Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
E-Mail Security: Issues and Solutions
Încărcat de
Ermin SehicTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
E-Mail Security: Issues and Solutions
Încărcat de
Ermin SehicDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
International Journal of Computer Information Systems,
Vol. 7, No.4, 2013
E-mail Security: Issues and Solutions
Sarika Choudhary/ M.tech (Network security) Rajesh Ghusinga/ B.tech (Civil Engineering)
School of Engineering and Sciences Indian Institute of Technology
BPS Mahila Vishwavidyalaya IIT, Bombay
Khanpur kalan, Sonepat (HR.) India Powai, Bombay, India
scpreety98@gmail.com rajesh.jms@gmail.com
differentiate between the regular mails and E-mails as the
Abstract— In this paper we’ll discuss about security of e-mails. postal system handles the regular mails and nobody can look
We’ll also investigate how to add confidentiality and integrity inside the letter, this is called by law. We expect high privacy
protection to ordinary email. with regular mails but ordinary E-Mails are not private, they
In everyday life you all use e-mail and think how much you relay are exposed to everyone.
on the accuracy of its contents? Think you receive an e-mail from
your mentor saying that you did so well in your course then you
were excused from doing any further work and what if you know
that message were a joke from your classmate. We always relay
on e-mail’s confidentiality and integrity for important data or
communication. Mostly ordinary e-mails have no confidentiality
and integrity.
Index Terms— encryption, forgery, interception, security,
spam, spoof.
I. INTRODUCTION
E-mail travels on the web so they are exposed to the intruders.
So, privacy of emails may be compromised b/w sender’s and
receiver’s side without giving any warning. In today’s A. How e-mails go and who can access it?
electronic world, e-mail becomes the backbone of the most Basically, E-Mails are based on point to point communication.
organizations’ daily activity. As we know email becomes most With the help of an example it becomes clear to you that who
frequent in the world so e-mail security becomes more can access the email. If kavita sends an email to Ritika. Then
important. For the security, organizations must control the Kavita’s computer system creates a virtual connection with
situations by taking any approach or invest wisely including Ritika’s system, it is called computer synchronization.
all the solutions. Messages between them are transferred by SMTP (Simple
Let consider the services provided by e-mail to the business, Mail Transfer Protocol). Consider Ritika is not online at the
email storage and management can be broken down into a moment and Kavita wants to send message to her. This
number of components like flow of the mail, storage of the message is stored at the server i.e. called POP (Post Office
mails, how do we exchange public keys, how do we assign Protocol) server. Next time whenever Ritika will be online,
trust and how user access the emails. These issues are the part she can download the message and can read them also.
of total security agenda. Kavita’s message is for Ritika and hence is private. So we
In section II you’ll study about how emails go and who can choose point to point communication but while the message is
access it and some threats to email, spamming, spoofing etc. sitting on the server, it is potentially exposed to everyone.
In section III you’ll study examples of email security means For better understanding we can consider another example i.e.
by taking a technique we can provide security to mails. let Sarika is an employee of large organization, it may be an
industry or any university or any other organization. So she
II. SECURING E-MAIL can’t create an outbound connection by herself. All her
messages are routed through a server and as a result her
E-Mails are most frequently used in today’s commerce. Now-
privacy is compromised. Another complication is aliases and
a-days these are the most convenient way of communication
forwarding agents – who add more mid points. By taking a
for ordinary users. E-Mails are public and can be seen by
simple case we can see that there’ll five points or parts:-
everyone at every point of communication between two users.
Hence, because of their exposed nature we can’t write
sensitive information in ordinary e-mails. We can
i. Kavita and her system
ii. Kavita’s organisation’s SMTP server
October Issue Page 42 of 63 ISSN 2229 5208
International Journal of Computer Information Systems,
Vol. 7, No.4, 2013
iii. Kavita’s ISP (Internet Service Provider) SENDER AUTHENTICITY: Means the receiver
iv. Ritika’s POP server knows that who was the sender and receiver is very
v. Ritika and her computer system confident about it.
