Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Module P-11
Încărcat de
ImmanuelDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Module P-11
Încărcat de
ImmanuelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P- 11
MODULE SUBJ. : PROCESS CONTROL
INSTRUMENTATION
Tasks:
Measuring Elements
11.1 Identify the different measuring element of process variables.
11.2 Explain how a pressure switch works.
11 3 Identify types of differential measuring elements (dP, dT etc.)
Control Loops
11.4 Explain with sketches control loops for process variables
11.5 Explain how a split range controller works
Operate (in manual and auto) a control loop and use radio to confirm
11.6
valve position in field.
11.7 Retrieve information from a cause and effect diagram (SD matrix)
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 1
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.1 Identify the different types of measuring elements.
Requirement – By Trainees :
The trainee should know and be familiar with different types of level,
pressure, flow and temperature measuring elements.
The trainee should demonstrate in the process area the different types
of pressure, flow, level and temperature measuring elements.
The different types of level measuring elements are:
1. Hydrostatic pressure uses.
2. Differential pressure.
3. Displacer’s
4. Bob and tape type float (VAREC) (Float and cable)
5. Capacitance.
Temperature measuring element’s are:
1. Bimetallic thermometer’s
2. Liquid in glass thermometer’s (capillary tube thermometer).
3. Thermocouples
4. Resistance thermal detector’s (RTD)
5. Filled system thermometer’s (gas filled or vapour filled)
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 2
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 3
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
LEVEL MEASUREMENT
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 4
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
DISPLACER OPERATING PRINCIPLE
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 5
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
FLOAT SWITCHES
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 6
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 7
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 8
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
The different types of pressure measuring elements are.
1- Manometer.
2- Bourdon tube. C-tube
Spiral Bourdon tube
Helical Bourdon tube.
3- Diaphragm
4- Bellows element.
The different types of flow measuring elements are
Indirect flow measurement
1. Orifice plate meter.
2. Venture tube.
3. Flow nozzel
4. rotameter.
5. Magnetic flow meter.
6. Turbine meter.
Direct flow measurement
Positive displacement neater. (PD meter).
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 9
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 10
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 11
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
BOURDON TUBE GAUGE ADJUSTMENT
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 12
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
INDIRECT FLOW MEASUREMENT
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 13
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
DIRECT FLOW MEASUREMENT
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 14
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.2 Explain how a pressure switch works.
Reference:
AFPC Training Manual (V.1), Introductory training.
Requirement – By Trainees :
The trainee should know and be familiar with how a pressure
switch works and its location at process area.
Pressure Switch
Pressure switch can be set at different values as per the rating of the switch. One
contact normally open or normally closed is selected when pressure is applied at the
set pressure. For example at 30 psi the switch contact should open or close giving an
electrical or pneumatic output.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 15
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.3 Identify different types of differential measuring
elements (dp, dt. Etc.)
:
Requirement – By Trainees :
The trainee should know and be familiar with the different
types of differential measuring elements (dp, dt etc..).
The trainee should demonstrate at process area the different
types of differential measuring elements.
The different types of dp measuring element’s
1. Pneumatic dp cell
2. Differential pressure bellow’s unit barton type.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 16
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE GAUGE
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 17
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.4 Explain with sketches control loops for process
variables.
:
Requirement – By Trainees:
The trainee should know and be familiar control loops for process
variables.
The trainee should demonstrate at process area the different types of
control loops.
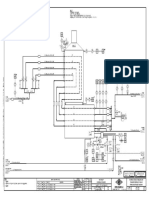
With regard to the above diagram it can be seen if the incoming process input
decreased the level in the separator with change. This change is noted by the level
transmitter which in turn sends in a signal (measured value) to the controller. The
controller will measure the deviation and correct it by sending a signal to the
correcting element (the control Value). This is a basic example of how the process
control loop functions.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 18
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 19
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.5 Explain how a split range controller works.
Reference:
AFPC Training Manual (V.1), Introductory training.
Requirement – By Trainees:
The trainee should know and understand how a split range
controller works.
Split range controller is one controller having one output controlling two final control
elements that is two control valves. One valve is operated from 3-9 psi and the other
valve is operated from 9-15 psi. One clear example is on the refrigerant skid of G.S.B
- the suction scrubber controller, control the propane (refrigerant) compressor
discharge and the recycle back to the suction scrubber.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 20
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.6 Operate (in manual and auto) a Control loop.
