
components from the given signals.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Dr. V. P. Shetkari Shikshan Mandal’s
Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology,
Budhgaon-416304
Department of Electronics Engineering
Circuit Simulation
Experiment No. : 11
Name of Experiment:
Roll Number :
Date Performed :
Date Checked :
Signature
(Batch In-charge)
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Title:
Study of Decade Counter using IC 7490
Aim:
To study Decade Counter using IC-7490
Objectives:
To understand principal of working of decade counter using IC 7490.
To understand the circuit arrangement decade counter using IC 7490.
To understand the procedure of ―decade counter using IC7490‖ using proteus.
To observe the simulation of circuit.
Outcomes:
Able to understand principal of working of decade counter using IC 7490
circuit.
Able to understand the circuit arrangement of decade counter using IC7490
circuit.
Able to understand the procedure of decade counter using IC7490 circuit using
proteus.
Able to observe the simulation of circuit.
Programme Educational Objective (PEO) Satisfied : 2,3
To enable student to analyse, solve electronics engineering problem by applying
basic principles of mathematics , sciences and engineering and also be able to use
modern engineering techniques , skills and tools to fulfill social needs
To enable to innovate , design and develop a variety of electronic and computer based
components and system for applications including signal processing , communication
, computer network and control system.
Theory:
A circuit used for counting the pulses is known as a Counter. Basically there
are two types of counter:
1. Asynchronous counter (ripple counter)
2. Synchronous counter
In case of asynchronous counter all the flip-flops are not clocked simultaneously,
whereas ,in a Synchronous counter all the flip-flops are clocked simultaneously. A Ring
counter and twisted ring counter is the examples of synchronous counter.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Figure below shows the internal structure of 7490.
Fig1. Internal Structure of 7490
It consists of four flip-flop internally connected to provide a mod-2 and a mod-5
Counter. The mod-2 and mod-5counters can be used independently or in Combination. There
are two reset inputs R1and R2 both of which are to be connected to logic 1level for clearing
all the flip-flops. The two inputs S1 and s2 when Connected to logic 1 level, are used for
setting the counter to 1001.
The 7490 integrated circuit counts the number of pulses arriving at its input.The
number of pulses counted (up to 9) appears in binary form on four pins of the ic.When the
tenth pulse arrives at the input, the binary output is reset to zero (0000) and a single pulse
appears at another output pin.
So for ten pulses in there is one pulse out of this pin. The 7490 therefore divides
the frequency of the input by ten.If this pulse is applied to the input of a second 7490 then
this second ic will count the pulses from the first ic. It will give one pulse out after 100 pulses
have been applied to the first ic.The 7490 can be connected to divide by other values.
Pin Diagram
Circuit Diagram of Decade Counter
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Decade Counter Truth Table
Clock Output bit Pattern Decimal
Count QD QC QB QA Value
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 1 1
3 0 0 1 0 2
4 0 0 1 1 3
5 0 1 0 0 4
6 0 1 0 1 5
7 0 1 1 0 6
8 0 1 1 1 7
9 1 0 0 0 8
10 1 0 0 1 9
11 Counter Resets its Outputs back to Zero
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Timing diagram of decade counter
Advantages of decade counter
1. Decade counter are easier to design.
2. With all clock inputs wired together there is no inherent propagation delay.
3. Overall faster operation may be achieved compared to any counters
4. Decade counter are faster and more reliable as they use the same clock signal for all flip-
flops.
Disadvantages of decade Counters:
1. An extra "re-synchronizing" output flip-flop may be required.
2. To count a truncated sequence not equal to 2n, extra feedback logic is required.
3. Counting a large number of bits, propagation delay by successive stages may become
undesirably large.
4. This delay gives them the nickname of "Propagation Counters".
5. Counting errors occur at high clocking frequencies. Components:- IC 7490, IC
7447,resistors.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Procedure using Proteus:
1. From main page of Proteus, click on ‗P‘ to click device from library.
2. In pick device, insert the component which has to be selected & click on ‗OK‘.
3. Then place the all components on the Proteus screen.
4. Right clik the component properties to change the required value
5. Add voltage probe at input and output of diagram.
6. Select the graph mode & choose AC sweep analysis option
7. Right click in the graph window and elect add traces(input & output trace).
8. Right click & activate simulate graph
9. Observe input & output waveforms and analysis the results.
Decade Counter using proteus
Result
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
Circuit Simulation using Proteus
Conclusion:
We understand that the 7490 integrated circuit counts the number of pulses arriving
at its input. The number of pulses counted (up to 9) appears in binary form on four pins of
the IC When the tenth pulse arrives at the input, the binary output is reset to zero (0000) and
a single pulse appears at another output pin.
