Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
SNMP Views Configuration
Încărcat de
lavidolacoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SNMP Views Configuration
Încărcat de
lavidolacoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) Views Configuration on the WAP121
and WAP321 Access Points
Objective
In SNMP, the Management Information Base (MIB) is a hierarchical information database
that contains a list of management object IDs (OID) that are supported by the system. MIB is
organized in a tree-like structure. A subtree within the managed object naming tree is a view
subtree. A MIB view is combination of a set of view subtrees or a family of view subtrees.
MIB views are created to control the OID range that SNMPv3 users can access. SNMPv3
Views configuration is essential to restrict a user to view only the limited MIB. The WAPs can
have up to sixteen views including the two default views.
This article explains how to configure SNMP Views on the Cisco WAP121 and WAP321
Access Points.
Applicable Devices
• WAP121
• WAP321
Software Version
• 1.0.3.4
SNMP View Configuration
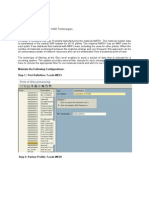
Step 1. Log in to the web configuration utility and choose SNMP > Views. The Views page
opens:
Note: By default, view-none and view-all are created and cannot be deleted.
Step 2. Click Add to add a new SNMP View.
Step 3. Check the check box that corresponds to the newly created view.
Step 4. Click Edit to enable the fields to enter the respective information.
Step 5. Enter a name to identify the new MIB view in the View Name field. View names can
contain up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
Step 6. Choose a type for the new view subtree from the Type drop-down list. The available
options are:
• Include — This option includes the view subtree or family of subtrees from the MIB view.
• Exclude — This option excludes the view subtree or family of subtrees from the MIB view.
Step 7. Enter an OID string for the new subtree to either include or exclude from the view in
the OID field. For example, if you want to specify the system subtree, enter 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.
Each number is used to locate information and each number corresponds to a specific
branch of the OID tree. OIDs are unique identifiers of managed objects in the MIB hierarchy.
The top-level MIB object IDs belong to different standards organizations, while lower-level
object IDs are allocated by associated organizations. Private branches can be defined by
vendors to include managed objects for their own products. MIB files map OID numbers to
human readable format. To translate the OID number to the object name, click here.
Step 8. Enter an OID mask in the Mask field. The mask field is used to control the elements
of the OID subtree that should be considered as relevant when you determine the view in
which an OID is, and the maximum is 47 characters in length. The format is 16 octets in
length and each octet contains 2 hexadecimal characters separated by a period or colon. To
determine the mask, count the number of OID elements and set that many bits to one. Only
hexadecimal formats are accepted in this field. Consider the example OID 1.3.6.1.2.1.1, it
has seven elements, so if you set seven consecutive 1s followed by one zero in the first
octet and all zeros in the second one, you get FE.00 as the mask.
Step 9. Click Save to save this configuration.
