Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tutorial 01 Combined Loading Analytical
Încărcat de
pilas_nikolaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tutorial 01 Combined Loading Analytical
Încărcat de
pilas_nikolaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
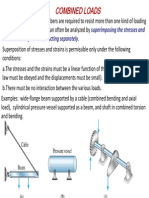
ENG5047 Mechanics and Dynamics Tutorial 1 Combined Loading Analytical
1. An axial tensile load of 10kN is applied to a 12mm diameter bar. Determine the maximum shearing
stress in the bar and the planes on which it acts. Calculate also the normal stresses on these planes.
ANS(44 MNm-2 at 45° and 135°, ±44 MNm-2)
2. A material is subjected to two mutually perpendicular stresses, one 60MNm-2 compressive and
the other 45 MNm-2 tensile. Determine the direct and shear stresses on a plane inclined at 60° to
the plane on which the 45 MNm-2 stress acts.
ANS(-33.8, 45.5 MNm-2)
3. The material of Problem 2 is now subjected to an additional shearing stress of 50MNm-2.
Determine the principal stresses acting on the material and the maximum shear stress.
ANS (65, -80, 72.5 MNm-2)
4. At a certain section in a material under stress, normal stresses of 45MNm-2 tensile and 75MNm2
tensile act on perpendicular planes together with a shear stress acting on these planes. If the
maximum stress in the material is limited to 150MNm-2 tensile
determine the maximum allowable value of .
ANS(88.7 MNm-2)
5. At a certain point in a material the following stresses act: a tensile stress of 150MNm2, a
compressive stress of 105MNm-2 at right angles to the tensile stress and a shear stress clockwise
in effect of 110MNm-2 acting on the plane bearing the 150MNm-2 stress. Calculate the principal
stresses and the directions of the principal planes.
ANS(191,-146 MNm-2; at 20.4° and 110.4° ccw to the 150 MNm-2 plane)
6. At a point in a strained material the stresses acting on planes at right angles to each
other are 200MNm-2 tensile and 80MNm-2 compressive, together with associated shear stresses
which may be assumed clockwise in effect on the 8 MNm-2 planes. If the principal stress is limited
to 320MNm-2 tensile, calculate:
a) the magnitude of the shear stresses,
ANS(219 MNm-2)
b) the directions of the principal planes,
ANS(28.7° & 118.7° ccw to 200 MNm-2 plane)
c) the other principal stress,
ANS(200 MNm-2)
d) the maximum shear stress.
ANS(260 MNm-2)
7. A shaft 100mm diameter is subjected to a twisting moment of 7kNm, together with a bending
moment of 2kNm. Find, at the surface of the shaft:
a) the principal stresses,
ANS(47.3, -26.9 MNm-2)
b) the maximum shear stress.
ANS(37.1 MNm-2)
Page 1 of 4 Ward after Lahr &Walker
ENG5047 Mechanics and Dynamics Tutorial 1 Combined Loading Analytical
8. The tightening of a bolt induces in the shank a tensile direct stress 155MNm-2 and a shear stress
due to the applied torque of 93MNm-2. Determine the magnitude and nature of the principal direct
stresses and the principal (maximum) shear stress induced in the shank of the bolt, together with
the inclination of the planes on which these stresses act. You may assume that the induced stresses
are uniformly distributed over the shank cross section.
ANS(198MNm-2, -43.5MNm-2 121MNm-2)
9. The 8mm diameter rivet (cross sectional area 50x10-6 m2) shown, is subjected to an axial tensile
force of 4kN due to the cooling of the rivet. Determine the shearing force "P" which may be applied
to the joint if the maximum principal stress must not exceed 150MNm-2.
ANS(5.13 kN)
10. A solid shaft 100mm in diameter is subjected to a torque of 3.4kNm and a bending
moment of 900Nm. Determine the principal stresses on the surface of the shaft.
11. A solid shaft 75 mm in diameter and spanning 3m between bearings has a pulley of mass 230kg
mounted at the center of the span. The maximum speed is to be 200rev/min when transmitting
30kW. Find the maximum principal stress in the shaft.
12. A structure is composed of circular members with diameter 20mm. At a particular point along
one member the loading is found to consist of a shear force of 10kN and a tensile force of 20kN.
Calculate the safety factor involved in the design if the maximum principal stress is not to exceed
350MNm-2.
13. The loading on a bolt consists of a tensile force of 10kN and a shear force of 5kN. Using a safety
factor of 3 calculate the minimum diameter d of the bolt if the maximum principal stress of the bolt
material should not exceed 280MNm-2.
14. A solid circular shaft of 125mm diameter rotates at 30rad/s. Owing to the configuration of the
bearings and the gearing, it is subjected to a maximum bending moment of 9kNm. If the maximum
principal stress should not exceed 300MNm-2, calculate the power which the shaft may transmit.
