Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bo Ring
Încărcat de
TanishaBiswas0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
36 vizualizări16 paginiTalks about machining
Titlu original
bo-ring
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentTalks about machining
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
36 vizualizări16 paginiBo Ring
Încărcat de
TanishaBiswasTalks about machining
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 16
Boring
Difference between boring and turning:
Boring is performed on the inside
diameter of an existing hole
Turning is performed on the outside
diameter of an existing cylinder
In effect, boring is internal turning operation
Boring machines
Horizontal or vertical - refers to the
orientation of the axis of rotation of
machine spindle
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 1
Vertical Boring Mill
Figure 22.12 A vertical boring mill – for large, heavy workparts.
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 2
Drilling
Creates a round
hole in a workpart
Compare to boring
which can only
enlarge an existing
hole
Cutting tool called
a drill or drill bit
Machine tool: drill
press
Figure 21.3 (b) drilling
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 3
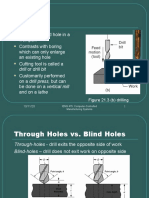
Through Holes vs. Blind Holes
Through-holes - drill exits opposite side of work
Blind-holes – does not exit work opposite side
Figure 22.13 Two hole types: (a) through-hole, and (b) blind hole.
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 4
Cutting Conditions in Drilling
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 5
Cutting Conditions in Drilling II
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 6
Reaming
Used to slightly
enlarge a hole,
provide better
tolerance on
diameter, and
improve surface
finish
Figure 22.14 Machining
operations related to drilling: (a)
reaming
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 7
Tapping
Used to provide
internal screw
threads on an
existing hole
Tool called a tap
Figure 22.14 (b) tapping
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 8
Counterboring
Provides a stepped
hole, in which a
larger diameter
follows smaller
diameter partially
into the hole
Figure 22.14 (c) counterboring
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 9
Drill Press
Upright drill press
stands on the floor
Bench drill similar
but smaller and
mounted on a
table or bench
Figure 22.15 Upright drill press
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 10
Radial Drill
Large drill press
designed for
large parts
Figure 22.16 Radial drill press
(photo courtesy of Willis
Machinery and Tools).
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 11
Work Holding for Drill Presses
Workpart in drilling can be clamped in any of
the following:
Vise - general purpose workholder with two
jaws
Fixture - workholding device that is usually
custom-designed for the particular workpart
Drill jig – similar to fixture but also provides
a means of guiding the tool during drilling
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 12
Machining Centers
Highly automated machine tool can perform
multiple machining operations under CNC
control in one setup with minimal human
attention
Typical operations are milling and drilling
Three, four, or five axes
Other features:
Automatic tool-changing
Pallet shuttles
Automatic workpart positioning
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 13
Figure 22.26 Universal machining center; highly automated,
capable of multiple machining operations under computer control in
one setup with minimal human attention (photo courtesy of
Cincinnati Milacron).
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 14
Figure 22.27 CNC 4-axis turning center (photo courtesy of
Cincinnati Milacron); capable of turning and related operations,
contour turning, and automatic tool indexing, all under computer
control.
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 15
Mill-Turn Centers
Highly automated machine tool that can perform
turning, milling, and drilling operations
General configuration of a turning center
Can position a cylindrical workpart at a
specified angle so a rotating cutting tool (e.g.,
milling cutter) can machine features into
outside surface of part
Conventional turning center cannot stop
workpart at a defined angular position and
does not include rotating tool spindles
MECH2118 - Dr Ghassan Al-Kindi - Lecture 10 16
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ec210b Pub20021241-I PDFDocument1.046 paginiEc210b Pub20021241-I PDFCholif 'oliph' Fadhilah100% (16)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: KOMATSU Supercoolant AF-NAC (50/50 Pre-Diluted)Document5 paginiMaterial Safety Data Sheet: KOMATSU Supercoolant AF-NAC (50/50 Pre-Diluted)Thais Roberta CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilmu KhotifDocument28 paginiIlmu KhotifAndré Martins78% (27)
- Groover Fundamentos Manual Soluciones C22Document10 paginiGroover Fundamentos Manual Soluciones C22Ayush BhadauriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 21Document11 paginiCH 21onlydlonly100% (9)
- Workshop Practice Lecture Week 02-ADocument17 paginiWorkshop Practice Lecture Week 02-AArham AmjadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machining Technology I MCQ and QuestionsDocument6 paginiMachining Technology I MCQ and QuestionsNauman AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 22 SolutionDocument13 paginiCH 22 SolutionElsaid SalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 22 ADocument81 paginiCH 22 AThiran Boy LingamÎncă nu există evaluări