Step 10. (Optional) The SNMPv3 Views table displays the current groups configured on the
Access Point. To remove a view from the list, check the appropriate check box and click
Delete.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SNMP Technology White PaperDocument16 paginiSNMP Technology White PaperDavid Gomez RomanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idocs in SAP R3Document73 paginiIdocs in SAP R3Noelia Enriquez100% (1)
- Notes - Step by Step Tutorial For Creating IdocsDocument23 paginiNotes - Step by Step Tutorial For Creating IdocsCathy GatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Import MIBsDocument4 paginiHow To Import MIBsinterceptincÎncă nu există evaluări
- MM Overview of IDOCs in MM-IMDocument5 paginiMM Overview of IDOCs in MM-IMSilva SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap Abap Ale and Idoc ExplainedDocument9 paginiSap Abap Ale and Idoc ExplainedLokesh BachaapÎncă nu există evaluări
- aPC MIB PDFDocument16 paginiaPC MIB PDFStuart MacPhailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step Procedure For IDOC CreationDocument28 paginiStep by Step Procedure For IDOC Creationku_gopi0% (1)
- IDOCs DDocument7 paginiIDOCs DamitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Webdynpro Interview QuestionsDocument15 paginiWebdynpro Interview QuestionsbhupathyrajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step Procedure For IDOC CreationDocument29 paginiStep by Step Procedure For IDOC CreationMilton Carboniere100% (1)
- Step by Step Procedure For Creation of IDOC Part2Document6 paginiStep by Step Procedure For Creation of IDOC Part2swadhin14Încă nu există evaluări
- Creation of Custom IDOC Type: 1. Business CaseDocument8 paginiCreation of Custom IDOC Type: 1. Business CaseSébastien Wilfart100% (1)
- Step by Step Procedure For Creation of IDOCDocument34 paginiStep by Step Procedure For Creation of IDOCjolliestÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Structure of An Idoc Interface: Seng-Houth HengDocument38 pagini1 Structure of An Idoc Interface: Seng-Houth HengjagankilariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuring SNMPC To Manage Any SNMP Enabled DeviceDocument13 paginiConfiguring SNMPC To Manage Any SNMP Enabled DeviceHoàngTrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap Abap Cross Applications by SantoshDocument80 paginiSap Abap Cross Applications by SantoshSantosh Ravindra NadagoudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About MibDocument13 paginiAll About MibMukesh BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Inbound IDoc Step by StepDocument15 paginiSAP Inbound IDoc Step by Stepmeristar100% (2)
- Inbound and Outbound Idoc ConfigurationDocument13 paginiInbound and Outbound Idoc Configurationamitava_bapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idoc CreationDocument5 paginiIdoc Creationharsh2019cps.ceeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Webdynpro Interview Questions and AnswersDocument10 paginiWebdynpro Interview Questions and AnswersNaveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IDOC Filtration: A Business ScenarioDocument8 paginiIDOC Filtration: A Business ScenarioalisnowkissÎncă nu există evaluări
- MQ48D Controller Web and SNMP Management Operating Manual PDFDocument14 paginiMQ48D Controller Web and SNMP Management Operating Manual PDFCristian Bandila100% (1)
- Configuring MIB SupportDocument6 paginiConfiguring MIB SupportSalkovićElvisÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDI - Inbound and Outbound Idoc Configuration StepsDocument4 paginiEDI - Inbound and Outbound Idoc Configuration StepsPadma RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ale IdocsDocument32 paginiAle IdocsSUDHARSANA SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps of Defining Segment: What Is A IDOC?Document4 paginiSteps of Defining Segment: What Is A IDOC?Sriram Suresh MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap Abap Idoc Documents & ProgramsDocument27 paginiSap Abap Idoc Documents & Programsraaman100% (1)
- Guide To ALE and IDocsDocument13 paginiGuide To ALE and IDocsLoredana BlanutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IDoc Step by StepDocument8 paginiIDoc Step by StepSivaprasad Madhusoodhanan100% (1)
- Configuring SAP For Inbound and Outbound ProcessingDocument29 paginiConfiguring SAP For Inbound and Outbound ProcessingSujith KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Management: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesDocument27 paginiNetwork Management: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesbrmonteiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALE Structure:: A CustomDocument9 paginiALE Structure:: A CustomKamal BatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNMP With Smi & MibDocument3 paginiSNMP With Smi & MibAnkit ChaharÎncă nu există evaluări
