Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tutorial Chapter 6 Introduction To Power System Epo244 - 2
Încărcat de
Muhammad Haziq HamdiTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tutorial Chapter 6 Introduction To Power System Epo244 - 2
Încărcat de
Muhammad Haziq HamdiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
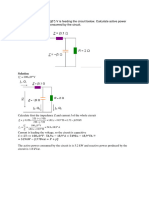
1) Construct a per phase per unit equivalent circuit of the power system network using a
base apparent power of 100 MVA and a base line voltage at generator G1 of 33 kV.
Then predict the actual fault current if a symmetrical fault occurs at bus 2.
1 2 3 4
G1 TX1 L1 TX2 G2
X = 115 Ω
S = 70 MVA S = 50 MVA S = 50 MVA S = 90 MVA
V = 33 kV V = 33/132 kV V = 132/33 kV V = 11 kV
X = j0.09 p.u. X = j0.19 p.u. X = j0.15 p.u. X = j0.09 p.u.
2) Using a base of 50 kVA and voltage reference as 2500 V at generator 1, calculate for
each reactance in pu and draw the single phase impedance diagram for the system. If a
three phase balanced fault occurs at Bus 3, determine the fault current at the fault point
in per unit as well as in ampere.
G1
S = 10 kVA 1 2 3 4
V = 2500V TX1 L1 TX2 M
X = j0.2 p.u.
G2 Z = 50+200j Ω
S = 20 kVA
V = 2500 V S = 40 kVA S = 80 kVA S = 25 kVA
X = j0.3 p.u. V = 2500/8000 V = 10000/5000 V = 4000V
V V X = j0.15 p.u.
X = j0.1 p.u. X = j0.09 p.u.
3) Consider the one line diagram of a simple power system shown in the following figure.
Calculate the new system data in per-unit on a 50 MVA base and voltage reference of
11.8 kV at generator 1. Hence, determine the 3Φ balanced fault current in actual and
per-unit if the fault occurs at bus 3.
M1 S = 20 MVA
V = 12 kV
4
G1 1 X = j0.15 p.u.
S = 25 MVA 3
2
V = 11.8 kV TX1 L1 TX2 M2
X = j0.2 p.u. S = 15 MVA
G2 V = 12 kV
S = 50 MVA 10+60j Ω X = j0.2 p.u.
V = 11.08 kV M3
X = j0.15 p.u. S = 90 MVA S = 90 MVA S = 30 MVA
V = 11/132 kV V = 11/132 kV V = 12 kV
X = j0.2 p.u. X = j0.2 p.u. X = j0.15 p.u.
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 1
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
4) A simple power system consisting of one synchronous generator and one synchronous
motor connected by two transformers and a transmission line is shown below. Create a per-
phase, per-unit equivalent circuit of this power system using a base apparent power of 100
MVA and a base line voltage of generator G1 of 13.8 kV.
5) Find the per-phase equivalent circuit for the power system shown below.
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 2
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
6) By referring a power system shown in Figure Q5b, calculate the balanced three-phase
fault current at bus 3.
G1 G2
j0.2 j0.3
j0.2 j0.3
j0.8
Bus 1 Bus 2
j0.4 j0.4
Bus 3 Fault
7) A single line diagram of a power system network is shown in Figure Q5c. The system
consists of generator, transformers and transmission lines supplying a load of
synchronous motor. Construct a per phase per unit equivalent circuit of the power
system network using a base apparent power of 100 MVA and a base line voltage at
generator G1 of 12 kV. Then predict the actual fault current if the fault occurs at point B.
B
G1 TX1 L1 TX2 M1
S = 100 MVA S = 50 MVA L1 = Impedance S = 50 MVA S = 50 MVA
V = 12 kV V = 11/120 kV X = j75 Ω V = 130/11 kV V = 11 kV
X = j0.9 p.u. X = j0.05 p.u. X = j0.05 p.u. X = j0.05 p.u.