NON-REPUDIATION: Means sender can’t deny that
B. Threats to E-mail: he/she has sent the messages.
So all these requirements must be fulfil for an ideal
There are so many threats to electronic-mail such as:
secure email. About confidentiality, Integrity and
Message confidentiality
encryption we’ll study in detail.
Message blocked delivery
Message content and origin modification 1) Confidentiality
Message content and origin forgery by outsider or We begin our description about security to provide
recipient. confidentiality enhancement to the several aspects.
Denial of message transmission To understand this, sender choose symmetric encryption
Message interception and subsequent algorithm key. By using this key sender encrypts the entire
message to be sent including FROM: TO: subject: etc. then
Encryption is used for confidentiality and data the message sender prep ends plaintext header. The sender
forgery. You can also defense against the replay encrypts the message key by using the recipient’s public key
attack. But in encryption we doesn’t use symmetric for the key management and attaches that with the massage.
encryption because it cannot protect against data Many network e-mail handlers use unprintable characters for
forgery by recipient, in symmetric encryption both control signals in the traffic stream. To avoid the transmission
sender and receiver share a common key. In this problem encrypted email converts the cipher text into plain
situation, you can use public key scheme for security. text characters.
In this, recipient only can decrypt but don’t do Encrypted email standard works most easily by using the both
encrypt. symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Encrypted e-mail
Sender and receiver can’t protect against the delivery standard supports multiple algorithms.
blocking because we have lack control over the For message confidentiality we use DES, Triple DES, and
middle points in the network. AES. For key exchange we use RSA and Diffie-Hellman.
C. What are the requirements and the solution??
Encrypted Message
For protection from data forgery and maintaining the
confidentiality, we create a list of requirements and solutions.
Receiver’s New Header
This list includes all the security and protection for securing
public key
any email.
i. Message Integrity
Encrypted
ii. Message Confidentiality
message data
iii. Message Authenticity
encryption key
iv. Non-repudiation
Public key
Encryption Encrypted
Message
Header+
Body
Message
encryption
key
Symmetric Key Encryption
MESSAGE INTEGRITY: It means what the receiver
seen and what we sent is matched or not. It helps to
maintain the integrity of the messages.
MESSAGE CONFIDENTIALITY: It makes sure that
the message is not exposed on any route while it is
Message Header+ Body
going to the receiver. 2) Integrity
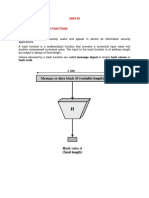
Integrity for e-mail security is as important as confidentiality.
Integrity is provided by hash function in the digital signature
October Issue Page 43 of 63 ISSN 2229 5208
International Journal of Computer Information Systems,
Vol. 7, No.4, 2013
called message integrity check (MIC). It is optional that Some organizations copy all emails sent from org. systems
encrypted email messages can be encrypted for daily as the evidence in legal issues. Many org. or companies
confidentiality. We can integrate original e-mail message or monitor their worker’s e-mail. Network administrator or ISP
encrypted e-mail messages so that a person can send enhanced (Internet Service Provider) also monitor the e-mails for
or non-enhanced messages. If sender sends enhanced message business purpose, traffic or detect spam etc. Org. monitor
so an extra bit of encrypted email processing is invoked on the emails for any legal purpose. So there is no expected privacy
sender’s end. Receiver should also remove the enhanced bits on network of your emails or general computer use.
for getting the original message but non-enhanced messages
E. Malicious e-mails (Spamming, Phishing, Spoofing)
flow through the mail handlers as usual they processed.
