Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
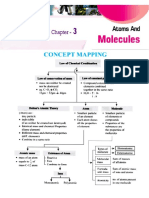
Concept Map 1
Încărcat de
Divanshu KapoorDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Concept Map 1
Încărcat de
Divanshu KapoorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
46 CONCEPT
CHEMISTRY TODAY | JUNE '15
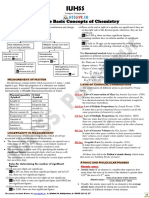
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Introduction of most fundamental and important tools of chemistry which help in various calculations.
SI Units Law of Conservation of Mass Masses
SI system has seven base units pertaining to Matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Atomic mass unit (amu or u) : Mass exactly
seven fundamental scientific quantities : equal to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of
C-12 isotope.
Physical quantity SI unit Law of Definite Proportions
Atomic mass of an element : Average
Length (l) metre (m) A given compound always contains exactly the relative mass of its atoms as compared to an
same proportion of elements by weight.
Mass (m) kilogram (kg) atom of C-12.
Average atomic mass : Given for isotopes.
Time (t) second (s) Xi Ai where Xi = % abundance
Law of Multiple Proportions
Electric current (I) ampere (A) X i Ai = atomic mass
If two elements can combine to form more than Gram atomic mass : Atomic mass of an
Thermodynamic kelvin (K)
one compound, the masses of one element that element expressed in grams.
temperature (T)
combine with a fixed mass of the other element, Molecular mass : Sum of atomic masses of
Amount of substance (n) mole (mol) are in the ratio of small whole numbers. all the elements present in a molecule.
Luminous intensity (Iv) candela (cd)
Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes Mole Concept
SI system allows the use of prefixes to
indicate the multiples or submultiples of a When gases combine or are produced in a Mole : Collection of 6.022 × 1023 particles
unit : chemical reaction they do so in a simple ratio In case of
by volume provided all gases are at same atomic substances :
deci - 10–1 deka - 101 temperature and pressure. 1 mole = Gram atomic mass = 1 gram atom
centi - 10–2 hecto - 102 = 6.022 × 1023 atoms
molecular substances :
milli - 10–3 kilo - 103
Avogadro's Law 1 mole = Gram molecular mass
micro - 10–6 mega - 106 = 1 gram molecule
nano - 10–9 giga - 109 Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature = 6.022 × 1023 molecules
pico - 10–12 tera - 1012 and pressure should contain equal number of gaseous substances :
molecules. 1 mole = 22.4 L at STP
Scientific Notation Dalton's Atomic Theory Percentage Composition
A number is represented as x × 10n Matter consists of indivisible atoms. It shows mass of a constituent in 100 parts of a
n is –ve if decimal is moved towards right All the atoms of a given element have compound.
and n is +ve if it is moved towards left. identical properties including identical Mass % of an element
mass. Atoms of different elements differ in Mass of that element in the compound
100
mass. Molar mass of the compound
Significant Figures Compounds are formed when atoms of
different elements combine in a fixed ratio.
These are all certain digits with last digit
Chemical reactions involve reorganisation
uncertain. Empirical Formula
of atoms. These are neither created nor
All non-zero digits are significant . It is the simplest whole number ratio of
destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Zeros preceding to first non-zero digit are different atoms present in a compound.
not significant. Steps to obtain empirical formula :
Zeros between two non-zero digits are
significant. Stoichiometry % age Change to
Molar ratio
Zeros on the right side of the decimal are At. mass
It deals with calculations based upon
significant.
chemical equations.
Molar ratio
Various steps involved in calculations are : Simplest molar ratio
Minimum molar ratio
Dimensional Analysis – Write balanced chemical equation.
– Write the relative number of moles or Change to
Required unit = Given value × conversion relative masses of reactants and products
factor Write the numbers below Simplest whole
involved below their formulae. number ratio =
the symbols of elements
Some useful conversion factors : – In case of gases write 22.4 L at STP in
–8 –10 Simplest ratio × Integer
Length – 1Å = 10 cm = 10 m place of 1 mole. Empirical formula
1 nm = 10–9 m, 1 pm = 10–12 m – Apply unitary method to make required
Volume – 1 L = 1000 mL calculations.
