Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Interim Revision Notes On Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Încărcat de
Rajat Gaur0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări10 paginiInterim Revision Notes on Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Titlu original
Interim Revision Notes on Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentInterim Revision Notes on Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări10 paginiInterim Revision Notes On Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Încărcat de
Rajat GaurInterim Revision Notes on Acts of BritishEra Civils360
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 10
PT Revision Notes civils360.
com
Intense Revision Notes by civils360
Module #3
Acts of British Era
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
PT Revision Notes Acts of British Era
● Regulating Act 1773
○ Started central administration in India
○ The limit for being a member of court of proprietors was raised from £500 to
£1000 share value which made court of proprietors compact.
○ Governor of Bengal was made Governor General of Bengal with Madras and
Bombay presidencies subordinate to him.
○ Company servants were prohibited from private trade and accepting presents and
bribes from public
○ A four membered executive council, Governor General in Council (Council of 4)
to assist Governor general with 3 members from Board of Directors and 1
Commander in Chief
○ Supreme Court established at fort William and a Chief Justice along with 3 judges
from England appointed Court of Directors to report civil, revenue, and military
affairs to British government
○ Recognized political and administrative function of the company
● Act of settlement 1781
○ Also called amending act of 1781
○ To rectify defects of regulating act 1773
○ Curtailed SC's right to action in revenue collection
● Pitt's India Act 1784
○ Named after British premier William Pitt
○ Also meant to address the short comings of 1773 Act
○ Indian affairs of East India company was brought under the direct control of
British Governmen
○ 6 membered body called Board of Control above court of directors President -
Chief official in London responsible for Indian affairs Chancellor of the
Exchequer 4 Privy councillors
○ Established system of Dual Government with Board of Control handling political
affairs, civil and military operations, and revenue of British possessions in India
(Company's territories in India were called British possessions in India for the
first time) and 'Court of Directors' handling commercial activities
● Amending Act 1786
○ Cornwallis was made GG
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ Addressed the problem between Governor general and executive council - C in C
brought under GG
● Charter Act 1793
○ Renewed Charter Act for another 20 years
○ GG's power was increased over subordinate presidencies
● Charter Act 1813
○ Renewed Charter Act for another 20 years
○ Expressly asserted crown's sovereignty over British India
○ Rs 1 lakh to promote education
○ Christian missionaries permitted in India
○ Separate account for company's territorial and commercial revenues
○ Commercial monopoly of company ended except for tea and China
● Charter Act 1833
○ GG of Bengal was made GG of India and vested in him civil and military powers
(William Bentinck)
○ Legislative powers were vested with GG and abolished legislative powers of
Madras and Bombay
○ Laws under previous acts were called regulations now ACTS
○ Commercial activities of company was ended which became an administrative
which kept Indian territory under company 'in trust for his majesty, his heirs and
successors
○ Attempted introduction of Indian Civil Service with open competition for
selection and affirmed Indians should not be barred but this was negated by
opposition from court of directors
○ GG's council was added with 4th member for legislative purposes and Lord
Macaulay constituted the law commission and the central legislative council was
formed
● Charter Act 1853
○ Higher posts in administration thrown open to competitive examination;
Macaulay committee 1854 was formed to enforce this
○ Higher posts in administration thrown open to competitive examination;
Macaulay committee 1854 was formed to enforce this
○ Law member was made the full member of GG's Exe. Council, who from there
on, carried out only executive functions after separation of legislative functions
○ Company's rule was extended without specifying the time period of extension,
which indicated the termination at any time
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ BOD reduced from 24 to 18, 6 nominated.
● Government of India Act 1858
○ ''Act for the good government of India''
○ Abolished East India Company and transferred the powers of governor, territories
and revenues to the British Crown
○ Abolished double government by abolishing Board Of Directors and Court of
Propreitors
○ GG of India was made Viceroy of India (Lord Canning)
○ Secretary of State for India vested with complete authority and control over
Indian administration, responsible ultimately to British Parliament
○ 15 member 'council of India' to assist S.O.S, an an advisory body chaired by SOS.