3) Encryption In this electronic world, it is very important for everyone to be
In this key management is a major problem. We can remove familiar with three thing i.e. spamming, spoofing, phishing.
this problem or difficulty with the use of certificates. These three terms seem to denote the same thing but they are
Certificates are used for key management, key exchange and different from each other and you should be aware. So let us
for associating an identity with a public encryption key. The take a look at their definitions.
problem with certificate is building a hierarchy. Now-a-days 1) Spam
many organizations have hierarchical structure but some Spam is junk e-mails also known as unsolicited bulk e-mail
organizations don’t have. So because of a problem of message or we can say unwanted messages. They are refers to
imposing a hierarchy on non-hierarchical world then PGP was send email to thousands of users as a chain letters. Mostly we
developed for such organizations. found that spam has also to be compromised of ads for
By using RSA encryption technique with long bit key we can products and services of questionable legality. Spam is
provide strong end-to-end security for e-mail. annoying but it’s not really dangerous. Sometimes, spam e-
mail spamming is combined with the spoofing so it is very
difficult to find out the actual originating email address of the
Compose Message sender. Some e-mail systems like outlook express have ability
View message
to block the e-mail with specified address. But because of
changing email address frequently, it is very difficult to
prevent some spam from reaching to your inbox. There are
two types of spam:
Intentional spam: it is comes from spammers who are
Yes No Crypto fraud or solicited products.
Encryption processing
Unintentional spam: it originates from computer
o
requested? Crypto
o Yes systems that are infected with the virus. Virus or
worms send bulk message from the infected system
Encrypted? without the knowledge of the computer owner.
2) Phishing
No Phishing is a type of spam in which sender enters its
personal account information (banking data) for the
purpose of breaking your account and theft of data
Send message for fraud-ness. Phishers can enhance the credibility
Receive message
by spoofing to convince source address. We can take
an example for better understanding, let you get a
false e-mail and this e-mail appear come from a
legitimate company like eBay, Yahoo, government
D. E-mail Interception universities etc. These messages look like they came
As other web content have privacy concern from interception from original source. These messages ask you to
risk such as e-mail also have the same concern while transmit update your records by entering your Date of Birth,
the message over the internet. bank account number and PIN etc. These sites collect
There are various techniques for encrypting e-mail. PGP and your personal data in order to theft your money,
S/MIME techniques are widely used. These techniques are identity etc.
mostly used in popular email handlers like Microsoft outlook, You just keep in mind that legitimate companies
Eudora, Netscape etc. These products protect emails over the or organisation already have your personal data, so
internet and from midpoints too etc. VPN (Virtual Private they will never ask you to give all this kind of
Network) can also provide data communication security or information. Whenever you think that any e-mail is
protect the data. But it provides limited protection between suspicious then don’t reply and even delete that
client’s workstation and some points. It uses router or firewall email.
at the point to which the sender belongs. For e.g.
communication is protected from a university student to the
edge of the university network.
October Issue Page 44 of 63 ISSN 2229 5208
International Journal of Computer Information Systems,
Vol. 7, No.4, 2013
3) Spoofing Generate a hash or message digest for message
When an email appears that it comes from the legitimate integrity or authentication.
source and in actual it comes from an imposter/ fraud. Sign the hash and encrypt it with sender’s private key.
Basically it is the forgery of email header so that it seems Then attach the encrypted session key with encrypted
original or actual. It is done by spammers often and it can be message and digest.
accomplished by changing the “FROM:” mail address. Finally transmit the message to the recipient.
E-mail spoofing can be done by different forms but all have
same result. Spoofing can be used for spreading virus or we When recipient receive the message it reverses these steps to
can say malicious purpose or it is a best trick to make user obtain the original message content.
confident and release sensitive information like password,
account no. or PIN no. of account. Mostly email spammers B. S/MIME (Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail
use spoofing so that receiver can get sender’s address or Extensions)
possibly respond. S/MIME is somewhat like PGP. It is an Internet standard and
To send spoofing email, sender enters command into the tells how e-mail is sent and received. Basic MIME represents
header portion that’ll alter the information. Someone could or describes the format of e-mail and handles e-mail
send spoofed message that appears to be a user with a attachments. The enhanced version of MIME with security is
message that he/she didn’t write. S/MIME (Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions).
