Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
Încărcat de
Jet Ray-Ann Garingan0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări2 paginiTitlu original
67990384-NCP-Ineffective-Cerebral-Tissue-Perfusion.doc
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
7 vizualizări2 paginiNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
Încărcat de
Jet Ray-Ann GaringanDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
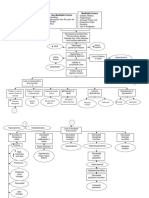
Admitting Diagnosis: Multiple Cerebral Infarction
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation
Subjective Ineffective Goal Determine factors related Influences choice of After 2-3
The client Cerebral Tissue The client will have to individual situation, interventions. Deterioration in weeks of
decreased cerebral neurological signs and
complained of Perfusion related an effective nursing
perfusion and potential for symptoms or failure to improve
slight difficulty of to interruption of cerebral tissue ICP. after initial insult may reflect intervention
breathing blood flow perfusion after 2 to decreased intracranial adaptive the client will
secondary to 3 weeks of proper capacity, which requires that be able to
Objective multiple cerebral nursing client be admitted to critical care demonstrate
- The patient infarctions as intervention area for monitoring of ICP and for increased
specific therapies geared to
appears lethargic manifested by perfusionm(e.g
maintaining ICP within a specified
altered level of Objectives range. If the stroke is evolving, ., vital signs
-P: 8 am 57 bpm consciousness, 1. To assess client can deteriorate quickly and within normal
12 pm 57 bpm changes in motor contributin require repeated assessment and range,
& sensory g factors progressive treatment. If the alert/oriented,
-BP: 8 am 130/70 response, and 2. To note stroke is “completed,” the free of
neurological deficit is
12 pm 140/80 language deficits degree of pain/discomfor
nonprogressive, and treatment is
impairmen geared toward rehabilitation and t)
-Speech t preventing recurrence.
abnormalities: 3. To
slurred speech maximize Assesses trends in LOC and
tissue potential for increased ICP and is
useful in determining location,
-Extremity perfusion Monitor and document extent, and progression or
weakness; pain neurological status resolution of CNS damage.
and discomfort frequently and compare
on lower with baseline.
Fluctuations in pressure may
extremities occur because
of cerebral pressure or injury in
Monitor vasomotor area of the brain.
-Restless; Keeps
vital signs noting: Hypertens Hypertension or hypotension may
on calling out for ion or hypotension have been a precipitating factor.
his wife and son
Visual and sensory/motor
-facial weakness changes/ involvement indicate
safety concerns and influence the
Determine the presence of choice of nursing intervention.
visual, sensory/motor
change, headache,
dizziness, altered mental To promote circulation/venous
status, personality changes drainage
Elevate HOB Some medications may be used
to decrease edema
Administer medications
(e.g. antihypertensives,
diuretics) Continual stimulation can
increase ICP. Absolute rest and
quiet may be needed to prevent
Maintain bedrest, provide recurrence of bleeding, in the
quiet environment, and case of hemorrhagic stroke.
restrict visitors or activities,
as indicated. Provide rest
periods between care
activities, limiting duration of
procedures.
Valsalva’s maneuver increases
ICP and potentiates risk of
bleeding.
Prevent straining at stool or
holding breath. Reduces hypoxemia.
Administer supplemental
oxygen, as indicated.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Dengue Fever: Jet Ray-Ann V. Garingan 24 May 14, 2019 Batch 51Document3 paginiDengue Fever: Jet Ray-Ann V. Garingan 24 May 14, 2019 Batch 51Jet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Resignation LetterDocument3 paginiResignation LetterJet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramJet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 paginiRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Chitale Dairy Uses RFID To Improve MilkYieldsDocument6 paginiChitale Dairy Uses RFID To Improve MilkYieldsAnnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Factors Affecting Demand For Soft DrinksDocument8 paginiFactors Affecting Demand For Soft Drinksخلود البطاحÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGT 338 Employability & Entrepreneurship: 1.0 Executive SummaryDocument21 paginiMGT 338 Employability & Entrepreneurship: 1.0 Executive Summaryeggie dan100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Px. Abdomen RadiologiDocument46 paginiPx. Abdomen RadiologiwagigtnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Climate Change, What Is It - Understanding The Basic Facts About Global WarmingDocument23 paginiClimate Change, What Is It - Understanding The Basic Facts About Global WarmingFer OssÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Overconfidence As A Cause of Diagnostic Error in Medicine PDFDocument22 paginiOverconfidence As A Cause of Diagnostic Error in Medicine PDFIulianZaharescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Housing StandardsDocument19 paginiHousing StandardsRashika Kala100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Toxicology Procedures ManualDocument206 paginiToxicology Procedures ManualDrMd IdrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypnotherapy To Reduce Post-Stroke Muscle Tension in IndonesiaDocument4 paginiHypnotherapy To Reduce Post-Stroke Muscle Tension in IndonesiaEndangAhmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON 1 - The Global North and SouthDocument9 paginiLESSON 1 - The Global North and SouthJeff Jeremiah PereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The X Factor 11Document31 paginiThe X Factor 11writerguy78Încă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- MMG 301 Study Guide For Exam 1Document14 paginiMMG 301 Study Guide For Exam 1Juyeon CheongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Psychoanalisis and PaediatricsDocument264 paginiPsychoanalisis and PaediatricsBlackKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mirizzi Syndrome - UpToDateDocument15 paginiMirizzi Syndrome - UpToDateEdgar Miguel ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper7 Syl22 Dec23 Set2 SolDocument20 paginiPaper7 Syl22 Dec23 Set2 SolAkash AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Daftar Obat Generik Klinik Citalang Medika Golongan Nama Obat Komposisi Golongan Nama ObatDocument2 paginiDaftar Obat Generik Klinik Citalang Medika Golongan Nama Obat Komposisi Golongan Nama ObattomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Antinociceptic Activity of Talisay ExtractDocument22 paginiAntinociceptic Activity of Talisay ExtractRein Paul Pascua TomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AimDocument52 paginiAimjapneet singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Factors of Internet Addiction Among AdolescentsDocument14 paginiRisk Factors of Internet Addiction Among AdolescentsM. F. MubinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent GangsDocument289 paginiAdolescent GangsReuben EscarlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpi 260 Client Feedback ReportDocument9 paginiCpi 260 Client Feedback ReportAlexandru ConstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brand Management of PatanjaliDocument22 paginiBrand Management of PatanjaliDarshan GohilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Modern Medical Center Z-Fold BrochureDocument2 paginiBlue Modern Medical Center Z-Fold BrochureAngela Shaine CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Edicted PG, StanDocument69 paginiEdicted PG, StanNwakpa Stanley OgbonnayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attending Physicians Statement - Form CDocument1 paginăAttending Physicians Statement - Form CPritam sarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio MEMSDocument16 paginiBio MEMStronghuynh12Încă nu există evaluări
- Facilities ManagementDocument21 paginiFacilities ManagementEduardo Viana100% (1)
- Biology Notes CHPTR 14Document7 paginiBiology Notes CHPTR 14Wan HasliraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pet Registration FormDocument1 paginăPet Registration FormBRGY MABUHAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules For Non Medical BusinessDocument1 paginăRules For Non Medical BusinessAbhijit AminpurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)