○ Constituted 'SOS in council' with a power to sue and be sued in India as well as
England
● Councils Act 1861
○ Reversed the centralisation - Madras and Bombay restored with legislative powers
○ New legislative councils for Bengal (1862), North Western Frontier (1866),
Punjab (1897)
○ Viceroy empowered to make rules and orders for the convenient transaction of
business
○ Recognised portfolio system introduced by Canning in 1858 Authorised Viceroy
to issue ordinances and even without appr
○ Authorised Viceroy to issue ordinances and even without approval of Legislative
council during emergencies
○ Viceroy could nominate Indians to law making process, by nominating Indians as
nonofficial members
○ Canning in1862 nominated
■ Raja of Benaras
■ Maharaja of Patiala
■ Sir Dinkar Rao
● Councils Act 1892
○ dealt exclusively with powers, functions and composition of legislative council
○ Increased the number of additional members in central and provincial legislative
council with official majority
○ Legislative council permitted to discuss budget and address questions to executive
○ Authorised Viceroy to nominate non officials to central legislative council as per
recommendations of provincial legislative councils and Bengal Chamber of
commerce
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ Governor to nominate non officials to provincial legislative councils on
recommendations of
■ District Boards
■ Municipalities
■ Universities
■ Trade Associations
■ Zamindars
■ chambers
● Councils Act 1909 (Morley-Minto Reforms)
○ Size of legislative councils at centre and provinces refixed
■ Centre - raised 16 to 60
■ Major province - 50
■ Minor Province - 30
○ Additional seats are both elected and nominated
○ Functional representation was followed
○ Retained official majority at centre but allowed non official majority at province
○ Allowed Indians in executive council
○ Satyendra Prasad Sinha first Indian Law member
○ Deliberative functions of legislative council enlarged; Permitted
○ Supplementary questions
○ Resolutions
○ communal electorate for Muslims, thus legalised communalism
○ Father of communal electorate' Lord Minto
○ No. of executive councillors in 3 major presidencies, Bombay, Madras and
Bengal increased
○ Separate representation for presidency corporations, chamber of commerce,
universities and zamindars
● Government of India Act 1919 (Montagu - Chelmsford Reforms)
○ Separated Central and Provincial subjects & respective legislatures were
authorised to make laws on their respective subjects
○ Diarchy at province; Provincial subjects were further divided into transferred
subjects and reserved subjects
○ Transferred subjects were to be administered by governors with the aid of
ministers responsible to leg
○ Reserved subjects were to be administered by governor with his executive council
without responsibility to legisature
○ Bicameralism introduced at centre
■ Council of states: Upper house
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
■ Legislative Assembly: Lower house
○ Majority of members are directly elected
○ Franchise granted according to property, tax or education i.e. to a limited number
of peope
○ Number of Indian members in the 6 member executive council of Viceroy became
3 other than CIC
○ Communal representation extended to Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians,
and Europeans
○ Provided a new office of High Commissioner of India in London and transferred
some of the functions of SOS to him; SOS to be paid salary out of British revenue
○ Central and Provincial budgets separated & provincial legislatures given power to
enact their budgets
○ Provided for the establishment of PSC (1926, for recruitment of civil servants)
○ Statutory commission to be appointed after 10 years to report on the working
○ For the purpose of 'responsible government'
● Simon Commission 1927
○ On recommendations of GOI Act 1919
○ 7 membered committee with John Simon as Chairman
○ ''Indian Statutory Commission''
○ Clement Atlee was one among the 7 members
○ Recommendations
■ Abolition of Diarchy
■ Representative responsible government in provinces
■ Federation of British India and Princely states
■ Separate electorate to be retained only until tensions persist between
Hindus and Muslims
■ 3 RTC held to consider the proposals with representation of British
government, British India and Princely States
■ 'White paper on constitutional reforms' were submitted for consideration
of 'joint select committee' of British Parliament
● Communal Award 1932
○ August 1932, British PM Ramsay McDonald announced communal
representation for minorities which extended to depressed Hindu Classes called
''Communal Award'' Gandhi took fast unto death and reached agreement with
depressed classes - Poona Pact
○ Retained Hindu joint electorate and gave reserved seats for the depressed classes
● Government of India Act 1935
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ W.R.T Federation
■ Establishment of an Indian federation consisting of princely states and