= 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 = 10–3 m3
Molecular Formula
Pressure – 1 atm = 760 mm or torr
= 101325 Pa It is the formula showing exact number of
Limiting Reagent
1 bar = 105 Nm–2 = 105 Pa atoms present in a molecule.
Energy – 1 calorie = 4.184 J The reactant which gets consumed completely Molecular formula = n × empirical formula
1 eV = 1.6022 × 10–19 J and limits the amount of product formed is
1 J = 10 7 ergs called limiting reagent.
CHEMISTRY TODAY | JUNE '15
Reactions in Solutions
wsolute
Mass percent (%) = 100
wsolution
HAVE A LOOK !
nA nB
Mole fraction (xA) = ,x
Mass is the quantity of matter contained in the substance and is constant whereas weight varies nA nB B nA nB
from place to place. w2 1000
Molarity (M) =
Exact numbers have an infinite number of significant figures. M2 V (in mL)
Molar volume of a gas is 22.7 L at 1 bar and 0°C. w2 1000
Molality (m) =
The number of molecules in 1 mL of a gas at STP is known as Loschmidt number. M2 w1(in g)
47
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Vacuum Engineering Calculations, Formulas, and Solved ExercisesDe la EverandVacuum Engineering Calculations, Formulas, and Solved ExercisesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- Chemistry Formula SheetDocument193 paginiChemistry Formula SheetGadde Gopala KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJSO Stage-I & II - Chemistry Sheet-2017-18Document23 paginiIJSO Stage-I & II - Chemistry Sheet-2017-18Himanshu ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirDocument112 paginiPhysical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirKritika SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument31 paginiBasic Concepts of ChemistryMohammadHussainKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)Document5 paginiIntroduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)BaaM TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mole Concept WorksheetDocument10 paginiMole Concept WorksheetNaman VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cargo Calculations - Ullage Surveys: GeneralDocument8 paginiCargo Calculations - Ullage Surveys: GeneralJorge Adrian Rojo UbedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Formula SheetDocument314 paginiChemistry Formula SheetAd Adarsh Navneet SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - June 2015Document1 paginăChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ne Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Document9 paginiNe Ne Ne: (Fractional Abundance X Mass of Isotope)Nathaniel Jay Rogador SumalinogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Reactions and StoichiometryDocument9 paginiChemical Reactions and StoichiometryNathaniel Jay Rogador SumalinogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument19 paginiAtoms and MoleculesAbhishek VashistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Academy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument4 paginiAcademy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryYash ShrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTRO TO CHEMISTRYDocument4 paginiINTRO TO CHEMISTRYIshhdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Document12 paginiAtoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic: Paper - 1Rezin ChÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Day OneDocument11 paginiSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: Day Onea85609616Încă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument116 paginiUntitledDeepanshu digariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 201Document15 pagini201RosheenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDocument29 paginiGeometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDinkar YeoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHY 40 Atoms, Molecules, Ions and StoichiometryDocument5 paginiCHY 40 Atoms, Molecules, Ions and StoichiometryYvonne SipalayÎncă nu există evaluări
- MOLE CONCEPTDocument4 paginiMOLE CONCEPTGaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM01 Co4 Lesson1 StoichiometryDocument2 paginiCHM01 Co4 Lesson1 Stoichiometrylucifer angelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mole ConceptDocument24 paginiMole ConceptRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 Atomic Structure and BondingDocument40 paginiLecture 2 Atomic Structure and Bondingannasullivan295Încă nu există evaluări
- Review of Fundamentals 1 (Student)Document6 paginiReview of Fundamentals 1 (Student)Rod BenavidesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)Document44 paginiAspire Mole Concept (17!4!21)sourav gargÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Chemistry 1 Week 2 DiscussionDocument12 paginiGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 2 Discussionpiatot6245Încă nu există evaluări
