Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TN010 - Raft Footing
Încărcat de
Star HODrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TN010 - Raft Footing
Încărcat de
Star HODrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
KMS / TECHNICAL DEPARTMENT
TECHNICAL NOTE 010
Raft Foundations,
s’– t Plots &
SPT-N Values
· We excel through experience and learning · Version 02, Jul 2013
Keywords An s’– t plot is shown in the following figure (using the
Raft foundations, s’– t plot, SPT-N values, soil friction angles laboratory test results for a site in Yuen Long).
600
Synopsis
This note explains, through examples, the use of triaxial test 500 ’
results to prepare s’– t plots for determination of soil friction
400
angle(s), ’. Published correlation data (Meyerhoff, 1956)
between SPT-N values and ’ is provided for counterchecking
t (kPa)
300
the result. Given the ’ value, the allowable bearing capacity of
shallow footing (or raft foundations) can be quickly assessed.
200
100
1.0 Introduction
Large raft foundations give very high allowable bearing 0
capacity, and in some cases, the bearing capacity might even 0 200 400 600 800 1000
be higher than the equivalent bearing capacity of driven H-piles.
s' (kPa)
For large rafts, settlement becomes the controlling factor.
Triaxial compression test results, if available, can be used to Two trend lines are shown in the above plot : the broken line is
prepare an s’– t plot for determination of soil friction angle(s). a best-fit line for the available data, and the solid line is a
The SPT-N values (field test results) can also be used to lower-bound line. The gradient of these lines is tan’, and the
correlate the soil friction angle and the soil compactness, effective soil friction angle, ’ is given by:
allowing one to gain some quick feel of the soil bearing capacity.
’ = sin-1 (tan’)
2.0 s’ – t Plots In the above plot, the values of tan’ and ’ are as follows:
Laboratory tests are normally conducted as part of a
ground investigation programme. Triaxial compression tests on Lines ’ tan’ ’
soil samples would usually be specified by a Designer.
Depending on the laboratory report format, the triaxial test Best-Fit 35° 0.613 42°
results are presented quite differently, ranging from full report Lower-Bound 27° 0.450 30°
on 3’, p’, q, s’, t to just some of these parameters. The most
useful values of c’ and ’ are usually not reported because
these values are subject to interpretation by the Designer. 3.0 SPT-N Values & Soil Friction Angles
The correlation between SPT-N values and granular soil
For the purpose of determining the soil friction angle, ’, we friction angels are shown in the table below for quick reference.
only need to focus on the values of s’ and t, where:
Soil Friction
s’ = (1’ + 3’) / 2 SPT-N Values Compactness
Angles, ’
t = (1’ – 3’) / 2
<4 < 30° Very loose
where 1’ is the applied axial load, and 3’ is the different 4 – 10 30° – 35° Loose
effective confining pressure(s) in triaxial tests, ie, Cell Pressure 10 – 30 35° – 40° Medium Dense
minus Measured Pore Water Pressure in soil sample.
30 – 50 40° – 45° Dense
NB – The values of s’ and t are stated readily in the test > 50 > 45° Very dense
report, and there is no need to re-calculate them using
01
the above equations.
TECHNICAL NOTE 010
Version 02, Jul 2013
KMS / TECHNICAL DEPARTMENT
Q2
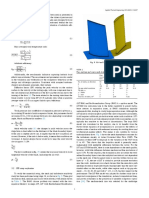
Q1
B = 50m
Qn L = 50m (into paper direction)
h = 8m
z z = 2m
qo s = 18 kN/m3
h
w = 10 kN/m3
' = 8 kN/m3
’ = 30°
FOS = 3
B
The SPT-N value in the drill logs for the site in Yuen Long
ranges from 10 to 24. According to the correlation table, the 100.0
soil is considered ‘compact’ and the corresponding soil friction
angle is within the range of 35° – 40°, which is in reasonable
agreement with value given by the best-fit line in the s’– t plot. 30.1
22.4
18.4
4.0 Bearing Capacity of Raft Foundations / Footing
The bearing capacity of a large raft foundation can be 10.0
very high. An assessment is made, based on GEOGUIDE 1, for
a raft foundation having the arrangement shown in the diagram Nc
above.