- IDOC StepsDocument4 paginiIDOC Stepsharshit aryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginner'S Guide To Ale and Idocs - A Step-By-Step ApproachDocument9 paginiBeginner'S Guide To Ale and Idocs - A Step-By-Step ApproachLokamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serialization of IDOC Message TypeDocument23 paginiSerialization of IDOC Message TypeSrinivas Somisetty50% (2)
- J2ME Life CycleDocument5 paginiJ2ME Life Cyclepoonam161287Încă nu există evaluări
- C Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingDe la EverandC Programming for the PIC Microcontroller: Demystify Coding with Embedded ProgrammingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Automated Trading Systems: With an Introduction to Visual C++.NET 2005De la EverandBuilding Automated Trading Systems: With an Introduction to Visual C++.NET 2005Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- MindMeld Kickstart: Your Roadmap to Conversational AI SuccessDe la EverandMindMeld Kickstart: Your Roadmap to Conversational AI SuccessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leveraging WMI Scripting: Using Windows Management Instrumentation to Solve Windows Management ProblemsDe la EverandLeveraging WMI Scripting: Using Windows Management Instrumentation to Solve Windows Management ProblemsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- IBM WebSphere Application Server Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDe la EverandIBM WebSphere Application Server Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Basic Programming:How To Develop Information System Using Visual Basic 2010, A Step By Step Guide For BeginnersDe la EverandVisual Basic Programming:How To Develop Information System Using Visual Basic 2010, A Step By Step Guide For BeginnersEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Microsoft Visual Basic Interview Questions: Microsoft VB Certification ReviewDe la EverandMicrosoft Visual Basic Interview Questions: Microsoft VB Certification ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDe la EverandJava/J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- UI5 User Guide: How to develop responsive data-centric client web applicationsDe la EverandUI5 User Guide: How to develop responsive data-centric client web applicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Security Architecture: Designing and Maintaining Secure Wireless for EnterpriseDe la EverandWireless Security Architecture: Designing and Maintaining Secure Wireless for EnterpriseÎncă nu există evaluări
- iOS 7 Programming Pushing the Limits: Develop Advance Applications for Apple iPhone, iPad, and iPod TouchDe la EverandiOS 7 Programming Pushing the Limits: Develop Advance Applications for Apple iPhone, iPad, and iPod TouchÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Route v6 Ch01Document73 paginiEn Route v6 Ch01Vasil MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco NX OS Design GuideDocument37 paginiCisco NX OS Design GuidelavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Route v6 Ch01Document73 paginiEn Route v6 Ch01Vasil MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- ServiceDefinition ScriptDocument11 paginiServiceDefinition ScriptlavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Route v6 Ch01Document73 paginiEn Route v6 Ch01Vasil MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Route v6 Ch01Document73 paginiEn Route v6 Ch01Vasil MirÎncă nu există evaluări
- CiscoLive BRKAPP-3003Document97 paginiCiscoLive BRKAPP-3003lavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PBX SignalingDocument24 paginiPBX SignalinglavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Steps To Secure and Harden Cisco RouterDocument6 pagini8 Steps To Secure and Harden Cisco RouterchiweekokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Arch EasyDocument44 paginiCisco Arch EasySahul HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catsw Arch Rst-2011Document50 paginiCatsw Arch Rst-2011lavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGP TroubleshootingDocument191 paginiBGP TroubleshootinglavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in BGP: BRKIPM-3005Document125 paginiAdvances in BGP: BRKIPM-3005Laura IancuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Access Design W. Nexus 5K-2K & VPCDocument66 paginiDC Access Design W. Nexus 5K-2K & VPCjnichols1009Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10: Routing in IP Networks Interdomain Routing With BGPDocument49 paginiWeek 10: Routing in IP Networks Interdomain Routing With BGPlavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGP TroubleshootingDocument191 paginiBGP TroubleshootinglavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Access Design W. Nexus 5K-2K & VPCDocument66 paginiDC Access Design W. Nexus 5K-2K & VPCjnichols1009Încă nu există evaluări