15. A sheet of a fibre reinforced composite material is subjected to a tensile stress of 80MNm-2. The
fibres in the composite all lie in a direction which is at 60° to the direction of the stress. The material
has a tensile strength of 150MNm-2 in the direction of the fibres but in the direction perpendicular to
the fibres the tensile strength is only 50MNm-2. Determine whether the sheet will fail.
Page 2 of 4 Ward after Lahr &Walker
ENG5047 Mechanics and Dynamics Tutorial 1 Combined Loading Analytical
16. A steel bolt has a diameter of 10mm and is used to withstand a tensile load of 11kN. During
installation, the bolt also receives a torque of 90Nm. Calculate the maximum shear stress in the bolt
during the tightening operation.
17. The figure shows a pulley which is fixed to the unsupported end of a solid circular shaft projecting
from a fixed bearing. The pulley carries a belt drive which has a tight tension of 4kN and a slack
tension of 1kN.
a) Identify the states (types) of stress in the shaft.
b) Identify the points on the shaft where the greatest principal stresses can be found.
c) Determine the values of the greatest principal stresses in the shaft.
d) Calculate the maximum shear stress in the shaft.
Page 3 of 4 Ward after Lahr &Walker
ENG5047 Mechanics and Dynamics Tutorial 1 Combined Loading Analytical
18. The figure shows a rectangular bar fixed securely to the end of a circular bar. The axis of the
rectangular bar is at 90° to the axis of the circular bar. The other end of the circular bar is rigidly
built-in.
a) Identify the states (types) of stress in the rectangular bar and the circular bar,
b) Identify the point on the circular bar where the greatest principal stresses can be
found,
c) At the point identified in (b) calculate:
i. the greatest principal stresses, ii. maximum shear stress in the circular bar.
Page 4 of 4 Ward after Lahr &Walker
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Problems CH-8 Complex Stresses (Blank)Document18 paginiProblems CH-8 Complex Stresses (Blank)محمد خريبط100% (1)
- Set 1 (Unit 2)Document15 paginiSet 1 (Unit 2)Tare Er Kshitij67% (9)
- Tutorials 2Document3 paginiTutorials 2Daemaro Liv Guud BremmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr220102 Strength of Materials IIDocument7 paginirr220102 Strength of Materials IISRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document3 paginiAssignment 3Kibrom GebremedhinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unsymmetrical Bending StressDocument2 paginiUnsymmetrical Bending StressPriyanka Dhurvey SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- T3 Online TestDocument3 paginiT3 Online TestDouglas OngomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Loading Exercise SheetDocument2 paginiCombined Loading Exercise Sheetsam joeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit1 CompoundStresses TutorialsDocument1 paginăUnit1 CompoundStresses TutorialsAll_regÎncă nu există evaluări
- Queastion Bank MOM 22 26Document5 paginiQueastion Bank MOM 22 26karvaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pagini9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cantilever Beam Load SolutionsDocument18 paginiCantilever Beam Load SolutionsHanamanagouda BevoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Th. of FailureDocument3 paginiTh. of Failureraja50% (2)
- ME1302 Design Machine Elements Question BankDocument21 paginiME1302 Design Machine Elements Question BankmeindyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial SheetDocument5 paginiTutorial SheetujjalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 paginiAssignment 1 FinalshishirÎncă nu există evaluări
- PartDocument9 paginiPartMahendranath Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- Solid MechanicsDocument6 paginiSolid MechanicsRameez FaroukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials: Prepared By: Engr. Jeric P. SarteDocument30 paginiStrength of Materials: Prepared By: Engr. Jeric P. SarteGiacomo EllieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Som Na (UBMCC09)Document13 paginiSom Na (UBMCC09)arjunguttula11Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter I-Stress: (66.7 Kpa, 115 Kpa)Document5 paginiChapter I-Stress: (66.7 Kpa, 115 Kpa)Irem DolekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Document3 paginiQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)annamalai_s873323Încă nu există evaluări
- Sheet - 3Document2 paginiSheet - 3Abdel Hamied EbrahemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument17 paginiModule 3 Prestressed Concrete DesignJoy lauria100% (1)
- B.Tech Assgn-1Document6 paginiB.Tech Assgn-1K Pushpendu PrashantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Elasticity - Structural EngineeringDocument7 paginiTheory of Elasticity - Structural EngineeringVijay Aravind100% (1)
- r13 Mos Old Q PapersDocument21 paginir13 Mos Old Q PapersSrinu ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials Exam QuestionsDocument83 paginiStrength of Materials Exam Questionsvenkyn88Încă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 paginiMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me2303 - Design of Machine ElementsDocument14 paginiMe2303 - Design of Machine ElementsGowtham RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMEN 326 - Combined Benidng and TorsionDocument15 paginiMMEN 326 - Combined Benidng and TorsionchegedennÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principal Stresses & Strains Theories of Failures Unit-IvDocument2 paginiPrincipal Stresses & Strains Theories of Failures Unit-IvSujeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignDocument8 paginiTUK University Exams June 2016 Mechanical Engineering Technology Advanced Machine DesignCharles OndiekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae 35 Solid MechanicsDocument4 paginiAe 35 Solid MechanicsRameez FaroukÎncă nu există evaluări