- mp1 170302175707Document60 paginimp1 170302175707uday245Încă nu există evaluări
- IENG 475 Lecture 06Document22 paginiIENG 475 Lecture 06patlninadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machining Operations and Machine ToolsDocument73 paginiMachining Operations and Machine ToolstmcoachingcentreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 11 Ch21 22 Machining OperationsDocument37 paginiWeek 11 Ch21 22 Machining OperationsJay Dee11Încă nu există evaluări
- Major Project (Gurpeet Sir) Group Final CompiledDocument23 paginiMajor Project (Gurpeet Sir) Group Final CompiledAbhinav MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Ii Forging2Document15 paginiUnit Ii Forging2Srinivas GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milling MachineDocument22 paginiMilling MachineSheikh Zakir100% (1)
- To Class DrillingDocument16 paginiTo Class DrillingvineethÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2Document77 pagini2Pothuri SuneeldathÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP I SubmissinDocument7 paginiMP I SubmissinAbhijeet PramanikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Through Holes vs. Blind Holes: Various Types of Drills and Drilling Operations. ReamingDocument4 paginiDrilling Through Holes vs. Blind Holes: Various Types of Drills and Drilling Operations. ReamingVenu Gopal AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shaper SlottingDocument34 paginiShaper SlottingAamer MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Sheet Metal Bending MachineDocument28 paginiPneumatic Sheet Metal Bending Machinek46207310Încă nu există evaluări
- Traditional Machining Processes: Manufacturing Engineering-I (Meng3181)Document49 paginiTraditional Machining Processes: Manufacturing Engineering-I (Meng3181)fitsum balkewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic Sheet Metal Bending MachineDocument27 paginiPneumatic Sheet Metal Bending MachineAMEY GHADIGAONKAR194014Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 1-Machining Operations IIDocument51 paginiLec 1-Machining Operations IIHammad RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G98 Return To Initial Rapid HeightDocument14 paginiG98 Return To Initial Rapid HeightAmr ElsakkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Oxford College of Engineering: Subject: Mechnical Department: Computer ScienceDocument24 paginiThe Oxford College of Engineering: Subject: Mechnical Department: Computer ScienceDeepak Saravana Kumar MÎncă nu există evaluări
- (MeChAnIcAl WoRkInG)Document6 pagini(MeChAnIcAl WoRkInG)bhavna agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fourth SemesterDocument18 paginiFourth SemesterGopinath NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Fabrication of Multiangle Drilling MachineDocument6 paginiDesign and Fabrication of Multiangle Drilling MachineVIVA-TECH IJRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Fixture For Full Bore Gate Valve - ReviewDocument31 paginiDesign of Fixture For Full Bore Gate Valve - ReviewAlpha Ray KingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 8Document7 paginiLab 8Malik Muhammad IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Development of Multipurpose Mechanical Machine: A Project Report ONDocument25 paginiDesign and Development of Multipurpose Mechanical Machine: A Project Report ONTSEYSETSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Introduction To Machining Operations: 2.1 LATHEDocument3 paginiChapter 2: Introduction To Machining Operations: 2.1 LATHEraghu gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typical Tolerances of Manufacturing Processes: EML 2322L - MAE Design and Manufacturing LaboratoryDocument7 paginiTypical Tolerances of Manufacturing Processes: EML 2322L - MAE Design and Manufacturing LaboratoryYathish Kumar MadanagopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me 330 Lab ManualDocument43 paginiMe 330 Lab ManualberhaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design, Analysis, Assembly and Installation of Multi Spindle Drilling MachineDocument48 paginiDesign, Analysis, Assembly and Installation of Multi Spindle Drilling MachineHitesh DhameliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrillingDocument11 paginiDrillingShehroze RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manuf. Tech. - Machining OperationsDocument49 paginiManuf. Tech. - Machining OperationsManuel Tikongyin WundengbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MT Ii Unit Iii MCQDocument9 paginiMT Ii Unit Iii MCQRanjith GopalakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME8462-Manufacturing Technology Laboratory - IIDocument5 paginiME8462-Manufacturing Technology Laboratory - IIBala AbimanyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop Practice DrillDocument6 paginiWorkshop Practice DrillMuhammad Zaid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2 ReportDocument7 paginiLab 2 ReportiwaleedwasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- VinayDocument64 paginiVinaySathish RoyalrajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages of ForgingDocument20 paginiAdvantages of ForgingPramod DhaigudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- H20 Formwork For Walls AU EN 2009-10 PDFDocument36 paginiH20 Formwork For Walls AU EN 2009-10 PDFAndreea NanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design & Manufacturing of 20 Ton Horizontal Hydraulic Press Machine For Pipe Squeezing & Flaring OperationDocument5 paginiDesign & Manufacturing of 20 Ton Horizontal Hydraulic Press Machine For Pipe Squeezing & Flaring Operationabdullah yousefiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: IntoductionDocument64 paginiChapter-1: IntoductionSathish RoyalrajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Injection Molding)Document9 pagini(Injection Molding)Apollo Optical SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Ch20Document12 paginiSolutions Ch20Joyce Casiano100% (2)