- Learners Science Academy: S B C CDocument4 paginiLearners Science Academy: S B C Cmujeebc 1972Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Chemistry NotesDocument249 paginiPhysical Chemistry NotesborntwofukÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHE-MM: XI - Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument2 paginiCHE-MM: XI - Basic Concepts of ChemistrymuhammadferosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02.stoichiometry TheoryDocument27 pagini02.stoichiometry Theoryshreyas bulbuleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument7 paginiChapter Notes Class: XI Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistrySridhar MarellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter:: Anything That Exhibits Inertia Is Called MatterDocument26 paginiMatter:: Anything That Exhibits Inertia Is Called MatterBvs TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edited Mole ConceptDocument22 paginiEdited Mole Conceptd anjilappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY STUDY MATERIAL XIDocument154 paginiCHEMISTRY STUDY MATERIAL XISHRUTI AGARWALAÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChemistryReview26 3 PosterDocument1 paginăChemistryReview26 3 PosterShruthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms, Elements, Compounds, Mixtures - Key Chemistry Terms ExplainedDocument1 paginăAtoms, Elements, Compounds, Mixtures - Key Chemistry Terms ExplainedIndianagrofarmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of Chemical ChangesDocument8 paginiLaws of Chemical ChangesHarold Q SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRYDocument3 paginiCHEMISTRYSAN JOSE, KRIZZIA FAYE U.Încă nu există evaluări
- Mole Concept: Mixture Pure SubstanceDocument9 paginiMole Concept: Mixture Pure SubstancePRITAM KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 1 Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument27 paginiSection 1 Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometryapi-3734333100% (2)
- CHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - SampleDocument22 paginiCHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - Sampleviswajithv66Încă nu există evaluări
- H:C Mass Ratio: Atomic StructureDocument2 paginiH:C Mass Ratio: Atomic StructureEunice C. LoyolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caie As Chemistry 9701 Theory v4Document27 paginiCaie As Chemistry 9701 Theory v4Adenekan Therhophic OrlanshilayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Chemistry NotesDocument3 paginiChapter 3 Chemistry NotesJu YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-IV Lecture-11 Publishers OverleadsDocument5 paginiUnit-IV Lecture-11 Publishers OverleadsRevilla Marco Robles RatillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument4 paginiAtoms and MoleculesJeyakumar RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryDocument5 paginiC15 Notes CH2 StoichiometryArnieÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM NotesDocument4 paginiCHEM NotesShayne BonayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry HandoutDocument4 paginiStoichiometry HandoutJohn Vincent D. PiastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main Short Notes Mole Concept and Stoichiometry - pdf-15Document9 paginiJEE Main Short Notes Mole Concept and Stoichiometry - pdf-15PUSHKAR SAINIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulae, equations and amounts of substancesDocument9 paginiFormulae, equations and amounts of substancesRawdatul JannahÎncă nu există evaluări
- List Definition ChemistryDocument9 paginiList Definition Chemistryrandi saputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document2 paginiLecture 1Meriza CabacunganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoms, Molecules, and Ions LawDocument5 paginiAtoms, Molecules, and Ions LawJohn Mark Clouie PlacaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY For IIT - Jee Mains and AdvancedDocument32 paginiCHEMISTRY For IIT - Jee Mains and Advancedtanishaasingh2506Încă nu există evaluări
- MATTER KMTPHDocument206 paginiMATTER KMTPHEng LuhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dalton's Atomic Theory Elements and CompoundsDocument10 paginiDalton's Atomic Theory Elements and CompoundsSamantha DumagpiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 102 - Materi Kimia ANORGANIKDocument19 pagini102 - Materi Kimia ANORGANIKradikalbebas2010Încă nu există evaluări