There is no way of prevention from receiving the spoofed e- S/MIME is the Internet standard for secure e-mail
mail. If you get message from any source that ask for attachments. PGP have predecessors that are PEM (Privacy
something personal or confidential information then you want Enhanced Mail) and RIPEM. S/MIME is very much like PEM
to know if it is really from the person it says it’s from you can and RIPEM as PGP too. It is now used in many commercial
look at the Internet Header. It shows that from where the products like Microsoft Outlook etc.
email actually originated.
If your email address is spoofed so that doesn’t mean that Principle difference between PGP and S/MIME is the way of
spammer or spoofer has access your mailbox. key exchange. In PGP each user exchanging keys with all the
trusted recipients and establish a ring of trust. In S/Mime, it
uses hierarchically validated certificate such as X.509 for key
III. EXAMPLES OF SECURE E-MAIL SYSTEM exchange. In this sender or receiver don’t need to have
Many sources provide encryption e-mail programs. Many exchanged keys as long as they have a common certifier or
universities or companies have created or developed their which they both trust. It works with many cryptographic
commercial version of encrypted e-mail. Here we are taking algorithms like DES, AES and RC2. It also performs security
two examples for security e-mail. These are: transformation similar to PGP. PGP only handles plaintext but
S/MIME handles or we can say secure all type of attachments
A. PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) like PPT, movies, sound files, graphic files etc.
It was invented by phil Zimmerman in 1991. After bought by S/MIME provides secure e-mail i.e. e-mail security and it is
network associates it became a commercial product in 1996. broadly used by many commercial e-mail packages.
Its freeware version is also available. It is widely used for
exchanging private e-mails.
PGP is used to address the problem of key distributed with IV. CONCLUSION
“ring of trust” or user’s “key ring”. Basically a user can give To secure e-mail there are some steps, in short:
its public key to another or it can take from a server. At the Generate an Identity
bottom of the message, many people include their PGP public
Configure secure e-mail software
keys. In this, one person can give second person’s key to
third, fourth, fifth and so on. Thus it creates a key association Get public keys for software
problem. If you are confident that an e-mail comes from the Get public keys for recipients
trusted person and there is no tempering, then you can use that Start sending secured messages
attached public key. If you trust that person then you should
also trust the keys that person gives you for other peoples. There are some tips so that you can save your e-mails:
If you are sending any key to another person then you sign First of all, backup your keys
each key whenever you give. The keys you send to another Trusting on a key after the suitable verification with
person may also been signed by other peoples.
the owner
PGP processing performs following actions depending upon
confidentiality, integrity, authenticity or non-repudiation. Revoke certificates from time-to-time or revoke PGP
First of all, create a random session key. keys if compromised
For message confidentiality encrypt the message using Always save your sensitive information elsewhere.
the session key.
Encrypt the session key with recipient’s public key. Now-a-days, by e-mail communication is the most common
way of exchanging information in almost every business and
October Issue Page 45 of 63 ISSN 2229 5208
International Journal of Computer Information Systems,
Vol. 7, No.4, 2013
organization. As all of us have taken e-mails granted, none of
us should neglect that the days of pure and safe internet are far
away so there is no excuse for shortcuts when it comes to
security. For prevention you should take precautions hence for
this you can take advantage of the public available solution
and always encourage our network administrator to
enforce/enhance the security policies.
REFERENCES
[1] Book: Security in Computing by Charles P. Pfleger.