- 26-Universal Bending MachineDocument59 pagini26-Universal Bending MachinesathishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Machine Tools and Machining OperationsDocument68 paginiChapter 1-Machine Tools and Machining OperationsHamandey AlhaykiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Justifying, Selecting and Implementing Tube Bending Methods: AuthorDocument30 paginiJustifying, Selecting and Implementing Tube Bending Methods: Authorsarge18Încă nu există evaluări
- HARTFORD "Mercury" Vertical Machining CenterDocument1 paginăHARTFORD "Mercury" Vertical Machining CenterWalkerMachineryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyraulics Press MachineDocument27 paginiHyraulics Press MachinePANDURANG PARABÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lathe & Drilling Machine Part 3Document3 paginiLathe & Drilling Machine Part 3angadsnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.pneumatic Operated Multi Purpose Grinding MachineDocument33 pagini6.pneumatic Operated Multi Purpose Grinding Machinevijay vijay100% (1)
- Workingholding Devices: Types of Work Holding DevicesDocument12 paginiWorkingholding Devices: Types of Work Holding DevicesAitzazMurtazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document17 paginiChapter 1shubhanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document28 paginiChapter 2GemedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mme 431 CH18Document39 paginiMme 431 CH18Khalid WaleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Js-Umum) Daftar Harga 01 Maret '23Document1 pagină(Js-Umum) Daftar Harga 01 Maret '23Kristin NataliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OKM 54MP FlyerDocument1 paginăOKM 54MP FlyerJohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module II Activated Sludge Math ProblemsDocument5 paginiModule II Activated Sludge Math ProblemsArashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalog Man 1Document116 paginiCatalog Man 1Petrov AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- E11133 MB Pin Definition v2 Print Vendor Only PDFDocument18 paginiE11133 MB Pin Definition v2 Print Vendor Only PDFLuciano MalancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O221771s - Mil Pipe Pro 450 RFC PDFDocument84 paginiO221771s - Mil Pipe Pro 450 RFC PDFJavier Isaac Berrocal Torres100% (1)
- Hypomineralised Second Primary Molars May Be Indicative of Future Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation PDFDocument6 paginiHypomineralised Second Primary Molars May Be Indicative of Future Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation PDFnha khoa NHƯ NGỌCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 9: Quarter-Wave-Transformer Matching.: R JZ L Z Z Z JR LDocument13 paginiLecture 9: Quarter-Wave-Transformer Matching.: R JZ L Z Z Z JR LRuth EnormeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidDocument16 paginiMotion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidGokul JeevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iron FistDocument2 paginiIron FistVictor PileggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CA InsideDocument1 paginăCA InsideariasnomercyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Coffee Shop Easy Reading - 152542Document1 paginăThe Coffee Shop Easy Reading - 152542Fc MakmurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Bomba HLXDocument16 paginiManual Bomba HLXVictor Manuel Hernandez GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Document3 paginiMHT-CET 2021 Question Paper: 25 September 2021Sank DamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools, Equipment, and ParaphernaliaDocument35 paginiTools, Equipment, and Paraphernaliajahnis lopez100% (1)
- BIOC32 Practice QuestionsDocument7 paginiBIOC32 Practice QuestionsLydia DuncanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02K inDocument1 pagină02K inAbbode HoraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Studies in American Popular History and Culture) Gail Fowler Mohanty - Labor and Laborers of The Loom - Mechanization and Handloom Weavers, 1780-1840 - Routledge (2006)Document292 pagini(Studies in American Popular History and Culture) Gail Fowler Mohanty - Labor and Laborers of The Loom - Mechanization and Handloom Weavers, 1780-1840 - Routledge (2006)Милош Станојловић100% (1)
- Ee115hw+sol03 06 N PDFDocument6 paginiEe115hw+sol03 06 N PDFthinkberry22100% (1)
- Definition of Logistics ManagementDocument4 paginiDefinition of Logistics ManagementzamaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schrodinger Wave EquationsDocument6 paginiSchrodinger Wave EquationsksksvtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsDocument76 paginiEmbedded Systems:: Hacking of Electronic EquipmentsKailashi Chandra SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthing ResistanceDocument4 paginiEarthing ResistanceNeeraj Purohit100% (1)
- Final Project ReportDocument83 paginiFinal Project ReportMohit SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DysphagiaDocument4 paginiDysphagiaMicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis On Population GeographyDocument6 paginiThesis On Population Geographyggzgpeikd100% (2)
- EI6704: UNIT 5 NotesDocument19 paginiEI6704: UNIT 5 NotesMadhu MithaÎncă nu există evaluări