Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
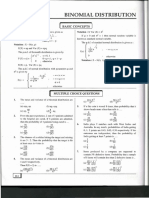
Binomial Distribution
Încărcat de
nskaz2067Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Binomial Distribution
Încărcat de
nskaz2067Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Binomial Distribution
A fair coin is tossed 500 times. Find the probability that the number of heads will not differ from
250 by
(a) More than 10
(b) More than 30
Solution:
1 1 1
np (500)( ) 250 npq (500)( )( ) 11.18
2 2 2
Since n large, so we use normal distribution to binomial distribution. Then,
Y ~ N( 250, 11.182)
(a) We require the probability that that the number of heads lie between 240 and 260 or
considering the data as continuous, between 239.5 and 260.5 (continuity correction)
239.5 250 260.5 250
P(Y 239.5) 0.94 and P(Y 260.5) 0.94
11.18 11.18
From standard normal table 0.94 = 0.3264
Required probability = (twice area)
= 2(0.3264) = 0.6528
(b) We require the probability that that the number of heads lie between 220 and 280 or
considering the data as continuous, between 219.5 and 280.5 (continuity correction)
219.5 250 260.5 250
P(Y 219.5) 2.73 and P(Y 280.5) 2.73
11.18 11.18
From standard normal table 2.73 = 0.4968
Required probability = (twice area)
= 2(0.4968) = 0.9936
Poisson Distribution
10% of the tools produced in a certain manufacturing process turn out to be defective. Find the
probability that in a sample of 10 tools chosen at random, exactly 2 will be defective, by using :
Then, compare the result.
(a) Binomial distribution
(b) The Poisson approximation to the Binomial distribution.
Solution :
(a) The probability of a defective tool is p = 0.1. Let X denote the number of defective
tools out of 10 chosen.
10
p( X 2) (0.1) 2 (0.9)8 = 0.1973
2
(b) We have np (10)(0.1) 1 .
x e
P( X x)
x!
12 e 1
P( X 2) 0.1839
2!
We can see that, the Poisson approximation is good if p 0.1 and np 5
Normal distribution
The mean inside diameter of a sample of 200 washers produced by a machine is 0.502 inches and
standard deviation is 0.005 inches. The purpose for which these washers are intended allows a
maximum tolerance in the diameter of 0.496 to 0.508 inches, otherwise the washers are
considered defective. Determine the percentage of defective washers produced by the machine,
assuming the diameter are normally distributed.
Solution :
(0.496 0.502) (0.508 0.502)
P(0.496 z 0.508) z
0.005 0.005
1.2 z 1.2
Nondefective washers = (area under normal curve between z = -1.2 and 1.2)
= (twice the area between z = 0 and z = 1.2)
= 2(0.3849) = 0.7698 = 77%
Therefore, the percentage of defective washers is 100% - 77 % = 23%
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 2.6 the Poisson Distribution 習題Document3 pagini2.6 the Poisson Distribution 習題sandywu930510Încă nu există evaluări
- Normal Distribution Probabilities and Standard ScoresDocument18 paginiNormal Distribution Probabilities and Standard ScoresAl AidenÎncă nu există evaluări
- P and S AssignmentDocument4 paginiP and S AssignmentzoopaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Dist Practice 1Document7 paginiNormal Dist Practice 1LCWWINno1inolpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionshDocument3 paginiProbability Distributionshمحمد سلامÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises LU5: Specific Probability DistributionsDocument8 paginiExercises LU5: Specific Probability DistributionsTiago PaulinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 283 - MCSE-004 D18 - Compressed PDFDocument5 pagini283 - MCSE-004 D18 - Compressed PDFPankaj SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dec2018 MCSE-004 PDFDocument5 paginiDec2018 MCSE-004 PDFbikash PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 QS (PC)Document17 paginiChapter 4 QS (PC)SEOW INN LEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 1 Multiple Choice Test Chapter Sources of Error COMPLETE SOLUTIONDocument6 paginiProblem Set 1 Multiple Choice Test Chapter Sources of Error COMPLETE SOLUTIONJet GamezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set#1 Multiple Choice Test Chapter 01.03 Sources of Error Complete Solution SetDocument6 paginiProblem Set#1 Multiple Choice Test Chapter 01.03 Sources of Error Complete Solution SetJH. channelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 01aae Sourceserror AnswersDocument6 paginiQuiz 01aae Sourceserror AnswersRock Of Rogue 1630Încă nu există evaluări
- Binomial DistributionDocument14 paginiBinomial DistributionsmpopadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability & Statistics Tutorial ProblemsDocument2 paginiProbability & Statistics Tutorial ProblemsBach Tran HuuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special DistributionsDocument14 paginiSpecial Distributionsjsmudher57Încă nu există evaluări
