Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Types of Footings
Încărcat de
markensteinsDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Types of Footings
Încărcat de
markensteinsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Legaspi, Mark Gerald P.
CE 501
What are the type of footings? When and where to use them?
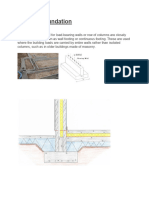
1. Continuous Wall Footing - Strip footings are commonly used as foundations of load-
bearing walls. The footing usually has twice the width as the load bearing wall, sometimes
it is even wider. The width as well as the type of reinforcement are depending on the
bearing capacity of the foundation soil.
2. Isolated Footing – It is defined as the footing, which is provided beneath the column to
distribute the loads safely to the bed soil. This kind of footing is used to support single-
columns and when the columns are arranged relatively at long distance.
3. Combined Footing - Combined footings are constructed for two or more columns when
they are close to each other and their foundations overlap. A combined footing is also
provided when the property line is so close to one column that a spread footing would be
eccentrically loaded when kept entirely within the property line.
4. Strip Footing - It is a continuous strip of concrete that serves to spread the weight of a
load-bearing wall across an area of soil. It is the component of a shallow foundation. Strip
footings can be used for both traditional timber and concrete floors.
5. Strap Footing - It is a type of combined footing, consisting of two or more
column footings connected by a concrete beam. A strap footing is often used in
conjunction with columns that are located along a building's property or lot line.
6. Raft Footing - It is a thick concrete slab reinforced with steel which covers the entire
contact area of the structure like a thick floor. Raft foundations are constructed for shallow
depths hence, it requires less excavation.
7. Pile Footing - Pile foundation, a kind of deep foundation, is actually a slender column or
long cylinder made of materials such as concrete or steel which are used to support the
structure and transfer the load at desired depth either by end bearing or skin friction.
8. Stepped Footing – It is a footing in which the desired width is secured by a series of steps
in about the proportion of one unit of horizontal dimension to two units of vertical
dimension.
9. Slope Footing - Sloped footings are trapezoidal footings. They are done with great care to
see that the top slope of 45 degree is maintained from all sides.
10. Mat Footing - Mat footings are used when the building load is so high, that spread or strip
footings could not bear the weight or their employment would be inefficient. Mat footings
are helping to reduce the varying settlements caused by construction on non-homogenous
soils or uneven load distribution on the footing.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Foundation Systems - RSW PR 01 - BTech 2 - Pigao, A.R.Document6 paginiFoundation Systems - RSW PR 01 - BTech 2 - Pigao, A.R.Alainstair Roe Pigao LabausaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foudation Ass 1Document1 paginăFoudation Ass 1Jea LagahitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-3 FoundationDocument53 paginiChapter-3 Foundationkader ArefeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCM Assignment Group 8Document18 paginiBCM Assignment Group 8Ashrutha HarshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation PDFDocument3 paginiFoundation PDFhamdan linjee SupaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geotechnical Engneering: What Is Foudation?Document7 paginiGeotechnical Engneering: What Is Foudation?starr awanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of ADocument12 paginiFoundation or Footing Is The Most Important and Basic Part of Ahabtamu abateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaitanya Mini Project PDFDocument11 paginiChaitanya Mini Project PDFMàyúr PàwàrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsDocument10 pagini1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation PlanDocument50 paginiFoundation PlanShaina Habib-AgilÎncă nu există evaluări
- BACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4Document14 paginiBACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4LORNA BACLIGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Document53 paginiChapter 5.1 Foundation (Part 1)Issack Mattew100% (1)
- Ar 373 BT 3 ReviewerDocument11 paginiAr 373 BT 3 ReviewerMelvin AlarillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shakib Sir URP - FoundationDocument48 paginiShakib Sir URP - FoundationHome Tutor Provider KhulnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A.P. Satashia Civil Dept., Ssasit SuratDocument17 paginiA.P. Satashia Civil Dept., Ssasit SuratParth AnajwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 FoundationDocument43 paginiCH 4 FoundationEyoatem Teferi100% (1)
- "In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Document37 pagini"In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Uzair SiddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Footing SlidesDocument19 paginiFooting SlidesColitz D. KhenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringDocument36 paginiCEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringRamu KakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Systems.Document9 paginiFoundation Systems.PRECIOUS AMY TITIWAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of FoundationDocument52 paginiTypes of FoundationMARUFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-22 FoundationDocument20 paginiChapter-22 Foundationdesubie bireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Building FoundationDocument4 paginiTypes of Building FoundationRajesh TandonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On FoundationsDocument14 paginiPresentation On FoundationsShiwangi NagoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.CEE 4101 3 MarchDocument44 pagini4.CEE 4101 3 MarchPranto KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shallow Foundation ReportDocument4 paginiShallow Foundation ReportTejasÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Foundation and Its RoleDocument8 paginiWhat Is Foundation and Its RoleSneha Anbalagan100% (1)
