Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
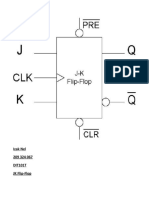
JK Flip Flop Is The Most Widely Used of All The Flip-Flop Designs and Is Considered
Încărcat de
dbircsTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentJK Flip Flop Is The Most Widely Used of All The Flip-Flop Designs and Is Considered
Încărcat de
dbircsSULA, DIANA T.
FEBRUARY 18, 2019
BS ECE 4B
Discussion:
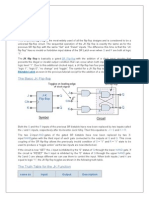
JK flip Flop is the most widely used of all the flip-flop designs and is considered
to be a universal flip-flop circuit. The two inputs labelled “J” and “K” are not
shortened abbreviated letters of other words, such as “S” for Set and “R” for Reset,
but are themselves autonomous letters chosen by its inventor Jack Kirby to
distinguish the flip-flop design from other types.
The sequential operation of the JK flip flop is exactly the same as for the previous SR
flip-flop with the same “Set” and “Reset” inputs. The difference this time is that the
“JK flip flop” has no invalid or forbidden input states of the SR Latch even
when S and R are both at logic “1”.
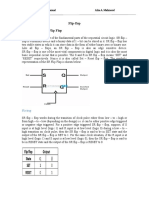
Observation:
The JK flip flop is basically a gated SR flip-flop with the addition of a clock input
circuitry that prevents the illegal or invalid output condition that can occur when
both inputs S and R are equal to logic level “1”. Due to this additional clocked input, a
JK flip-flop has four possible input combinations, “logic 1”, “logic 0”, “no change” and
“toggle”. If the circuit is now “SET” the J input is inhibited by the “0” status
of Q through the lower NAND gate. If the circuit is “RESET” the K input is inhibited by
the “0” status of Q through the upper NAND gate. As Q and Q are always different
we can use them to control the input. When both inputs J and K are equal to logic
“1”, the JK flip flop toggles as shown in the following truth table. Then the JK flip-flop
is basically an SR flip flop with feedback which enables only one of its two input
terminals, either SET or RESET to be active at any one time thereby eliminating the
invalid condition seen previously in the SR flip flop circuit.
Also when both the J and the K inputs are at logic level “1” at the same time, and the
clock input is pulsed “HIGH”, the circuit will “toggle” from its SET state to a RESET
state, or visa-versa. This results in the JK flip flop acting more like a T-type toggle flip-
flop when both terminals are “HIGH”.
Conclusion:
Although this circuit is an improvement on the clocked SR flip-flop it still suffers from
timing problems called “race” if the output Q changes state before the timing pulse
of the clock input has time to go “OFF”. To avoid this the timing pulse period ( T )
must be kept as short as possible (high frequency). As this is sometimes not possible
with modern TTL IC’s the much improved Master-Slave JK Flip-flop was developed.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Basic JK Flip-FlopDocument4 paginiThe Basic JK Flip-Flopom1444100% (1)
- The JK FlipDocument4 paginiThe JK Flipraj2510Încă nu există evaluări
- Learn Digital and Microprocessor Techniques on Your SmartphoneDe la EverandLearn Digital and Microprocessor Techniques on Your SmartphoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2.2Document15 paginiChapter 2.2OzzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- JK FlilflopDocument6 paginiJK FlilflopImran AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The J K Flip FlopDocument3 paginiThe J K Flip FlopSaanguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip Flop Counters PDFDocument15 paginiFlip Flop Counters PDFAdarsh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical: 14 To Study J - K Flip Flop: Sohil Vohra (Lecturer - Shri K.J. Polytechnic College, Bharuch (C.E. Deptt) )Document5 paginiPractical: 14 To Study J - K Flip Flop: Sohil Vohra (Lecturer - Shri K.J. Polytechnic College, Bharuch (C.E. Deptt) )Sohil VohraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt 12Document5 paginiExpt 12Dhrrishith VikalÎncă nu există evaluări
- J-K Flip FlopDocument5 paginiJ-K Flip FlopNagham Hikmat AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- JK Flip FlopDocument11 paginiJK Flip FlopprakashpacetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopDocument34 paginiFlip Flopqwrr rewqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 8Document8 paginiChap 8mailusman9835Încă nu există evaluări
- Project ReportDocument11 paginiProject Reportamiethurgat100% (2)
- Flip-Flop Introduction To SR Flip FlopDocument22 paginiFlip-Flop Introduction To SR Flip FlopljjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequential Digital Circuits: Flip FlopsDocument27 paginiSequential Digital Circuits: Flip FlopsSubrahmanyam GuduruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cream and Brown Minimalist Let's Learn PresentationDocument25 paginiCream and Brown Minimalist Let's Learn PresentationReychille AbianÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between Latch and Flip FlopDocument12 paginiWhat Is The Difference Between Latch and Flip FlopJOYCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- FlipssDocument8 paginiFlipssOrion Starbwoy BlackstockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title ObjectiveDocument4 paginiTitle ObjectiveShekhar ShuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Clocked RS Flip-FlopDocument4 paginiThe Clocked RS Flip-Flopabhisheksikka17Încă nu există evaluări