- PPTDocument34 paginiPPTasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability and Stochastic Processes ProblemsDocument7 paginiProbability and Stochastic Processes ProblemsSudipta GhoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Discrete Probability Distributions Ch6.1 Discrete Random VariablesDocument10 paginiChapter 6 Discrete Probability Distributions Ch6.1 Discrete Random Variablesadinda nurfitriyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ratio of Dishes Restaurant Should PrepareDocument37 paginiRatio of Dishes Restaurant Should Prepareshidupk5 pkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability and Statistics Exam QuestionsDocument3 paginiProbability and Statistics Exam QuestionsMunialo GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Et 101 (B)Document5 paginiEt 101 (B)PUSHPA SAINIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISOM 2500 Fa21 - Quiz - 2 - Ch8-Ch12 - SolDocument15 paginiISOM 2500 Fa21 - Quiz - 2 - Ch8-Ch12 - Solyantelau.Încă nu există evaluări
- Ques Pre-Pspm KMPPDocument4 paginiQues Pre-Pspm KMPPewine0529Încă nu există evaluări
- Assign. Mathematics III M (CSE) 301Document2 paginiAssign. Mathematics III M (CSE) 301amit davaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 1 - Me-451Document10 paginiHW 1 - Me-451BDHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous DistributionsDocument59 paginiContinuous DistributionsGhian Carlo Garcia CalibuyotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2019Document7 paginiAssignment 2 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2019UBAID ULLAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- LU5 Exercises SolutionsDocument27 paginiLU5 Exercises SolutionsTiago PaulinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROBABILITY OF BATTERY LIFETIMESDocument27 paginiPROBABILITY OF BATTERY LIFETIMESasif MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionDocument14 paginiProbability DistributionAditi Gupta SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS - Work SheetDocument3 paginiPROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS - Work SheetRavindra BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability and Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists 1st Edition Michael Akritas Solutions ManualDocument18 paginiProbability and Statistics With R For Engineers and Scientists 1st Edition Michael Akritas Solutions Manuala3880087880% (1)
- Solved Problems: SolutionDocument5 paginiSolved Problems: SolutionChecken JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionsDocument11 paginiProbability Distributionsxpertwriters9Încă nu există evaluări
- POISSON DISTRIBUTION GROUPDocument7 paginiPOISSON DISTRIBUTION GROUPngoufor atemafacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam 1 HW (Gradescope)Document5 paginiExam 1 HW (Gradescope)MelianaWanda041 aristaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2: Operations On Single Random VariablesDocument11 paginiUnit-2: Operations On Single Random VariablesHarini VemulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths QuestionnerDocument4 paginiMaths QuestionnerJames MelwynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Review W Sols Part IDocument4 paginiChapter 7 Review W Sols Part ICopetanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HKDSE M1 Probability DistributionsDocument15 paginiHKDSE M1 Probability Distributions15 15Încă nu există evaluări
- Sreenidhi Institute of Science & Technology Probability and Statistics ExamDocument2 paginiSreenidhi Institute of Science & Technology Probability and Statistics ExamzzzzzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Probability DistributionDocument18 paginiStandard Probability DistributionRi chalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution To Assignment 5Document4 paginiSolution To Assignment 5johnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poisson Assgn.Document33 paginiPoisson Assgn.Daman DhimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Tuto HW3 Chap 3Document6 pagini3 Tuto HW3 Chap 3443990117Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 Solutions PDFDocument7 paginiAssignment 4 Solutions PDFMarcioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Segunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La Ingeniería Química 2016 IDocument5 paginiSegunda Asignación de Estadística Aplicada A La Ingeniería Química 2016 IKevin RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curves & SplinesDocument49 paginiCurves & SplinesAmit DostÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM 38Document25 paginiSM 38ayushÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Dec. MA202-G - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagini2019 Dec. MA202-G - Ktu QbankThe WolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 6 SolutionDocument64 paginiCHAPTER 6 SolutionNaira Classified67% (3)
- Homework #1: Problem 1Document3 paginiHomework #1: Problem 1雷承慶Încă nu există evaluări
- Mod I-II - III - Study Material BL 4 - 5 - 6Document7 paginiMod I-II - III - Study Material BL 4 - 5 - 6God is every whereÎncă nu există evaluări
- R RRRR: STA 4702/5701 - Exam 3 Practice ProblemsDocument5 paginiR RRRR: STA 4702/5701 - Exam 3 Practice Problemsبا قرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Solution for "Uncertainty, Data and JudgmentDocument5 paginiExam Solution for "Uncertainty, Data and JudgmentGonçalo RibeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- F2020STAT213: Answer(s) Submitted: - 18 - 2 - 60 - 12 - 68 - 12Document3 paginiF2020STAT213: Answer(s) Submitted: - 18 - 2 - 60 - 12 - 68 - 12Mayankjot SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- MA2040: Probability, Statistics and Stochastic Processes Problem Set-IIDocument4 paginiMA2040: Probability, Statistics and Stochastic Processes Problem Set-IIRam Lakhan MeenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- F1 - Kesamaan SerentakDocument6 paginiF1 - Kesamaan Serentaknskaz2067Încă nu există evaluări