Requirement – by Trainees
The trainee should know and be familiar with different types control loops.
Pressure control loop.
Level Control loop.
Temperature Control, loop.
The Trainee should demonstrate in the process area or arrange with the training
center (Work shope) to conduct a actual Training using the available simulators.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 21
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
MODULE NO. : P11 Process Control Instrumentation
TASK NO. 11.7 Retrieve information from a cause and effect
diagram (SD matrix).
:
Reference:
AFPC Training Manual (D matrix)
Requirement – By Trainees :
The trainee should know how to use cause and effect diagram
(SD matrix)
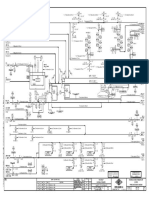
A cause and effect is a document which contains valuable information for the
operator/supervisor prior to conducting any test or change in the plant.
On the left hand side of the document you will have the causes and on the right hand
side you will see it’s effects for example in the accompanying chart - the first cause
on V-591 shows LSHH-591-1 and the resultant effects will be.
1. Close SDV-591-2 HP Gas SDV.
2. Close the station gas outlet shut down valve.
3. Shut down the compressor panel.
4. Shut down the glycol panel.
5. You will receive LSHH-591-1 first out indicator on the panel.
6. There will be an audible horn.
7. Compression facility S/D alarm.
8. Audible horns on the glycol/compression panel.
From the above we can see the list of events occurring when we have an LSHH-591-
1. Thus it is said that every operator should have a sound knowledge on how to read
the S/D matrix of the cause and effect. Because it will save him a lot of work for a
simple reason if a calibration check has to be done on LSHH-591-1 he can take the
necessary precautionary measures.
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 22
AL FURAT PETROLEUM COMPANY TASK DETAILING MANUAL
IHRDC Module – P – 11 (REV. 1) Aug. 1999 Page. 23
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Troubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreDe la EverandTroubleshooting Rotating Machinery: Including Centrifugal Pumps and Compressors, Reciprocating Pumps and Compressors, Fans, Steam Turbines, Electric Motors, and MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sea Max Manual 2010Document31 paginiSea Max Manual 2010adrian_jvÎncă nu există evaluări
- P&ID SymbolsDocument119 paginiP&ID SymbolsaswinkovilakamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Pumps: Types, Applications & PerformanceDocument19 paginiIndustrial Pumps: Types, Applications & Performancedevasree reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Type Heat Exchangers: Operation & Maintenance ManualDocument24 paginiPlate Type Heat Exchangers: Operation & Maintenance ManualasjkhjshdjkashdashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sylabus For Piping TrainingDocument5 paginiSylabus For Piping TrainingDilip YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation & Process Control CertificateDocument4 paginiInstrumentation & Process Control Certificateheka2006Încă nu există evaluări
- BrochureDocument28 paginiBrochurePapa100% (1)
- P&id - 1Document5 paginiP&id - 1dasubhai100% (1)
- August 2012 IssueDocument56 paginiAugust 2012 IssueGas, Oil & Mining Contractor Magazine100% (1)
- Basics of instrumentation and control concepts introductionDocument222 paginiBasics of instrumentation and control concepts introductionSamuel OnyewuenyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workbook CENTUM VP PDFDocument160 paginiWorkbook CENTUM VP PDFSyed Mian Fahim Kakakhail50% (2)
- INST-U01 Trainers Resource MaterialDocument16 paginiINST-U01 Trainers Resource MaterialkhalafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Petroleum Gas Compression 3Document55 paginiPetroleum Gas Compression 3Медетбек ҒайноллаÎncă nu există evaluări
- h2s Napt - TRNG - M - 002Document14 paginih2s Napt - TRNG - M - 002ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Technician (GM - T&D - TM) Program Handbook 2014-2015Document16 paginiMechanical Technician (GM - T&D - TM) Program Handbook 2014-2015Anonymous SlyvspdBÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP LP BypassDocument37 paginiHP LP BypassSCE RIHANDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method of Statement For SPI366 Pump Sump Cleaning Without Confined Space EntryDocument5 paginiMethod of Statement For SPI366 Pump Sump Cleaning Without Confined Space EntryKarpana Devi LetchumananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 P & ID SymbolsDocument32 paginiUnit 5 P & ID SymbolskhalimnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Introduction To Intrumentatio and Control EngineeringDocument64 pagini1.1 Introduction To Intrumentatio and Control EngineeringZenobia Joy VillarbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rig Mechanic Shagaya JegestinDocument4 paginiRig Mechanic Shagaya JegestinDIJU100% (1)
