Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
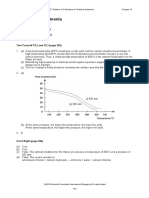
Reproduction in Humans: Test Yourself 18.1 (Page 335)
Încărcat de
leeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Reproduction in Humans: Test Yourself 18.1 (Page 335)
Încărcat de
leeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Biology Matters G.C.E.
'O' Level (2nd Edition): Textbook Answers Chapter 18
Chapter 18 Reproduction in Humans
Test Yourself 18.1 (page 335)
Sperms require a temperature slightly lower than that of the body to develop properly.
Test Yourself 18.2 (page 338)
1. (a) A – uterus
B – urinary bladder
C – urethra
D – oviduct
E – ureter
F – ovary
G – rectum
H – vagina
(b) (i) H
(ii) D
(iii) A
(iv) F
(v) F
2. The funnel-like opening of the oviduct, lying close to the ovary
Test Yourself 18.3 (page 343)
1. While 28 days is generally taken as representative of the average menstrual cycle in
women, cycle length may vary, ranging from 21 to 33 days. This is called natural
variation in the length of the menstrual cycle.
2. (a) Oestrogen causes the repair and growth of the uterine lining.
Progesterone maintains the uterine lining by causing it to thicken further and
be supplied with blood capillaries.
(b) Luteinising hormone (LH)
(c) 12th–16th day
(d) Part of the uterine lining breaks down and is shed together with some blood
in the menstrual flow.
Test Yourself 18.4 (page 348)
1. Sperms released into the vagina will swim up into the oviduct to meet the egg. The
acrosome of the sperm releases an enzyme to disperse the follicle cells that surround
the egg. Only one haploid sperm nucleus enters the egg and fuses with the haploid egg
nucleus to give rise to a fertilised egg or diploid zygote.
2. Progesterone and oestrogen maintain the thickness of the uterine lining to support the
growing fetus. They also cause the uterine lining to be well-supplied with blood vessels
which supply oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus as well as remove excretory
products from the fetus's blood.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
18.1
Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2nd Edition): Textbook Answers Chapter 18
Test Yourself 18.5 (page 350)
Sexually transmitted infections are caused by bacteria or viruses and may be spread through
sexual intercourse. The more sex partners a person has, the more opportunities there are for
the disease-causing microorganisms to be transmitted to the person. Moreover, the sex
partners may have numerous sex partners themselves, increasing the risk of contracting a
sexually transmitted infection.
Get It Right (page 352)
(a) False
Sperm and urine passes out of the body through the urethra.
(b) True
(c) False
Ovulation occurs on day 14 in a 28-day menstrual cycle.
(d) True
(e) False
HIV from the mother can affect the fetus.
Let’s Review (page 352 – 353)
Section A: Multiple-Choice Questions
1. C
2. C
Section B: Structured Questions
1. (a) Menstruation occurs. The uterine lining breaks down and flows from the body
via the vagina together with some blood.
(b) 5 days
(c) The uterine lining is repaired. It grows and thickens.
(d) The uterine lining thickens and become well-supplied with blood.
(e) Students should place the X at point B.
2. (a) A – sperm duct
B – prostate gland
C – urethra
D – testis
E – ureter
F – urinary bladder
G – epididymis
(b) (i) C
(ii) A
(iii) D
(c) Testis epididymis sperm duct urethra outside
3. Progesterone.
Progesterone prevents ovulation. Hence, no fertilisation can occur.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
18.2
Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2nd Edition): Textbook Answers Chapter 18
* 4. (a) A – amniotic cavity / amniotic fluid
B – placenta
C – amnion
D – urinary bladder
E – vagina
(b) Any of the following for each:
A: – Supports and cushions the fetus before birth
– Absorbs shock and protects the fetus against pressure from sudden
movements of its mother's body
– Protects the fetus against physical injury
– Lubricates and reduces friction in the vagina or birth canal during birth
– Allows fetus to move freely during growth
B: – Allows oxygen and dissolved food substances like glucose to diffuse from
the mother's
blood into the fetus's blood
– Allows excretory products like urea to diffuse from the fetus's blood into
the mother's blood
– Allows protective antibodies to diffuse from the mother's blood into the
fetus's blood so that the fetus is protected against certain diseases
– Produces progesterone which maintain uterine lining in a healthy state
during pregnancy
(c) (i) P – umbilical artery
Q – umbilical vein
Any of the following reasons:
– P has a thicker wall than Q.