- GSP LatestDocument22 paginiGSP Latestnskaz2067Încă nu există evaluări
- SMK Pengkalan Hulu Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Mathematics Form 2Document15 paginiSMK Pengkalan Hulu Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Mathematics Form 2nskaz2067100% (1)
- SMK Pengkalan Hulu Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Mathematics Form 2Document15 paginiSMK Pengkalan Hulu Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Mathematics Form 2nskaz2067100% (1)
- Valentines Mystery Graph1Document1 paginăValentines Mystery Graph1Fatos ShuliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan EdtpaDocument15 paginiLesson Plan Edtpaapi-238284715Încă nu există evaluări
- BinomialDocument6 paginiBinomialPaula De Las AlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proba 2Document17 paginiProba 2Aman PlusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Probability Distributions: Bernoulli, Binomial, PoissonDocument12 paginiDiscrete Probability Distributions: Bernoulli, Binomial, PoissonLibyaFlowerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Statistics Chapter on Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument5 paginiEngineering Statistics Chapter on Random Variables and Probability DistributionsnurulattiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Udacity Enterprise Syllabus Data Analyst nd002Document16 paginiUdacity Enterprise Syllabus Data Analyst nd002IaksksksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4.7 PDFDocument14 paginiChapter 4.7 PDFRainie Su ChingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poisson Distribution EssayDocument4 paginiPoisson Distribution EssaySiti Rania Norazli Sham100% (1)
- IFY Maths (Science) Appendix C Formula Booklet 2021-22Document16 paginiIFY Maths (Science) Appendix C Formula Booklet 2021-22chiomamoronu08Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Practice Quizzes With Solutions U4nqniDocument31 paginiChapter 6 Practice Quizzes With Solutions U4nqniParker McGinleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam STS 201 Business Statistics II Spring 2021Document2 paginiFinal Exam STS 201 Business Statistics II Spring 2021Sadman SakibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling BookDocument234 paginiModeling Book梁嫚芳Încă nu există evaluări
- ECON1203 Business and Economic Statistics Quiz 1-4 SolutionsDocument8 paginiECON1203 Business and Economic Statistics Quiz 1-4 SolutionsSheharyar100% (1)
- Bernoulli Trials Binomial DistributionDocument7 paginiBernoulli Trials Binomial Distributionola momo nonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Package Dismo': R Topics DocumentedDocument68 paginiPackage Dismo': R Topics DocumentedHugo BampiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telengana Board of Intermediate Education II Year Math IIA SyllabusDocument2 paginiTelengana Board of Intermediate Education II Year Math IIA SyllabusYagna Panuganti100% (1)
- Undergraduate Statistics Curriculum StructureDocument26 paginiUndergraduate Statistics Curriculum StructurepjpawaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Miller Freunds Probability and Statistics For Engineers 8th Edition 0321640772Document37 paginiSolutions Manual To Accompany Miller Freunds Probability and Statistics For Engineers 8th Edition 0321640772antjwfgarza100% (6)
- Quiz 1020618Document3 paginiQuiz 1020618黃良初Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 ProbabilityDocument34 paginiChapter 5 ProbabilityNaqi AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agresti 1992 A Survey of Exact Inference For Contingency TablesDocument24 paginiAgresti 1992 A Survey of Exact Inference For Contingency TablesagustinzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAT 540 Statistical Concepts For ResearchDocument28 paginiMAT 540 Statistical Concepts For Researchnequwan79Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Advance StatisticsDocument18 paginiModule 1 Advance StatisticsMark Niel BalinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability and Statistics 2019 June QBDocument16 paginiProbability and Statistics 2019 June QBsravaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CFA Level I SmartSheet 2020Document9 paginiCFA Level I SmartSheet 2020yousefÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Discrete Probability SpacesDocument22 pagini1.1 Discrete Probability SpacesSaipavanesh GuggilapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Exams April/May 2019 - Probability & Queueing Theory QuestionsDocument6 paginiAnna University Exams April/May 2019 - Probability & Queueing Theory QuestionsVani RajasekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eda Presentation ContinuousDocument27 paginiEda Presentation Continuousjosel catubing (jcat)Încă nu există evaluări
- ES209 Module 4Document26 paginiES209 Module 4HALLASGO BENJIEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceptance Sampling PlansDocument8 paginiAcceptance Sampling PlansSourav DasÎncă nu există evaluări