[2] www.wikipedia.org
[3] www.CISCO.com
[4] www.purdue.edu/decurepurdue/docs/training/using_secure_email.pdf
[5] www.csrc.nist.gov
[6] www.cs.columbia.edu/~smb/classes/so9/11.org
[7] www.cypherpunles.to/~peter/T5_email.pdf
[8] www.pgp.com
[9] http://www.helpnetsecurity.com/
[10] www.marknoble.com/tutorial/smime/smime.aspx
AUTHORS PROFILE
Sarika Choudhary is pursuing M.tech (CSE)
with specialization in Network Security from BPS
University Khanpur, Sonepat. She has done her
B.tech (CSE) from the same university. At present
she is a student and has great interest in
networking and security.
October Issue Page 46 of 63 ISSN 2229 5208
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Client Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandClient Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWP - Chapter 1Document53 paginiPWP - Chapter 1Mayur NarsaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandNetwork Management System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDocument6 paginiETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Online Feedback SystemDocument1 paginăOnline Feedback SystemSonal DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Atmospheric Disaster Management Natural and Man-madeDe la EverandEarth and Atmospheric Disaster Management Natural and Man-madeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winter Nis Model Ans 2022Document28 paginiWinter Nis Model Ans 2022Pranit ShitoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Documentation A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandNetwork Documentation A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weather Forecasting ProjectDocument18 paginiWeather Forecasting ProjectFitnesska mantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On CryptographyDocument25 paginiSynopsis On CryptographyVisitor Play0% (1)
- Ede Micro Project For Tyco StudentsDocument10 paginiEde Micro Project For Tyco StudentsAditya YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Level Password Authentication System MechanismDocument5 paginiThree Level Password Authentication System MechanismIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGT Micro ProjectDocument21 paginiMGT Micro ProjectVaibhav MalkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swapnil (Black Book) FULLDocument45 paginiSwapnil (Black Book) FULLSwapnil Narad0% (1)
- ETI-Chapter 2Document13 paginiETI-Chapter 2kenny jenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5G Technology Info::-Biradar Ganesh Taterao .:-CF15 ETI Micro-Project PresentationDocument11 pagini5G Technology Info::-Biradar Ganesh Taterao .:-CF15 ETI Micro-Project PresentationBiradar GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloud Computing Final ReportDocument29 paginiCloud Computing Final ReportKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Create IPV6 Based Small Computer Network Using A Simulator.: I. Practical SignificanceDocument6 paginiCreate IPV6 Based Small Computer Network Using A Simulator.: I. Practical Significance28-TYCM-1-SANDESH KADAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Summer Model Answer Paper PDFDocument31 pagini2016 Summer Model Answer Paper PDFMahesh DahiwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- JSPM'S Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic, Wagholi 2022 - 2023: Department of Computer EngineeringDocument28 paginiJSPM'S Bhivrabai Sawant Polytechnic, Wagholi 2022 - 2023: Department of Computer Engineeringyash kaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project Report ON "Retail Chain Management": Diploma IN Computer EngineeringDocument34 paginiA Project Report ON "Retail Chain Management": Diploma IN Computer EngineeringSai PrintersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Project Report: " Climate Change An Global Issue. "Document13 paginiMicro Project Report: " Climate Change An Global Issue. "Assad MujawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thakur Polytechnic Department of Computer EngineeringDocument10 paginiThakur Polytechnic Department of Computer EngineeringJivan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report Format For Final MCADocument5 paginiProject Report Format For Final MCAitworld3271% (7)
- MAD - Ch5 & 6 Notes PDFDocument85 paginiMAD - Ch5 & 6 Notes PDFShaikh Wasima100% (1)
- DCC Lab Manual - 2020-2021Document43 paginiDCC Lab Manual - 2020-2021Jay PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 CE - IS - Practical List and IndexDocument3 pagini7 CE - IS - Practical List and IndexronakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document2 paginiAssignment 1arvi.sardarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Database Security and PrivacyDocument357 paginiDatabase Security and PrivacyKartik DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- WMN ProjectDocument16 paginiWMN ProjectIFAnupma JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infosys Test PaperDocument31 paginiInfosys Test PaperShreya ShettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Password Cracker Using MPI: Project ReportDocument33 paginiPassword Cracker Using MPI: Project ReportManohar Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCC Microproject Group 2 PresentationDocument8 paginiDCC Microproject Group 2 PresentationYash Dasouni0% (1)