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 3
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
8) Figure Q6c shows the single line diagram of three phase power system with a fault at
Bus B. Data for the components are given below. Using a base of 100 MVA and voltage
reference of 13.2 kV at generator GA as shown in figure:
i) Determine the base voltage at each zone.
ii) Convert the schematic into an equivalent per-unit circuit.
iii) Calculate the new per-unit reactance and actual fault current that occur at the
indicated zone.
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 4
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
9)
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 5
Tutorial 6 EPO244 2nd Edition May 18
10)
SITI SUFIAH BTE ABD WAHID Page 6
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Chapter 2 Discrete Data Control SystemsDocument78 paginiChapter 2 Discrete Data Control SystemsAmruth ThelkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMF Equation for DC MachinesDocument10 paginiEMF Equation for DC Machinestejashraj93Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamDocument31 paginiElectrical Machines EE-260: Instructor: DR Mehmood AlamSaif Ur RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Wire Earth Return Application GuideDocument45 paginiSingle Wire Earth Return Application Guidetony6sung100% (1)
- Line Distance Protection Rel670 650Document8 paginiLine Distance Protection Rel670 650igorsfaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Farm Modelling PSSEDocument6 paginiWind Farm Modelling PSSERahul Chakrabarti100% (2)
- Conductor Dimensioning For HV Surge ArrestersDocument3 paginiConductor Dimensioning For HV Surge ArrestersmartinpellsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mam 200Document24 paginiMam 200Taufan JustvandsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOSFET Biasing Using A Current MirrorDocument5 paginiMOSFET Biasing Using A Current MirrorSandeep Pandey100% (1)
- TransformerprotectionDocument65 paginiTransformerprotectionRK KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Circuit and Short Circuit On Single Phase TransformerDocument9 paginiOpen Circuit and Short Circuit On Single Phase TransformerManju KommojuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example 1: S S KV V MVA SDocument7 paginiExample 1: S S KV V MVA SKidist kefelegnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction Manual of Recloser Controller - R-200Document111 paginiInstruction Manual of Recloser Controller - R-200Rafael David Rincon Villamizar75% (4)
- MiCOM P132 - TechnicalDataSheetDocument44 paginiMiCOM P132 - TechnicalDataSheetcatalinccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bender-Main Catalogue Part 1 - 2004Document134 paginiBender-Main Catalogue Part 1 - 2004HanWee LowÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIT Feed Stop Sensor FaultDocument28 paginiIIT Feed Stop Sensor FaultValdemarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Monastir Correction TD 1 : Circuit magnétiques et Bobine à noyau de ferDocument8 paginiEcole Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Monastir Correction TD 1 : Circuit magnétiques et Bobine à noyau de ferwiem kahwech100% (1)
- Three Phase Transformer Model For TransientsDocument10 paginiThree Phase Transformer Model For TransientsYeissonSanabriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Intelligent Application To Power System ProtectionDocument8 paginiArtificial Intelligent Application To Power System Protectionheru100% (1)
- Simulation Studies of JeJu AC Power System ModelingDocument4 paginiSimulation Studies of JeJu AC Power System ModelingsiamaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EET301/4 Power Systems Engineering Tutorial Chapter 2 Impedance DiagramsDocument5 paginiEET301/4 Power Systems Engineering Tutorial Chapter 2 Impedance DiagramsNaasir SheekeyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Document4 paginiPower System Analysis Tutorial Sheet 01Goyal100% (1)
- PSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSDocument33 paginiPSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSMahesh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 Per Unit PDFDocument4 paginiTutorial 1 Per Unit PDFSofia Nadhirah Binti Amluddin100% (1)