- CiscoLive BRKAPP-3003Document97 paginiCiscoLive BRKAPP-3003lavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGP ExplainedDocument74 paginiBGP ExplainedlavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WorksDocument562 paginiWorkslavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccie Rs Lab PrepDocument461 paginiCcie Rs Lab PreplavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco 360 Performance LabDocument3 paginiCisco 360 Performance LablavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRKDCT 2048Document80 paginiBRKDCT 2048lavidolaco100% (1)
- 1697SECEGDocument3 pagini1697SECEGlavidolacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 paginiHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Review of Literature and Studies Related LiteratureDocument21 paginiReview of Literature and Studies Related LiteratureKavin Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motec: Direction of Vehicle TravelDocument1 paginăMotec: Direction of Vehicle TravelJuan Ramón Pérez LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oo LabDocument327 paginiOo Labtamilarasi87thulasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Electric Cable Pulling and Termination Work ITP) FINAL Rev1Document25 pagini(Electric Cable Pulling and Termination Work ITP) FINAL Rev1Aous HÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mickey Mouse Clubhouse 1Document4 paginiMickey Mouse Clubhouse 1Dany JacobsÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Performance Drmos: Power Management and MultimarketDocument29 paginiHigh-Performance Drmos: Power Management and MultimarketVitaliy BespalovÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEOPHYSICS TRAINING WORKSHOP Earth Resis PDFDocument25 paginiGEOPHYSICS TRAINING WORKSHOP Earth Resis PDFHuu Van TranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deltav Function 2 PDF Free (196 271)Document76 paginiDeltav Function 2 PDF Free (196 271)Александр ГончарÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Blockchain Technology and Trust Relationships in Trade FinanceDocument9 pagini2021 Blockchain Technology and Trust Relationships in Trade FinanceMai AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - V Strom 650 ADocument111 pagini2 - V Strom 650 AMarcelo GomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- InvoiceDocument2 paginiInvoicekirankumar43254Încă nu există evaluări
- Weekly MeetingDocument2 paginiWeekly MeetingSenior Software Engineer Emil RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carroll Low Bed Spirit SelectDocument120 paginiCarroll Low Bed Spirit Selectdnavarro00Încă nu există evaluări
- AS350 B2 - CH 06 - Tail RotorDocument20 paginiAS350 B2 - CH 06 - Tail RotorEX919Încă nu există evaluări
- TRUMPF Genuine Parts Catalog enDocument116 paginiTRUMPF Genuine Parts Catalog encrazy hackerÎncă nu există evaluări
- THC 5 - Micro Perspective of Tourism and Hospitality Rev. 2Document5 paginiTHC 5 - Micro Perspective of Tourism and Hospitality Rev. 2Juwinderly Dublin LocaylocayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10% Sangguniang Kabataan Youth Development Plan Barangay Guisguis 10% SK Supplemental FundDocument3 pagini10% Sangguniang Kabataan Youth Development Plan Barangay Guisguis 10% SK Supplemental FundJan Alleana FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model 747 Lead Shield: Description FeaturesDocument2 paginiModel 747 Lead Shield: Description Featureshndk89Încă nu există evaluări
- S310 Manual (English) V03Document69 paginiS310 Manual (English) V03Muhammad JunaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel Desktop Board VC820: Technical Product SpecificationDocument122 paginiIntel Desktop Board VC820: Technical Product Specificationshriram1082883Încă nu există evaluări
- AQ Singapore CharacteristicsDocument2 paginiAQ Singapore Characteristicschia simÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 MCQDocument48 paginiUnit 4 MCQsakshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acrolinx: Tone of VoiceDocument12 paginiAcrolinx: Tone of VoiceMark OwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality For All.: The Kalmar DRU450 Essential ReachstackerDocument9 paginiQuality For All.: The Kalmar DRU450 Essential ReachstackerNokiabhre WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 650lec - 11 - Form & Space & OrganizationDocument37 pagini650lec - 11 - Form & Space & OrganizationCandy Law100% (1)
- Resume For Walmart StockerDocument8 paginiResume For Walmart Stockerxdqflrobf100% (2)
- Attendence Monitoring System: November 2019Document24 paginiAttendence Monitoring System: November 2019manish guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dell Emc Powerstore: Vmware Vsphere Best PracticesDocument25 paginiDell Emc Powerstore: Vmware Vsphere Best PracticesBalasubramanian ReguramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Email CorrespondenceDocument10 paginiEmail CorrespondenceOSHIN KUMARIÎncă nu există evaluări
- WL Series User ManualDocument16 paginiWL Series User ManualAjay KastureÎncă nu există evaluări