- LECTURE 4 Boyles LawDocument1 paginăLECTURE 4 Boyles LawAna May RafalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Unique Selective Detectors For Gas Chromatography: Nitrogen and Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectorsDocument15 paginiReview Unique Selective Detectors For Gas Chromatography: Nitrogen and Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectorsnmmMJKJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidróxido de Sodio: Nombre: Ruber Torrez TupaDocument2 paginiHidróxido de Sodio: Nombre: Ruber Torrez TupaJessica FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Experimental Techniques: Chromatography, Separation & PurificationDocument4 paginiIGCSE Experimental Techniques: Chromatography, Separation & PurificationFabian Obame0% (1)
- Colour Coding of The Most Important Gas Cylinders - CompressDocument1 paginăColour Coding of The Most Important Gas Cylinders - CompressMOHAMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D CFD simulation of flare flowDocument16 pagini3D CFD simulation of flare flowIlman IhzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Part 3 NotesDocument52 paginiThermodynamics Part 3 NotesFrancis CometaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantum Dots PaperDocument6 paginiQuantum Dots Paperdewesh1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Ceramics Chapter 1Document38 paginiFundamentals of Ceramics Chapter 1Tamiru MisikirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristic Reactions of Organic HalidesDocument6 paginiCharacteristic Reactions of Organic HalidesJules Patrick JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 6 - Analytical Chem - Complexation and Precipitation Part 2Document22 paginiSession 6 - Analytical Chem - Complexation and Precipitation Part 2MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Methacrylate Co-Agents On Peroxide Cured PP Epdm Thermoplastic VulcanizatesDocument17 paginiEffect of Methacrylate Co-Agents On Peroxide Cured PP Epdm Thermoplastic VulcanizatesFairmont Ind Quality DivisionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Energy: Linfeng ZhangDocument39 paginiSustainable Energy: Linfeng ZhangLuli NikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Convection of Heat Transfer ModeDocument105 paginiBasics of Convection of Heat Transfer ModeSamir YehyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phosgene Micro Reactor A I CheDocument9 paginiPhosgene Micro Reactor A I CheJorge RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Solutions Manual To Accompany Miller Freunds Probability and Statistics For Engineers 8Th Edition 0321640772 PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Solutions Manual To Accompany Miller Freunds Probability and Statistics For Engineers 8Th Edition 0321640772 PDF Docx Full Chapter Chaptersecrecy.tetradic.0s46al100% (12)
- Degrees of Freedom Analysis for Process UnitsDocument7 paginiDegrees of Freedom Analysis for Process UnitsAhmed AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Chemical Bonds, Water, CarbonDocument16 paginiTypes of Chemical Bonds, Water, CarbonRam Kewal TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrometallurgy: Gui Liu, Zhongwei Zhao, Ahmad Ghahreman TDocument20 paginiHydrometallurgy: Gui Liu, Zhongwei Zhao, Ahmad Ghahreman TShivansh MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledDocument11 paginiAn Overview of The Production and Use of Ammonia in NSR + SCR CoupledCicero LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Document70 paginiSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)NOREEN KAYE ROYOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ain Shams University: Different Silicon Growth TechniquesDocument11 paginiAin Shams University: Different Silicon Growth TechniquesAhmed Elswify100% (1)
- Pattern of Kolkata BOE ExaminationDocument7 paginiPattern of Kolkata BOE ExaminationRaag SÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiffusionDocument2 paginiDiffusionAnkita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kim ReformerDocument2 paginiKim ReformeralejandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Emulsion System To Breakup W-O EmulsionsDocument5 paginiMicro Emulsion System To Breakup W-O EmulsionsArmando SorondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TE 223: Mechanical Engineering: EntropyDocument17 paginiTE 223: Mechanical Engineering: EntropyShahnewaz BhuiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LS-DYNA Manual Vol2 971R700Document1.121 paginiLS-DYNA Manual Vol2 971R700loganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaporative Cooler - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 paginiEvaporative Cooler - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediabzkizo_sbbÎncă nu există evaluări