- Designing a Regulated Power Supply CircuitDocument19 paginiDesigning a Regulated Power Supply CircuitejalzzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configure analog inputs on ABB RTU560Document7 paginiConfigure analog inputs on ABB RTU560TalibÎncă nu există evaluări
- EcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpDocument33 paginiEcodialAdvanceCalculation HelpChàng NgốcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure DEYE Hybride SUN XKDocument6 paginiBrochure DEYE Hybride SUN XKSINES FranceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Relay with ArduinoDocument5 paginiControl Relay with ArduinoMallikarjun RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee8353 Electrical Drives and Controls PDFDocument1 paginăEe8353 Electrical Drives and Controls PDFSha K ThyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pole Slip Protection: ANSI 78PS (For Motor)Document6 paginiPole Slip Protection: ANSI 78PS (For Motor)YousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0243Ch4Document46 pagini0243Ch4fwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TLP 250 ADocument6 paginiTLP 250 AbnnmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCPSTDocument9 paginiTCPSTmartinezjose192Încă nu există evaluări
- DC Ac ConverterDocument51 paginiDC Ac ConverteraswardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- D000011316 E850 Tech Data SheetDocument10 paginiD000011316 E850 Tech Data SheetstrahinjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classes of Motor DutyDocument20 paginiClasses of Motor DutyvishnuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nanometrical Devices - MOSFET in Synopsys SentaurusDocument15 paginiNanometrical Devices - MOSFET in Synopsys SentaurusJuan VALVERDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radial Distribution NetworkDocument8 paginiRadial Distribution Networkdallisrinivas14100% (1)
- Essential Parts of A Shaded-Pole MotorDocument16 paginiEssential Parts of A Shaded-Pole MotorShoaib Khan100% (3)
- CYCLOCONVERTER TITLEDocument40 paginiCYCLOCONVERTER TITLEMD. SADEKUL ISLAM RIMON 1502084Încă nu există evaluări
- Sect2-3 PDFDocument10 paginiSect2-3 PDFBlaiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Machine: Construction &types TypeDocument9 paginiSynchronous Machine: Construction &types TypeProma GurÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Quantities ExplainedDocument7 paginiAC Quantities Explainedsrinivas100% (1)
- EEET 205 Lab - 102Document53 paginiEEET 205 Lab - 102Franch Maverick Arellano LorillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation of Generator Connected to Infinite BusDocument6 paginiOperation of Generator Connected to Infinite BuspremameÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1151 RBDocument54 pagini1151 RBManuel A. Silva PainénÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Simulation of A PV System With Battery Storage Using Bidirectional DC DC Converter Using Matlab Simulink PDFDocument8 paginiDesign and Simulation of A PV System With Battery Storage Using Bidirectional DC DC Converter Using Matlab Simulink PDFDobrea Marius-AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC to AC Converters (Inverters) ExamplesDocument8 paginiDC to AC Converters (Inverters) Examplesbits_who_am_iÎncă nu există evaluări
- IELR464 - Cap 1 - Deber 03 - BIDocument16 paginiIELR464 - Cap 1 - Deber 03 - BIFrancisco Topón CaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied Electronics II Chapter 1: Feedback AmplifiersDocument200 paginiApplied Electronics II Chapter 1: Feedback Amplifiersabel berhanemeskelÎncă nu există evaluări
- TutorialDocument11 paginiTutorialEd SilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines DiagramDocument22 paginiElectrical Machines DiagramArivumani100% (1)
- Flyback Converter: J. FisherDocument16 paginiFlyback Converter: J. FisherDaniel NimabwayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micom SI Px40 PSL DétailsDocument21 paginiMicom SI Px40 PSL DétailsahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPE491 AC Circuits Power TutorialDocument3 paginiEPE491 AC Circuits Power TutorialMohdFirdausÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hence To Keep The CT Burden Lower, CT With 1A Secondary Is PreferableDocument1 paginăHence To Keep The CT Burden Lower, CT With 1A Secondary Is PreferableAjay PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- L293D Motor Control Shield: FeaturesDocument6 paginiL293D Motor Control Shield: FeaturesJefferson HenriqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE360 - 3-Phase CircuitsDocument64 paginiEE360 - 3-Phase Circuitsبدون اسمÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sm1223 CadDocument1 paginăSm1223 CadYEINER HERNAN ACUÑA VEGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorDocument5 paginiHopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorVarun VadluriÎncă nu există evaluări