- Priority Scheduling ImplementationDocument6 paginiPriority Scheduling ImplementationGirija KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ReportDocument40 paginiProject ReportAnamika SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Management SystemDocument7 paginiStudent Management SystemWahidul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planning and Organizing at Supervisory LevelDocument115 paginiPlanning and Organizing at Supervisory LevelsujitÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIS (Tech) BookDocument130 paginiNIS (Tech) BookGanesh EkambeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2626 Internship Offer Letter Combined-702Document2 pagini2626 Internship Offer Letter Combined-702Muhammed AkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text Editor Using Python: Title of The ProjectDocument6 paginiText Editor Using Python: Title of The Projectak sheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 12 Python Project TypingDocument21 paginiClass 12 Python Project TypingSUPPORT CARRYMINATIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - II User Authentication & Access ControlDocument11 paginiUnit - II User Authentication & Access ControlJayesh DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyber Forensics Unit - 1 Computer ForensicsDocument17 paginiCyber Forensics Unit - 1 Computer ForensicsDevika DakhoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scheme - G Third Semester (Ej, Et, En, Ev, Ex, Is, Ic, Iu, De, Mu, Ie, Ed, Ei)Document39 paginiScheme - G Third Semester (Ej, Et, En, Ev, Ex, Is, Ic, Iu, De, Mu, Ie, Ed, Ei)digisagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Week 2: 1. What Are The Characteristics of A Mobile Computing Environment?Document5 paginiTutorial Week 2: 1. What Are The Characteristics of A Mobile Computing Environment?saneel kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- VISADocument9 paginiVISAsmoulikarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knapp's ClassificationDocument6 paginiKnapp's ClassificationSubi PapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer - 19 Examination Subject Name: Operating System Model Answer Subject CodeDocument28 paginiSummer - 19 Examination Subject Name: Operating System Model Answer Subject CodeRushikesh KadamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ETI MicroprojectDocument11 paginiETI MicroprojectDigvijay DevareÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Access Layer PDFDocument84 pagini6 Access Layer PDFAllen Chandler50% (2)
- MCQ Mad MCQDocument31 paginiMCQ Mad MCQSaquibh ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design ER Diagram For Library: A Micro Project OnDocument14 paginiDesign ER Diagram For Library: A Micro Project OnVirendra NawkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Koradi Thermal Power Station (KTPS) IsDocument17 paginiKoradi Thermal Power Station (KTPS) IsBappa ChaclickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Plan For Notepad ApplicationDocument2 paginiTest Plan For Notepad ApplicationRohit GadekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Computer Networks - CoSc-6111-Lecture-4Document80 paginiAdvanced Computer Networks - CoSc-6111-Lecture-4AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osy Microproject ReportDocument13 paginiOsy Microproject ReportHarish chafakarandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 AbstractDocument9 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 Abstractaabid mullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management (22509) Subject MicroprojectDocument16 paginiManagement (22509) Subject MicroprojectKunal Shankar TherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document111 paginiChapter 5Kaustubh ParthasarathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Interface Design: Definitions, Processes and PrinciplesDocument66 paginiUser Interface Design: Definitions, Processes and PrinciplesErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typesofmemory UpdatedDocument8 paginiTypesofmemory UpdatedErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanet - ST 013438038X PDFDocument623 paginiSanet - ST 013438038X PDFErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seth 740 Fall13 Module3.5 Main Memory Part1Document69 paginiSeth 740 Fall13 Module3.5 Main Memory Part1Ermin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory HierarchyDocument30 paginiMemory HierarchyAli ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typesofmemory UpdatedDocument8 paginiTypesofmemory UpdatedErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer MemoryDocument12 paginiComputer MemoryErmin Sehic100% (1)