- Izak Nel 209 324 067 DIT101T JK Flip-FlopDocument10 paginiIzak Nel 209 324 067 DIT101T JK Flip-FlopZack NelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec # 06 - DLDDocument30 paginiLec # 06 - DLDSunny 17Încă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopsDocument11 paginiFlip FlopsZakaria JubarnÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Gondar Institute of TechnologyDocument50 paginiUniversity of Gondar Institute of TechnologyamareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopDocument6 paginiFlip FlopMuzakki SathorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiplexer, Decoder and FlipflopDocument10 paginiMultiplexer, Decoder and FlipflopShachi P GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 5 - Flip Flops Sequential CircuitsDocument16 paginiTopic 5 - Flip Flops Sequential CircuitsShivneet KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequential Logic: Unit-IDocument86 paginiSequential Logic: Unit-IMonika RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip Flop Play HokeyDocument7 paginiFlip Flop Play HokeyCherryPratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT1Document37 paginiUNIT1Azliana Mohd Taib0% (1)
- Flip FlopsDocument3 paginiFlip FlopsnikomuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopDocument32 paginiFlip FlopAnoop KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopsDocument7 paginiFlip FlopsFord StephenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip-Flops: Lecturer Uzma Hasan, CSE Department, MISTDocument21 paginiFlip-Flops: Lecturer Uzma Hasan, CSE Department, MISTRafinÎncă nu există evaluări
- M7 Sequentials Circuits-1Document67 paginiM7 Sequentials Circuits-1joelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing of Flip Flops: Mehran University of Engineering & Technology JamsoroDocument8 paginiDesigning of Flip Flops: Mehran University of Engineering & Technology JamsoroAakash Devdat KolhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE331L Experiment #4: Written By: Shehab Alaa Ramadan Group: C University ID Number: 022180589Document19 paginiEE331L Experiment #4: Written By: Shehab Alaa Ramadan Group: C University ID Number: 022180589Shehab RamadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registers in Digital ElecronicsDocument4 paginiRegisters in Digital Elecronicsdhirajkumar_1Încă nu există evaluări
- EXPT:-Study of J K Flip Flop Using IC 7476 Apparatus:-IC 7476, Breadboard, Single Stand WiresDocument4 paginiEXPT:-Study of J K Flip Flop Using IC 7476 Apparatus:-IC 7476, Breadboard, Single Stand WiresPoonam GholapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 3Document4 paginiExperiment 3Ishan Satya PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dic Assignment Latches and Flip FlopsDocument6 paginiDic Assignment Latches and Flip FlopsMisha WaseemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrator Comparater Etc and OthersDocument4 paginiIntegrator Comparater Etc and Othersshaik jilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY 234 - Week Fourth - Lecture 2Document15 paginiPHY 234 - Week Fourth - Lecture 2Fatima KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report 1 (D2, Digital)Document10 paginiReport 1 (D2, Digital)Kian YingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Flip-Flop CircuitDocument2 paginiBasic Flip-Flop CircuitSyieda ZamryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Flip Flops in Digital ElectronicsDocument10 paginiBasic Flip Flops in Digital ElectronicsDharneeshkarDandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sekuensial SirkitDocument24 paginiSekuensial SirkitfakhriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 Sequential CircuitDocument21 paginiUnit 5 Sequential CircuitAnurag GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Slave Flip FlopDocument2 paginiMaster Slave Flip FlopShruti ChandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopsDocument60 paginiFlip FlopsA10-14Rajat KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name:-Bharat Arora Section: - A Rollno: - 18 University Rollno: - 191500212Document6 paginiName:-Bharat Arora Section: - A Rollno: - 18 University Rollno: - 191500212Deepam AsnaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About Flip FlopsDocument6 paginiAll About Flip FlopsSriharsha Pidaparthi100% (1)
- Expt No.9Document5 paginiExpt No.9Rithika 318030Încă nu există evaluări
- DLD AssignmentDocument11 paginiDLD Assignmenttaibaarshad85Încă nu există evaluări
- DPCO Unit 2 Two Marks Q&ADocument23 paginiDPCO Unit 2 Two Marks Q&Akanimozhi rajasekarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flip FlopDocument4 paginiFlip FlopTara SeebabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3,4,5Document36 paginiUnit 3,4,5testÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of EngineeringDocument2 paginiDhanalakshmi Srinivasan: College of Engineeringhamsalakshmi cÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aegps Protect 8 enDocument8 paginiAegps Protect 8 enJose EspinozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSSEMA 2023 PosterDocument1 paginăNSSEMA 2023 Postersumitravashisht1954Încă nu există evaluări
- Magico M6 TAS February 2020Document10 paginiMagico M6 TAS February 2020Héritier NealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Seminar DocumentationDocument44 paginiTechnical Seminar DocumentationvenkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Dfx1000 BladeDocument2 paginiBrochure Dfx1000 BladeabdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester Project: Ahmad Yama FA16-EPE-168 Fazal Rahim FA16-EPE-165 Mir Alam FA16-EPE-179 Hammad Afzal FA16-EPE-062Document5 paginiSemester Project: Ahmad Yama FA16-EPE-168 Fazal Rahim FA16-EPE-165 Mir Alam FA16-EPE-179 Hammad Afzal FA16-EPE-062Mir AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in ITDocument15 paginiReviewer in ITclara san miguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 2 Digital ProcessorDocument22 paginiSession 2 Digital Processor吴川斌Încă nu există evaluări
- Voice Over LTEDocument19 paginiVoice Over LTEGabriele Spina100% (2)
- Mainboard Esc Model-P23gDocument28 paginiMainboard Esc Model-P23gOrlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Ch5 Multistage AmplifierDocument12 paginiAnalog Ch5 Multistage Amplifierskgupta4281Încă nu există evaluări