- R7220103 Strength of Materials - IIDocument1 paginăR7220103 Strength of Materials - IIsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMDocument8 paginiSMShounak KossambeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSNA COLLEGE STRENGTH OF MATERIALSDocument5 paginiPSNA COLLEGE STRENGTH OF MATERIALSBalaji GandhirajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MosDocument10 paginiMosalagar krishna kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined loading analysis of structuresDocument42 paginiCombined loading analysis of structuresDaniel Laurence Salazar ItableÎncă nu există evaluări
- VMKV Engineering College Question Bank on Machine Design ElementsDocument14 paginiVMKV Engineering College Question Bank on Machine Design ElementsSatwik PriyadarshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Question Bank on Strength of MaterialsDocument19 paginiCivil Engineering Question Bank on Strength of MaterialsSanjay TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- QBDocument18 paginiQBMudrikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Sheet No 5Document2 paginiProblem Sheet No 5akbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial - Strength of Materials and StructuresDocument13 paginiTutorial - Strength of Materials and Structuresdearsaswat100% (1)
- Exsheet1 14-15Document3 paginiExsheet1 14-15David MenesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Engineering: Analysis of Connecting Rod Under Different Loading Condition Using Ansys SoftwareDocument9 paginiDesign Engineering: Analysis of Connecting Rod Under Different Loading Condition Using Ansys SoftwaregestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - Chapter 1 - DHRUVKUMAR PATELDocument4 paginiAssignment - Chapter 1 - DHRUVKUMAR PATELDhruv PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Mechanics Question BankDocument2 paginiSolid Mechanics Question BankSIVANESANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Solids-II MEC-206ADocument3 paginiMechanics of Solids-II MEC-206AManish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- elasticity problemsDocument5 paginielasticity problemsMohamed AbdelazizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Document22 pagini11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- Ce2201 QB2Document15 paginiCe2201 QB2Balaji KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce8395 QB PDFDocument10 paginiCe8395 QB PDFMohan Ragava LawrenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module #1 – Simple StressDocument38 paginiModule #1 – Simple StressJeffrey ManansalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Solids Jun2003 NR 210302Document8 paginiMechanics of Solids Jun2003 NR 210302Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology Library100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDe la EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Calculations of probabilities using binomial, hypergeometric and Poisson distributionsDocument7 paginiCalculations of probabilities using binomial, hypergeometric and Poisson distributionspilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Chapter 8Document14 paginiSolutions Chapter 8pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Chapter 10Document11 paginiSolutions Chapter 10pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENG5052 NumericalAnalysis Assign 2016 2017Document7 paginiENG5052 NumericalAnalysis Assign 2016 2017pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Lecture Mohr's Circle PDFDocument16 pagini02 Lecture Mohr's Circle PDFpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Chapter 7Document16 paginiSolutions Chapter 7pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Chapter 6Document8 paginiSolutions Chapter 6pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EVWorksheet 2Document3 paginiEVWorksheet 2pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENG5052 Numerical Analysis Exam 2015 2016Document8 paginiENG5052 Numerical Analysis Exam 2015 2016pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z Transforms WorksheetsDocument4 paginiZ Transforms Worksheetspilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euler WorksheetDocument2 paginiEuler Worksheetpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euler Lec 2Document5 paginiEuler Lec 2pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Worksheets FeedbackDocument10 paginiFourier Worksheets Feedbackpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bending Lecture PDFDocument11 paginiBending Lecture PDFpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Analysis Practice Exam Questions 1415Document10 paginiNumerical Analysis Practice Exam Questions 1415pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometric Properties of SectionsDocument6 paginiGeometric Properties of Sectionspilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Engineering and Environment Division of Engineering Design and Manufacturing Systems Applied Thermodynamics Gas ProcessesDocument2 paginiTechnology Engineering and Environment Division of Engineering Design and Manufacturing Systems Applied Thermodynamics Gas Processespilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To MatlabDocument15 paginiIntroduction To Matlabpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Eng. (Hons) in Engineering Modular Degree Programme Mathematical Analysis UG1 Partial DifferentiationDocument15 paginiB.Eng. (Hons) in Engineering Modular Degree Programme Mathematical Analysis UG1 Partial Differentiationpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Worksheets FeedbackDocument3 paginiFourier Worksheets Feedbackpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourier Worksheets FeedbackDocument10 paginiFourier Worksheets Feedbackpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z Transforms WorksheetsDocument4 paginiZ Transforms Worksheetspilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- .... sin (7x) 7 1 sin (5x) 5 1 sin (3x) 3 1 sin (x) π 4 1 f (x)Document4 pagini .... sin (7x) 7 1 sin (5x) 5 1 sin (3x) 3 1 sin (x) π 4 1 f (x)pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagrams and Transfer Functions: y (T) U (T) H (T)Document1 paginăBlock Diagrams and Transfer Functions: y (T) U (T) H (T)pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp XN WorksheetDocument9 paginiComp XN Worksheetpilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine 2Document7 paginiEngine 2pilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtons Laws - SolutionsDocument6 paginiNewtons Laws - Solutionspilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slider Crank ExampleDocument2 paginiSlider Crank Examplepilas_nikolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTRACT MANUAL FOR PULSE-JET FABRIC FILTERDocument5 paginiCONTRACT MANUAL FOR PULSE-JET FABRIC FILTERAmit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation and Servicing Instructions: Gas Fired Condensing Wall Hung Combination BoilersDocument64 paginiInstallation and Servicing Instructions: Gas Fired Condensing Wall Hung Combination BoilersCelebrul DanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanitary FixturesDocument11 paginiSanitary Fixturesyash goyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS En-12952-2-2021Document46 paginiBS En-12952-2-2021TANK INSPECTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Csyc12mkf Service ManualDocument71 paginiCsyc12mkf Service ManualcoronaqcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specifications: Project: Proposed Two (2) Storey Residential Location: OwnerDocument4 paginiSpecifications: Project: Proposed Two (2) Storey Residential Location: OwnerJ.P.Almera ArDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Froling P1 Pellet Installation Operating InstructionsDocument74 paginiFroling P1 Pellet Installation Operating InstructionsAlastair MortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consol SivakuganDocument29 paginiConsol SivakuganJothi RamanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hanlan UpdateDocument6 paginiHanlan Updaterobert_trewarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent (19) : (22 Filed: June 4, 1976 Assistant Examiner-James C. YeungDocument8 paginiUnited States Patent (19) : (22 Filed: June 4, 1976 Assistant Examiner-James C. YeungHarshal TalsaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1.1 Reinforced Concrete: ReinforcementDocument18 pagini1.1.1 Reinforced Concrete: ReinforcementiffahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm A182 - Astm A182Document7 paginiAstm A182 - Astm A182phresendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Place To Put Down Your Roots.: Stock Image For Representation OnlyDocument8 paginiA Place To Put Down Your Roots.: Stock Image For Representation OnlyKartick PaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edward Resume 102908Document2 paginiEdward Resume 102908edwardblanco03Încă nu există evaluări
- Fly Ash UtilizationDocument6 paginiFly Ash Utilizationbhoj raj singalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Code ABBD MatrixDocument4 paginiMatlab Code ABBD MatrixmehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sin1111500 13 3 25Document95 paginiSin1111500 13 3 25asyrafmuhddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhatia Gummidipoondi WHRSG O&m Manual FinalDocument224 paginiBhatia Gummidipoondi WHRSG O&m Manual Finalt_syamprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 - CablesDocument25 pagini5 - Cableshanyalramady100% (1)
- Town Hall, MumbaiDocument2 paginiTown Hall, MumbaipayalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire: en 13501 The European Standard Owacoustic Ceilings Reaction To Fire Fire ResistanceDocument12 paginiFire: en 13501 The European Standard Owacoustic Ceilings Reaction To Fire Fire Resistanceradubotinesteanu100% (3)
- Structural Engg NotesDocument139 paginiStructural Engg NotesVicky MateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harga Satuan 2023Document12 paginiHarga Satuan 2023Ratih MelatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN 1092-1 PN-40 Steel Pipe Flange - Valvias PDFDocument5 paginiEN 1092-1 PN-40 Steel Pipe Flange - Valvias PDFHoria ZecheruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiler Structure Erection MethodDocument76 paginiBoiler Structure Erection MethodSuman GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civl311 Civl911 2018 Week 6 Design of One Way Slab Student 1Document71 paginiCivl311 Civl911 2018 Week 6 Design of One Way Slab Student 1johan.hafiz6926Încă nu există evaluări
- Sublimation Heat Press Quick Guide 1Document2 paginiSublimation Heat Press Quick Guide 1renato jr baylasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coffers & Troughs: Product CatalogueDocument20 paginiCoffers & Troughs: Product CatalogueMrr KuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometrical Figures and Mechanical Properties QuizDocument13 paginiGeometrical Figures and Mechanical Properties QuizEng Zeeshan TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whessoe: Before Installation These Instructions Must Be Fully Read and UnderstoodDocument1 paginăWhessoe: Before Installation These Instructions Must Be Fully Read and UnderstoodradanpetricaÎncă nu există evaluări