- One-Line Diagram - Study View (Edit Mode) : Network Feeder 500 Mvasc 33 KV Network Feeder 500 Mvasc 33 KVDocument1 paginăOne-Line Diagram - Study View (Edit Mode) : Network Feeder 500 Mvasc 33 KV Network Feeder 500 Mvasc 33 KVBhavik PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boost DesignDocument4 paginiBoost DesignmuthukumartharaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photovoltaic Water Pumping System With Three-Level NPC InverterDocument10 paginiPhotovoltaic Water Pumping System With Three-Level NPC InverterTI Journals PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Elet 2 2017 2018Document4 paginiTest Elet 2 2017 2018fazfrito lacaviataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step-Down Chopper Overview and ProceduresDocument4 paginiStep-Down Chopper Overview and ProceduresKsr AkhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut 1Document4 paginiTut 1Abhijit PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Lab#03 Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersDocument24 pagini3-Lab#03 Single Phase Uncontrolled RectifiersRizwan Ahmad Muhammad AslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lic TemplateDocument117 paginiLic TemplateAkshaya M -108Încă nu există evaluări
- Computer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABDe la EverandComputer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Power System AssinmentDocument3 paginiAdvanced Power System AssinmentJara FeyisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Exercises 1 With SolutionsDocument4 paginiHome Exercises 1 With SolutionsOskari OllilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unta BeranakDocument6 paginiUnta Beranakharis kunkunÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSG 07-012 Rev A Multiplexing FaultsDocument16 paginiTSG 07-012 Rev A Multiplexing FaultsAshoka Sudharaka0% (1)
- Problems of Circuit InterruptionDocument20 paginiProblems of Circuit Interruptioneeng812450% (2)
- Manual Change History: Date Section Procedure Number Procedure Title Update ReasonDocument37 paginiManual Change History: Date Section Procedure Number Procedure Title Update ReasoninterloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersDocument22 paginiSample: Maintain HV Power System Circuit BreakersedgardÎncă nu există evaluări
- HiundayDocument24 paginiHiundayHenry HuayhuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7pg21 Solkor R RF Catalogue SheetDocument26 pagini7pg21 Solkor R RF Catalogue SheetsmcraftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schneider Electric Masterpact 2015 CatalogDocument184 paginiSchneider Electric Masterpact 2015 Catalogalbrodz100% (1)
- SPR Manual PDFDocument97 paginiSPR Manual PDFAshish GhadojeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Circuit Current Calculation Using Base KVA Method (39Document5 paginiShort Circuit Current Calculation Using Base KVA Method (39Idham A. DjufriÎncă nu există evaluări
- K01 0000137 04 CPS3500 5000PIE CPS3500 5000PRO - User+ManualDocument20 paginiK01 0000137 04 CPS3500 5000PIE CPS3500 5000PRO - User+ManualSaulean StefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MiCOM P139 Feeder Management and Bay ControlDocument4 paginiMiCOM P139 Feeder Management and Bay Controlshaikhsajid242Încă nu există evaluări
- Fusibles MT Smd1a PDFDocument20 paginiFusibles MT Smd1a PDFLuis Quilla MoronÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETAP Short-Circuit Report AnalysisDocument4 paginiETAP Short-Circuit Report Analysisdaniel.cabasa2577Încă nu există evaluări
- Cesc HTDocument14 paginiCesc HTJennifer Richmond0% (1)
- BB grb150Document16 paginiBB grb150grudwara2011Încă nu există evaluări
- NGR Installation Manual PDFDocument15 paginiNGR Installation Manual PDFSangeet BhandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1029C1 PDFDocument29 pagini1029C1 PDFAnonymous dPyHoLÎncă nu există evaluări