– P has a smaller lumen than Q. The umbilical cord contains two
umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein.
(ii) P transports metabolic waste products such as urea and carbon dioxide
from the fetus to the placenta.
Q transports oxygen and nutrients like glucose and amino acids from the
placenta to the fetus.
Section C: Free-Response Question
– Menstrual flow stage
Menstruation begins
Anterior pituitary gland secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
– Follicle stage
FSH stimulates follicles to develop into Graafian follicle
FSH stimulates follicles to secrete oestrogen
Oestrogen causes uterine lining to repair and thicken
High levels of oestrogen inhibit FSH production, no more follicles develop and
stimulates LH production.
– Ovulation
Luteinising hormone (LH) causes ovulation on the 14th day
LH also causes corpus luteum formation
LH stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone and some oestrogen
– Corpus luteum stage
Progesterone stimulates uterine lining to thicken further and to become well-
supplied with blood capillaries
Progesterone inhibits ovulation and FSH production
If no fertilisation occurs, high progesterone level in the blood inhibits LH
production.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
18.3
Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2nd Edition): Textbook Answers Chapter 18
Corpus luteum breaks down and the production of progesterone decreases.
Menstruation begins again.
© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited
18.4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Heredity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 359)Document2 paginiHeredity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 359)lee0% (1)
- Our Impact On The Ecosystem: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 438)Document3 paginiOur Impact On The Ecosystem: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 438)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)Document3 paginiHormones: Test Yourself 15.1 (Page 287)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure Bio CH 14 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 14 Textbook Answers PDFlee0% (1)
- Homeostasis: Test Yourself 12.1 (Page 246)Document3 paginiHomeostasis: Test Yourself 12.1 (Page 246)lee100% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 9 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 paginiPure Bio CH 9 Textbook Answers PDFMahamIsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)Document4 paginiRespiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)lee67% (3)
- Ecology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)Document4 paginiEcology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)Document2 paginiExcretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)Document3 paginiTransport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)lee100% (3)
- Nutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)Document3 paginiNutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)lee100% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure Bio CH 7 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 paginiPure Bio CH 7 Textbook Answers PDFlee50% (8)
- Molecular Genetics: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 389) 1Document2 paginiMolecular Genetics: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 389) 1leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)Document3 paginiTransport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)lee100% (3)
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFno one100% (3)
- Pure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFlee0% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 1 Textbook AnswersDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 1 Textbook Answerslee60% (5)
- Cell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)Document2 paginiCell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)lee100% (2)
- Pure Bio CH 5 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 5 Textbook Answers PDFMahamIsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammonia: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 381)Document4 paginiAmmonia: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 381)Jack Kowman100% (3)
- Alkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Document3 paginiAlkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)khalil rehman100% (2)
- CM TB Answers C17Document3 paginiCM TB Answers C17khalil rehman100% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 paginiPure Bio CH 17 Textbook Answers PDFashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Document5 paginiSpeed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Jack Kowman25% (4)
- An Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 414)Document3 paginiAn Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 414)Jack Kowman75% (8)
- This Study Resource Was: WavesDocument5 paginiThis Study Resource Was: WavesAhmad Ahsan100% (2)
- Writing Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Document1 paginăWriting Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Zeeshan MunirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSDocument3 paginiChemistry Matters Ch13 Textbk ANSZeneon50% (6)
- CM TB Solutions C04Document2 paginiCM TB Solutions C04Robot Ninja67% (3)
- Chemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSDocument3 paginiChemistry Matters Ch19 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (1)
- Chemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSDocument4 paginiChemistry Matters Ch07 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (12)
- Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Test Yourself 23.1 and 23.2 (Page 453)Document2 paginiAlcohols and Carboxylic Acids: Test Yourself 23.1 and 23.2 (Page 453)khalil rehman40% (5)
- The Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)Document2 paginiThe Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)khalil rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metals: Test Yourself 14.1 (Page 250)Document4 paginiMetals: Test Yourself 14.1 (Page 250)Jack Kowman100% (2)
- The Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Document10 paginiThe Mole: Test Yourself 9.1 and 9.2 (Page 139)Ahmad Ahsan40% (5)
- Chemistry Matters Ch06 Textbk ANSDocument2 paginiChemistry Matters Ch06 Textbk ANSZeneon79% (14)
- Chemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSDocument3 paginiChemistry Matters Ch17 Textbk ANSZeneon100% (3)
- Chemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSDocument2 paginiChemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSZeneon63% (8)
- PM TB Solutions C11Document6 paginiPM TB Solutions C11Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (8)
- Chemical Calculations: Mass of Cucl .2H O Molar Mass of Cucl .2H O 3.42 64 + (2 ! 35.5) + (2 ! 18)Document5 paginiChemical Calculations: Mass of Cucl .2H O Molar Mass of Cucl .2H O 3.42 64 + (2 ! 35.5) + (2 ! 18)khalil rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Document7 paginiAlkanes and Alkenes: Test Yourself 22.1 (Page 429)Jack Kowman100% (1)
- Writing Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)Document1 paginăWriting Chemical Equations: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 130)khalil rehman100% (2)
- CM TB Solutions C06Document3 paginiCM TB Solutions C06Nisha75% (8)
- Chemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSDocument3 paginiChemistry Matters Ch11 Textbk ANSZeneon82% (17)
- Practical Electricity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 365)Document5 paginiPractical Electricity: Test Yourself 19.1 (Page 365)Jack Kowman67% (6)
- Chemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSDocument3 paginiChemistry Matters Ch05 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (12)
- CM TB Solutions C01Document3 paginiCM TB Solutions C01MahamIsmail86% (7)
- Chemistry Matters Ch04 Textbk ANSDocument2 paginiChemistry Matters Ch04 Textbk ANSZeneon67% (21)
- PM TB Solutions C04Document5 paginiPM TB Solutions C04Vishwajeet Ujhoodha75% (4)
- Magnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Document6 paginiMagnetism: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 388)Jack Kowman80% (5)
- Chap 7 CMDocument4 paginiChap 7 CMhajraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Matters GDocument2 paginiBiology Matters Gno one50% (2)
- PM TB Solutions C08Document4 paginiPM TB Solutions C08Vishwajeet Ujhoodha80% (5)
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Document5 paginiTransfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Jack Kowman100% (8)
- Multiple Choice Questions: ReproductionDocument12 paginiMultiple Choice Questions: ReproductionJohn Osborne100% (1)
- ch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Document15 paginich-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Turani SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Reproduction: Points To RememberDocument9 paginiHuman Reproduction: Points To RememberPREM277272Încă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Bio 16 (D) - Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument6 paginiIGCSE Bio 16 (D) - Sexual Reproduction in Humans다윤Încă nu există evaluări
- Important Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionDocument17 paginiImportant Questions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 - Human ReproductionYuvraj MehtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Genetics: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 389) 1Document2 paginiMolecular Genetics: Test Yourself 20.1 (Page 389) 1leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)Document2 paginiCell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)lee100% (2)
- Ecology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)Document4 paginiEcology: Test Yourself 21.1 (Page 405)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproduction in Plants: Test Yourself 17.1 (Page 316)Document3 paginiReproduction in Plants: Test Yourself 17.1 (Page 316)lee100% (1)
- The Nervous System: Test Yourself 13.1 (Page 258)Document2 paginiThe Nervous System: Test Yourself 13.1 (Page 258)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook AnswersDocument2 paginiEnzymes: Biology Matters G.C.E. 'O' Level (2 Edition) : Textbook Answerslee40% (5)
- Pure Bio CH 1 Textbook AnswersDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 1 Textbook Answerslee60% (5)
- Respiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)Document4 paginiRespiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)lee67% (3)
- Excretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)Document2 paginiExcretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)Document3 paginiNutrition in Humans: Test Yourself 6.1 (Page 96)lee100% (1)
- Transport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)Document3 paginiTransport in Humans: Test Yourself 8.1 (Page 140)lee100% (3)
- Transport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)Document3 paginiTransport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)lee100% (3)
- Pure Bio CH 7 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 paginiPure Bio CH 7 Textbook Answers PDFlee50% (8)
- Movement of Substances: Investigation 3.1 (Page 34)Document3 paginiMovement of Substances: Investigation 3.1 (Page 34)leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 4 Textbook Answers PDFlee0% (1)
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFDocument2 paginiPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFleeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gender and PsychotherapyDocument12 paginiGender and PsychotherapyEhh EnNaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Sensitive Proteins in Beer by Nephelometry - Submitted On Behalf of The Analysis Committee of The European Brewery ConventionDocument4 paginiDetermination of Sensitive Proteins in Beer by Nephelometry - Submitted On Behalf of The Analysis Committee of The European Brewery ConventionChí HữuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument570 paginiPDFEshaal FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LPL - Amit Sharma FPSC Loni Road-Gzb Shop No-4, Saharanpur Road, Loni Road, Main Tiraha, Loni, Ghaziabad, Loni S.ODocument3 paginiLPL - Amit Sharma FPSC Loni Road-Gzb Shop No-4, Saharanpur Road, Loni Road, Main Tiraha, Loni, Ghaziabad, Loni S.OKaran PrabhakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cham PowerpointDocument19 paginiCham PowerpointElizabeth GenotivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileDocument22 paginiZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileJoaquín Eduardo Sepúlveda AstudilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisDocument190 paginiThe Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisTomas De Wael100% (2)
- CS Audi - Case Study DRAFTDocument21 paginiCS Audi - Case Study DRAFTcahlahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indira Renganathan 2018 18Document1.992 paginiIndira Renganathan 2018 18shubham vedakÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Your Internal Terrain On Your FasciaDocument16 paginiThe Impact of Your Internal Terrain On Your Fasciazzip1961100% (1)
- Proposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsDocument17 paginiProposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsAbhiram muddanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesDocument9 paginiMuscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesRosa AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recent DevelopmentsDocument295 paginiRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch8 (C)Document28 paginiCh8 (C)fkjujÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angiogenesis and Direct Myocardial RevascularizationDocument364 paginiAngiogenesis and Direct Myocardial RevascularizationPerdana SidaurukÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 - Lipid MetabolismDocument35 pagini19 - Lipid MetabolismcheckmateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest TubesDocument34 paginiChest TubesMuhd ShafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Span: HumanDocument738 paginiLife Span: HumanWAJEEHA GOHARÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Ultrasound Report Template 2Document1 paginăOB Ultrasound Report Template 2PriyankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Test 22: Questions 1-10Document7 paginiPractice Test 22: Questions 1-10Несибели НаурызбаеваÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer ResearchDocument8 paginiCancer Researchmibs2009Încă nu există evaluări
- A Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaDocument13 paginiA Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaAlexander DeckerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocument32 pagini6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Published January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2Document9 paginiPublished January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2himanshuchawla654Încă nu există evaluări
- Biosensors For Environmental ApplicationsDocument15 paginiBiosensors For Environmental ApplicationsBenjamin HonorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles Medico Ii - TP 5Document3 paginiIngles Medico Ii - TP 5Rodrigo Anelli De OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Document91 paginiBIOL 3121 - Lecture 13 - 081116Sara HuebnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kimia Daun PandanDocument4 paginiKimia Daun Pandanlutfi_alhayathullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of Tannia PlantDocument104 paginiCharacterization of Tannia PlantSolomon FantawÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without ReferencesDocument5 paginiCV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without Referencesapi-399765628Încă nu există evaluări