Nq
The ultimate bearing capacity, qult is given by the following
equation (Please note that the cohesion term, c’, for granular N
soil is usually small and can be ignored): 1.0 ’
qult
0 10 20 30 40 50
=½ ' B N s + qo Nq sq
where N and Nq are bearing capacity factors, and s and sq are
correction factors to account for footing shape.
0.1
The bearing capacity factors, Nc, Nq, N have been derived by
different soil mechanics researchers. Those used in GEOGUIDE The allowable bearing capacity for the raft foundation having
1 – Figure A2 are shown in the graph on the right. The the above parameters is approximately 1783 kPa. It is
calculated values of these factors are shown below for ’ = 30°. unlikely that a field plate loading test would give prediction of
this bearing capacity, ie, using field plate loading test(s) to try
Nc = 30.1 ; sc = 1.61 to verify the above bearing capacity will not be very meaningful.
However, an assessment of the likely settlement should be
Nq = 22.4 ; sq = 1.58 carried out to ensure the movements are acceptable for the
N = 18.4 ; s = 0.60 proposed structures.
Also, qo = 18×2 + 8×(8 – 2) - End -
= 84 kPa
Thus, qult = 0.5×8×50×18.4×0.6 + 84×22.4×1.58
= 5180.9 kPa
This technical note is for internal circulation only.
For enquiry, please contact
The allowable bearing capacity, qall is given by applying a factor
of safety (FOS) to the qult (Please note that the FOS is not Gary Chou
applied to the overburden pressure, qo , which is expected to KMS / AGM (Technical)
exist throughout the life time of the foundations). Technical Department
Chun Wo Construction & Engineering Co Ltd
qall = [(5180.9 – 84) / 3] + 84 E gary.chou@chunwo.com
= 1782.9 kPa T 3758 8379
F 2744 6937
TECHNICAL NOTE 010
Version 02, Jul 2013
02
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99De la EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Încă nu există evaluări
- TECHNICAL NOTE 010 Raft Foundations, S' - T Plots and SPT-N ValuesDocument2 paginiTECHNICAL NOTE 010 Raft Foundations, S' - T Plots and SPT-N Valuesapirakq100% (1)
- 09 Site Investigations IIIDocument13 pagini09 Site Investigations IIIAlvaro B. Galarce JerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 513 Week8Document58 pagini513 Week8matsoul100% (3)
- Load Capaciy of Piles by SPT - CPT Dhimitri Et - AlDocument8 paginiLoad Capaciy of Piles by SPT - CPT Dhimitri Et - AlSaroj BhattaraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiDe la EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET Lab ManualDocument14 paginiET Lab ManualANANDKUMAR SÎncă nu există evaluări
- TECHNICAL NOTE 013 Steel Sheet Piling - Drivability Vs SPT-N Values - Vibrations and Noise LevelDocument3 paginiTECHNICAL NOTE 013 Steel Sheet Piling - Drivability Vs SPT-N Values - Vibrations and Noise LevelRaed Naim Khammash100% (1)
- Esnel EquationsDocument26 paginiEsnel Equationsmt21215015 Navdeep GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffraction Exp-2Document4 paginiDiffraction Exp-2Saksham PasrichaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0038080620319995 Main - 2Document19 pagini1 s2.0 S0038080620319995 Main - 2mahdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tangent GalvanometerDocument19 paginiTangent GalvanometerChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Angle 2Document4 paginiFriction Angle 2Yutong LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Time:3: Building Construction ExamDocument9 paginiFinal Time:3: Building Construction ExamsosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5offtakes FDocument1 pagină5offtakes FPooya ShayestehÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument5 paginiInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringTian SeahÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH Stability AnalysisDocument46 paginiPH Stability AnalysisAkshay DuggalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical Basis.: 1.1) Correlation With SPTDocument25 paginiTheoretical Basis.: 1.1) Correlation With SPTEmiliano AgostiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skempton - Standard Penetration Test Procedures and Effects in Sands of Overburden, Relative Density, Ageing and OverconsolidationDocument23 paginiSkempton - Standard Penetration Test Procedures and Effects in Sands of Overburden, Relative Density, Ageing and OverconsolidationDEBASIS100% (3)