- Reversible Logic SynthesisDocument17 paginiReversible Logic SynthesisMekala RamaraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVDC Notes PDFDocument22 paginiHVDC Notes PDFupender raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEC 62841-1 2014 2020-06-10 Provisional Testing - Measurement EquipmentDocument6 paginiIEC 62841-1 2014 2020-06-10 Provisional Testing - Measurement EquipmentRobert LegaultÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual ACS80 GBDocument23 paginiUser Manual ACS80 GBJosef VacikÎncă nu există evaluări
- I C Controlled 4.5A Single Cell USB/Adapter Charger With Narrow VDC Power Path Management and USB OTGDocument46 paginiI C Controlled 4.5A Single Cell USB/Adapter Charger With Narrow VDC Power Path Management and USB OTGjuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SamsungSetTopBox BR 0Document6 paginiSamsungSetTopBox BR 0topannurhakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Motherboard I. Computer Motherboard: Property of STIDocument4 paginiComputer Motherboard I. Computer Motherboard: Property of STIRachelle GandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Electronics 56d98751129c1Document32 paginiDigital Electronics 56d98751129c1nicolas silvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dong, Roy - Application NoteDocument7 paginiDong, Roy - Application Notepritam kalaimaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Es5 120 73eb - DatDocument2 paginiEs5 120 73eb - DatCharmin CoronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 745-b5 - 7 Modbus MultilinDocument68 pagini745-b5 - 7 Modbus MultilinJorge William Bermudez GaviriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless - 2.1 (Mobile Radio Propgation Large Scale Path Loss) NewnewDocument108 paginiWireless - 2.1 (Mobile Radio Propgation Large Scale Path Loss) Newnewapi-3856938Încă nu există evaluări
- Ieee 1147Document48 paginiIeee 1147Jose Antonio EstofaneroÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ - Unit No - 1 and 2 B.X.EDocument30 paginiMCQ - Unit No - 1 and 2 B.X.ERohit GhereÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpaceXin Motion Decision FCCDocument16 paginiSpaceXin Motion Decision FCCmichaelkan1Încă nu există evaluări
- ETI 2413 Digital Communication Principles - 2Document20 paginiETI 2413 Digital Communication Principles - 2Kevin NdemoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DE10-Lite User Manual: June 5, 2020Document56 paginiDE10-Lite User Manual: June 5, 2020SferreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Branding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsDe la EverandBranding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (32)
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowDe la EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (388)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationDe la EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (6)
- How to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyDe la EverandHow to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (27)
- Evaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsDe la EverandEvaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Social Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeDe la EverandSocial Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueDe la EverandThe YouTube Formula: How Anyone Can Unlock the Algorithm to Drive Views, Build an Audience, and Grow RevenueEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (33)
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessDe la EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesDe la EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (9)
- Blender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)De la EverandBlender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)Încă nu există evaluări
- NFT per Creators: La guida pratica per creare, investire e vendere token non fungibili ed arte digitale nella blockchain: Guide sul metaverso e l'arte digitale con le criptovaluteDe la EverandNFT per Creators: La guida pratica per creare, investire e vendere token non fungibili ed arte digitale nella blockchain: Guide sul metaverso e l'arte digitale con le criptovaluteEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (15)
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineDe la EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wordpress 2023 A Beginners Guide : Design Your Own Website With WordPress 2023De la EverandWordpress 2023 A Beginners Guide : Design Your Own Website With WordPress 2023Încă nu există evaluări
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyDe la EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (421)
- App Innovator's Guide: Mobile App Development for Android and iOS: Building Cross-Platform SolutionsDe la EverandApp Innovator's Guide: Mobile App Development for Android and iOS: Building Cross-Platform SolutionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosDe la EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersDe la Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Get Into UX: A foolproof guide to getting your first user experience jobDe la EverandGet Into UX: A foolproof guide to getting your first user experience jobEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- Blender 3D Basics Beginner's Guide Second EditionDe la EverandBlender 3D Basics Beginner's Guide Second EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Web Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyDe la EverandWeb Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- iPhone 15 Pro User Guide for Beginners and SeniorsDe la EverandiPhone 15 Pro User Guide for Beginners and SeniorsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightDe la EverandKill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (240)
- Software Engineering: Architecture-driven Software DevelopmentDe la EverandSoftware Engineering: Architecture-driven Software DevelopmentEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)