- SPECIAL REPORT: Identifying Sources Key To Detailed Troubleshooting of Amine FoamingDocument9 paginiSPECIAL REPORT: Identifying Sources Key To Detailed Troubleshooting of Amine FoamingAbhishek ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 Factory Acceptance TestingDocument6 pagini3.1 Factory Acceptance TestingJean-Pierre AwuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schedule Tci 2017 Oil and Gas TrainingDocument7 paginiSchedule Tci 2017 Oil and Gas TrainingEM Rifqi Wilda PradanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Instruction No.007 Blinding and Deblinding of EquipmentdocDocument2 paginiWork Instruction No.007 Blinding and Deblinding of Equipmentdocrichard carlo del mundoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship Report: Noman DilberDocument42 paginiInternship Report: Noman Dilberfarhan9125Încă nu există evaluări
- Remote measurement and control principlesDocument128 paginiRemote measurement and control principlesPATEL ANANDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Yokogawa PDFDocument59 paginiControl Yokogawa PDFmiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contaminants and EffectsDocument24 paginiContaminants and EffectsdediodedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Torque WrenchDocument21 paginiHydraulic Torque Wrenchstarway indiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contamnant Reporting in Amine Gas Treating ServiceDocument21 paginiContamnant Reporting in Amine Gas Treating ServiceagadeilagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organism and PopulationDocument24 paginiOrganism and PopulationKM_ArunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anilkumar Kanjibhai Patel (Mechanical Technician) Updated CVDocument5 paginiAnilkumar Kanjibhai Patel (Mechanical Technician) Updated CVpavitravpatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification and Designation of Common Pump TypesDocument3 paginiClassification and Designation of Common Pump TypesPradeep KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV Ani Puspita Sari - Process Eng PDFDocument6 paginiCV Ani Puspita Sari - Process Eng PDFAgung PartadirtjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muhammed Harish: ObjectiveDocument4 paginiMuhammed Harish: ObjectiveJas JashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air-cooled heat exchangers: Reliable cooling solutionsDocument22 paginiAir-cooled heat exchangers: Reliable cooling solutionsAnkit LonareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Syllabus For First PUCDocument13 paginiChemistry Syllabus For First PUCsmi_santhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Al-Khor Community: 8th Oil & Gas Cricket Tournament 2011Document9 paginiAl-Khor Community: 8th Oil & Gas Cricket Tournament 2011swa.deepakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadratic Relation and FunctionsDocument37 paginiQuadratic Relation and FunctionsKayla DollenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gasket BrochureDocument26 paginiGasket BrochureAreeb KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haskel Catalogo Dei Gas BoostersDocument36 paginiHaskel Catalogo Dei Gas BoosterslorytechÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Industrial Heat TransferDocument12 paginiBasics of Industrial Heat TransferPinaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAINTENANCE or MECHANICAL TECHNICIANDocument2 paginiMAINTENANCE or MECHANICAL TECHNICIANapi-79058143Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Torque WrenchDocument16 paginiHydraulic Torque WrenchMr. S.L. AdvaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Subsea QuestionsDocument111 pagini8 - Subsea QuestionssouthernorÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntegerDocument10 paginiIntegerSACHIN SONIÎncă nu există evaluări
- TapcoEnpro: Petrochemical Valve & Control ExpertiseDocument4 paginiTapcoEnpro: Petrochemical Valve & Control ExpertiseInspection EngineerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 000-API 510 Pressure Vessel Iinspector Preparation Course BROCHUREDocument9 pagini000-API 510 Pressure Vessel Iinspector Preparation Course BROCHUREInstech Premier Sdn BhdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Vitae: S.Bebin RoyDocument3 paginiCurriculum Vitae: S.Bebin RoyDIJUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process and Instrument Diagram SymbolsDocument24 paginiProcess and Instrument Diagram SymbolsBabak Hosseini100% (1)