Department of Electronics Engg., P.V.P.I.T., Budhgaon
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 3 - Multistage Amplifier (Cascode)Document26 paginiChapter 3 - Multistage Amplifier (Cascode)GakushaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersDocument36 paginiUnit - Ii Single Phase and Three Phase Controlled RectifiersSukhpal Singh100% (2)
- Digital Electronics Circuits: Experiment: 10Document9 paginiDigital Electronics Circuits: Experiment: 10movab100% (1)
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 paginiRC Phase Shift OscillatorReddyvari Venugopal67% (3)
- Half and Full SubractorDocument6 paginiHalf and Full Subractorguru20064040100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument41 paginiLab ManualSyaoran7Li80% (5)
- UJT Triggering CircuitDocument6 paginiUJT Triggering Circuittmukesh62100% (1)
- Expt 10 Bistable MultivibratorDocument4 paginiExpt 10 Bistable MultivibratorsamarthÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEEE Important Questions 16 MarksDocument5 paginiBEEE Important Questions 16 Marksaeroheroz25% (4)
- Clipping Problems and Solutions - 2 PDFDocument7 paginiClipping Problems and Solutions - 2 PDFIlham Santoso100% (1)
- EE8411-Electrical Machines Laboratory-II-Lab Manual PDFDocument80 paginiEE8411-Electrical Machines Laboratory-II-Lab Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- Exp 11 Voltage Regulator Using IC 723Document5 paginiExp 11 Voltage Regulator Using IC 723Savio Pereira67% (3)
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 paginiSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- L08 Power Amplifier (Class A)Document24 paginiL08 Power Amplifier (Class A)mkrasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3) RC Half & Full Wave Firing Circuit - RFCDocument8 pagini3) RC Half & Full Wave Firing Circuit - RFCPradeep KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIC Lab ManualDocument79 paginiLIC Lab ManualSakthikumar Balasundaram67% (3)
- Ladder & Non Ladder NetworksDocument6 paginiLadder & Non Ladder NetworksPrashant Sharma100% (1)
- Experiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheoryDocument5 paginiExperiment: 5: AIM: Study of CB & CE Characteristics of Transistor TheorysanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual Full Wave RectifierDocument5 paginiLab Manual Full Wave RectifierVivek SuranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi ChawlaDocument27 paginiUnijunction Transistor: By: Smridhi Chawlasmridhi chawla100% (1)
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument6 paginiHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifierBilal KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bec303 - Lesson PlanDocument6 paginiBec303 - Lesson Planlubna0% (1)
- TCVR (Thyristor Control Voltage Regulator)Document10 paginiTCVR (Thyristor Control Voltage Regulator)17TUEE247 VISHNUPRIYA.JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDocument111 paginiEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- Measurement of Resistance - PPT PDFDocument20 paginiMeasurement of Resistance - PPT PDFAmrendra kumar0% (1)
- IC 723 Voltage RegulatorsDocument16 paginiIC 723 Voltage RegulatorsAtheessh .B0% (1)
- Transistor Biasing: Self Bias CircuitDocument17 paginiTransistor Biasing: Self Bias CircuitEquix3n60% (5)
- U1 L5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuits.Document6 paginiU1 L5 Biasing in MOS Amplifier Circuits.Shivani ParhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 4: Integrator and Differentiator Using 741 Op-AmpDocument4 paginiExperiment No. 4: Integrator and Differentiator Using 741 Op-AmpPrasad mohiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorDocument2 paginiExperiment No:9: Op-Amp As A DifferentiatorBhadresh Renuka100% (1)
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument8 paginiHalf Wave and Full Wave Rectifierbolbo naÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 paginiPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BÎncă nu există evaluări
- ComparatorDocument32 paginiComparatorShiv MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cycloconverter: 3.1 Principle of Operation of CycloconverterDocument19 paginiCycloconverter: 3.1 Principle of Operation of CycloconverterS JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18ECL48 Lab ManualDocument66 pagini18ECL48 Lab Manualsystech techniques100% (1)
- DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiDC and AC Load Linearjuna4306100% (1)
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDocument12 paginiBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRKeerthana Kejal50% (2)
- Unit 3 ComparatorsDocument54 paginiUnit 3 ComparatorsSoundararajan RajagopalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turn ON and Off Characteristics of SCRDocument17 paginiTurn ON and Off Characteristics of SCRVedant .Chavan100% (2)
- Swinburne'S Test: AIM: To Pre-Determine The Efficiency of A D.C Shunt Machine by PerformingDocument6 paginiSwinburne'S Test: AIM: To Pre-Determine The Efficiency of A D.C Shunt Machine by PerformingAshutosh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drives and Control Lab ManualDocument36 paginiDrives and Control Lab ManualKabilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee3271 - Ec LabDocument87 paginiEe3271 - Ec LabPALANIAPPAN C100% (3)
- Experiment No 2 (Fet)Document4 paginiExperiment No 2 (Fet)Jaideep Singh100% (1)
- Experiment No. 6 Op-Amp As Comparator & Schmitt Trigger: Analog Circuits LAB ManualDocument14 paginiExperiment No. 6 Op-Amp As Comparator & Schmitt Trigger: Analog Circuits LAB ManualchaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- V-I Characteristics of SCRDocument6 paginiV-I Characteristics of SCRRohitRaj100% (1)
- EXP17 Class A Power AmplifierDocument3 paginiEXP17 Class A Power AmplifierMohammed Dyhia AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorDocument3 paginiExperiment No.2: Colpitt OscillatorBhadresh Renuka50% (2)
- DC Position ControlDocument5 paginiDC Position ControlRamesh Babu100% (2)
- Unijunction TransistorDocument12 paginiUnijunction TransistorGogoi LeftoverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Document69 paginiElectronic Principles and Circuits Lab Manual - BEC303 - 18-11-2023Maithira H0% (1)
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualDocument148 paginiMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab Manualsramiz_1987100% (1)
- Full Wave RectifierDocument10 paginiFull Wave RectifierVenkata PavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 03 - CycloconvertersDocument29 paginiLecture 03 - CycloconvertersdaudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Multisim SimulationDocument3 paginiFull Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Multisim Simulationmohamed elfeky0% (1)
- Master Slave Flip FlopDocument3 paginiMaster Slave Flip FlophimanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXPERIMENT No 5 - MuX and DeMuxDocument6 paginiEXPERIMENT No 5 - MuX and DeMuxSaksham DhawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Act PtedDocument8 paginiFinal Act PtedCARLIN JOSH MENDOZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendoza FinalActivityPTEDDocument8 paginiMendoza FinalActivityPTEDCARLIN JOSH MENDOZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bec Report1Document41 paginiBec Report1Tilak shastriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Diabetic Retinopathy Thesis Report Edited Nge Weng ShengDocument55 paginiDiabetic Retinopathy Thesis Report Edited Nge Weng ShengAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administration Budget (RM) Marketing Budget (RM) Operation and Production Budget (RM)Document2 paginiAdministration Budget (RM) Marketing Budget (RM) Operation and Production Budget (RM)Anie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEE20901 MKS 2 ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING LABORATORY II Speed Control SystemDocument26 paginiBEE20901 MKS 2 ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING LABORATORY II Speed Control SystemAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploitation of Microwave System For Control of Insect Infestation in Rice GrainDocument8 paginiExploitation of Microwave System For Control of Insect Infestation in Rice GrainAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dominica Attacks A Wide Range of Stored Cereals and Breeds Extensively in A Warm Climate (S. JDocument20 paginiDominica Attacks A Wide Range of Stored Cereals and Breeds Extensively in A Warm Climate (S. JAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploitation of Microwave System For Control of Insect Infestation in Rice GrainDocument8 paginiExploitation of Microwave System For Control of Insect Infestation in Rice GrainAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSM Project Proposal Form Fkee PDFDocument1 paginăPSM Project Proposal Form Fkee PDFAnie SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyc 118A ManualDocument12 paginiHyc 118A ManualrafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controlador Del Motor de Tracción SemDocument38 paginiControlador Del Motor de Tracción SemRamon Arredondo100% (1)