- Case Studies On Performance Based Seismic Design Using Capacity Spectrum MethodDocument8 paginiCase Studies On Performance Based Seismic Design Using Capacity Spectrum MethodMouhamad ArrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 12 Bearing Capacity Using Field TestsDocument22 paginiLecture 12 Bearing Capacity Using Field TestsAli RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8423 26836 1 PB PDFDocument8 pagini8423 26836 1 PB PDFKarunanithi NagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modified Nicolson-Ross-Weir (NRW) Method To Retrieve The Constitutive Parameters of Low-Loss MaterialsDocument5 paginiModified Nicolson-Ross-Weir (NRW) Method To Retrieve The Constitutive Parameters of Low-Loss MaterialsAbdoelCholilTjahsholehÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Strength of Struts: A C K eDocument21 paginiThe Strength of Struts: A C K eLênon Guimarães Silva AlípioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications - Polarizing Beam SplitterDocument8 paginiApplications - Polarizing Beam Splittermt21215015 Navdeep GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 4 Pendulum Oscillation With PC Interface: Principle and TaskDocument5 paginiExperiment 4 Pendulum Oscillation With PC Interface: Principle and TaskNguyễn Đức MạnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- CL FE HandoutsDocument59 paginiCL FE HandoutsweldsvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gearing AgmaDocument17 paginiGearing AgmaDomingos AzevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supercritical Airfoil and CharacteristicsDocument7 paginiSupercritical Airfoil and CharacteristicsABHISHEK MANI TRIPATHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burland and Burbidge 1985Document57 paginiBurland and Burbidge 1985Jawad AbidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notch Fatigue Behaviour Ofsae1045 Steel: Steel Short Crack Fracture MechanicsDocument8 paginiNotch Fatigue Behaviour Ofsae1045 Steel: Steel Short Crack Fracture MechanicstaichiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impedance Characteristics of Power TransDocument8 paginiImpedance Characteristics of Power TransAbderrahmane BoursasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock Mechanics PTR 339: Tishk International University Engineering Faculty Petroleum & Mining Eng. DepartmentDocument11 paginiRock Mechanics PTR 339: Tishk International University Engineering Faculty Petroleum & Mining Eng. DepartmentHassn LukakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bearing Capacity of Bored PilesDocument8 paginiBearing Capacity of Bored PilesRinsunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground Improvement H.W 1Document15 paginiGround Improvement H.W 1jobaydaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axial CompressorDocument64 paginiAxial CompressorElmer100% (1)
- Mohammadi Nikudel 36C1 1 SkalaDocument5 paginiMohammadi Nikudel 36C1 1 SkalaAli IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- API Soil Model ValidationDocument37 paginiAPI Soil Model ValidationUnwanus Sa'adahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question & Answer Set-2Document4 paginiQuestion & Answer Set-2hatemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Op-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument7 paginiOp-029. Interpretation of Ciu Test: Work Instructions For EngineersNadeem AbbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo-Reporting - Scheme-V3 - Latest - Use This FileDocument34 paginiGeo-Reporting - Scheme-V3 - Latest - Use This FileBinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Expression For RMS DC Link Capacitor Current in A Three-Level InverterDocument6 paginiAnalytical Expression For RMS DC Link Capacitor Current in A Three-Level InverterNishantÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBC Last Stage Blades DesignDocument12 paginiBBC Last Stage Blades Designantoniomambro100% (1)
- Geo Reporting - Scheme v3Document44 paginiGeo Reporting - Scheme v3Г. СүхбатÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS GCE Physics A 2822 January 2006 Question PaperDocument16 paginiAS GCE Physics A 2822 January 2006 Question PaperpeterbbbÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Situ Soil Testing - Lab Tests - Estimation of Properties From in Situ TestsDocument26 paginiIn Situ Soil Testing - Lab Tests - Estimation of Properties From in Situ Testsabcdef456100% (1)
- Natural Convection LatestDocument35 paginiNatural Convection LatestPradyumna DhamangaonkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ram HBMDocument12 paginiRam HBMkkkoooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Composite BeamsDocument10 paginiChapter 6 Composite BeamsDem Austria EspinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modification of Larson-Miller Parameter Technique For Predicting Creep Life of MaterialsDocument5 paginiModification of Larson-Miller Parameter Technique For Predicting Creep Life of MaterialsAlok SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress-Intensity Factors ForDocument19 paginiStress-Intensity Factors ForMaria Camila RestrepoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applying The Wheatstone Bridge CircuitDocument36 paginiApplying The Wheatstone Bridge CircuitMichael Kang0% (1)