provinces (not implemented as princely states opposed
■ Division of power
● Federal List - 59 items
● Provincial List - 54 items
● Concurrent List - 36 items
■ Residuary powers vested in viceroy
■ Adopted Diarchy at Centre with federal list divided into transferred and
■ reserved subjects (not implemented)
■ Council of India (1858) abolished
■ Establishment of Reserve Bank
■ Establishment of Federal Court (1937)
○ W.R.T Provinces
■ Diarchy was Abolished and Provincial autonomy was introduced
■ Governor was required to act with the advice of ministers responsible to
Provincial legislature (came into effect in 1937; withdrawnin1939)
■ Bicameralism at 6 of the 11 provinces; Bihar, Bengal, Madras, Bombay,
Assam, United Provinces
○ Miscellaneous
■ Communal representation to depressed classes, women and labour
■ Extended Franchise with which 10% of total population got voting right
■ Federal, Provincial & Joint (two or more provinces) Public Service
Commissions
● Nehru Report (1928)
○ Lord Birkenhead challenged Indians to frame a constitution acceptable to all
○ All party conference at Delhi 1928, constituted a committee with Motilal Nehru
as Chairman by February
○ Report came in 6 months; Aug 1928, Nehru Report
○ INC ratified it by Dec 1928 Calcutta session
○ Recommended responsible government at province
● August Offer 1940
○ By 1939, after the resignation of members from legislative assembly, INC
demanded the status of independence of India or at least Provincial National
Government
○ Viceroy Lord Linlithgow turned down the request by August 8, 1940; called
'August Statement'
○ Instead suggested the following (aimed at Indian Support for WW2)
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ Expansion of Viceroy's executive council with more number of Indian members
○ Representative constitution making body to be set up after war
○ War advisory council to be set up consisting of representatives of British India
and the Indian states
○ Viceroy promised league and other minorities that British govt would never agree
to a constitution or govt in India w/o their support
○ INC rejected the August offer
○ Muslim league proclaimed themselves satisfied only with a partitition
● Cripps Mission 1942
○ Under the pressure of US president Roosevelt and Chinese president Chiang Kai
Shek, Churchill decided to send a mission to India to seek active cooperation
against Japan to whom Rangoon had fallen to
○ Stafford Cripps submitted the following suggestions after discussing with leaders
of various political parties
○ British govt is to provide dominion status to India
○ Fresh elections to all provincial legislature, after which a constitution making
body would be set up, after the war. Members of this body will be elected by
provincial assemblies and nominated by princely states
○ Govt of Britain would accept the constitution with a provision that if any Indian
province disagrees to accept the constitution, will reside outside Indian union and
can negotiate directly or separately with Britain
○ During war, executive council composed of leaders of principal sections of Indian
people. British Govt will have complete control over defence and military
operations.
○ INC rejected it seeking action for promise; League rejected it demanding partition
● Wavell Plan and Simla Conference 1945
○ To resolve political deadlock after 1939, Viceroy went to England for
consultation and to create conducive atmosphere for dialogue ordered in March
1945
○ 4th June 1945, all the working committee members of INC were realeased
○ Proposed a new executive council of 14 members with all Indians except Viceroy
& CIC (Muslims even though only 25% of the population, was over represented
with 6 members
○ All portfolios except defence were to be under the control of Indian members
● Cabinet Mission 1946
○ Announced on 19th Feb 1946
○ Members
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
■ Sir Pethick Lawrence - SOS for India
■ Sir Stafford Cripps - President of the board of trade
■ A V Alexander - 1st Lord of Admiralty
● Obectives
○ Find out means and ways for peaceful transfer of power
○ Suggest measures for the formation of constitution making machinery
○ To setup interim Govt
○ Formation of constitution making body and developments leading to Indian
Independence act 1947
○ 14 membered Interim govt formed - 1946
● Features of Schemes
○ Total strength of constituent assembly 389
○ British India 296
○ Princely States 93
○ Seats to be allowed w.r.t population
○ From three principal communities
■ Muslims
■ Sikhs
■ Others
○ Representatives of community to be selected by members of the respective
community from provincial assembly through proportional representation
○ Members of princely states are to be nominated by respective heads
○ Members are to be indirectly elected by provincial assemblies
○ Elections were held by July August 1946
○ INC 208; ML 73; Others 15
○ 93 princely states remained vacant
○ first meeting on December 9,1946; boycotted by ML demanding Pakistan and
there were only 211 member