- Computer Memory Applications and ManagementDocument11 paginiComputer Memory Applications and ManagementErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Document62 paginiIPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Ermin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protocols in IPTVDocument36 paginiProtocols in IPTVManish Das83% (6)
- E-Mail Security Issues and SolutionsDocument4 paginiE-Mail Security Issues and SolutionsErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 paginiTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Ermin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Parallel Programming 2015Document38 paginiIntro Parallel Programming 2015Ermin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- DHCP Handbook 2ed 2003 enDocument11 paginiDHCP Handbook 2ed 2003 enErmin SehicÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCP-IP SunDocument272 paginiTCP-IP SunNguyễnHòaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The DHCP HandbookDocument623 paginiThe DHCP Handbookductv100% (1)
- Cryptography With CertificatesDocument5 paginiCryptography With CertificatesramtulsipurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sam Security CertificationsDocument12 paginiSam Security CertificationspkjmesraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Security (1030106508)Document13 paginiInformation Security (1030106508)Dhruv SojitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab5 Digital Security, Ethics, and Privacy Threats, Issues and DefensesDocument44 paginiBab5 Digital Security, Ethics, and Privacy Threats, Issues and Defensesciaaq00Încă nu există evaluări
- Lenovo Anti Theft ProtectionDocument2 paginiLenovo Anti Theft Protectionabu dujanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A10 Training 05 HTTPSDocument11 paginiA10 Training 05 HTTPSMario AlcazabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1Document42 paginiModule 1A BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrator Accounts:: Dynamic RolesDocument8 paginiAdministrator Accounts:: Dynamic RolesCrypto DudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Secure Information SystemDocument27 paginiDeveloping Secure Information SystemjayamalarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live! Lab: Use Kerberos To Control Access To NFS SharesDocument16 paginiLive! Lab: Use Kerberos To Control Access To NFS SharesHarsha TheegalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Classical EncryptionDocument16 pagini2 Classical Encryptionrahul88anandÎncă nu există evaluări
- OWASP Top 10 - Threats and MitigationsDocument54 paginiOWASP Top 10 - Threats and MitigationsSwathi PatibandlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Deduplication and Secure Sharing in Cloud StorageDocument5 paginiData Deduplication and Secure Sharing in Cloud StorageInitz TechnologiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIS Mid-Term ExaminationDocument8 paginiMIS Mid-Term ExaminationOWAIS AHMED NISAR AHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azure AD Mastery Training PlanDocument4 paginiAzure AD Mastery Training PlanArif Mohammed RangrezzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cns Unit IIIDocument22 paginiCns Unit IIIAyush GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Kratikal Com Blog How To Stay Cyber Secure While You Work From HomeDocument7 paginiWWW Kratikal Com Blog How To Stay Cyber Secure While You Work From HomePallavi DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Information and Computer SecurityDocument42 paginiIntroduction To Information and Computer SecurityBaburam KumaraswaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rani 2015Document4 paginiRani 2015Red ReddingtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital One Hack AdvisoryDocument3 paginiCapital One Hack AdvisoryJinto T.K.Încă nu există evaluări
- Information Security Management System (ISMS) Overview PDFDocument30 paginiInformation Security Management System (ISMS) Overview PDFnandaanujÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Wireless Network SecurityDocument33 pagini10-Wireless Network SecurityNam BuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange PDFDocument6 paginiDiffie-Hellman Key Exchange PDFZxzxzxz007Încă nu există evaluări
