Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Primary Education Is The First Stage of Compulsory Education. It Is Preceded by Pre-School or
Încărcat de
Thomas LeeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Primary Education Is The First Stage of Compulsory Education. It Is Preceded by Pre-School or
Încărcat de
Thomas LeeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Source: Wikipedia
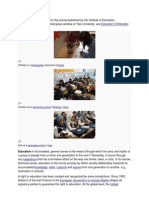
Primary education is the first stage of compulsory education. It is preceded by pre-school or
nursery education and is followed by secondary education. In North America this stage of
education is usually known as elementary education and is generally followed by middle
school.
In most countries, it is compulsory for children to receive primary education, though in many
jurisdictions it is permissible for parents to provide it. The transition to secondary school or
high school is somewhat arbitrary, but it generally occurs at about eleven or twelve years of
age. Some educational systems have separate middle schools with the transition to the final
stage of education taking place at around the age of fourteen.
The major goals of primary education are achieving basic literacy and numeracy amongst all
pupils, as well as establishing foundations in science, mathematics, geography, history and
other social sciences. The relative priority of various areas, and the methods used to teach
them, are an area of considerable political debate.
Typically, primary education is provided in schools, where the child will stay in steadily
advancing classes until they complete it and move on to high school/secondary school.
Children are usually placed in classes with one teacher who will be primarily responsible for
their education and welfare for that year. This teacher may be assisted to varying degrees by
specialist teachers in certain subject areas, often music or physical education. The continuity
with a single teacher and the opportunity to build up a close relationship with the class is a
notable feature of the primary education system.
Traditionally, various forms of corporal punishment have been an integral part of early
education. Recently this practice has come under attack, and in many cases been outlawed,
especially in Western countries.
Secondary education is the stage of education following primary school. Secondary education is
generally the final stage of compulsory education. However, secondary education in some countries
includes a period of compulsory and a period of non-compulsory education. The next stage of
education is usually college or university. Secondary education is characterized by transition from the
typically compulsory, comprehensive primary education for minors to the optional, selective tertiary,
"post-secondary", or "higher" education (e.g., university, vocational school) for adults. Depending on
the system, schools for this period or a part of it may be called secondary schools, high schools,
gymnasia, lyceums, middle schools, colleges, vocational schools and preparatory schools, and the
exact meaning of any of these varies between the systems.
Higher education refers to a level of education that is provided at academies, universities,
colleges, seminaries, institutes of technology and certain other collegiate-level institutions,
such as vocational schools, trade schools, and career colleges, that award academic degrees or
professional certifications.
Since 1950, Article 2 of the first Protocol to the European Convention on Human Rights
obligates all signatory parties to guarantee the right to education. At the world level, the
United Nations International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966,
guarantees this right under its Article 13, which states that "higher education shall be made
equally accessible to all, on the basis of capacity, by every appropriate means, and in
particular by the progressive introduction of free education".
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lesson 6 EducationDocument4 paginiLesson 6 EducationDan FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Intro: Systems of Formal EducationDocument16 paginiEducation Intro: Systems of Formal EducationBadiuzaman Al-AyubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education Systems Around the WorldDocument10 paginiEducation Systems Around the WorldgeetukumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Education and SchoolingDocument3 paginiDifference Between Education and SchoolingNguyễn HóaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EducationDocument105 paginiEducationAngel BenganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Formal Education Explored in Wikipedia ArticleDocument6 paginiTypes of Formal Education Explored in Wikipedia ArticleRaf echeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preschool: Early Childhood EducationDocument6 paginiPreschool: Early Childhood EducationKristine Joy PitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education: For Other Uses, SeeDocument24 paginiEducation: For Other Uses, Seeapurvagomes_44807123Încă nu există evaluări
- Education WikepediaDocument292 paginiEducation WikepediaRuth OyeyemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education in Its Broadest, General Sense Is The Means Through Which The Aims and Habits of ADocument24 paginiEducation in Its Broadest, General Sense Is The Means Through Which The Aims and Habits of AMuhammad ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teachers Students Subjects Reading Writing Mathematics Science History Schooling Higher Learning Vocational Informal LevelDocument14 paginiTeachers Students Subjects Reading Writing Mathematics Science History Schooling Higher Learning Vocational Informal LevelrahulcoolrulzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Education in USDocument4 paginiGuide To Education in USHarsha19111999Încă nu există evaluări