○ Satchithanand Sinha was elected pro term chairman (French practice to select
senior most member)
○ objective resolution by Nehru on 13 December 1946, approved by assembly on
22nd January 1947; later modified as the preamble of Indian Constitution
○ Interim government was formed with the members of viceroys executive council,
on September 2,1946
○ February 20,1947, Clement Atlee declared that British rule in India will end by
June 30, 1948
○ Balkan/ June 3/ Mount Batten plan accepted partition and right to secede from
British Commonweal
● Indian Independence Act 1947
PT Revision Notes civils360.com
○ Enacted by the acceptance of Mount Batten plan by INC and ML
○ British rule to be over by 15 August 1947
○ Partition into two dominions and right to secede from British Commonwealth
○ Viceroy's office was abolished and replaced by Governor General for each
dominion, to be appointed by British monarch, GOB has no responsibility w.r.t
GOI and GOP
○ Authorised constituent Assemblies of both dominions to enact laws with respect
to their dominion till the new Constitution is framed; Acts of British Parliament is
not applicable after 15 August 1947
○ Office of SOS abolished
○ British paramountcy over princely states and treaties with tribal areas were done
away with Princely states
○ Princely states were free to join any of the dominion
○ Governor General of India and provincial governors were made nominal heads as
they had to act as per the council of ministers Appointments to civil services and
reservation of p
○ Appointments to civil services and reservation of posts by SOS was stopped
○ British monarch was made to remove emperor of India from Royal styles and
titles
●
●
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Constitutional Development in India: Key Acts and Reforms</bDocument22 paginiConstitutional Development in India: Key Acts and Reforms</bPratibha VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern India Acts 1773-1862 SummaryDocument5 paginiModern India Acts 1773-1862 SummaryVaidehiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development Pre Partition PDFDocument39 paginiDevelopment Pre Partition PDFMuhammadIqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Background of The ConstitutionDocument30 paginiHistorical Background of The ConstitutionGopal KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muslim Rule and British Colonial Expansion in IndiaDocument28 paginiMuslim Rule and British Colonial Expansion in IndiaMuqadsa ZainebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constitutional DevelopmentDocument3 paginiConstitutional DevelopmentNazargunjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Background of PolityDocument8 paginiHistorical Background of PolityShivam YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polity NotesDocument31 paginiPolity NotesShivam YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crux EH - Historical Background - 1684246588Document37 paginiCrux EH - Historical Background - 1684246588Sephali MoharanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History - Regulating and Pitt's India Act Updated - English - 1612536242Document9 paginiHistory - Regulating and Pitt's India Act Updated - English - 1612536242Akash GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Various Topics Under Part-1: Historical BackgroundDocument8 paginiVarious Topics Under Part-1: Historical Backgroundkush_112Încă nu există evaluări
- Constitutional Development in Colonial IndiaDocument28 paginiConstitutional Development in Colonial IndiaFarahmustafa04Încă nu există evaluări
- Contitutional Development 1773 1947Document16 paginiContitutional Development 1773 1947Deshiha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module - I: Pda Xerox & StationaryDocument125 paginiModule - I: Pda Xerox & StationaryWadi SharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Rule in India: Key Acts and DevelopmentsDocument8 paginiBritish Rule in India: Key Acts and Developmentskamal RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 2: History of ConstitutionDocument5 paginiChapter - 2: History of ConstitutionVaishal GoswamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of the Indian Constitution from British-era ReformsDocument6 paginiEvolution of the Indian Constitution from British-era ReformssarifnÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Indian ActsDocument3 paginiBritish Indian ActsSenthil PrabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Government Gains Control Over India Through 1784 ActDocument2 paginiBritish Government Gains Control Over India Through 1784 Actjaivik_ce7584Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 17 - British Administration 1757-1857 Lyst8895Document18 paginiLesson 17 - British Administration 1757-1857 Lyst8895Deepak ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5Document11 paginiLecture 5Pinku BorahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pitt's India Act 1784 Established Dual ControlDocument3 paginiPitt's India Act 1784 