- On The Size of Drops in Pulsed and VibratingDocument4 paginiOn The Size of Drops in Pulsed and VibratingArunÎncă nu există evaluări
- TL21035 - BTD3343 - Technical Report 1 - Final VersionDocument5 paginiTL21035 - BTD3343 - Technical Report 1 - Final VersionEdryna AntasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDA Test - Result AnalysisDocument13 paginiPDA Test - Result AnalysisNazmul100% (1)
- Article: Stepped Hss T-And Cross - Connections Under Branch In-Plane and Out - Of-Plane BendingDocument5 paginiArticle: Stepped Hss T-And Cross - Connections Under Branch In-Plane and Out - Of-Plane Bendinggv Sathishkumar KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piles Paper 5IYGEC 2015Document42 paginiPiles Paper 5IYGEC 2015ShubhadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement of Plate Load TestDocument5 paginiMethod Statement of Plate Load TestStar HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Excavations FoundationsDocument182 paginiDeep Excavations Foundationsbannasengineer94% (18)
- Some Myths of Consolidation Settlement - Philip Chung PDFDocument21 paginiSome Myths of Consolidation Settlement - Philip Chung PDFStar HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toyo ScaffoldDocument8 paginiToyo ScaffoldStar HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- IStructE Appraisal of Existing Structure (2nd Edition)Document54 paginiIStructE Appraisal of Existing Structure (2nd Edition)Star HO100% (3)
- +steel SECTION PROPERTIESDocument54 pagini+steel SECTION PROPERTIESStar HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- CF249 - Firecut FM-900 PDFDocument7 paginiCF249 - Firecut FM-900 PDFStar HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monokote MK6Document2 paginiMonokote MK6Star HOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.2 (Aircraft Mat PDFDocument13 paginiModule 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.2 (Aircraft Mat PDFJunaid YounusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hermetic Pumpen Kaelte e 11 2014Document28 paginiHermetic Pumpen Kaelte e 11 2014goodspeed_phÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finetrol Rotary Control Valve: Added SecurityDocument14 paginiFinetrol Rotary Control Valve: Added SecurityAmine KhÎncă nu există evaluări
- SolManEngineering Vibration 4th Edition by InmanDocument36 paginiSolManEngineering Vibration 4th Edition by Inmansmirnov2591100% (1)
- The Anatomy of The Airfoil: General Aviation Aircraft Design Ó 2014 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument63 paginiThe Anatomy of The Airfoil: General Aviation Aircraft Design Ó 2014 Elsevier Inc. All Rights ReservedmiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Selection and Design For Delivery Drone PropellersDocument6 paginiMaterial Selection and Design For Delivery Drone PropellersRicardo DíazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Jet ValveDocument18 paginiHydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Jet ValveEng-CalculationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Documentation Engine Spare Parts Catalogue: MAN Diesel & TurboDocument450 paginiTechnical Documentation Engine Spare Parts Catalogue: MAN Diesel & TurboMrberkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Displacement Based Seismic DesignDocument11 paginiDisplacement Based Seismic DesignGyorgy AdrienneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climatology: - Ar. Akshay GuptaDocument43 paginiClimatology: - Ar. Akshay GuptaYogendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 paginiSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- Wheel LoaderDocument2 paginiWheel LoaderfitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric-Resistance-Welded Low-Carbon Steel Pipe For The Chemical IndustryDocument6 paginiElectric-Resistance-Welded Low-Carbon Steel Pipe For The Chemical IndustryReginaldo SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Center TelehandlersDocument12 paginiApplication Center TelehandlersQXNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelwise Nov-2014 PDFDocument5 paginiSteelwise Nov-2014 PDFJatinTankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nv2 Sdof 25mar2021 Vtaf01Document43 paginiNv2 Sdof 25mar2021 Vtaf01abd devÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Steam TracingDocument4 paginiWhat Is Steam TracingahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Cylinder For Use WTH:-HVL, HPS, HLS, HSS, Has, HHS, HHR, Hda & HgsDocument8 paginiHydraulic Cylinder For Use WTH:-HVL, HPS, HLS, HSS, Has, HHS, HHR, Hda & HgsKundan Kumar MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9853 1213 01i Fluids and Lubricating GreasesDocument18 pagini9853 1213 01i Fluids and Lubricating GreasespressisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wire Rope Hoist 2 TonDocument5 paginiWire Rope Hoist 2 Tonafrozashirahatti20Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-5 Stresses in BeamsDocument16 paginiChapter-5 Stresses in BeamsFitsum OmituÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wsat-Xee: Installation Use and Maintenance ManualDocument68 paginiWsat-Xee: Installation Use and Maintenance ManualAncuta CosmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- WKB ApproximationDocument14 paginiWKB Approximationamitsk144Încă nu există evaluări
- Free-Body DiagramsDocument20 paginiFree-Body Diagramssatish448100% (1)
- AAR-001-ISOLATED FDN - IS 456 - Node 1 - 2Document42 paginiAAR-001-ISOLATED FDN - IS 456 - Node 1 - 2ask.kulkarni KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cable Racking Oline Catalogue - 2011 Pages 84 86Document3 paginiCable Racking Oline Catalogue - 2011 Pages 84 86jonodo89Încă nu există evaluări
- IITD-Courses-of-Study MEMDocument1 paginăIITD-Courses-of-Study MEMMohit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Analyti Transfe Cal and Er Func D Nume Ction in Bound Erical e N Ducts Dary Co Estimat S Consi Ondition Tion of Dering Ns F Acous G Gener Stic RalDocument10 paginiA Analyti Transfe Cal and Er Func D Nume Ction in Bound Erical e N Ducts Dary Co Estimat S Consi Ondition Tion of Dering Ns F Acous G Gener Stic Ralpela210Încă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet-Novus 30Document1 paginăDatasheet-Novus 30PrethevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Electric Vehicle Drive Train: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument64 paginiUnit 3 Electric Vehicle Drive Train: Department of Mechanical EngineeringPraveen RathodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsDe la EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3De la EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDe la EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDe la EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDe la EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (21)
- The HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesDe la EverandThe HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesDe la EverandA New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringDe la EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (11)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsDe la EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationDe la EverandDistillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Fun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksDe la EverandFun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlDe la EverandLees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Principles and Case Studies of Simultaneous DesignDe la EverandPrinciples and Case Studies of Simultaneous DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Chemical Engineer in the Palm Oil Milling IndustryDe la EverandA Chemical Engineer in the Palm Oil Milling IndustryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDe la EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDe la EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- High Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesDe la EverandHigh Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersDe la EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Chemical Thermodynamics for GeoscientistsDe la EverandPractical Chemical Thermodynamics for GeoscientistsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersDe la EverandPhysical and Chemical Equilibrium for Chemical EngineersEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- First U.K. National Conference on Heat Transfer: The Institution of Chemical Engineers Symposium Series, Volume 2.86De la EverandFirst U.K. National Conference on Heat Transfer: The Institution of Chemical Engineers Symposium Series, Volume 2.86Încă nu există evaluări
- The Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringDe la EverandThe Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringS. S. GillEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)