- Types of FoundationsDocument9 paginiTypes of Foundationsjorgerecinos172Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Foundations PDFDocument30 paginiTypes of Foundations PDFHuzaifa TanzeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of FoundationsDocument30 paginiTypes of FoundationsFahad Areeb100% (1)
- FOUNDATION ShallowDocument4 paginiFOUNDATION ShallowAngie BitesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Part 2 Elements of Building ConstructionDocument27 paginiUnit 1 Part 2 Elements of Building Constructiontanishk00756Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 Chapter 3 Part 1 Foundations.Document40 pagini3 Chapter 3 Part 1 Foundations.Enanye AragawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1 Lecture NoteDocument15 paginiChapter-1 Lecture NoteWendimu TolessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 LectureDocument37 pagini4 LecturePranto KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH-2 Types of Shallow FoundationsDocument35 paginiCH-2 Types of Shallow Foundations19CE535 Mandar GawandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buildings-Types of FoundationsDocument5 paginiBuildings-Types of FoundationsRonit ChariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Report On Isolated FootingDocument22 paginiFull Report On Isolated Footingabidur77100% (2)
- BCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021Document21 paginiBCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021hyperloop707 designÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCE Lecture 9Document11 paginiBCE Lecture 9MurgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Construction Lecture Note .2Document198 paginiBuilding Construction Lecture Note .2amu aytuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3Document149 paginiModule 3Owsu KurianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2 Types of Foundations PDFDocument36 paginiLec 2 Types of Foundations PDFUsman AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Design System: Submitted By: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. Arch #13Document8 paginiBuilding Design System: Submitted By: Hafiz Uzair Naeem Ud Din M. Arch #13Uzair SiddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Foundation and Their UsesDocument6 paginiTypes of Foundation and Their UsesChelsea EspirituÎncă nu există evaluări
- Builiding FoundationDocument16 paginiBuiliding FoundationSanjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Foundation 1Document14 paginiTypes of Foundation 1Olawale AdebesinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of FoundationDocument7 paginiTypes of FoundationNino Celso AstilleroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document14 paginiLecture 1Erica Jane TatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shallow Foundation Assignment 1 (Finals)Document2 paginiShallow Foundation Assignment 1 (Finals)Lensearfwyn NamocatcatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer BT3Document7 paginiReviewer BT3Ron RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- FoundationsDocument32 paginiFoundationsSriLaxmi BulusuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strip FoundationDocument44 paginiStrip FoundationRajesh KhadkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Always Try To Do The Best in Your LifeDocument79 paginiAlways Try To Do The Best in Your LifeNamrata PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Shallow FoundationDocument6 paginiTypes of Shallow FoundationJaisurya Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Types of FondationDocument21 paginiChapter 3-Types of Fondationbereket gÎncă nu există evaluări
- FoundationDocument17 paginiFoundationIshita DhingraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 FoundationDocument11 paginiChapter 3 FoundationtofshomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionDe la EverandStrength Of Beams, Floor And Roofs - Including Directions For Designing And Detailing Roof Trusses, With Criticism Of Various Forms Of Timber ConstructionÎncă nu există evaluări
- JLWH Additional Works - Tire RacksDocument6 paginiJLWH Additional Works - Tire RacksmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4: Organizing Technical Activities: Bayas Legaspi Miranda MongcalDocument36 paginiChapter 4: Organizing Technical Activities: Bayas Legaspi Miranda MongcalmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- File PDFDocument8 paginiFile PDFmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mega Structure: Afable - Culanding - Legaspi - Nievra - VirtudazoDocument20 paginiMega Structure: Afable - Culanding - Legaspi - Nievra - VirtudazomarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts of Prestressing: Basic Concept Method C-Line Method Load-Balancing MethodDocument28 paginiBasic Concepts of Prestressing: Basic Concept Method C-Line Method Load-Balancing Methodmarkensteins50% (2)