- AtomDocument3 paginiAtomRich ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLANT 19 Blowdown SystemDocument2 paginiPLANT 19 Blowdown SystemGhuna UcihaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model 5 Operating and Maintenance Manual - Low Water VolumeDocument120 paginiModel 5 Operating and Maintenance Manual - Low Water VolumeJuan C FrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 370D4 2F 6RStandardsDocument1 pagină370D4 2F 6RStandardsAlejandro ParradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAD Designer or CAD TechnicianDocument1 paginăCAD Designer or CAD Technicianapi-79041757Încă nu există evaluări
- P&ID drawing symbology guideDocument36 paginiP&ID drawing symbology guideSterling GordianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offshore Technicians Recruitment Programme 2001: Operations Technician Interview QuestionsDocument15 paginiOffshore Technicians Recruitment Programme 2001: Operations Technician Interview QuestionsJohnYuillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aocp PDFDocument38 paginiAocp PDFSANJAYKUMAR chaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Addition and SubtractionDocument31 paginiMental Addition and SubtractionBea DatayÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASME Flange & PN RatingDocument7 paginiASME Flange & PN Ratinggetz_meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questions 1 TCSDocument3 paginiInterview Questions 1 TCSSrinivas TumpalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irshad Resume Instrument TechnicianDocument5 paginiIrshad Resume Instrument Technicianmallickss97Încă nu există evaluări
- 15K 10-26-18 MainCatalog PDFDocument279 pagini15K 10-26-18 MainCatalog PDFNico Jeria100% (1)
- 12 - OLGA UGM Curtin PresentationDocument40 pagini12 - OLGA UGM Curtin PresentationGui Do Esp100% (1)
- English 1Document96 paginiEnglish 1sidiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Boilers ExplainedDocument1 paginăTypes of Boilers Explainedrafique08Încă nu există evaluări
- Senior Pump Operator: Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandSenior Pump Operator: Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air ComprDocument118 paginiAir ComprMoaaz KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05-Annex - D1-Air-ConditionersDocument10 pagini05-Annex - D1-Air-Conditionersarben1672Încă nu există evaluări
- Penentuan Parameter PID Dengan Metode Ziegler-Nichols Untuk Pengendalian Flow Indicator Controller 12 - FIC - 219 Pada Control Valve 12 - FV - 219Document8 paginiPenentuan Parameter PID Dengan Metode Ziegler-Nichols Untuk Pengendalian Flow Indicator Controller 12 - FIC - 219 Pada Control Valve 12 - FV - 219maulia farahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4653 036 - PD 109a - Rev 2Document1 pagină4653 036 - PD 109a - Rev 2ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- craneTroubleshootingWhitePaper PDFDocument6 paginicraneTroubleshootingWhitePaper PDFneurolepsia3790Încă nu există evaluări
- 4653 036 - PD 110 - Rev 2Document1 pagină4653 036 - PD 110 - Rev 2ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4653 036 - PD 109 - Rev 2Document1 pagină4653 036 - PD 109 - Rev 2ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omar Cpf. List of Pumps and Motors Name: .. 23-10-08Document4 paginiOmar Cpf. List of Pumps and Motors Name: .. 23-10-08ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4653 036 - PD 108 - Rev 2Document1 pagină4653 036 - PD 108 - Rev 2ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typical Centrifugal CompressorDocument25 paginiTypical Centrifugal CompressorImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packed column pressure drop and flooding experimentDocument4 paginiPacked column pressure drop and flooding experimentSantosh ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TP 157 HSS RemovalDocument7 paginiTP 157 HSS RemovalSufyan_KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TIP01Document7 paginiTIP01ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 106r Coupling Gear Cms 106r Version 1.2Document4 pagini106r Coupling Gear Cms 106r Version 1.2amariei_niculinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Analysis Program: CCR Technologies IncDocument2 paginiSample Analysis Program: CCR Technologies IncImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Report Steven de Rijke - CO2 Removal by Amine Absorption and Condensed Rotational SeparationDocument123 paginiFinal Report Steven de Rijke - CO2 Removal by Amine Absorption and Condensed Rotational SeparationImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proximity SensorsDocument11 paginiProximity SensorsImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreasing Contactor Temperature Could Increase PerformanceDocument23 paginiDecreasing Contactor Temperature Could Increase PerformanceyusoffdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Of Fire In: A.K. Mukhopadhyay and P.P. SinghDocument13 paginiOf Fire In: A.K. Mukhopadhyay and P.P. SinghImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load CellsDocument10 paginiLoad Cellstricky777Încă nu există evaluări
- Relay - A Relay Is An Electrically Operated Switch. PowerDocument3 paginiRelay - A Relay Is An Electrically Operated Switch. Powertricky777Încă nu există evaluări
- MCCDocument7 paginiMCCImmanuel100% (1)
- Photoelectric Sensors With ApplicationsDocument15 paginiPhotoelectric Sensors With ApplicationsImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- FurnaceDocument11 paginiFurnaceharshj111Încă nu există evaluări
- Fire Fighting01Document1 paginăFire Fighting01ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sam SafetyDocument3 paginiSam SafetyImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Boat - Level 1: Name: - Position: - Points: - /50Document2 paginiLife Boat - Level 1: Name: - Position: - Points: - /50ImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication: Name: - Position: - PointsDocument1 paginăCommunication: Name: - Position: - PointsImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximo Modules Name: - Position: - PointsDocument2 paginiMaximo Modules Name: - Position: - PointsImmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Philosophy Continuous Pan Jay Shree Sugar MillDocument12 paginiControl Philosophy Continuous Pan Jay Shree Sugar MillSachinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Control Systems-Engineering Foundations and Cyber-Physical Attack LifecycleDocument133 paginiIndustrial Control Systems-Engineering Foundations and Cyber-Physical Attack LifecyclegigantischreinerelchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens PCS7 Training ManualsDocument46 paginiSiemens PCS7 Training Manualsabdulahadkhan165Încă nu există evaluări
- Diagrams For Understanding Chemical ProcessesDocument6 paginiDiagrams For Understanding Chemical ProcessesJaime Coronado CarmonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 20302 D A PPT 00 Introduction To Instrumentation Process Control 38s (Lecture Seule)Document19 pagini1 20302 D A PPT 00 Introduction To Instrumentation Process Control 38s (Lecture Seule)Morgan SidesoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams: Mark Ludwigson, P.E., PMPDocument42 paginiPiping and Instrumentation Diagrams: Mark Ludwigson, P.E., PMPEnrique DguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSPX Alarms & Fault FindingDocument40 paginiMSPX Alarms & Fault FindingRaghunath MajeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping and Instrument DiagramsDocument10 paginiPiping and Instrument DiagramsBrigidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dcs DisplaysDocument20 paginiDcs Displayshabaga1835Încă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation & Process Control Fundamentals: Designed By: Hossam A. HassaneinDocument39 paginiInstrumentation & Process Control Fundamentals: Designed By: Hossam A. HassaneinDeepanshu DagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISA PNID StandardsDocument14 paginiISA PNID StandardsHanif PayandehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process and Instrument Diagram SymbolsDocument24 paginiProcess and Instrument Diagram SymbolsBabak Hosseini100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To Marine Automation PDFDocument46 pagini1 Introduction To Marine Automation PDFMira RedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 2 Sem 2 LATEST PDFDocument149 paginiTask 2 Sem 2 LATEST PDFMuthu KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drying ManualDocument51 paginiDrying ManualKiann DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 10-Feedback ControlDocument34 paginiWeek 10-Feedback ControlMohd Aizad100% (1)
- Heatexchanger PDDocument29 paginiHeatexchanger PDbhavinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ys 1700 SettingsDocument4 paginiYs 1700 SettingsvjÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.melsec Q Process ControlDocument13 pagini4.melsec Q Process ControlLeader OneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Control Report No.1Document21 paginiProcess Control Report No.1IbrahimDewaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Areas Required To Become A Successful Instrument Engineer and Instrument Technician Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument3 paginiKnowledge Areas Required To Become A Successful Instrument Engineer and Instrument Technician Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringNGASSAKI ATONGUI Christ HubertÎncă nu există evaluări
- RT 674 Flow Level Control Demonstration Unit Gunt 1241 PDF - 1 - en GBDocument3 paginiRT 674 Flow Level Control Demonstration Unit Gunt 1241 PDF - 1 - en GBAmarÎncă nu există evaluări