Established Dual ControlSargam BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Different Charter - ActsDocument19 paginiThe Different Charter - Actsaaditya PatwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- All British - ActsDocument12 paginiAll British - ActsMAHESH PATLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal and Constitutional History NotesDocument318 paginiLegal and Constitutional History NotesritwikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 and 4 Brief HistoryDocument18 paginiLecture 3 and 4 Brief Historytaimoor akbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pitts India Act 1784 - 14221775 - 2023 - 12 - 07 - 13 - 19Document4 paginiPitts India Act 1784 - 14221775 - 2023 - 12 - 07 - 13 - 19deekshaa685Încă nu există evaluări
- CNI - Constitutional DevDocument17 paginiCNI - Constitutional Devkhushi chauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Areas in Modern IndiaDocument10 paginiImportant Areas in Modern Indiasandeep-ponnaganti-4471Încă nu există evaluări
- 1599624088088_CONSTITUTIONALISM LectureDocument22 pagini1599624088088_CONSTITUTIONALISM LectureIla SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning of Colonial Rule in India-Chapter Notes (1) - WatermarkDocument6 paginiBeginning of Colonial Rule in India-Chapter Notes (1) - WatermarkhypextornadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Background of The Constitution of IndiaDocument7 paginiHistorical Background of The Constitution of IndiaStaffy KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charter Act of 1833Document6 paginiCharter Act of 1833gouri pmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical BackgroundDocument30 paginiHistorical BackgroundSanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Background PDFDocument4 paginiHistorical Background PDFShashvat SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attachment Historical Background Lyst1937Document53 paginiAttachment Historical Background Lyst1937sachin saurabhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consti NotesDocument10 paginiConsti NotesPratiksha PraveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constitution ProjectDocument23 paginiConstitution ProjectanamikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constitution ProjectDocument17 paginiConstitution ProjectShaurya BakshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-IV Indian Councils Act of 1858, 1861 and 1892Document9 paginiUnit-IV Indian Councils Act of 1858, 1861 and 1892Yash BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constitutional Development of India Upsc Notes 23Document6 paginiConstitutional Development of India Upsc Notes 23Deshiha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.BEST Legal and Constitutional History NotesDocument318 pagini6.BEST Legal and Constitutional History NotesAkki ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConstitutionDocument10 paginiConstitutionNikhil ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Constitution - Handbook (For Reference) PDFDocument121 paginiIndian Constitution - Handbook (For Reference) PDFKrishit PanchalÎncă nu există evaluări
- On What Is Legal and Constitutional History DevelopmentDocument36 paginiOn What Is Legal and Constitutional History DevelopmentritwikÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMP Amendment ActsDocument29 paginiIMP Amendment ActsMANJU IASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical BackgroundDocument6 paginiHistorical Backgroundshivam kanojiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- History Part 2Document22 paginiHistory Part 2arunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1813, 1833 and Codification of LawDocument26 pagini1813, 1833 and Codification of LawBhuvaneswari Ram MotupalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulating Act 1773 & Rise of British Rule in IndiaDocument14 paginiRegulating Act 1773 & Rise of British Rule in IndiaziddumurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-Evolution of CoiDocument9 pagini1-Evolution of CoiGaurav ScribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medieval HistoryDocument92 paginiMedieval HistoryAmbarish ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LA EX Historical Evolution 2020Document8 paginiLA EX Historical Evolution 2020Rashid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulating Act 1773Document9 paginiRegulating Act 1773Dinesh PKÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Acts in India till 1857Document37 paginiBritish Acts in India till 1857pratham mohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of East India Company Rule in IndiaDocument17 paginiHistory of East India Company Rule in IndiaSANTOSH CHAUHANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncert Notes On Government of India Act 1919 For Upsc 34985322Document5 paginiNcert Notes On Government of India Act 1919 For Upsc 34985322k.ganesh024Încă nu există evaluări
- Charter Act of 1833Document9 paginiCharter Act of 1833Ritesh MahlawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolityDocument4 paginiPolityBidyut MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positive and Negative Affect Schedule - Expanded VersionDocument2 paginiPositive and Negative Affect Schedule - Expanded VersionRajat GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sem 8 Updated Notes, Nov. 2014Document29 paginiSem 8 Updated Notes, Nov. 2014Rajat GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concurrency ControlDocument14 paginiConcurrency ControlRajat GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Rise of Adolf HitlerDocument4 paginiThe Rise of Adolf HitlerRajat GaurÎncă nu există evaluări
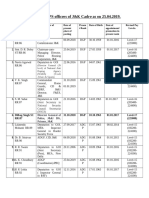
- Civil List of IPS and SPS As On 25.04.2019Document14 paginiCivil List of IPS and SPS As On 25.04.2019bluehacker133777Încă nu există evaluări
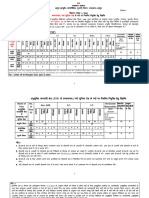
- LRS-ULB-UDA Wise Status of in Principle Patterns As On 24-02-2022Document3 paginiLRS-ULB-UDA Wise Status of in Principle Patterns As On 24-02-2022Santtosh Kummar AgathamudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPSC Civil Services Exam 2023Document21 paginiUPSC Civil Services Exam 2023Amrish TrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Way Bill: Government of IndiaDocument1 paginăE-Way Bill: Government of IndiaVIVEK N KHAKHARAÎncă nu există evaluări
- MaharashtraDocument260 paginiMaharashtraRishi WadhwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Critical Analysis of The 42nd Amendment ActDocument8 paginiA Critical Analysis of The 42nd Amendment ActHet DoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LawNotes: Bonded Labour CaseDocument20 paginiLawNotes: Bonded Labour CaseRiya RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Land Development Rules Amended for YSR HousingDocument2 paginiAP Land Development Rules Amended for YSR HousingSri Harsha KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tamilnadu School Book 12 TH Political ScienceDocument232 paginiTamilnadu School Book 12 TH Political SciencevenkatesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PG DamodaramSanjivayyaNationalLawUniversityDSNLUVisakhapatnam PDFDocument2 paginiPG DamodaramSanjivayyaNationalLawUniversityDSNLUVisakhapatnam PDFSom Dutt VyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- IAS4Sure Government Schemes Notes For Prelims 2022Document198 paginiIAS4Sure Government Schemes Notes For Prelims 2022Kranthi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospitalii Vacancy - Part1Document2 paginiHospitalii Vacancy - Part1Bhavagna SaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zambia Decentralisation PolicyDocument35 paginiZambia Decentralisation PolicyMaugahn Muff-Wheeler100% (1)
- Civils Polity McqsDocument39 paginiCivils Polity Mcqsdukkasrinivasflex100% (1)
- Ram JethmalaniDocument4 paginiRam JethmalaniJaisurya SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Case 19-11-2018 PDFDocument75 paginiNew Case 19-11-2018 PDFsunita beharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GST AssignmentDocument7 paginiGST Assignmentshivam tiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCS Pension Rules SummaryDocument176 paginiCCS Pension Rules Summaryabhishek singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upsc Notification SyllabusDocument44 paginiUpsc Notification SyllabusAhmedAliKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Listof TORsDocument6 paginiListof TORsKetan V. JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Pay Commission Salary and Arrears Calculator IndiaDocument41 pagini6th Pay Commission Salary and Arrears Calculator Indiaanon-793202100% (13)
- 07 Chapter 2Document154 pagini07 Chapter 2HiteshPansheriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Simhadri STPP (Stage I & II) Bhel 3 Sipat STPP (Stage - I) DoosanDocument9 pagini2 Simhadri STPP (Stage I & II) Bhel 3 Sipat STPP (Stage - I) DoosanKoushik DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notification Ayurveda Dept Rajasthan Compounder PostsDocument15 paginiNotification Ayurveda Dept Rajasthan Compounder PostsankurÎncă nu există evaluări
- North and Middle Andaman District Pin Code ListDocument3 paginiNorth and Middle Andaman District Pin Code Listfaiyaz432Încă nu există evaluări
- 4375.201.125 Fy 22-23Document99 pagini4375.201.125 Fy 22-23Star ColourparkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifa (Border Roads) Manual: Controller General of Defence Accounts West Block-V, R.K. Puram, New Delhi-110066Document293 paginiIfa (Border Roads) Manual: Controller General of Defence Accounts West Block-V, R.K. Puram, New Delhi-110066mailme_vijuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft Writ - Mohd Akbar (9.8.19)Document61 paginiDraft Writ - Mohd Akbar (9.8.19)Aliza Noor100% (2)
- FR CSM 21 Engl 300522 - 0Document15 paginiFR CSM 21 Engl 300522 - 0VIKAS SANGWANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Border Security ForceDocument7 paginiBorder Security Forceswai singhÎncă nu există evaluări