- Title Proposal Template A: Lyceum of The Philippines University Cavite CampusDocument1 paginăTitle Proposal Template A: Lyceum of The Philippines University Cavite CampusmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doubletees 10ldt24and10ldt24Document1 paginăDoubletees 10ldt24and10ldt24markensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work and Energy Problems SolutionsDocument7 paginiWork and Energy Problems SolutionsmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment in PrestressedDocument1 paginăAssignment in PrestressedmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- OBE Syllabus Consumer Protection Law and Competition Law PLM L SebastianDocument26 paginiOBE Syllabus Consumer Protection Law and Competition Law PLM L SebastianmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transpo Samplex PDFDocument24 paginiTranspo Samplex PDFmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Problem 2.C4: OutputDocument27 paginiComputer Problem 2.C4: OutputmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PokemonDocument4 paginiPokemonmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pokemon: Gardevoir Type:psychic, Fairy Type 2:feelingDocument4 paginiPokemon: Gardevoir Type:psychic, Fairy Type 2:feelingmarkensteinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cupolex Slab On GradeDocument10 paginiCupolex Slab On GradeFábio SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JKR Geotechnical SpecificationDocument9 paginiJKR Geotechnical SpecificationSousei No Keroberos100% (1)
- Butwal Regional Office: Nepal Electricity AuthorityDocument2 paginiButwal Regional Office: Nepal Electricity AuthoritySujit RasailyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathcad Soil Supported Combined FootingDocument8 paginiMathcad Soil Supported Combined FootingTarek Ed EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Code 2017Document111 paginiFoundation Code 2017Cheung Lee100% (1)
- Geoplast Slabs Solution English BrochureDocument52 paginiGeoplast Slabs Solution English BrochureMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contemporary Architecture 09At5Dccoa: Content Compiled by Ar. Sahana. SDocument12 paginiContemporary Architecture 09At5Dccoa: Content Compiled by Ar. Sahana. SShifa TalathÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPALLA Report Rev.2 PDFDocument25 paginiSPALLA Report Rev.2 PDFmascalzoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Livespot Soil Test ReportDocument35 paginiLivespot Soil Test ReportNadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mill Owners Association - PresentationDocument22 paginiMill Owners Association - PresentationGargi KoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Proposal: For A Detailed Survey, Soil Investigation, Detailed Design and Cost Estimate of Bridge, PyuthanDocument22 paginiTechnical Proposal: For A Detailed Survey, Soil Investigation, Detailed Design and Cost Estimate of Bridge, PyuthanNepali KanchooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Engneers Directory 2021Document58 paginiStructural Engneers Directory 2021Mcr KumaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SABP005-Sorage Tank Ringwall FoundationsDocument18 paginiSABP005-Sorage Tank Ringwall FoundationsgiovanniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 6059677664669600275 PDFDocument3 pagini5 6059677664669600275 PDFgopala krishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Residential FloorsDocument47 paginiGuide To Residential Floors_at_to_67% (3)
- Design IconDocument29 paginiDesign Iconคณกฎ ปิยะวงศ์สมบูรณ์Încă nu există evaluări
- Strucural Design and Assembly of TreetDocument8 paginiStrucural Design and Assembly of TreetFelipe DiezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Deep FoundationsDocument98 paginiTypes of Deep FoundationsRuli Aprillianto67% (3)
- Small ToiletDocument64 paginiSmall ToiletYogendra BastakotiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ssignment Rief: P Btec C & B E 30. A S D (5)Document5 paginiSsignment Rief: P Btec C & B E 30. A S D (5)hafiz zain100% (1)
- 2012.11.14 - How To Read and Understand A Geotechnical Report (Part 2)Document24 pagini2012.11.14 - How To Read and Understand A Geotechnical Report (Part 2)UALU333Încă nu există evaluări
- Mat Foundations (Part B) : DR Nor Faizah BawadiDocument20 paginiMat Foundations (Part B) : DR Nor Faizah Bawadiabas ibrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Structural Designs For Low Rise Residential Buildings in RC ConstructionDocument130 paginiStandard Structural Designs For Low Rise Residential Buildings in RC Constructionsreejit77100% (1)
- Course Book - Foundation Engg. Water ResourcesDocument3 paginiCourse Book - Foundation Engg. Water ResourcesRafi Mahmoud SulaimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide Canterbury Earthquake RevisedDocument140 paginiGuide Canterbury Earthquake RevisedDavid HamberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Piled Raft Foundation-A Geo-Structural ApproachDocument68 paginiAnalysis of Piled Raft Foundation-A Geo-Structural Approachنعمان سولکرÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 - Need & Function of Pile FoundationDocument2 pagini12 - Need & Function of Pile FoundationMUTHUKKUMARAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Building Construction IDocument2 paginiCourse Building Construction Ihafiz hilmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Basics of Soil Mechanics Finished (Compatibility Mode)Document145 paginiModule 1 - Basics of Soil Mechanics Finished (Compatibility Mode)Sahil Jawa100% (1)
- FOUNDEN-05 Geotechnical Desgn of Spread FootingDocument47 paginiFOUNDEN-05 Geotechnical Desgn of Spread FootingPeter John RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări