Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hvac Assignment
Încărcat de
Chethan. M.D.100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
688 vizualizări27 paginiN
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentN
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
688 vizualizări27 paginiHvac Assignment
Încărcat de
Chethan. M.D.N
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 27
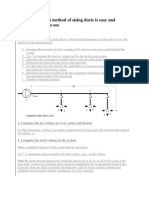
HVAC ASSIGNMENT
1.What is local comfort cooling
system?
Comfort cooling is the same type of cooling
system that can be found in residential
houses and office buildings. It is designed
to cool spaces primarily to create
comfortable temperatures for occupants.
2.What is Centralised Air System?
Central air conditioning (or central A/C) is
a system in which air is cooled at a central
location and distributed to and from rooms
by one or more fans and ductwork. The
compression of the refrigerant gas enables
it to discharge heat out of the house, which
is how the cool air is created.
3. What Is Constant Volume System?
Constant air volume (CAV) is a type of
heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning
(HVAC) system. In a simple CAV system,
the supply air flow rate is constant, but the
supply air temperature is varied to meet the
thermal loads of a space. Most
CAV systems are small, and serve a single
thermal zone.
4. What Is Variable Air Volume System
& Dual Duct System?
Variable Air Volume units vary the airflow
individually between separate hot and cold
inlet ducts for highly accurate temperature
and comfort control.
5. What Is Hydronic System Or Air-
water System?
Hydronic is the use of water as the heat-
transfer medium in heating and cooling
systems. A hydronic piping system is used
to circulate chilled or hot water with the
connections between the piping and the
terminal units made in a series loop.
6.How Vapour Compression Cycle
Works ?
At this stage of the Vapour Compression
Refrigeration Cycle, the refrigerant is at a
lower temperature than its surroundings.
Therefore, it evaporates and absorbs latent
heat of vaporization. Heat extraction from
the refrigerant happens at low pressure
and temperature.
7.What is vapour Compression cycle?
Vapour Compression cycle, in which the
refrigerant undergoes phase changes, is
one of the many refrigeration cycles and is
the most widely used method for air-
conditioning of buildings and automobiles.
8. Why Is A Compressor Used In
Refrigeration?
The compressor then has to raise the
pressure of the refrigerant to a level at
which it can condense by rejecting heat to
the cooling medium in the condenser.
9. What Is Auto Refrigeration?
Auto-refrigeration is a phenomenon
common to liquefied compressed gases.
Liquefied compressed gases exist in both
the liquid and gaseous phases at ambient
temperatures with pressures ranging from
2 psig up to 2,500 psig. That is, there is a
gaseous layer over the liquefied gas within
the pressure vessel. Some common
liquefied gases are shown in the following
table.
10. How Does A Refrigerant
Compressor Work?
The refrigerant absorbs the heat inside the
fridge when it flows through the evaporator
coils, cooling down the air inside the fridge.
Last, the refrigerant evaporates to a gas
due to raised temperature, and then flows
back to the compressor, where the cycle
starts all over again.
11. Why Capacity Of Air Conditioner Is
Measured In Tons?
The use of tons to
measure cooling capacity comes from this
time. A ton refers to the amount of heat it
takes to completely melt a ton of ice.
Melting this amount of ice requires
286,000 Btu (British thermal units).
12. What Is The Meaning Of 1 Ton Of
Ac?
A ton is the cooling capacity of an air
conditioning system. One ton is equal to
the amount of heat required (288,000 Btu)
to melt one ton of ice in a 24-hour period.
A one-ton air conditioner is rated at 12,000
Btu.
14. What Is Btu?
The acronym stands for British Thermal
Unit, which is the unit used to measure
thermal (heat) energy. Specifically, it is the
amount of energy needed to raise 1 pound
of water 1°F at sea level.
15. What Is The Meaning Of Btu In Air Conditioners?
15. What Is The Meaning Of Btu In Air
Conditioners?
which indicates the amount of heat it can
remove from a room. A higher
number means more cooling power for a
larger room. Compare your room size to
the BTU rating: 150 to 350 sq ft look for a
5,000- to 8,000-BTU unit.
16. What Is Cfm & Infiltration?
The infiltration rate is the volumetric flow
rate of outside air into a building, typically
in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or liters per
second (LPS). The air exchange rate, (I), is
the number of interior volume air changes
that occur per hour, and has units of 1/h.
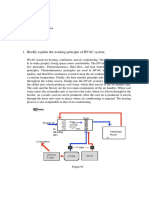
17. What Is The Hvac System?
The initials HVAC stand for Heating,
Ventilation and Air Conditioning. They
describe the functions of an HVAC system. This
mechanical system’s design is primarily an
attempt to take control of the environmental
conditions inside the space you work.
18. What Does A HVAC Engineer Do?
An HVAC engineer's job duties can include
the design, installation, maintenance, and
repair of heating, ventilation, air
conditioning, cooling, and refrigeration
systems. ... These professionals can work
for consulting or design firms, government
agencies, facilities offices,
or HVAC equipment sales offices.
19. What Is Psychometric?
A psychometric chart is a graphical
representation of the psychometric
processes of air. Psychometric processes
include physical and thermodynamic
properties such as dry bulb temperature,
wet bulb temperature, humidity, enthalpy,
and air density.
20. What Are The Types Of Air
Conditioning Systems?
6 Different Types of Air Conditioners.
Central Air Conditioning
Ductless, Mini-Split Air Conditioner
Window Air CoPortabler
Portable Air Conditioner
Hybrid Air Conditioners
Geothermal Heating & Cooling
22. What Is The Function Of Ahu?
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is used to re-
condition and circulate air as part of a
heating, ventilating and air-conditioning
system. The basic function of the AHU is
take in outside air, re-condition it and
supply it as fresh air to a building.
23. How Does The Ahu Work?
An air handler unit (often abbreviated to
AHU), is a device used to regulate and
circulate air as a part of heating, ventilating,
and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. ... Air
handlers usually connect to a ductwork
ventilation system that distributes the
conditioned air through the building and
returns it to the AHU.
24. What Is The Purpose Of Air
Handling Units?
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is used to re-
condition and circulate air as part of a
heating, ventilating and air-conditioning
system. The basic function of the AHU is
take in outside air, re-condition it and
supply it as fresh air to a building.
25. Where The Fcu’s Are Used?
It is part of an HVAC system found in
residential, commercial, and industrial
buildings. A fan coil unit is a diverse device
sometimes using ductwork, and is used to
control the temperature in the space where
it is installed, or serve multiple spaces.
26. What Is The Fcu?
A fan coil unit is a simple device consisting
of a heating or cooling heat exchanger or
'coil' and fan. It is part of an HVAC system
found in residential, commercial, and
industrial buildings.
27. What Is The Meaning Of FAHU?
FAHU is the abbreviation used for FRESH
AIR HANDLING UNIT. These are usually
centralized units employed to induce fresh
air quantities to the confines spaces.
28. What Is An Air Conditioner
Condenser?
A condenser unit used in central air
conditioning systems typically has a heat
exchanger section to cool down and
condense incoming refrigerant vapour into
liquid, a compressor to raise the pressure
of the refrigerant and move it along, and a
fan for blowing outside air through the heat
exchanger section to cool the space.
29. how Does A Condenser In A
Refrigerator Work?
condenser, where it condenses from
vapour form to liquid form, giving off heat in
the process.
30. What Is The Main Function Of A
Condenser?
In systems involving heat transfer, a
condenser is a device or unit used to
condense a substance from its gaseous to
its liquid state, by cooling it. In so doing, the
latent heat is given up by the substance
and transferred to the surrounding
environment.
31. How Does A Condensing Unit
Work?
A condenser unit used in central air
conditioning systems typically has a heat
exchanger section to cool down and
condense incoming refrigerant heat vapour
into liquid.
32. What Are The Types Of
Condensers?
The three main types of condensers used
in general refrigeration systems are:
air-cooled.
water-cooled.
evaporative.
33. What Is A Rotary Air Compressor?
A rotary-screw compressor is a type of gas
compressor, such as an air compressor,
that uses a rotary-type positive-
displacement mechanism. The gas
compression process of a rotary screw is a
continuous sweeping motion, so there is
very little pulsation or surging of flow, as
occurs with piston compressors.
34. What Is A Gas Compressor Used
For?
Compression of a gas naturally increases
its temperature. When the gas is air, the
machine is called an air compressor.
Compressors are similar to pumps: both
increase the pressure on a fluid and both
can transport the fluid through a pipe. As
gases are compressible, the compressor
also reduces the volume of a gas.
35. What Is The Use Of Compressor In
Refrigeration?
The compressor does exactly as its name
says it compresses the refrigerant. The
compressor receives low pressure gas
from the evaporator and converts it to high
pressure gas. As mentioned earlier, as the
gas is compressed, the temperature rises.
The hot refrigerant gas then flows to the
condenser.
MCQ’s
1. Two locations where a cold air return
should be installed:
a. Open area of wall and low to the
ground.
b. Behind appliances and high on the wall.
c. Open area of wall and high on the wall.
d. Behind appliances and low to the
ground.
2. Which of the following is a law of
thermodynamics:
a. Heat is a form of matter.
b. Heat moves toward a place with higher
intensity.
c. Heat moves toward a place with lower
intensity.
d. Heat moves toward a place with a
higher temperature.
3. Sensible heat describes
_________________________.
a. How fast heat will travel.
b. The quantity of heat.
c. The volume of heat.
d. How hot something feels.
4. Latent heat measures
_______________________.
a. The temperature of heat in a
substance.
b. The quantity of heat in a substance.
c. The velocity of heat in a substance.
d. The heat potential of a substance.
5. Latent heat is measured in
____________________.
a. Degrees Celsius, Fahrenheit and
Kelvin b. International System of Units
c. British Thermal Units d.
Board of Trade Unit
6. If 1 pound of water warms to 60 degrees F
from 55 degrees F, what btu of latent heat
will it have absorbed?
a. 2.5
b. 5
c. 10
d. 15
7. What is the amount of heat energy
required to evaporate 1 pound of water?
a. 370 btu
b. 570 btu
c. 770 btu
d. 970 btu
8. In an air conditioning and refrigeration
system, what occurs in an evaporator?
a. The refrigerant absorbs the latent
heat.
b. The refrigerant evaporates latent
heat.
c. Latent heat is condensed.
d. Latent heat is released.
9. In an air conditioning and refrigeration
system, what occurs in a condenser?
a. The refrigerant absorbs the latent
heat.
b. The refrigerant releases the latent
heat.
c. Latent heat is pressurized.
d. Latent heat is increased.
10. In a sealed system, pressure and
temperature _________________.
a. are inversely proportional
b. go in opposite directions up and
down
c. are equal
d. follow each other up and down
11. Which of the following is not a type of
compressor?
a. Lateral
b. Reciprocating
c. Rotary
d. Screw
e. Centrifugal
12. In Fahrenheit, the boiling point of water is
_____________.
a. 100 degrees
b. 112 degrees
c. 212 degrees
d. 221 degrees
13. To change Fahrenheit to Celsius, which
formula is used?
a. C =(F+32)÷ 1.8 b. C=(F-32) x 1.8 c.
C=(F-32) ÷ 1.8
d. C= (F-32)+1.8
14. Which of the following is not a method by
which heat may be transferred from a
warmer substance to a colder substance?
a. Conduction
b. Retraction
c. Convection
d. Radiation
15. What btu of heat is required to raise 1
pound of ice 1 degree F when the
temperature is below 32 degrees F?
a. .25
b. .5
c. 1
d. 1.5
16. What btu of heat is required to raise 1
pound of steam 1 degree F above the
temperature of 212 degrees F?
a. .25
b. .5
c. 1
d. 1.5
17. A day-ton of refrigeration is the amount of
refrigeration produced by melting 1 ton of ice
at a temperature of 32 degrees F in 24 hours.
A) True B) false
18. Ice exerts pressure ________________.
a. Upwards
b. Laterally
c. Downwards
d. In all directions
19. Pressure is usually measured in
___________.
a. Pounds per square foot
b. Pressure per square foot
c. Pounds per square inch
d. Pressure per square inch
20. When one rises into the atmosphere, the
atmospheric pressure decreases by 1 psi for
every_________________.
a. 2,343 feet
b. 3,334 feet
c. 2,500 feet
d. 5,280 feet
21. Vaporization can be increased by
_____________ the pressure on a liquid.
a. Increasing b. Equalizing
c. Reducing
22. Every mechanical refrigeration system has
__________ different pressure levels.
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 5
23. Pressure on the high pressure side of a
mechanical refrigeration unit is called
_______________.
a. suction pressure
b. discharge or head pressure
c. differential l pressure
d. absolute pressure
24. The exertion of pressure on a substance
with a constant temperature increases its
volume in proportion to the increase in
pressure.
True
False
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hvac ReportDocument52 paginiHvac ReportlokeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Interview Questions and Answers HVAC SIMPLIFIEDDocument7 paginiHVAC Interview Questions and Answers HVAC SIMPLIFIEDMalek AqlanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MECH3005 - Building Services Load CalculationsDocument46 paginiMECH3005 - Building Services Load CalculationsAzher MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of HVAC PSYCHOMETRICS AIR PARAMETERS PDFDocument96 paginiFundamentals of HVAC PSYCHOMETRICS AIR PARAMETERS PDFSanjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ducting ME LabDocument33 paginiDucting ME LabMichael Pedernal IlaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Air Conditioning Systems ReviewDocument23 paginiCentral Air Conditioning Systems ReviewlalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Air Conditioning DuctsDocument15 paginiDesign of Air Conditioning Ductsabidch143Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 ACMV SystemsDocument293 pagini4 ACMV SystemsMorgan HengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Document4 paginiHeat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Michael LagundinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- % Outdoor Air CalculationDocument6 pagini% Outdoor Air Calculationamirin_kingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigerant and Environmental RefrigerantsDocument66 paginiRefrigerant and Environmental Refrigerantsسامح الجاسم33% (3)
- Carrierdes1 PDFDocument163 paginiCarrierdes1 PDFDomingo RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- VENTILATION SYSTEMSDocument28 paginiVENTILATION SYSTEMSIzzat AdibÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP13 - 1999 MV and AC in BuildingDocument56 paginiCP13 - 1999 MV and AC in Buildingbozow bozowlÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEC551 Assignment - Design June2017Document6 paginiMEC551 Assignment - Design June2017Muhd Syafiq OthmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 The Air Distribution SystemDocument40 paginiChapter 3 The Air Distribution SystemMuhammad Abdullah86% (7)
- Residential Cooling Load CalculationDocument24 paginiResidential Cooling Load CalculationAngeloTomalonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paint Booth HVAC Control SystemDocument6 paginiPaint Booth HVAC Control SystemPraveenkumar KashyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- 425-3-Cooling Load-2007Document15 pagini425-3-Cooling Load-2007zulkifroÎncă nu există evaluări
- AirConditioning & Ventilation TCX Methodology Rev# 1.1Document12 paginiAirConditioning & Ventilation TCX Methodology Rev# 1.1Non Etabas GadnatamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Spec for AHUDocument6 paginiTechnical Spec for AHUreddyrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 39 Space Air DistributionDocument25 pagini39 Space Air DistributionPRASAD326100% (3)
- Air-Conditioning System DesignDocument42 paginiAir-Conditioning System DesignRaj Verma100% (2)
- Air-Conditioning Load EstimationDocument23 paginiAir-Conditioning Load Estimationtkm2004Încă nu există evaluări
- INTERNSHIP PROJECT Catia FinalDocument23 paginiINTERNSHIP PROJECT Catia Finalsynrinxlangthasa1874Încă nu există evaluări
- Duct DesignDocument13 paginiDuct DesignamitÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 VAV Boxes Energy Efficiency, Air Leakage and ASHRAE 90.1Document29 pagini2012 VAV Boxes Energy Efficiency, Air Leakage and ASHRAE 90.1din_thorpe3248Încă nu există evaluări
- Selecting the Right AHUDocument24 paginiSelecting the Right AHUrahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- The equal friction method for sizing ductsDocument8 paginiThe equal friction method for sizing ductsRamil BelmonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moist Air Properties and Conditioning ProcessesDocument94 paginiMoist Air Properties and Conditioning Processespamsanchezmd100% (1)
- Air Distribution Engg GuideDocument8 paginiAir Distribution Engg GuideNiong DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- DuctSox 230215Document32 paginiDuctSox 230215Aeon SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refr Sys DesignDocument13 paginiRefr Sys Designعبدالله عمرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equal Friction MethodDocument2 paginiEqual Friction MethodApurv GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Air, All Water, and Air-Water Hvac SystemsDocument3 paginiAll Air, All Water, and Air-Water Hvac SystemsAnonymous JvqLFbBsF100% (2)
- Ventilation Lecture 4 PH Alleen LezenDocument25 paginiVentilation Lecture 4 PH Alleen LezenNazimAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Filters: Dr. Ahmed Elsafty yDocument55 paginiAir Filters: Dr. Ahmed Elsafty yAhmed Sherif100% (1)
- Mep Hvac 3Document133 paginiMep Hvac 3Muhammad Musa100% (1)
- Materaial For Question 3. - Cooling Load CLTD Example Ashrae PDFDocument5 paginiMateraial For Question 3. - Cooling Load CLTD Example Ashrae PDFkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation and Maintenance Manual of Air Conditioning System in Klinik Tawau, Klinik Kesihatan Jenis 2Document21 paginiOperation and Maintenance Manual of Air Conditioning System in Klinik Tawau, Klinik Kesihatan Jenis 2LeslieYewMinYunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 paginiExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Data: Iso 9001 Certified CompanyDocument32 paginiEngineering Data: Iso 9001 Certified CompanyKhaleelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.ACMV (Air Cooled Split Unit) - PDFDocument3 pagini3.ACMV (Air Cooled Split Unit) - PDFIswadi Bin ZulkarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooling TowerDocument23 paginiCooling TowerBevelyn L. Barreto HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- VENTILATION REPORT SUMMARYDocument13 paginiVENTILATION REPORT SUMMARYSwasti DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precooled Ahu CalculationDocument3 paginiPrecooled Ahu CalculationEdmund YoongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air ConditioningDocument37 paginiAir Conditioningfirst lastÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC System SelectionDocument10 paginiHVAC System SelectionNisargPatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- AHU Vs FCU Comparison PDFDocument5 paginiAHU Vs FCU Comparison PDFamirin_kingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ahu & Chiller OkDocument40 paginiAhu & Chiller OkAndy DwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Questions and AnswersDocument3 paginiHVAC Questions and AnswersAli ShamakhÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadDocument4 paginiHVAC Interview Questions and Answers PDF DownloadVenkatesh100% (1)
- 35 Basic HVAC Interview Questions & Answers: Follow Us On LinkedinDocument7 pagini35 Basic HVAC Interview Questions & Answers: Follow Us On Linkedinshaul hameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- HVAC Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 paginiHVAC Interview Questions and AnswersmananÎncă nu există evaluări
- 35 Basic HVAC Interview Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagini35 Basic HVAC Interview Questions & AnswersAnsys Design CFDÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 paginiUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument7 paginiRefrigeration and Air ConditioningManjunatha EikilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbstractDocument4 paginiAbstractafiqzalhasmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbstractDocument10 paginiAbstractabushasolomon75% (4)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemDe la EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rry'S Chemical Engineers' Handbook: Seventh EditionDocument2 paginiRry'S Chemical Engineers' Handbook: Seventh EditionRamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microporous and Mesoporous Materials: Sean M.W. Wilson, Vida A. Gabriel, F.Handan TezelDocument11 paginiMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials: Sean M.W. Wilson, Vida A. Gabriel, F.Handan TezelEcÎncă nu există evaluări
- BP - 10 - SC - Pre Board - Set-2Document1 paginăBP - 10 - SC - Pre Board - Set-2Manju MaliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admixtures and Shotcrete DurabilityDocument7 paginiAdmixtures and Shotcrete DurabilityMulyawan WIdiasmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressive Strength of GypsumDocument9 paginiCompressive Strength of GypsumSalwa MuzafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionDocument2 paginiEdicto - Thermodynamics Lab - Heat FusionEdicto, Beatrice CarolineÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States: Patent OfficeDocument4 paginiUnited States: Patent OfficesherlybonitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTC 25062-MS-Dr MuzDocument5 paginiOTC 25062-MS-Dr Muzazmi68Încă nu există evaluări
- Khaled El Deeb Aquence 866 Process - ManualDocument39 paginiKhaled El Deeb Aquence 866 Process - ManualNew Wrld100% (1)
- EVA Test PropeetiesDocument37 paginiEVA Test Propeetiessimon sembiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trunnion Ball Valves PDFDocument24 paginiTrunnion Ball Valves PDFbenabdallah131Încă nu există evaluări
- SIS 2.0 Refill Capacities (M0124697-02)Document6 paginiSIS 2.0 Refill Capacities (M0124697-02)Carlos U. CallirgosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyzing 1H NMR Spectra of PDMSDocument5 paginiAnalyzing 1H NMR Spectra of PDMSAsrina RoslanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Satriana Et Al 2019 - European Journal of Lipid Science and TechnologyDocument1 paginăSatriana Et Al 2019 - European Journal of Lipid Science and TechnologyMuhammad Dani SupardanÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Chapter 1) Fluid Mechanics For Mechanical EngineeringDocument38 pagini(Chapter 1) Fluid Mechanics For Mechanical EngineeringAnn Razon0% (1)
- 1D Nano Porous Silicon Optical Sensor Detects Methyl ParathionDocument7 pagini1D Nano Porous Silicon Optical Sensor Detects Methyl ParathionhesoyamyecgaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Relative Fluorescence Quantum Yield Using The Agilent Cary EclipseDocument6 paginiDetermination of Relative Fluorescence Quantum Yield Using The Agilent Cary EclipseRosinaldo AparicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terluran GP-22: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Document3 paginiTerluran GP-22: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)Mahdi VolgarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emperical and Molecular FormulaDocument58 paginiEmperical and Molecular FormulaAl-Rajhi PumbayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum Heat Mass Transfer For Chemical and Food EngineeringDocument37 paginiMomentum Heat Mass Transfer For Chemical and Food EngineeringTigrigna TenagariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm E1269 Standard Test Method For CP by DSCDocument6 paginiAstm E1269 Standard Test Method For CP by DSCWMJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eutronic - Arc - Spray 4HFDocument4 paginiEutronic - Arc - Spray 4HFMuhammad irfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automated Process Design and Optimization in Oil and Gas DevelopmentDocument221 paginiAutomated Process Design and Optimization in Oil and Gas DevelopmentMurali MuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be 14112017Document73 paginiBe 14112017Nikhil GobhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch11 CastingProcessesDocument102 paginiCh11 CastingProcessesFahmi PrayogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refineria de Cartagena (Reficar) Refinery Expansion - Hydrocarbons TechnologyDocument3 paginiRefineria de Cartagena (Reficar) Refinery Expansion - Hydrocarbons TechnologyGjorgeluisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Completing The Puzzle:: 100% Plant-Derived PETDocument4 paginiCompleting The Puzzle:: 100% Plant-Derived PETAtif AzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocument12 paginiElisa: Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent AssayAmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silva Et Al., 2013 Coffee FerDocument13 paginiSilva Et Al., 2013 Coffee FerYon SadisticÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spectrofotometru SpectroDirect (De La Lovibond)Document360 paginiSpectrofotometru SpectroDirect (De La Lovibond)FlaviusÎncă nu există evaluări