- Configuración Juniper para Cliente ZoomDocument3 paginiConfiguración Juniper para Cliente ZoomJoan ViloriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Network AttacksDocument15 paginiComputer Network AttacksRadhey RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 IAS)Document41 paginiChapter 2 IAS)Abduu MizaabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument4 paginiCryptography and Network SecurityMary HelenÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT ResearchDocument4 paginiIT ResearchMatt Morrie AñanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- guideTOM - en - 2015 - Tehnical Security SwissDocument29 paginiguideTOM - en - 2015 - Tehnical Security SwissGabiIordacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMZ Lab Security PolicyDocument3 paginiDMZ Lab Security PolicyRyan PramudyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading the Constitution: Why I Chose Pragmatism, not TextualismDe la EverandReading the Constitution: Why I Chose Pragmatism, not TextualismÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Perversion of Justice: The Jeffrey Epstein StoryDe la EverandPerversion of Justice: The Jeffrey Epstein StoryEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- For the Thrill of It: Leopold, Loeb, and the Murder That Shocked Jazz Age ChicagoDe la EverandFor the Thrill of It: Leopold, Loeb, and the Murder That Shocked Jazz Age ChicagoEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (97)
- Insider's Guide To Your First Year Of Law School: A Student-to-Student Handbook from a Law School SurvivorDe la EverandInsider's Guide To Your First Year Of Law School: A Student-to-Student Handbook from a Law School SurvivorEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Hunting Whitey: The Inside Story of the Capture & Killing of America's Most Wanted Crime BossDe la EverandHunting Whitey: The Inside Story of the Capture & Killing of America's Most Wanted Crime BossEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (6)
- Nine Black Robes: Inside the Supreme Court's Drive to the Right and Its Historic ConsequencesDe la EverandNine Black Robes: Inside the Supreme Court's Drive to the Right and Its Historic ConsequencesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning to Disagree: The Surprising Path to Navigating Differences with Empathy and RespectDe la EverandLearning to Disagree: The Surprising Path to Navigating Differences with Empathy and RespectÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingDe la EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (97)
- Conviction: The Untold Story of Putting Jodi Arias Behind BarsDe la EverandConviction: The Untold Story of Putting Jodi Arias Behind BarsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (16)
- All You Need to Know About the Music Business: 11th EditionDe la EverandAll You Need to Know About the Music Business: 11th EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lady Killers: Deadly Women Throughout HistoryDe la EverandLady Killers: Deadly Women Throughout HistoryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (154)
- Get Outta Jail Free Card “Jim Crow’s last stand at perpetuating slavery” Non-Unanimous Jury Verdicts & Voter SuppressionDe la EverandGet Outta Jail Free Card “Jim Crow’s last stand at perpetuating slavery” Non-Unanimous Jury Verdicts & Voter SuppressionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Law of the Land: The Evolution of Our Legal SystemDe la EverandThe Law of the Land: The Evolution of Our Legal SystemEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- The Myth of Equality: Uncovering the Roots of Injustice and PrivilegeDe la EverandThe Myth of Equality: Uncovering the Roots of Injustice and PrivilegeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (17)
- Reasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemDe la EverandReasonable Doubts: The O.J. Simpson Case and the Criminal Justice SystemEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (25)
- All You Need to Know About the Music Business: Eleventh EditionDe la EverandAll You Need to Know About the Music Business: Eleventh EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldDe la EverandThe Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (104)
- Can't Forgive: My 20-Year Battle With O.J. SimpsonDe la EverandCan't Forgive: My 20-Year Battle With O.J. SimpsonEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (3)
- The Edge of Innocence: The Trial of Casper BennettDe la EverandThe Edge of Innocence: The Trial of Casper BennettEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Chokepoint Capitalism: How Big Tech and Big Content Captured Creative Labor Markets and How We'll Win Them BackDe la EverandChokepoint Capitalism: How Big Tech and Big Content Captured Creative Labor Markets and How We'll Win Them BackEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (20)
- The Private Diary of an O.J. Juror: Behind the Scenes of the Trial of the CenturyDe la EverandThe Private Diary of an O.J. Juror: Behind the Scenes of the Trial of the CenturyEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)