- Secondary Education - Current Trends, International Issues - HISTORY OFDocument5 paginiSecondary Education - Current Trends, International Issues - HISTORY OFYasmeen JafferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educational Systems in Western CountriesDocument2 paginiEducational Systems in Western CountriesKaren May UrlandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education - Wikipedia PDFDocument23 paginiEducation - Wikipedia PDFChuahgegeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Current Education System in The United States of AmericaDocument5 paginiThe Current Education System in The United States of Americadayna-um100% (1)
- Educate Education (Chittenden Memorial Window)Document17 paginiEducate Education (Chittenden Memorial Window)Deepak Kumar AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education 2Document6 paginiEducation 2FaroXXXÎncă nu există evaluări
- UK Education SystemDocument3 paginiUK Education SystemThe Sun and The SeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 8690875867897Document101 paginiChemistry 8690875867897mohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education: Name: Imas Adelia Al Burdah Nim: P27820113014 Class: II Reguler ADocument1 paginăEducation: Name: Imas Adelia Al Burdah Nim: P27820113014 Class: II Reguler AImas Adelia Al BurdahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education System in the US: Grades, Standards and TrendsDocument4 paginiEducation System in the US: Grades, Standards and Trendsmaiden mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 34059034756Document101 paginiBiology 34059034756mohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- American School System Suport CursDocument3 paginiAmerican School System Suport CursVlad CocuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 87905789Document102 paginiMath 87905789mohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Learning SystemDocument3 paginiAlternative Learning SystemBRYAN VILLEGAZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Introduction in Qualitative ResearchDocument5 paginiResearch Introduction in Qualitative ResearchMelissa Ann PatanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SecondaryDocument2 paginiSecondaryRei Diaz ApallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Right To EducationDocument23 paginiRight To EducationRobert Kane ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Schools ExplainedDocument102 paginiTypes of Schools Explainedmohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physicws 098967909Document102 paginiPhysicws 098967909mohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- RrdyDocument2 paginiRrdyjedimetalÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 24761378Document102 paginiEnglish 24761378mohammadali mathÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Education SystemDocument10 paginiAmerican Education Systemcristixavier05Încă nu există evaluări
- Education 2Document1 paginăEducation 2Леся СтроченкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- American System of EducationDocument11 paginiAmerican System of EducationIustin Danciu100% (1)
- American EducationDocument1 paginăAmerican EducationKlaus Rosmanitz100% (1)
- SchoolDocument1 paginăSchoolJonah PangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Stages in EducationDocument2 paginiTypes and Stages in EducationPrasanth Kurien MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Culture Final Exam Guide Aug-Dec 22 Guillermo RossanoDocument24 paginiBritish Culture Final Exam Guide Aug-Dec 22 Guillermo Rossanonicolas ramirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Практика мовленняDocument13 paginiПрактика мовленняАнна ФурманÎncă nu există evaluări
- A List of Vocabulary Items Related To EducationDocument3 paginiA List of Vocabulary Items Related To EducationAna SzerencsesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formal EducationDocument2 paginiFormal EducationAyshÎncă nu există evaluări
- ...Document1 pagină...NeltroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academia: Higher Education Research Athens PlatoDocument19 paginiAcademia: Higher Education Research Athens PlatoAmartuya DorjpalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gervacio Educational StructureDocument1 paginăGervacio Educational StructureRosemarie HagnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pop TinDocument5 paginiPop TinHope SerquiñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SchoolDocument1 paginăSchoolclumsy16Încă nu există evaluări
- JapaneseEducationSystem Grades10!12!1702796885503Document13 paginiJapaneseEducationSystem Grades10!12!1702796885503chambwesimeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 65Document14 paginiTema 65Jose HerediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Culture Final Exam GuideDocument24 paginiBritish Culture Final Exam GuideJUANÎncă nu există evaluări
- SchoolDocument1 paginăSchoolEliseo BlancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- High School in USADocument3 paginiHigh School in USAMydays31Încă nu există evaluări
- Education in Its General Sense Is A Form Of: Ēducātiō Ēdūcō Ēdūcō Ē-DūcōDocument19 paginiEducation in Its General Sense Is A Form Of: Ēducātiō Ēdūcō Ēdūcō Ē-DūcōEidysPaulinaRivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education System in The Philippines and AmericaDocument4 paginiEducation System in The Philippines and AmericaMaggi Mae J. MorillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Education in The United States Is Primarily Provided by The GovernmentDocument12 paginiEducation in The United States Is Primarily Provided by The GovernmentDoung PichchanbosbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academic Paper SamplerDocument34 paginiAcademic Paper SamplerOfficial Administrator75% (4)
- La scuola innovativa aperta al territorio come contrasto alla dispersione ed alla povertà educativaDe la EverandLa scuola innovativa aperta al territorio come contrasto alla dispersione ed alla povertà educativaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The School System Comparison between the United States of America and FinlandDe la EverandThe School System Comparison between the United States of America and FinlandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Power Is Produced by Controlled (I.e., Non-Explosive)Document14 paginiNuclear Power Is Produced by Controlled (I.e., Non-Explosive)Thomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Areas: Preschool Education or Infant Education Is The Provision of Education ForDocument16 paginiDevelopmental Areas: Preschool Education or Infant Education Is The Provision of Education ForThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source: Wikipedia: TechnologyDocument3 paginiSource: Wikipedia: TechnologyThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to EconomicsDocument19 paginiIntroduction to EconomicsThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics 3Document7 paginiEconomics 3Thomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- History: Philosophy of Education Is A Field ofDocument9 paginiHistory: Philosophy of Education Is A Field ofThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- History: Homeschooling or Homeschool (Also CalledDocument8 paginiHistory: Homeschooling or Homeschool (Also CalledThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definitions: Globalization (Or Globalisation) Describes A Process by Which Regional Economies, SocietiesDocument18 paginiDefinitions: Globalization (Or Globalisation) Describes A Process by Which Regional Economies, SocietiesThomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics 2Document18 paginiEconomics 2Thomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singapore Context Notes 2016Document20 paginiSingapore Context Notes 2016Thomas LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- GP Politics Essay QuestionsDocument2 paginiGP Politics Essay QuestionsThomas Lee100% (1)
- Community Profile of Brgy. Batasan HillsDocument7 paginiCommunity Profile of Brgy. Batasan HillsAldriannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Pre-School & Day Care in Balepur, Navi MumbaiDocument3 paginiList of Pre-School & Day Care in Balepur, Navi MumbaiSantosh sÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Community Service Ideas for TeensDocument1 pagină10 Community Service Ideas for TeensCynthia Paracuelles RadazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kindergarten I-Ready Readiness RedactedDocument3 paginiKindergarten I-Ready Readiness Redactedapi-360100126Încă nu există evaluări
- Attention SpanDocument1 paginăAttention SpanOliver MacaraegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teachers College Press 2015 CatalogDocument91 paginiTeachers College Press 2015 CatalogDave StraussÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dog Sled RaceDocument1 paginăDog Sled RaceQuynh Le100% (1)
- Krislyn Antonellis: DucationDocument4 paginiKrislyn Antonellis: Ducationapi-397035932Încă nu există evaluări
- Educational Toys and Postwar American CultureDocument29 paginiEducational Toys and Postwar American CultureSarah HearneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bese 66 emDocument5 paginiBese 66 emFirdosh Khan100% (1)
- Resume 2017Document2 paginiResume 2017api-363236767Încă nu există evaluări
- Child AbuseDocument4 paginiChild AbuseDiana VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarva Shiksha AbhiyanDocument14 paginiSarva Shiksha AbhiyanRamprasad Naik100% (1)
- Newsletter 24 TH FebDocument1 paginăNewsletter 24 TH FebmrvaughanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brent International School ManilaDocument2 paginiBrent International School ManilaSerje BualÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Edc ResumeDocument1 paginăFinal Edc Resumeapi-242780651Încă nu există evaluări
- KHST ActivityDocument3 paginiKHST Activityapi-340485132Încă nu există evaluări
- Famous Movie Quotes Activity TitleDocument8 paginiFamous Movie Quotes Activity TitleIris DariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reggio EmiliaDocument5 paginiReggio EmiliaAnonymous a0cuWVM100% (3)
- Edt 313 Oatmeal Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiEdt 313 Oatmeal Lesson Planapi-317245187Încă nu există evaluări
- Baby WiseDocument3 paginiBaby Wisemnishiok100% (1)
- Ryerson October 2012Document6 paginiRyerson October 2012Gill_VilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- KindergartenDocument7 paginiKindergartenAnushka KhatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nicole Arianna Johnson ResumeDocument1 paginăNicole Arianna Johnson Resumeapi-273657621Încă nu există evaluări
- Ansley Moore Resume Revised Jan 2018Document2 paginiAnsley Moore Resume Revised Jan 2018api-307747499Încă nu există evaluări
- Google Reader PDFDocument16 paginiGoogle Reader PDFAnonymous K8q40txBdDÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Nova Concepção de Creche Pós-LDBDocument8 paginiA Nova Concepção de Creche Pós-LDBEdianara Milkiewicz Da Silva TomacheskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equivalent Pattern Easy1Document2 paginiEquivalent Pattern Easy1Nandini VaittinadaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Importance of Free Play To Children S DevelopmentDocument8 paginiThe Importance of Free Play To Children S DevelopmentImam Khoirul FajriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toolkit NewsletterDocument4 paginiToolkit Newsletterhullaballoo3697Încă nu există evaluări