- Dectection of Microbial Concentration in Water: Meron Taye GemedaDocument52 paginiDectection of Microbial Concentration in Water: Meron Taye GemedaباسمالنمرÎncă nu există evaluări
- 002MCQDocument15 pagini002MCQAhmed FarahatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optics Lab PracticalDocument33 paginiOptics Lab PracticalReddyvari VenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bee Unit 5Document50 paginiBee Unit 5DOMAKONDA NEHA SE(H)2019Încă nu există evaluări
- W471-E1-01 CP1L OperationManualDocument673 paginiW471-E1-01 CP1L OperationManualGumer Santiago FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Sensor FundamentalsDocument34 pagini1 Sensor Fundamentalshmr4everÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Investigatory Project CBSE 2017-18Document24 paginiPhysics Investigatory Project CBSE 2017-18Mukul100% (1)
- Acs300 ManualDocument101 paginiAcs300 ManualAnonymous pgR5O1UpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.XII Physics Question PaperDocument8 pagini6.XII Physics Question PaperEMMANUEL PHILIP REJI CLASS XÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Paul Lorrain) Solutions Manual For ElectromagnetiDocument93 pagini(Paul Lorrain) Solutions Manual For ElectromagnetiHarrisson David Assis Santos0% (1)
- Chapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerDocument48 paginiChapter One Controlling The Operation of Wind-Solar Hybrid Power System Using Arduino-Based Hybrid MPPT ControllerOdebunmi NathanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 26 Problems 1,, Straightforward, Intermediate, 6Document12 paginiChapter 26 Problems 1,, Straightforward, Intermediate, 6omboookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pin Programmable Precision Voltage Reference: C Max, 0 C To 70 C (AD584L) C Max, - 55 C To +125 C (AD584T)Document12 paginiPin Programmable Precision Voltage Reference: C Max, 0 C To 70 C (AD584L) C Max, - 55 C To +125 C (AD584T)budi0251Încă nu există evaluări
- Capacitor ExplanationDocument2 paginiCapacitor ExplanationMirza Mohammad YasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baumer Capacitive SensonDocument60 paginiBaumer Capacitive SensoncsystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC QnaDocument8 paginiPLC QnaMoses MberwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 195421055-Electronics-Symbols-Cheat-Sheet 2 PDFDocument14 pagini195421055-Electronics-Symbols-Cheat-Sheet 2 PDFfissionstarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTM 5 Srichaitanya 2023Document36 paginiGTM 5 Srichaitanya 2023yuvaanii565Încă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Phase Interleaved LLC-SRC and Its Digital Control SchemeDocument6 paginiMulti-Phase Interleaved LLC-SRC and Its Digital Control Scheme章肇珩Încă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Breaker LTB D With Motor Drive. Motor Drive. ABB PP - H - HV - Page 1. Ed 2006-04Document29 paginiCircuit Breaker LTB D With Motor Drive. Motor Drive. ABB PP - H - HV - Page 1. Ed 2006-04Phạm Lê Quốc ChínhÎncă nu există evaluări
- C3704Document2 paginiC3704Ardillah PrawiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Components and Laboratory EquipmentDocument10 paginiElectronic Components and Laboratory EquipmentKenneth SablayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Document24 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/41Gcmarshall82Încă nu există evaluări
- Emerson Door Inverter ManualDocument107 paginiEmerson Door Inverter Manualhidyatama85% (27)
- Lecture 5 Introduction To Electro PneumaticDocument46 paginiLecture 5 Introduction To Electro PneumaticMary Hazel Sarto, V.Încă nu există evaluări
- Cbse Physics INBO Olympiad Question Papers 2019 EnglishDocument30 paginiCbse Physics INBO Olympiad Question Papers 2019 Englishwani mohsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual - BigMuff - Green RussianDocument10 paginiManual - BigMuff - Green RussianBen KussauerÎncă nu există evaluări